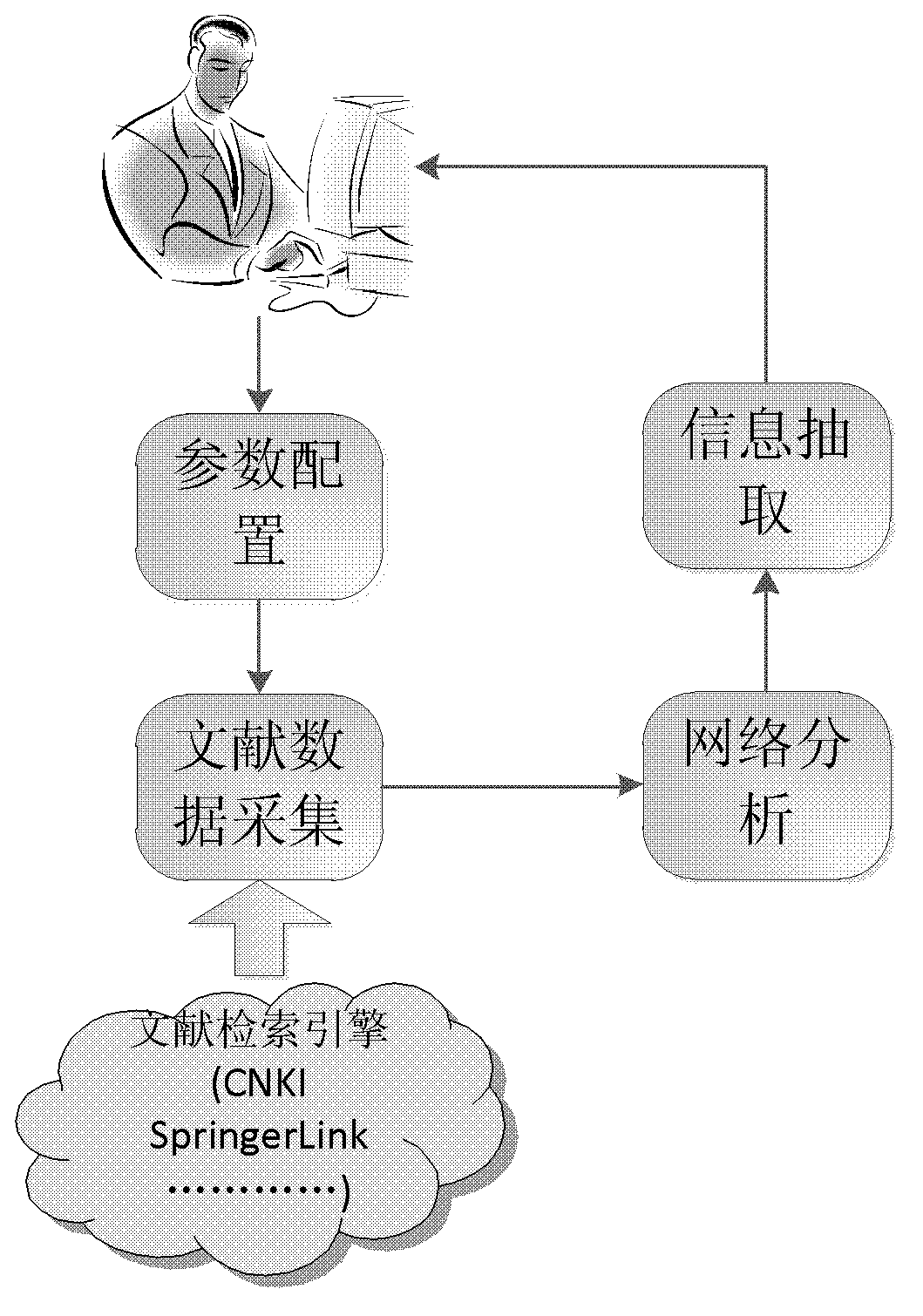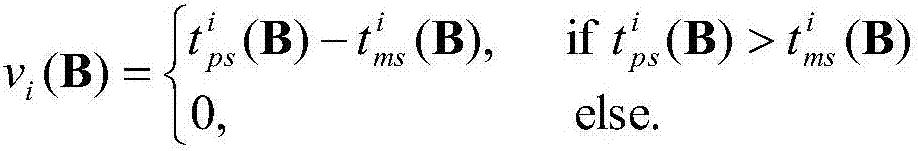Patents
Literature
37 results about "Cooperative group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
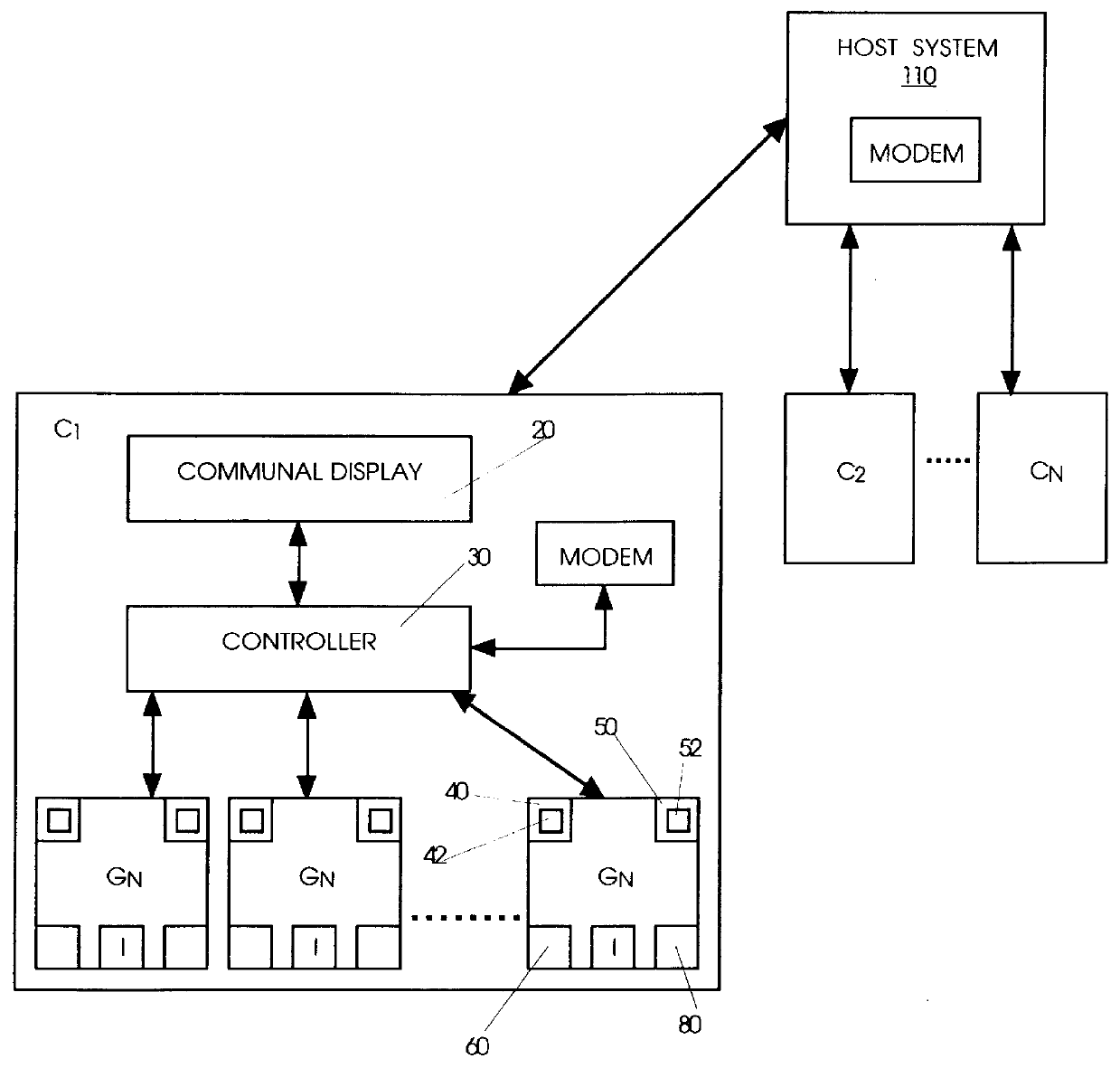
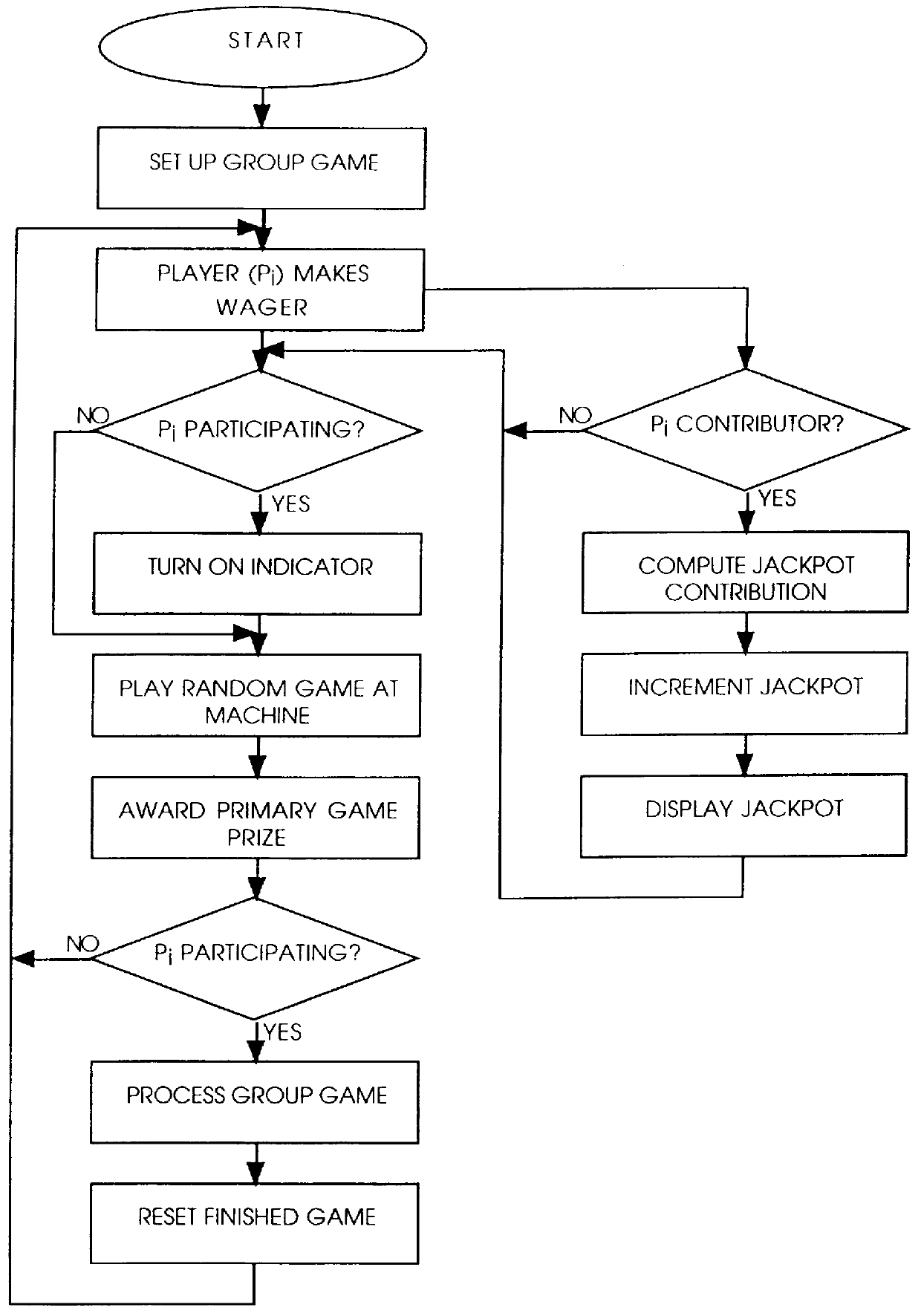
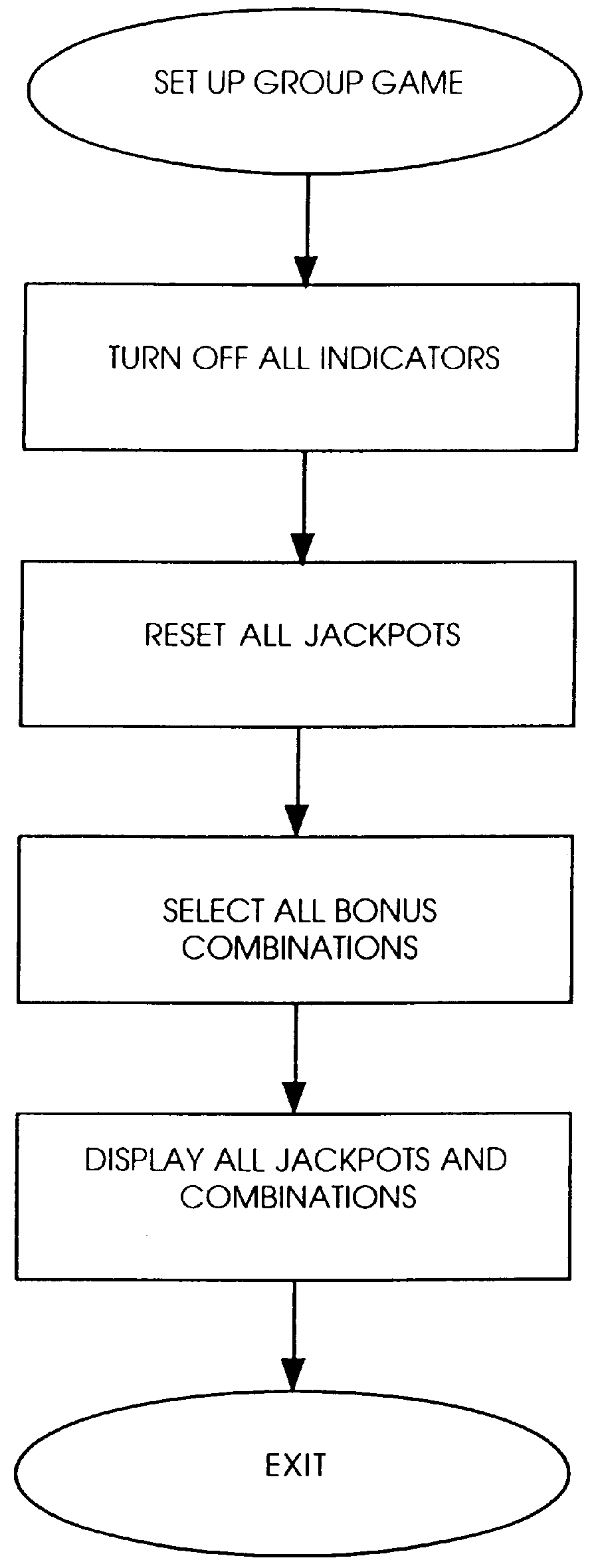
Cooperative group gaming system: apparatus and method
InactiveUS6077162AIncrease player gratificationEnvironmental promotionBoard gamesCard gamesGame playerEngineering
A cooperative group gaming apparatus and method therefore including a plurality of gaming machines including means for individual play, means for communal play and communal payout means influenced by any gaming machine participating in cooperative group play, said plurality of gaming machines operatively coupled to at least one controller which, inter alia, communicates with at least one display means for displaying the effects of cooperative group play to game players.
Owner:CASINO DATA SYST
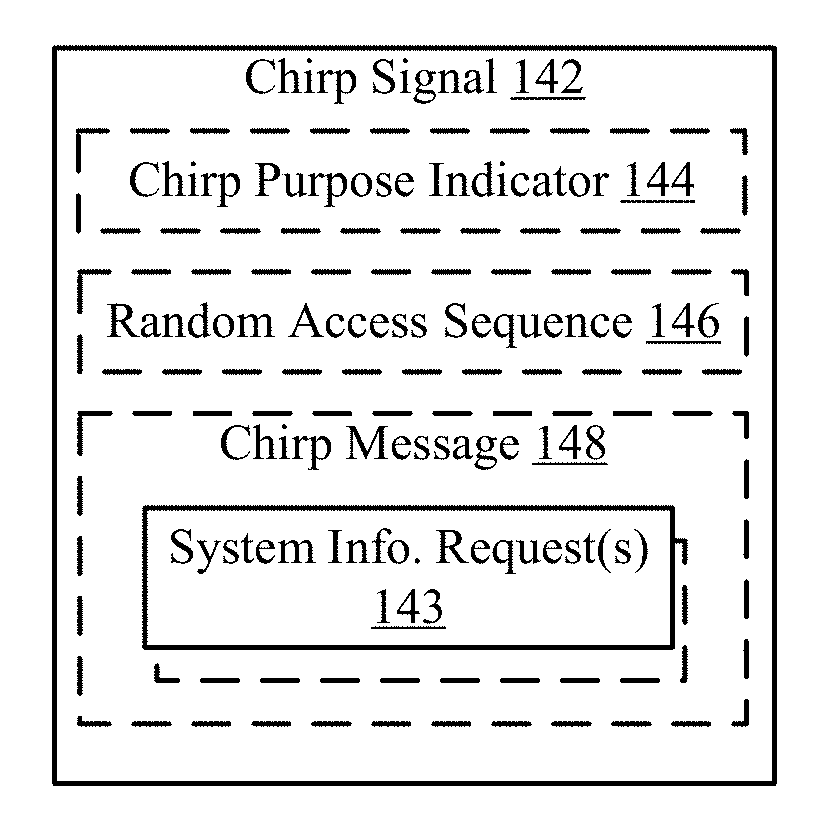
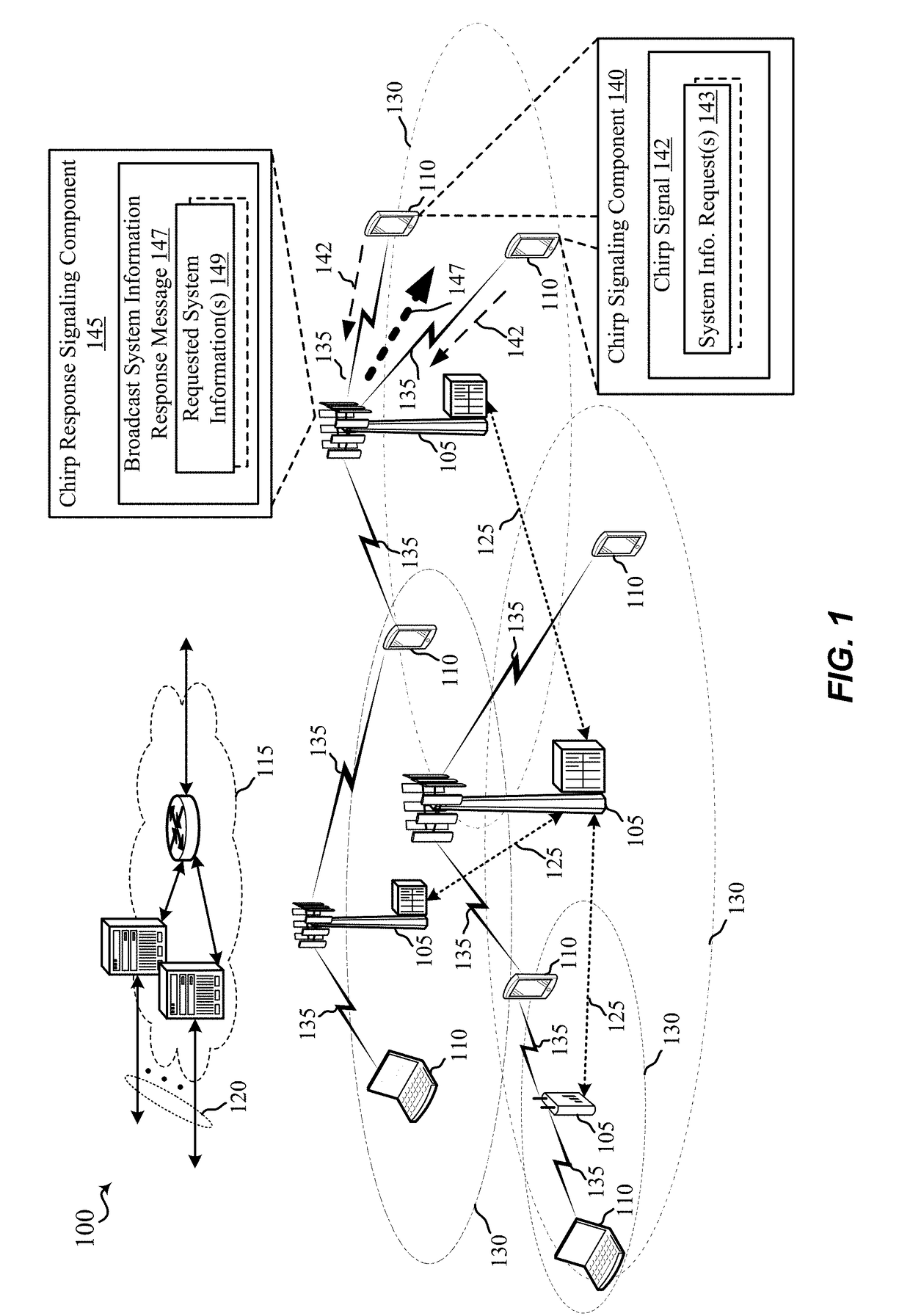
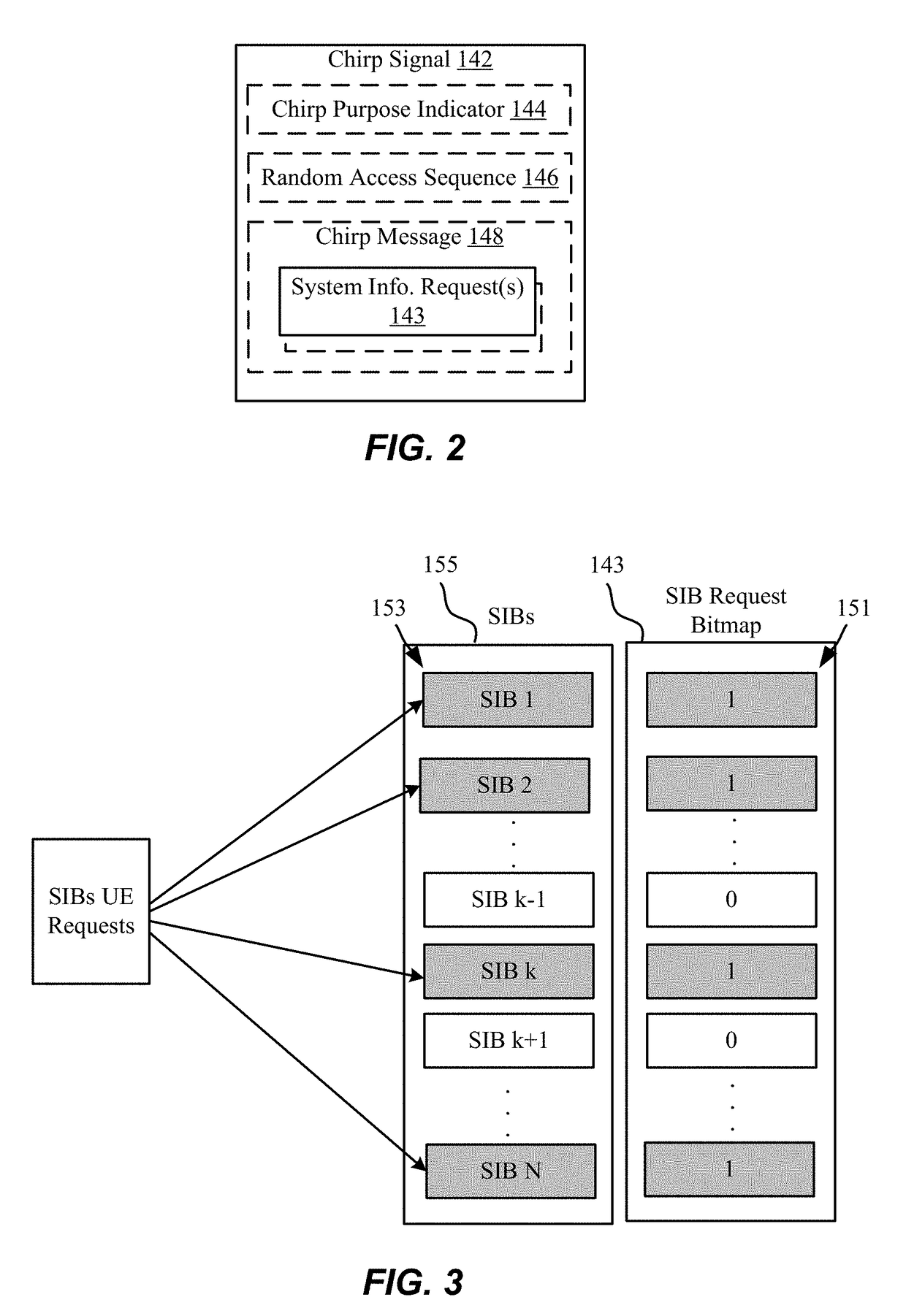
Cooperative group broadcasting of on-demand system information
Aspects described herein include receiving, at a base station operating in a wireless communication network, at least one chirp signal including at least one system information block request bitmap that identifies one or more of a plurality of system information blocks corresponding to each of one or more system information requests, identifying the one or more system information requests, generating a message in response to the one or more system information requests, encoding at least the portion of the message based at least in part the at least one system information block request bitmap to define an encoded message; and transmitting, over a broadcast channel, the encoded message in response to the chirp signal. A user equipment may include aspects for transmitting the chirp signal and receiving the encoded message.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
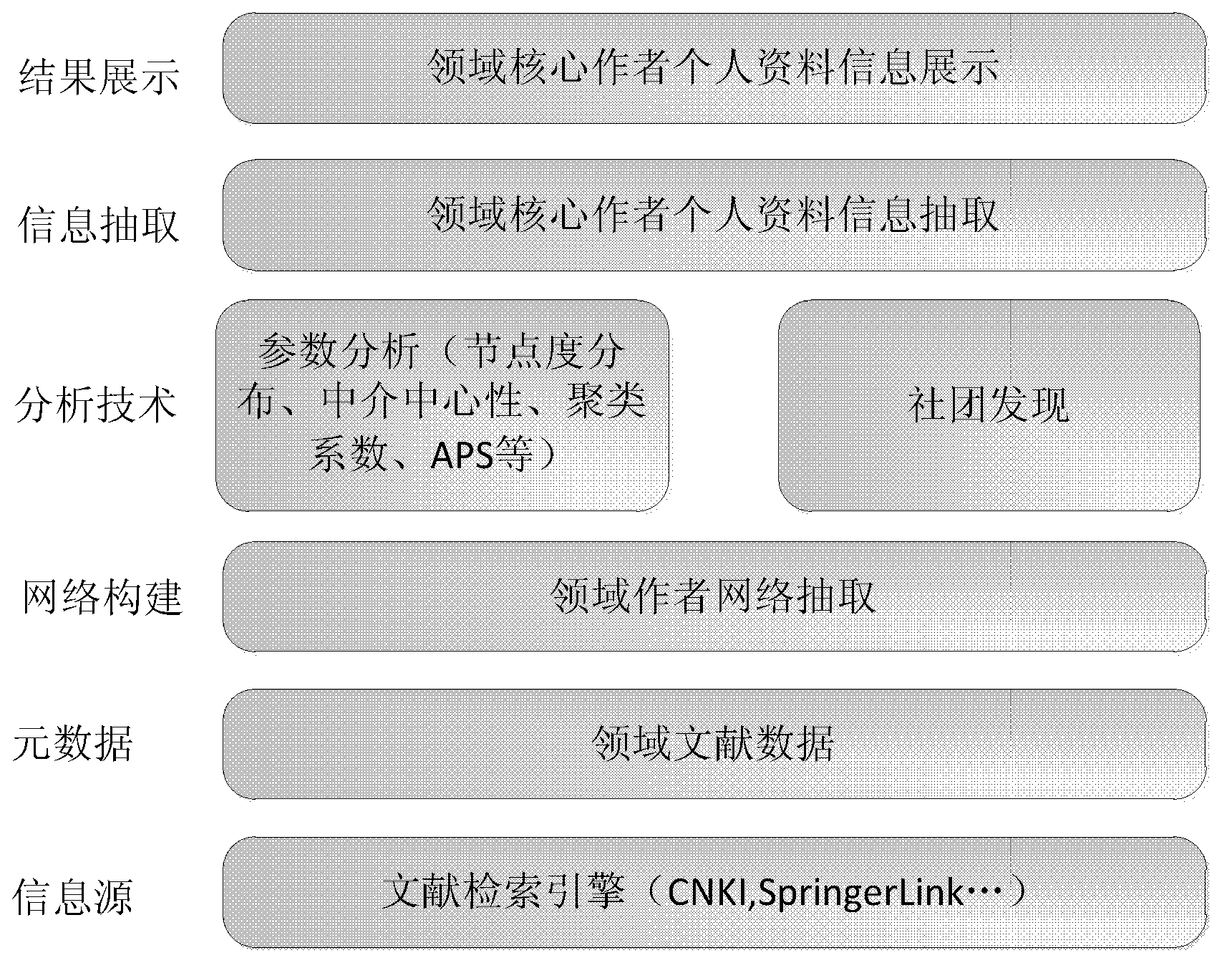
Academic core author excavation and related information extraction method and system based on complex network
The invention belongs to the field of data mining, aims to solve the problem of excavating core authors in an academic field and intelligently extracting related information of the authors, and provides an improved academic core author excavation and information extraction method and system based on a core node discovery algorithm in the social network analysis technology. The method combines the vertical search technology, the social network analysis technology and the text analysis technology, and can find the core authors or groups of the academic field in the mass of information to further obtain related information of the authors. The method uses the vertical search technology to collect open source literature data, uses the bibliometric technology and the complex network analysis technology to analyze the importance of a variety of social entities in the data, and utilizes a community discovery algorithm to perform entity clustering based on the closeness degree of relationships between entities to find out an academic community. Users can find the core authors or an institution according to an entity importance ranking, and find the leadership team according to published articles amount distribution of cooperative groups.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
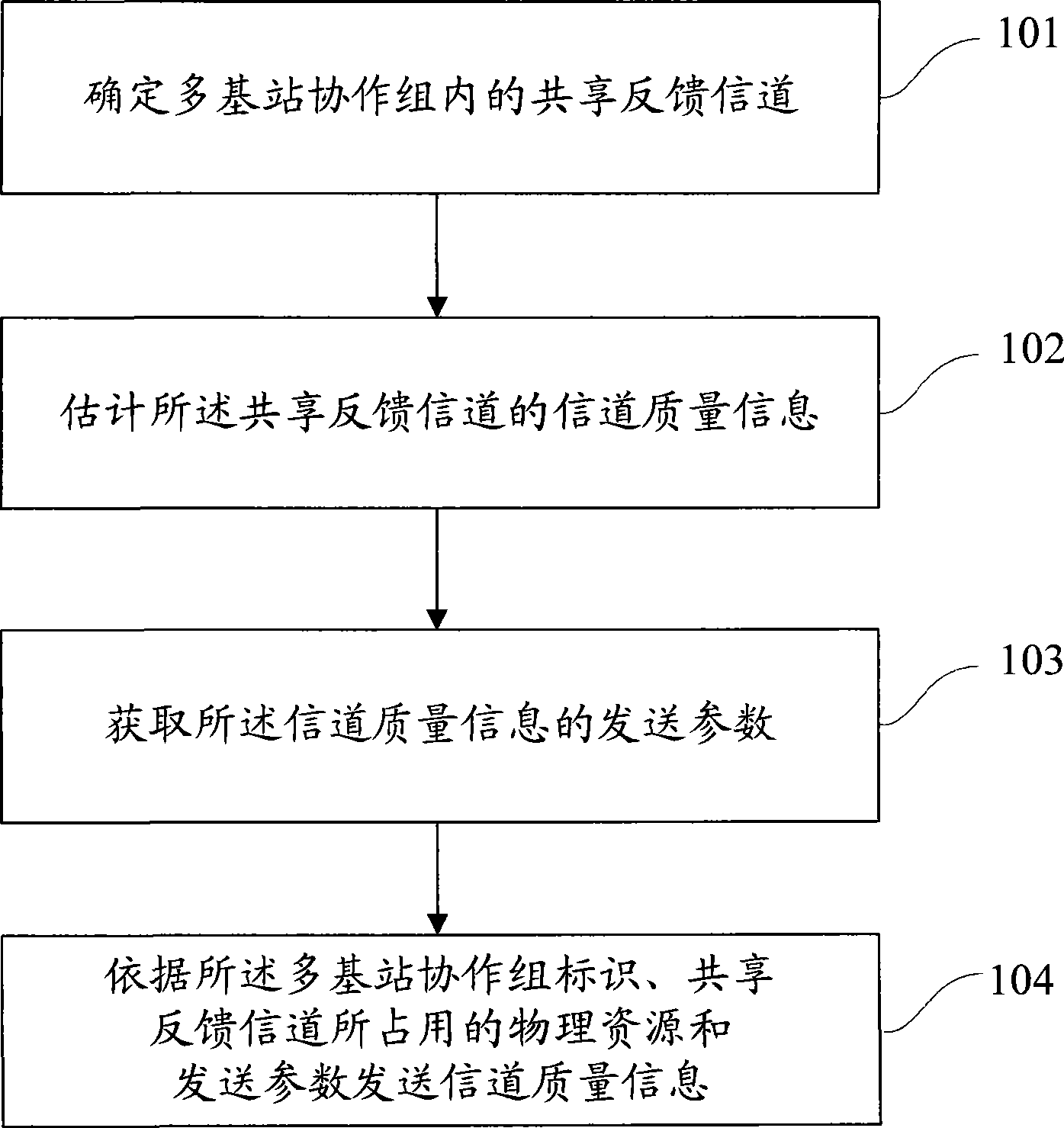
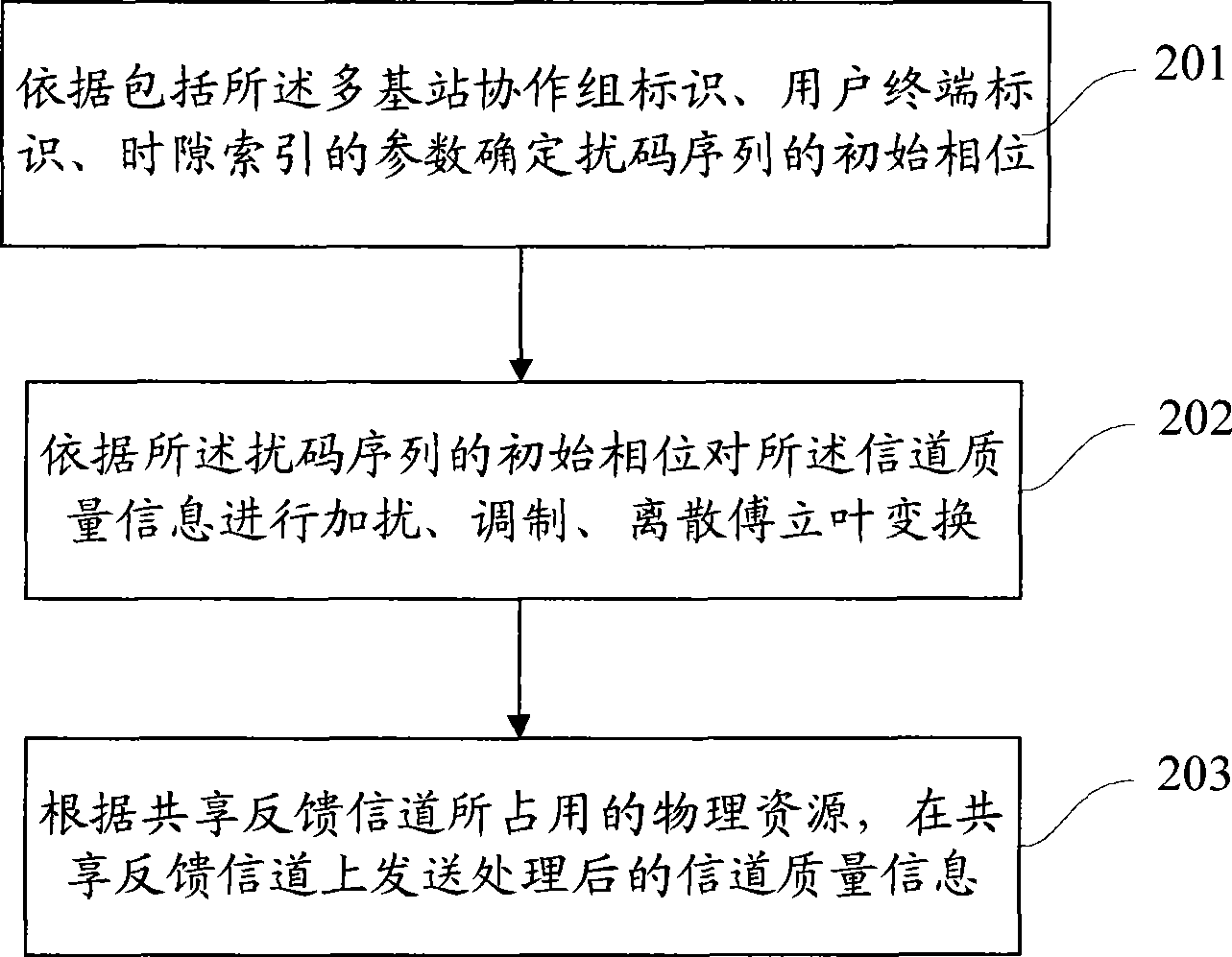
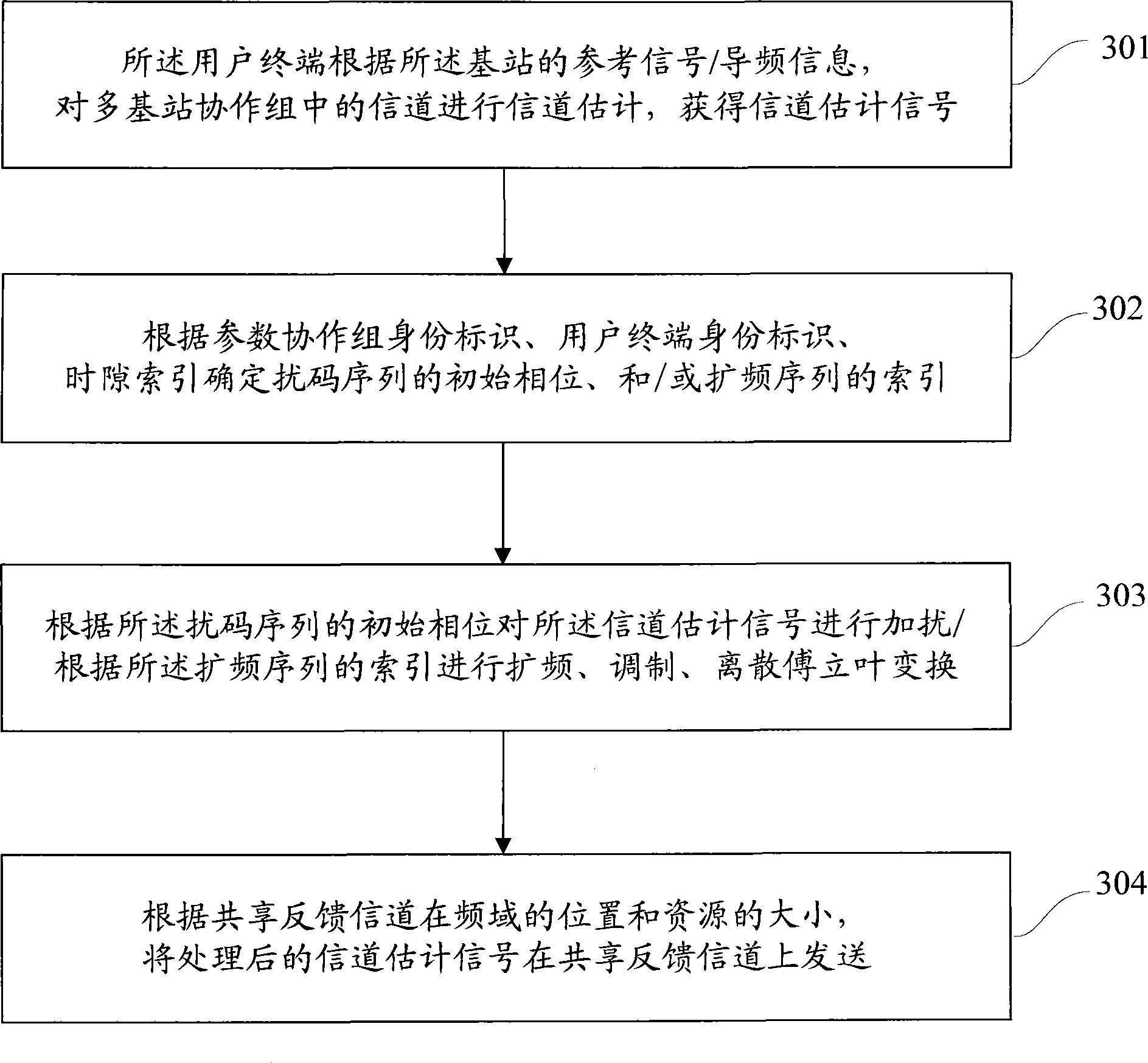
Channel quality feedback method, device and user terminal for multiple base station collaboration group
InactiveCN101394378AError prevention/detection by using return channelMulti-frequency code systemsCo operativeBase station
The invention discloses a channel quality feedback method of a multi-base-station cooperative group, a device and user terminals. The multi-base-station cooperative group comprises a plurality of base stations distributed in different cells, and user terminals covered by the base station, wherein share feedback channels are formed between different cells and occupy corresponding physical resources; and the multi-base-station cooperative group has corresponding mark. The feedback method comprises the following steps: determining the share feedback channels in the multi-base-station cooperative groove; estimating the channel quality of the share feedback channels; and acquiring the transmission parameters of the channel quality information, and transmitting the channel quality information according to the mark of the multi-base-station cooperative group, the physical resources occupied by the share feedback channels, and transmission parameters. The method can achieve channel quality feedback in the multi-base-station cooperative grope so as to provide feasibility for performance gain of multi-base-station cooperation.
Owner:新奇点智能科技集团有限公司
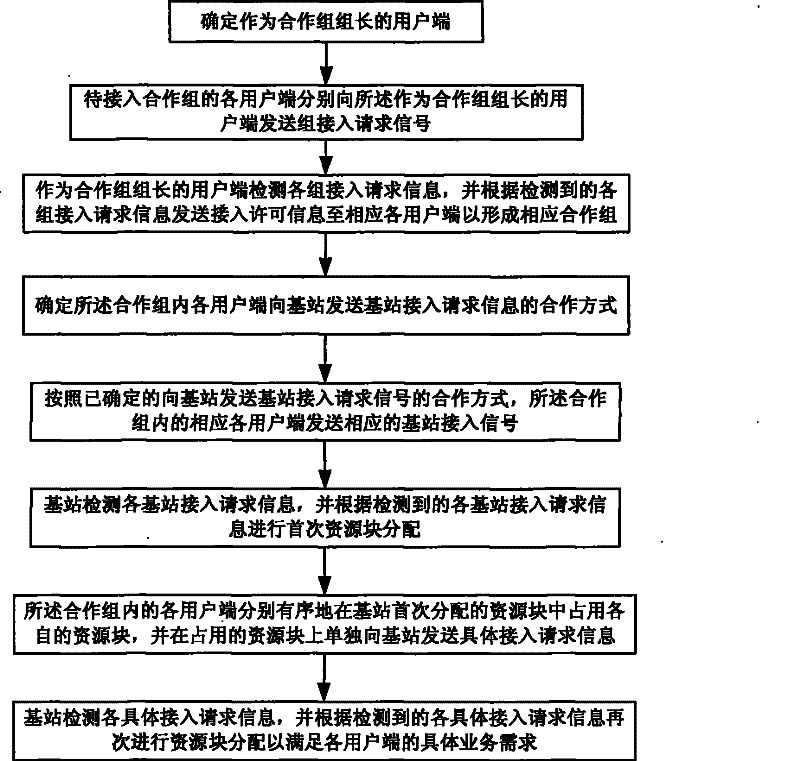
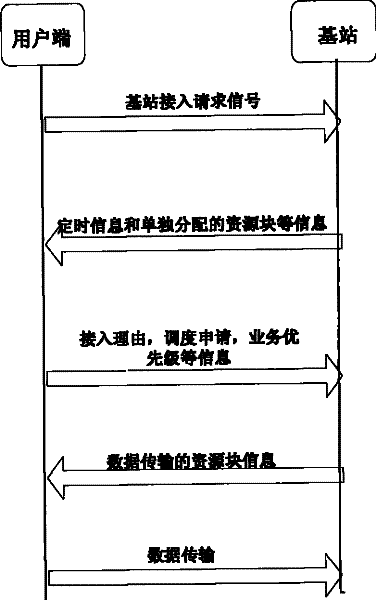
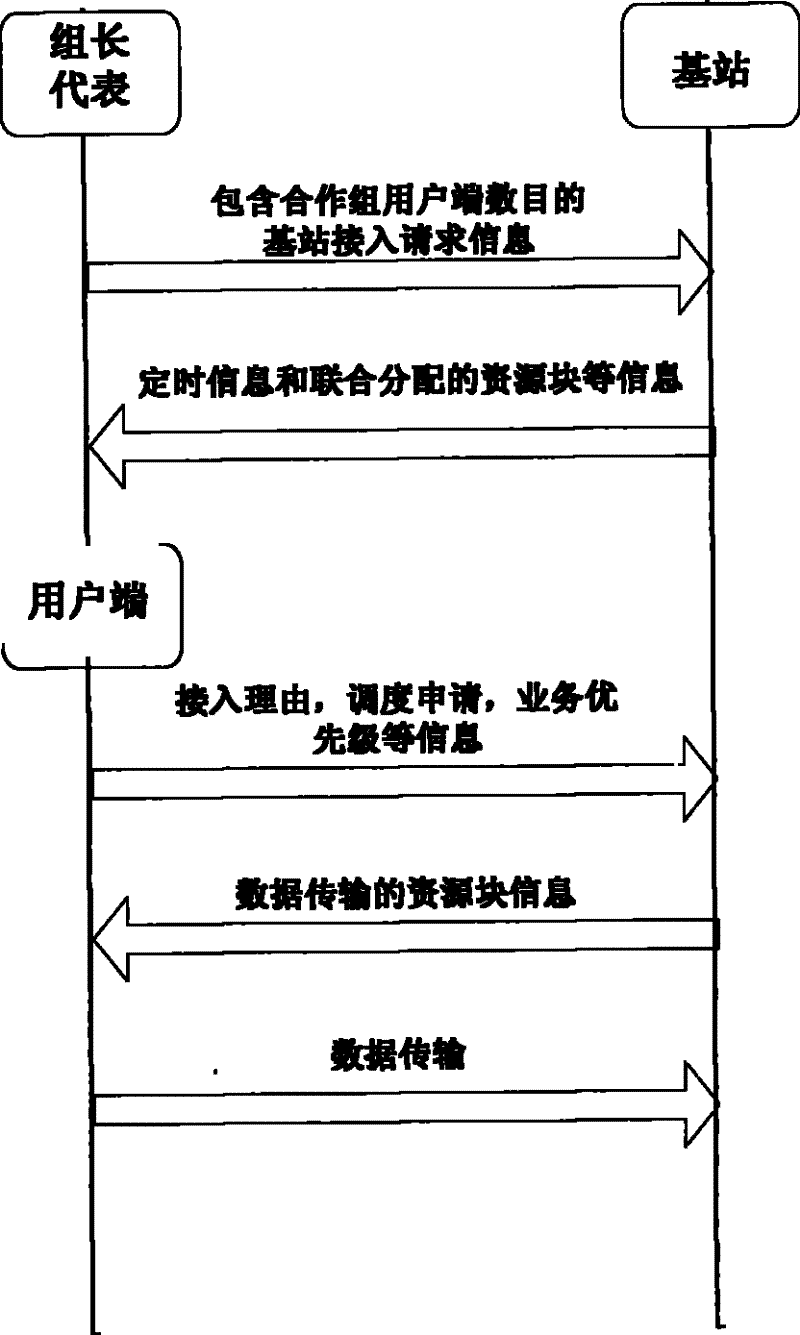
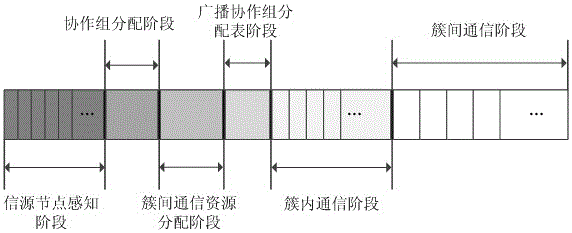
Stochastic access method based on user side cooperative grouping in collaboration cellular network
InactiveCN101365220AAvoid collisionReduce the probability of collisionEnergy efficient ICTRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAccess methodResource block
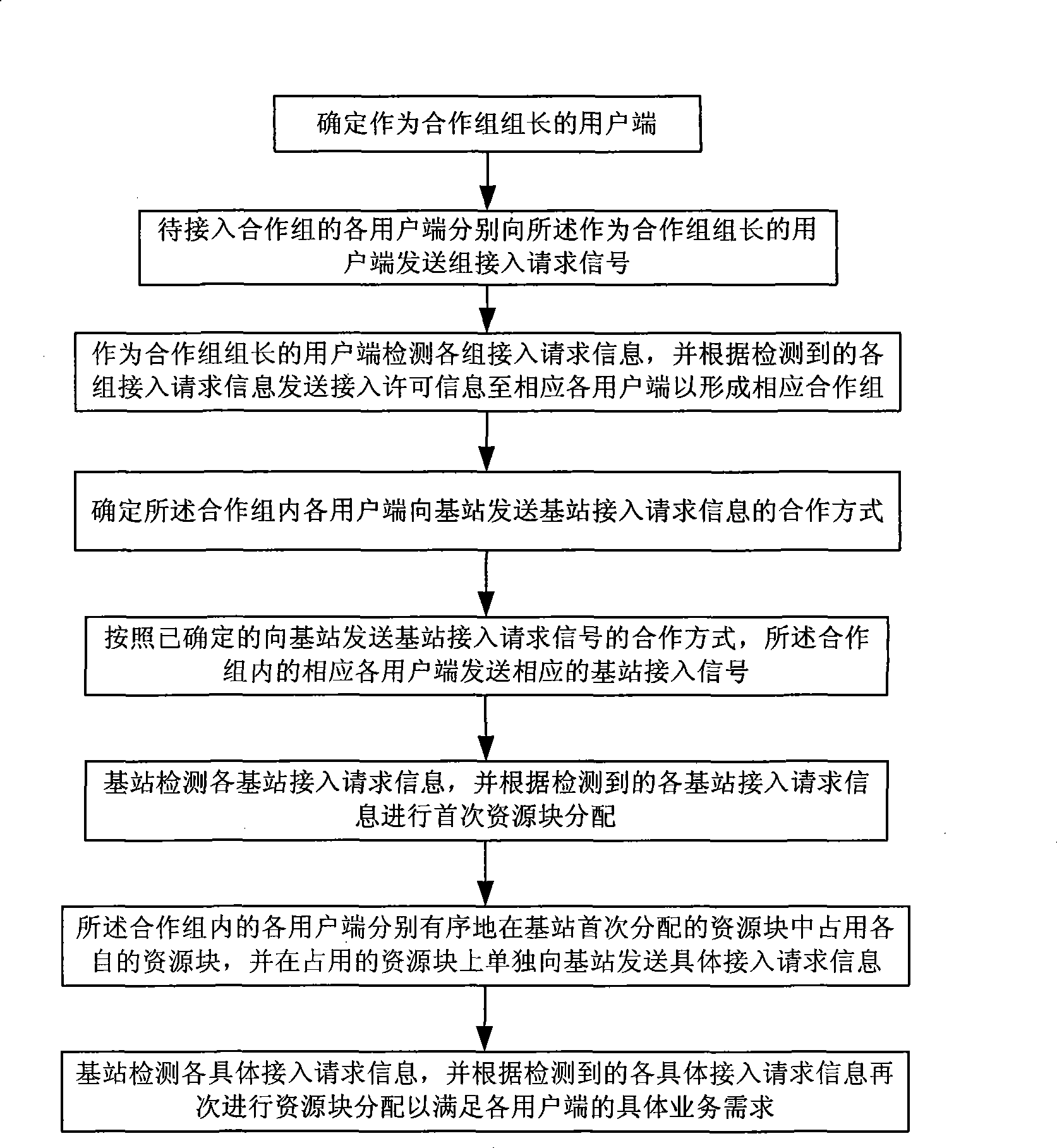
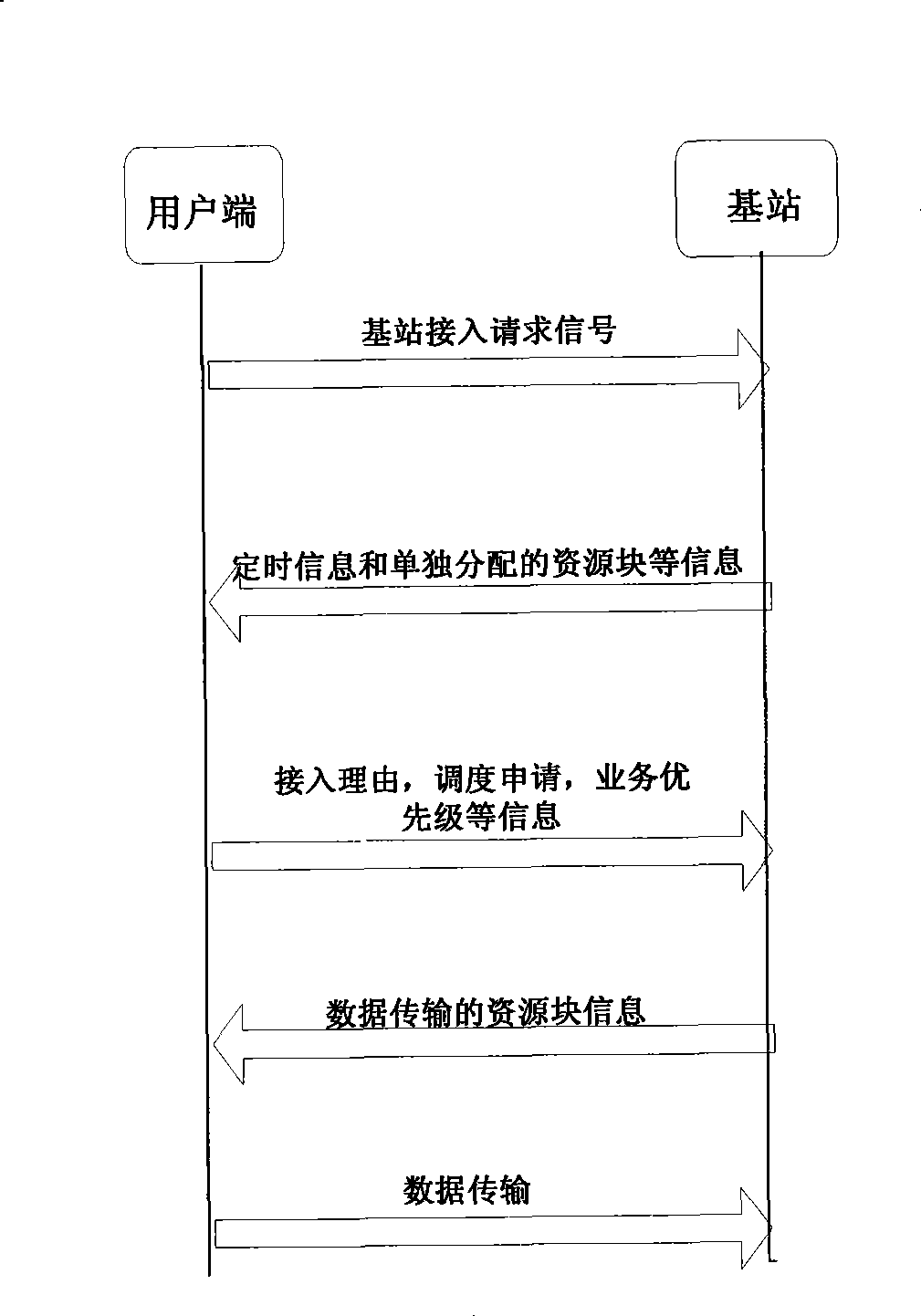
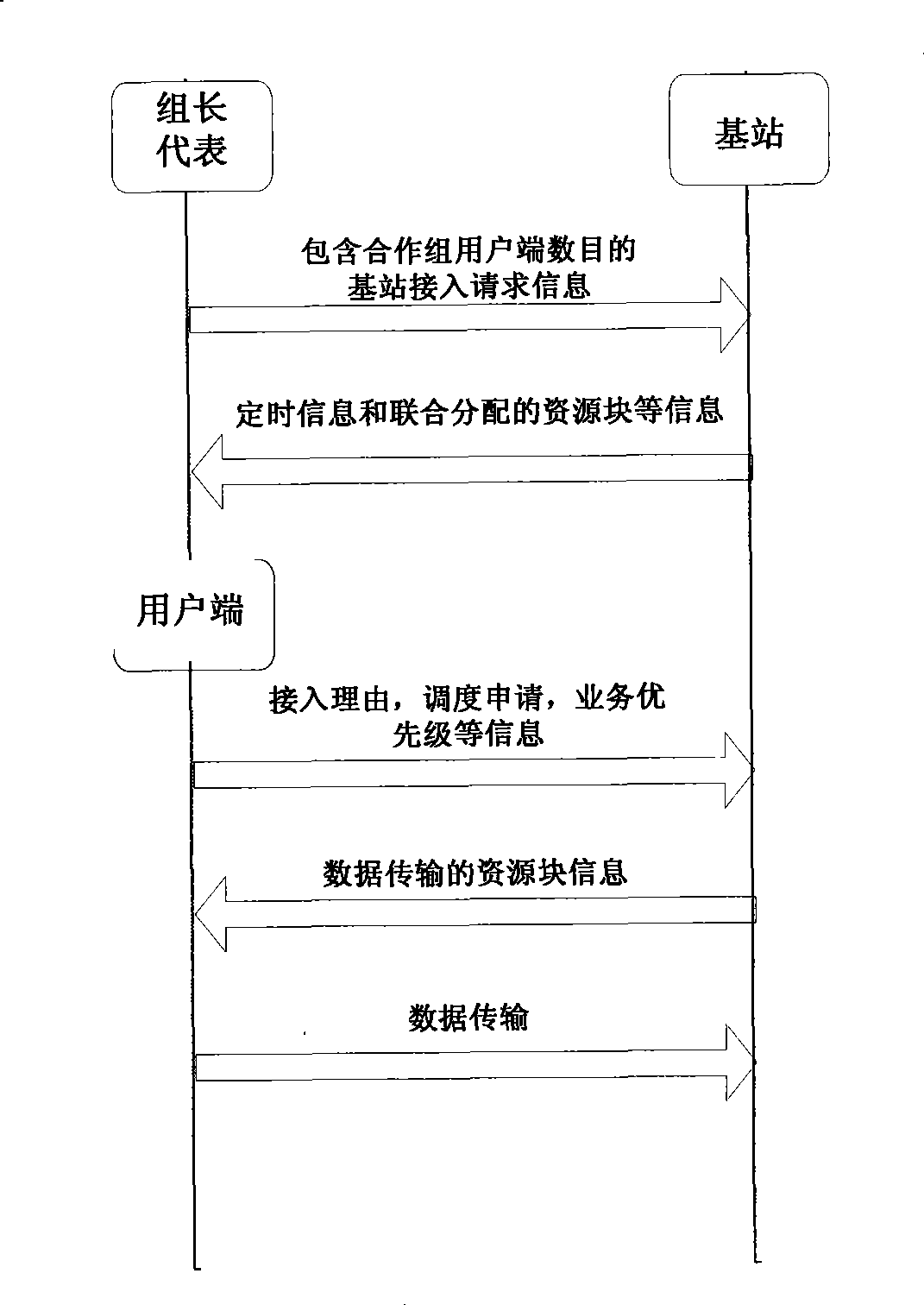
A random access method based on the cooperation and the grouping of user ends of a collaborative cellular network comprises the following steps: the user end is determined as a cooperation group leader; each user end is accommodated by the cooperation group leader into a group to form a corresponding cooperation group; and each user end in the cooperation group sends a corresponding signal of request for base station access to a base station in an established cooperation mode. When the base station conducts the initial allocation of resources according to the detected signal of request for base station access, each user end in the cooperation group occupies a resource block initially allocated by the base station in sequence, and sends a concrete message of request for access to the base station independently. At last, the base station dispatches the resource blocks again to satisfy the actual operational requirements of each user end. Through the cooperation and the grouping of each user end during the random access process, the method can reduce the probability of collision and conflict between the user ends and reduce the energy consumption thereof, thus further improving the random access performance of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
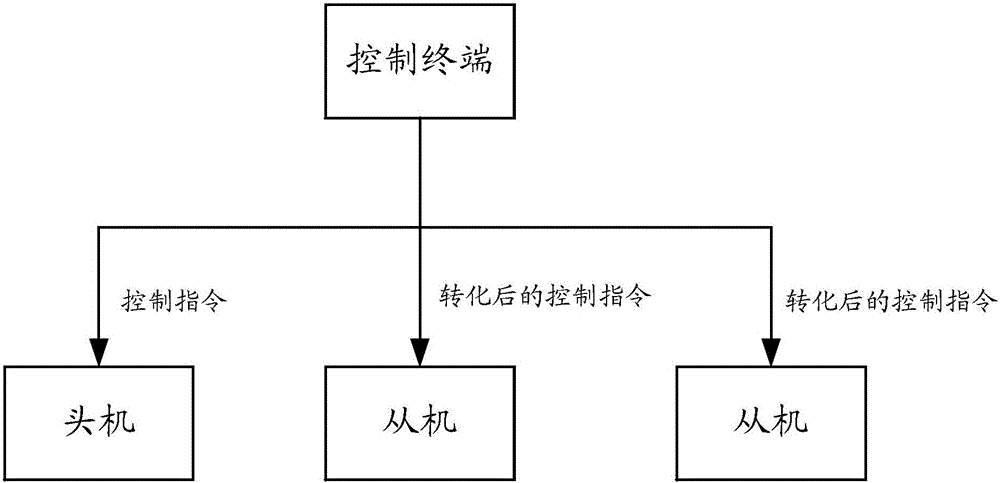
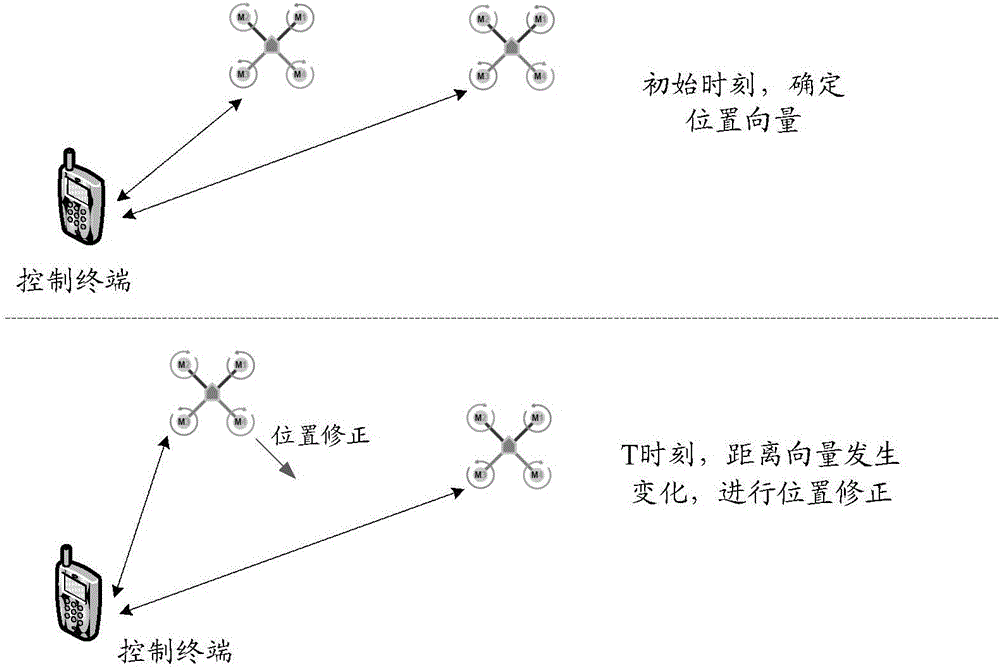
Control method and control terminal of aircraft
ActiveCN105892476AEnsure safetyEasy to controlAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsAerospace engineeringCooperative group
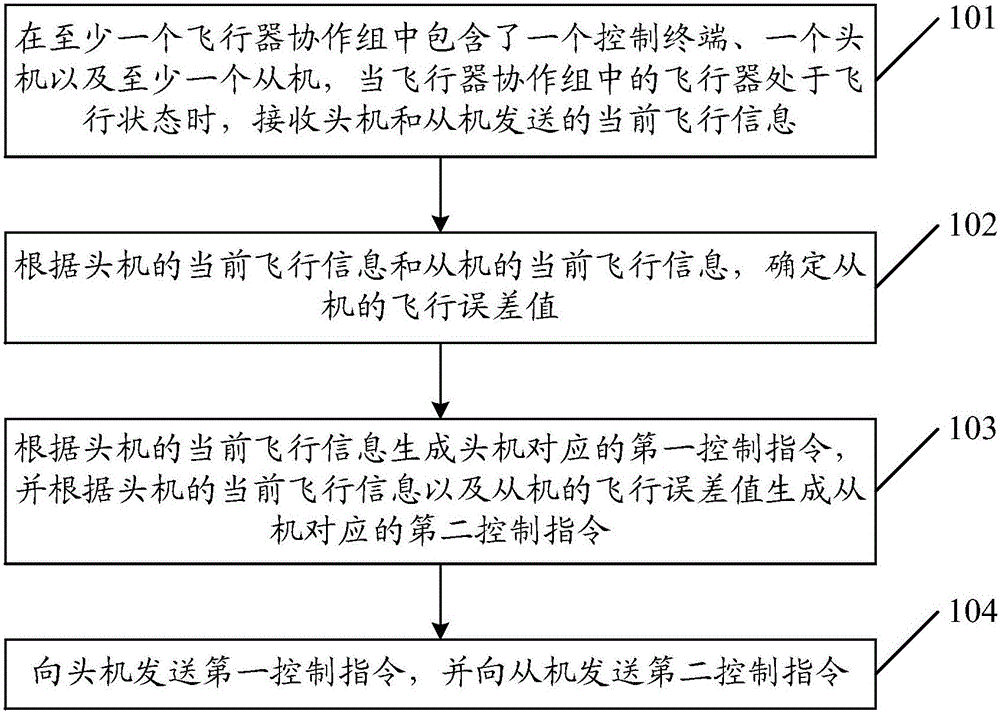
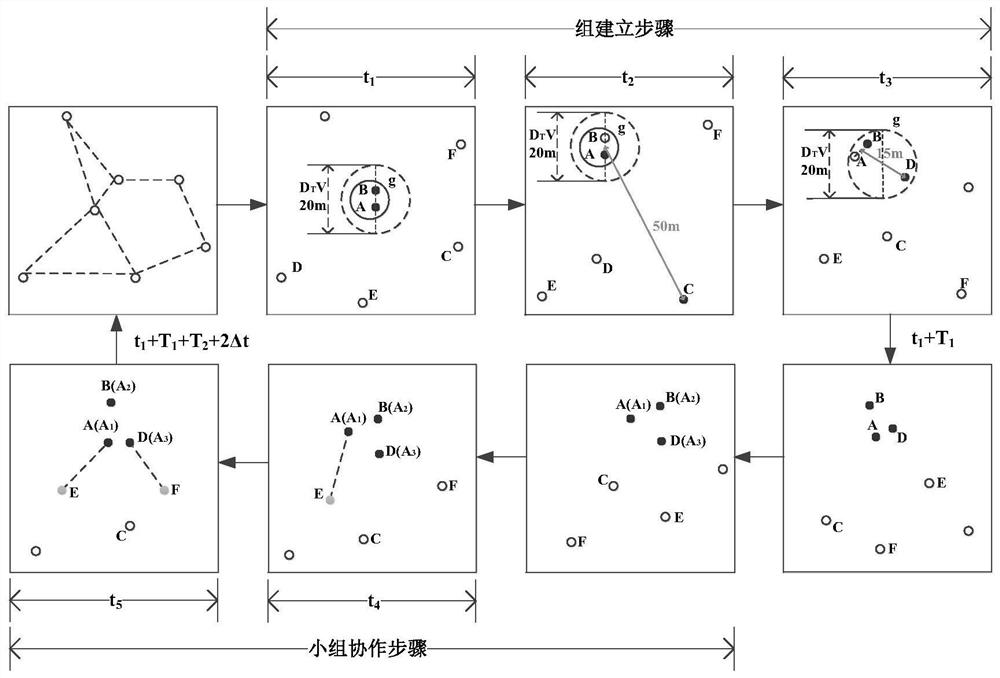
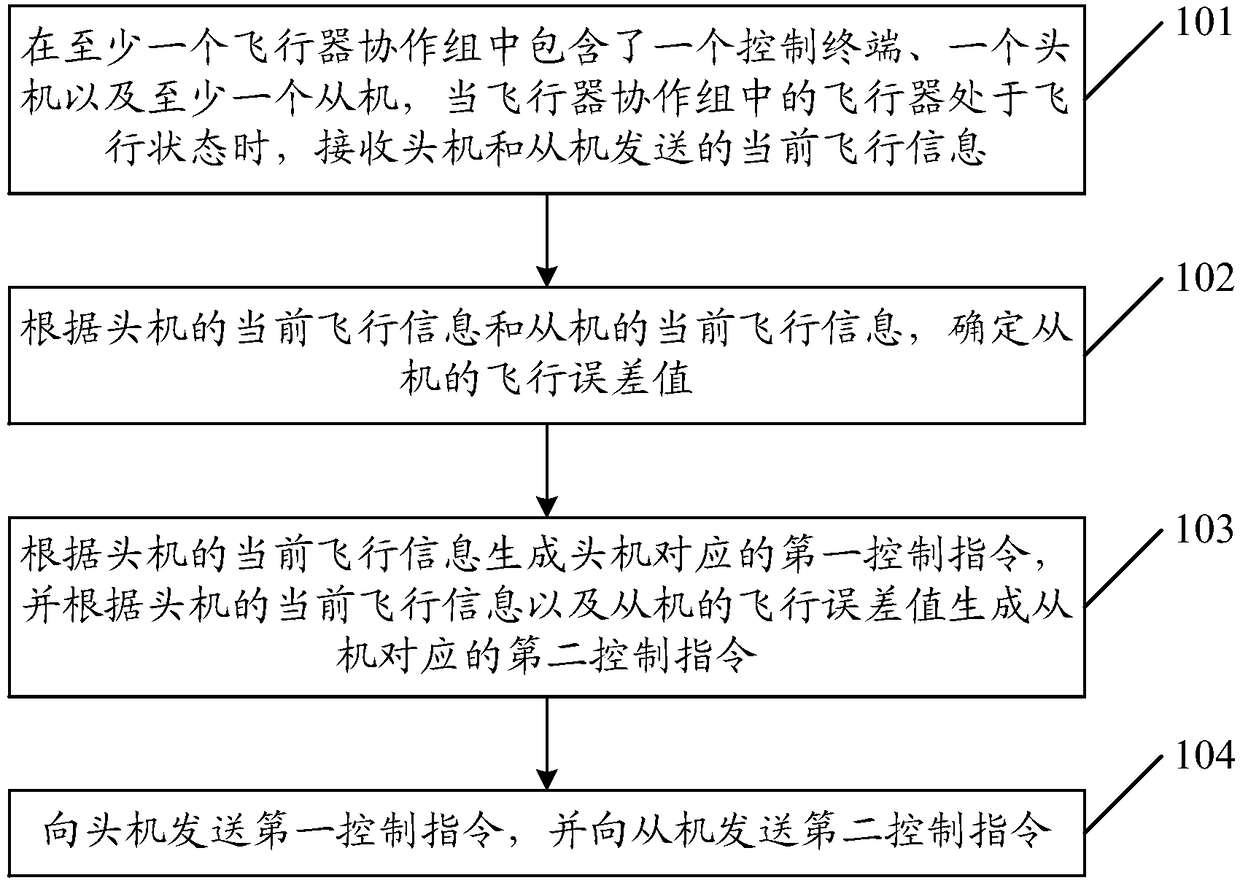
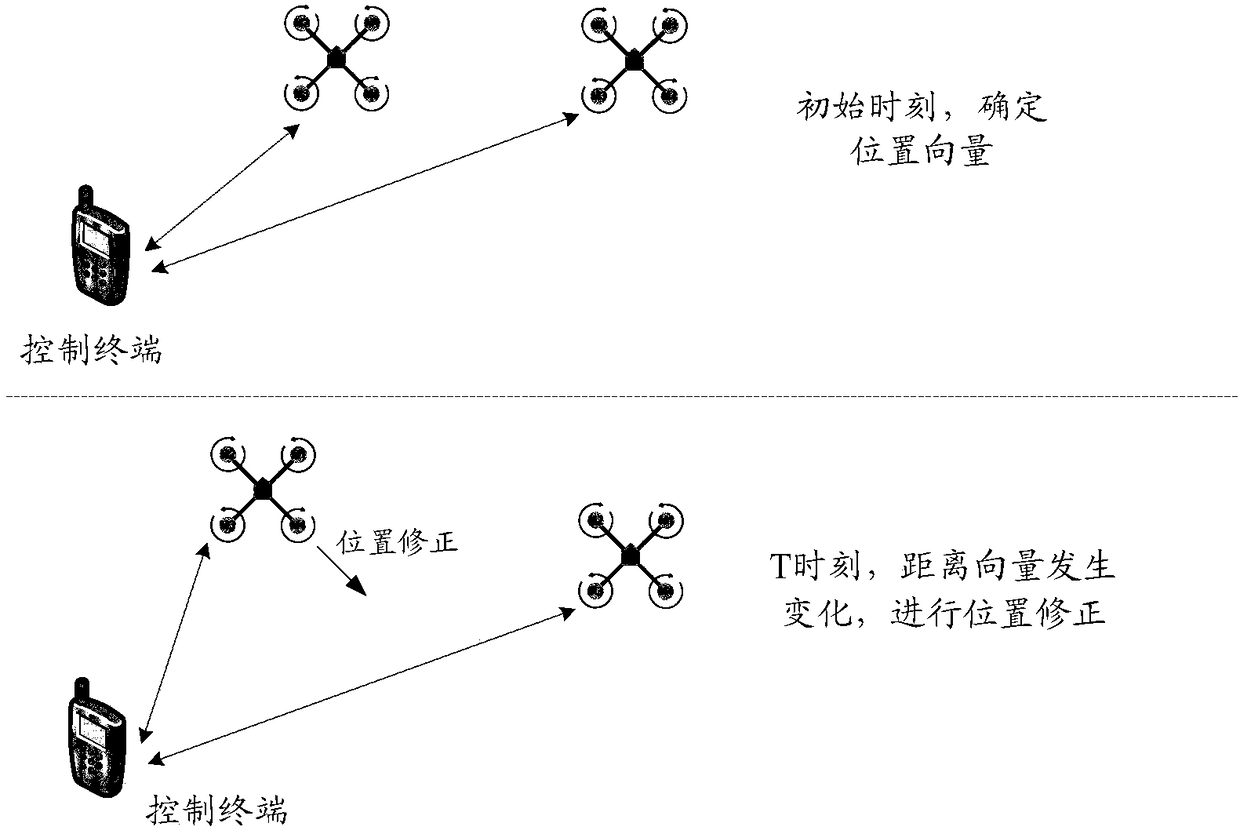
The embodiment of the invention discloses a control method of an aircraft. The method is applied to at least one aircraft cooperative group which comprises a control terminal, a master unit and at least one slave unit. The method comprises the following steps: when the aircraft is in a flying state, receiving current flying information transmitted by the master unit and the slave units; determining a flying error value of each slave unit according to the current flying information of the master unit and the slave units; generating a first control instruction of the master unit according to the current flying information of the master unit, and generating a second control instruction of the slave units according to the current flying information and the flying error value of the slave units; transmitting the first control instruction to the master unit, and transmitting the second control instruction to the slave units. The embodiment of the invention further provides the control terminal. One control terminal can be used for simultaneously controlling a plurality of aircrafts to fly under a condition of no mutual collision, to guarantee the safety during flying and keep a formation during flying; the control terminal is favorable for letting an operator control the aircraft.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
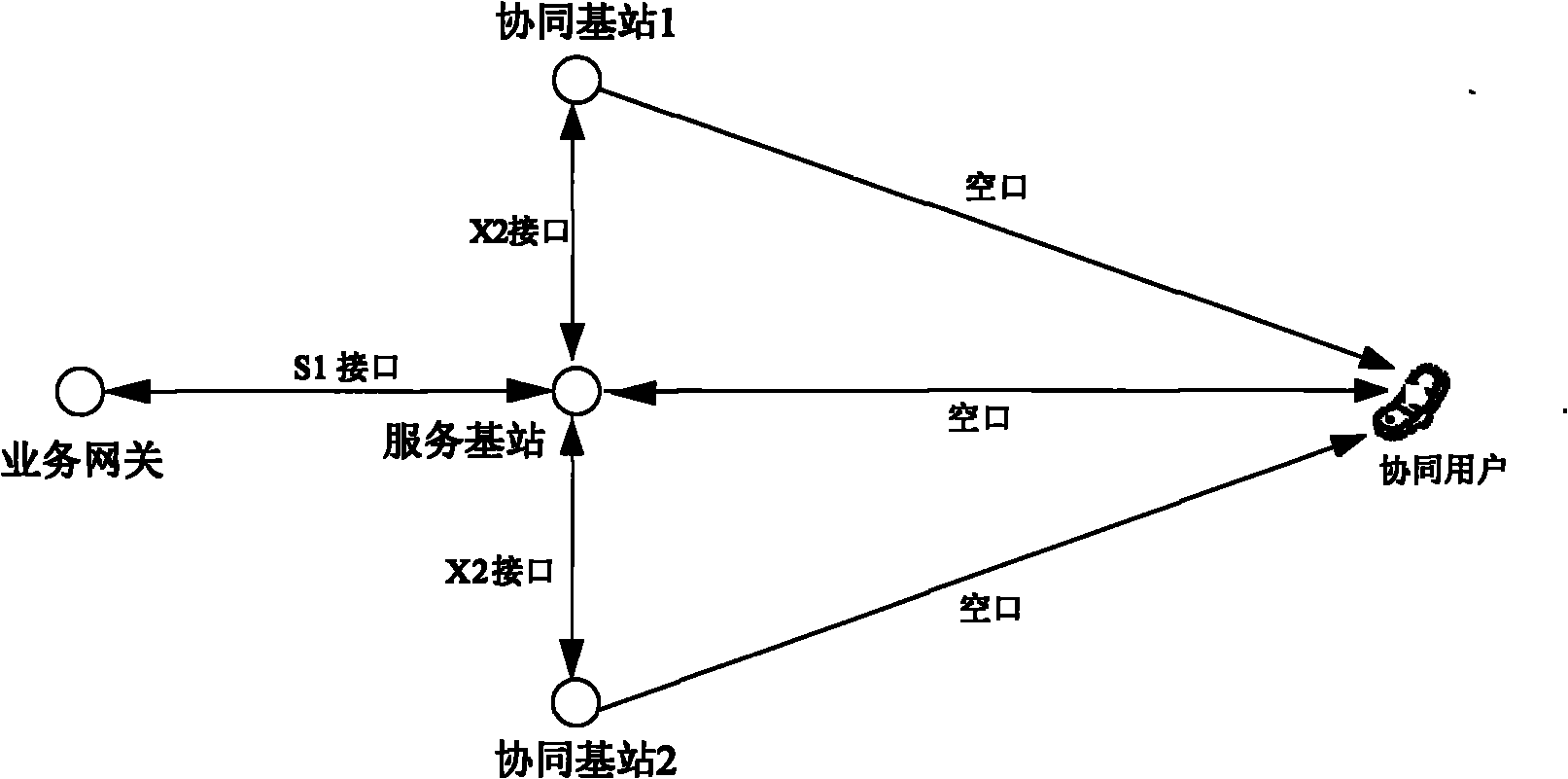
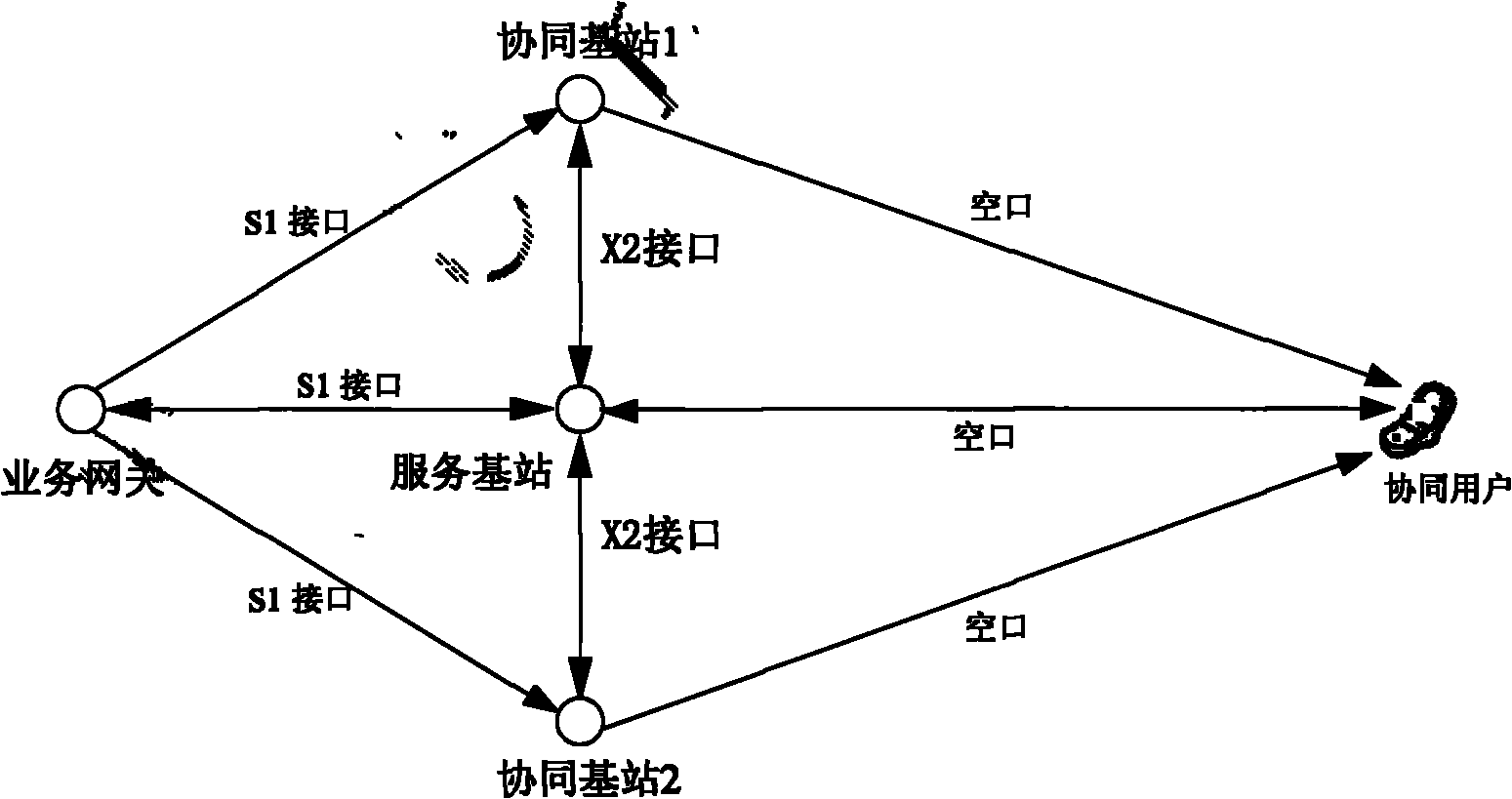
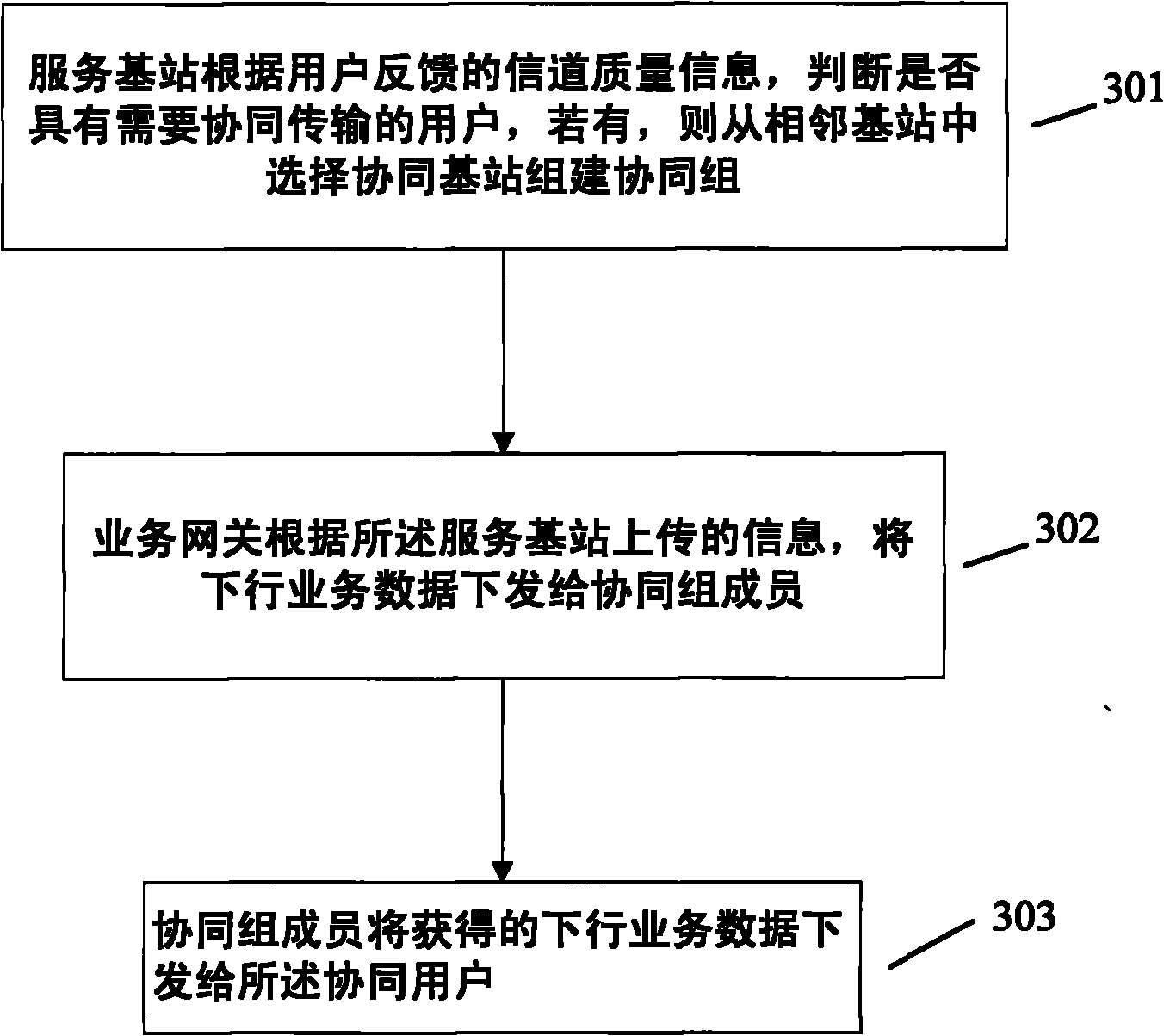
Cooperative data transmission method and system
InactiveCN101883402ASolve the real problemDistribution impactSpatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringAccess networkUser needs
The invention discloses a cooperative data transmission method and a cooperative data transmission system. In the scheme of the invention, a service base station judges whether a user needing cooperative transmission exists or not according to channel quality information fed back by the user, if so, the service base station builds a cooperative group, a service gateway transmits downlink service data to cooperative group members through an S1 interface according to information uploaded by the service base station and the cooperative group members transmit obtained downlink service data to the cooperative user through an X2 interface. The method and the system have the advantages of solving the problem of downlink service data in cooperative transmission, allowing the service base station and each cooperative base station to obtain the downlink service data of the cooperative user, performing cooperative transmission on the cooperative user, meeting the requirement on downlink data distribution in a joint processing mode, adding additional processing for an access network side or improving gateway capability without causing any effect on the service distribution of non-cooperative users.
Owner:ZTE CORP
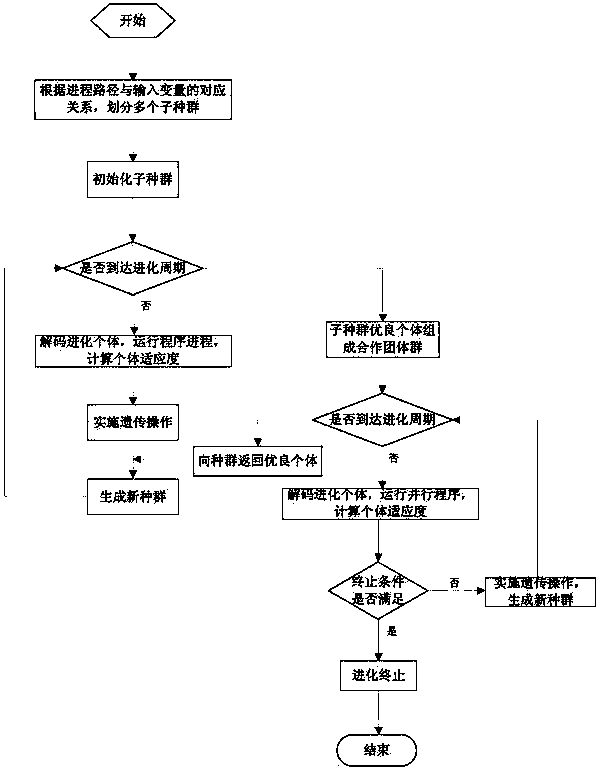
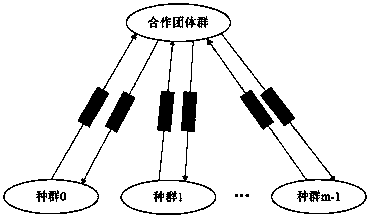
Method for generating test data covering parallel program paths based on coevolution
InactiveCN103902457AGenerate efficientlyGenetic modelsSoftware testing/debuggingMathematical modelTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a method for generating test data covering parallel program paths based on coevolution, and aims to provide a method for automatically and efficiently generating test data covering parallel program objective paths. The method includes the following specific steps that firstly, a mathematical model of a test data generation problem is built, and a problem for generating the test data covering the parallel program paths is modeled into a single-object optimization problem; secondly, a coevolution genetic algorithm is designed to solve the model. According to the method, groups are divided into a plurality of sub groups and a cooperative team group according to the correlation of course paths and program input components. Each sub group is used for independently optimizing a part of input components relevant to one certain course path. After the sub groups are evolved into a certain period, excellent individuals of the sub groups are combined to form an initial individual of the cooperative team group so as to be used for optimizing complete program input. After the cooperative group is evolved into a certain period, the excellent individuals are returned to the sub groups. Through alternate coevolution of the cooperative team group and the sub groups, the expected test data are generated.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
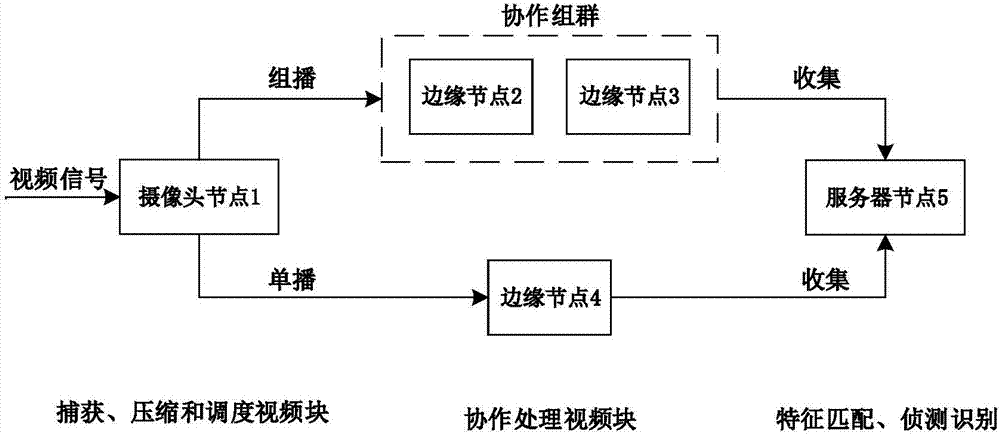
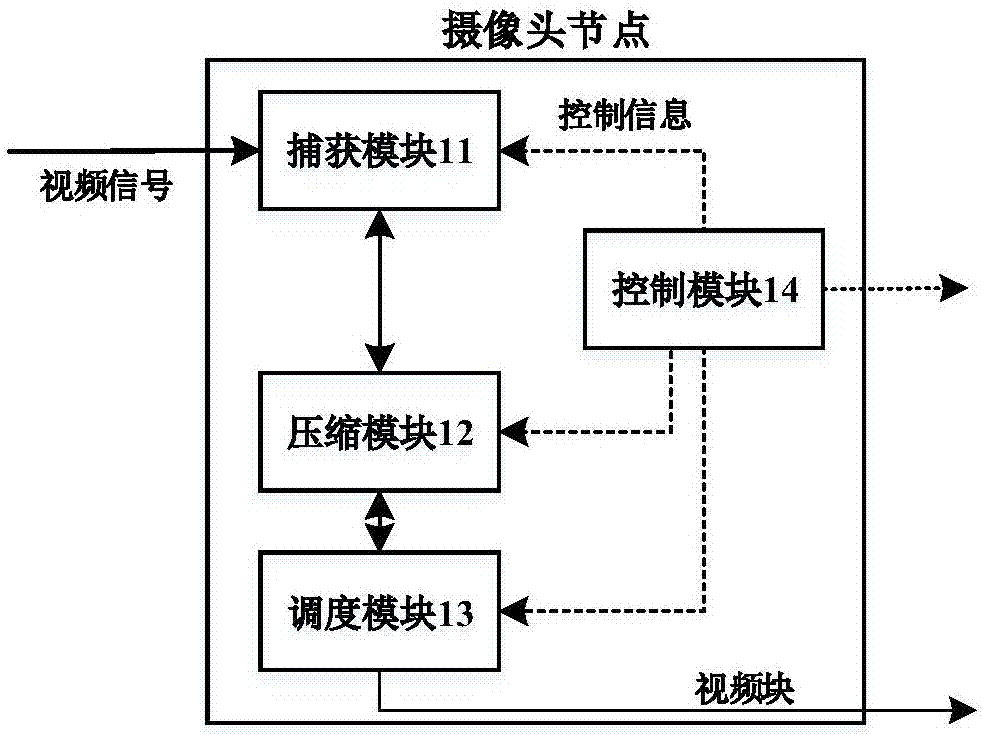
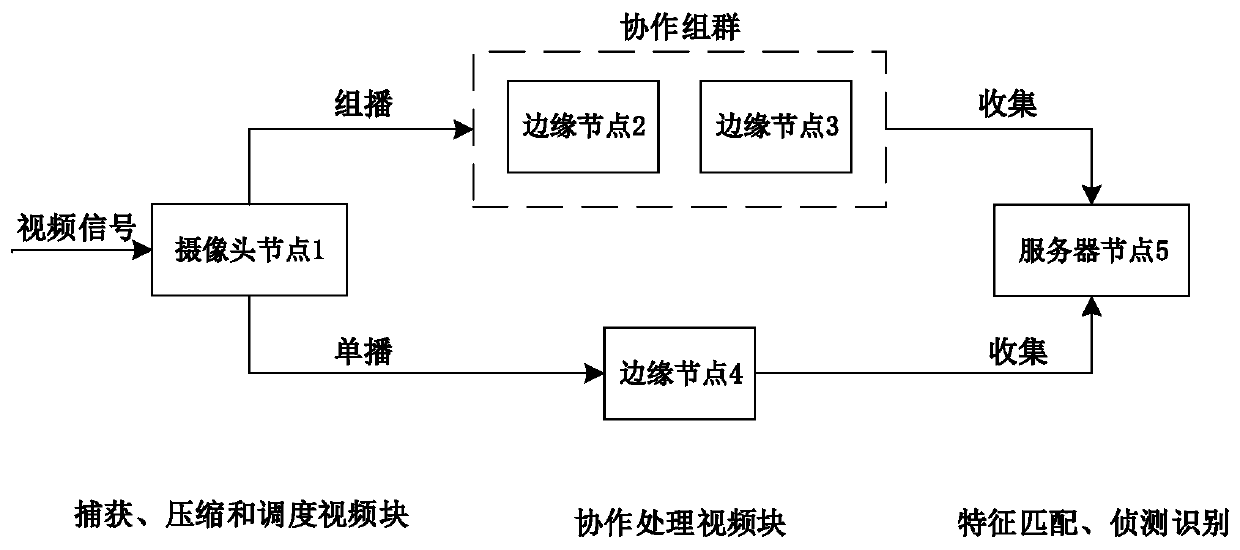
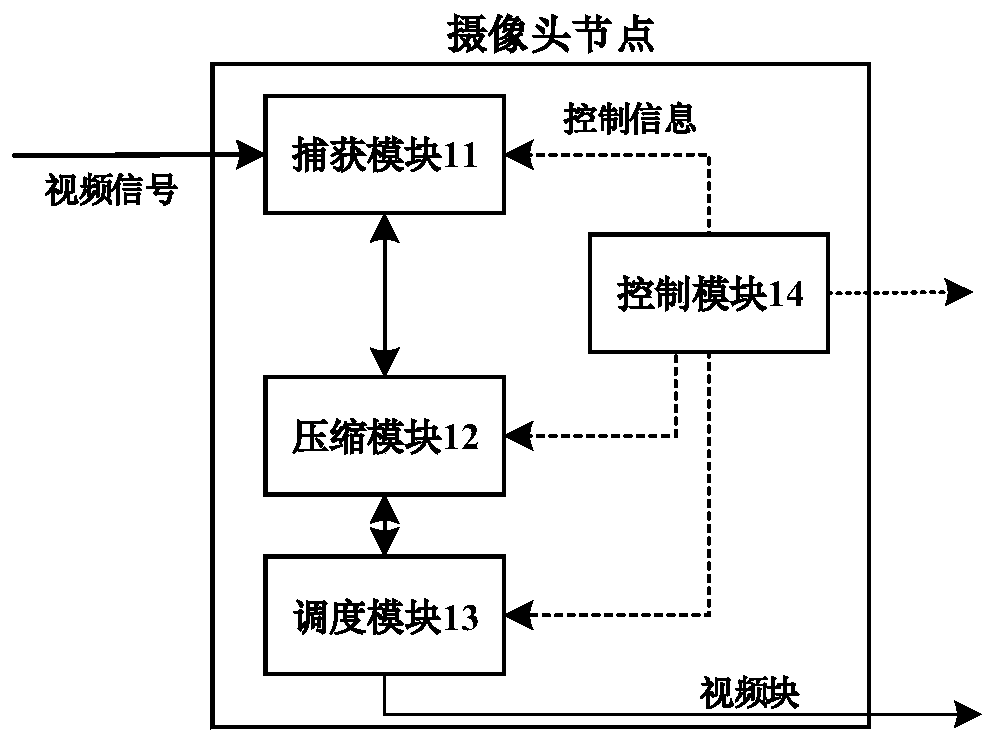
Video processing system based on cooperative grouping mechanism
ActiveCN107241577AAchieving Detection AccuracyReduce computational complexityNetwork topologiesClosed circuit television systemsBlock schedulingVideo processing
The invention discloses a video processing system based on a cooperative grouping mechanism and belongs to the field of video wireless communication. The system disclosed by the invention comprises a camera node, an edge node and a server node, wherein a control module of the server node forms a cooperative group through a channel condition and computing ability information of the edge node received based on a relationship between an average video code rate and an object sensing precision by means of cooperative processing of the edge node and constructs a video block scheduling mechanism, so that the object sensing precision is effectively improved; and meanwhile, problems of a computing delay due to camera node processing, a transmission delay due to far end server processing, computing resource waste of residual edge nodes in a non-cooperative processing mechanism and sub task scheduling due to difference of transmission rates are solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
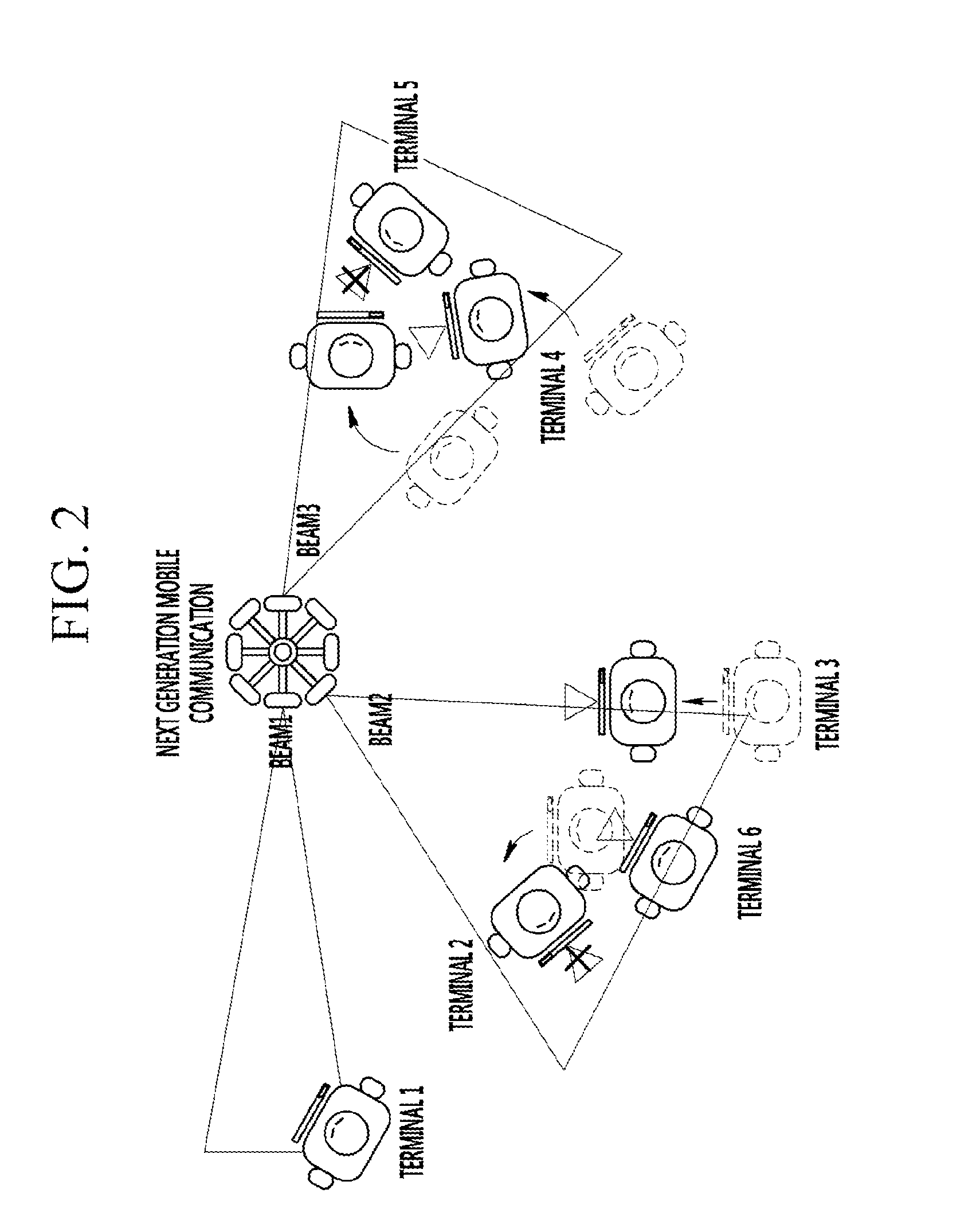
Method and apparatus for communication to prevent communication link failure in millimeter band communication system
ActiveUS20160127170A1Site diversitySpatial transmit diversityMillimeter wave communication systemsTelecommunications link
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for communication in a millimeter band communication system. In a case in which a first terminal obtains a list including members of a cooperative group in which terminals receive a service with the same beam as a first terminal's beam, the first terminal informs a second terminal, corresponding to a member of the list, of communication link failure when the failure occurs, and requests a cooperative service. After that, the first terminal receives information on the service from a base station through the second terminal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
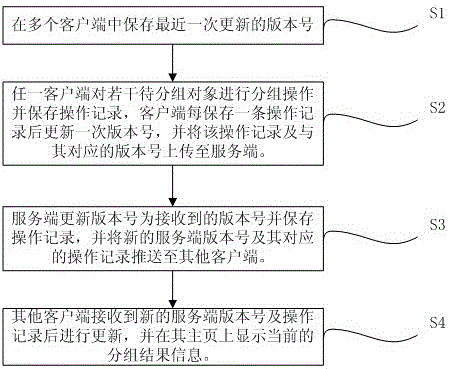
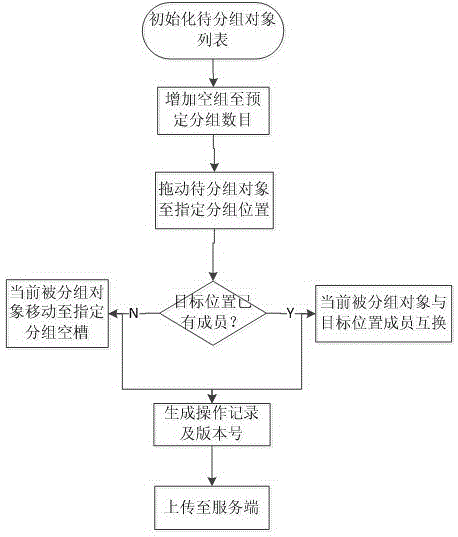
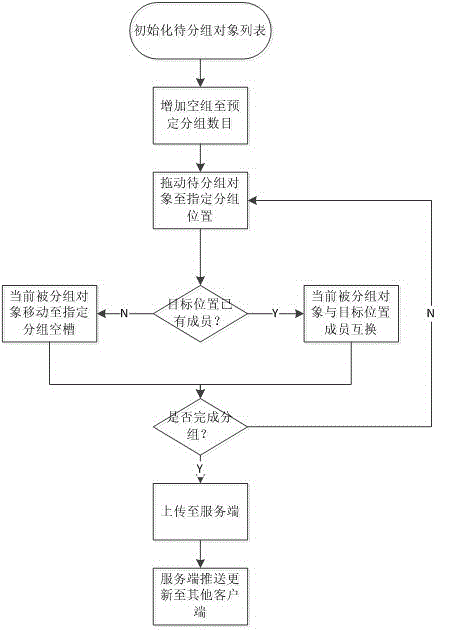
Multi-client cooperative grouping and displaying method
InactiveCN105005499ACollaborative grouping is orderly and effectiveMultiprogramming arrangementsProgram loading/initiatingHome pageClient-side
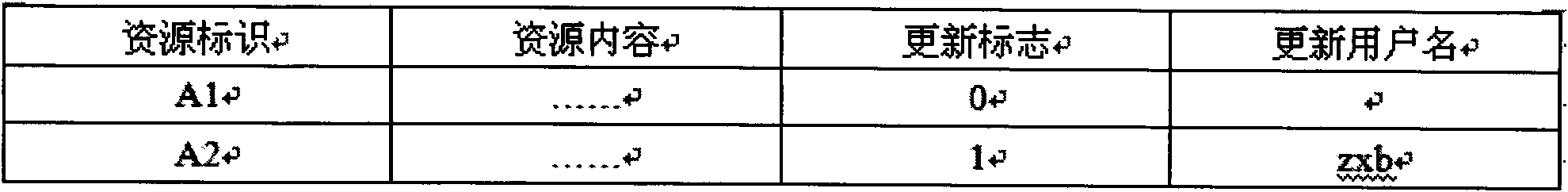
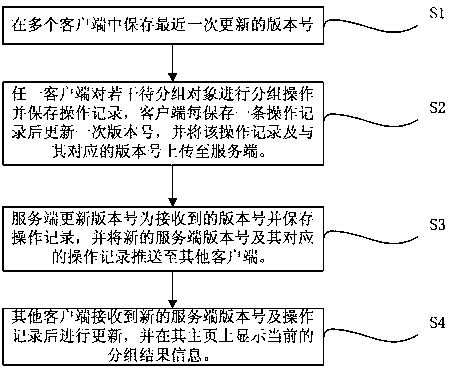
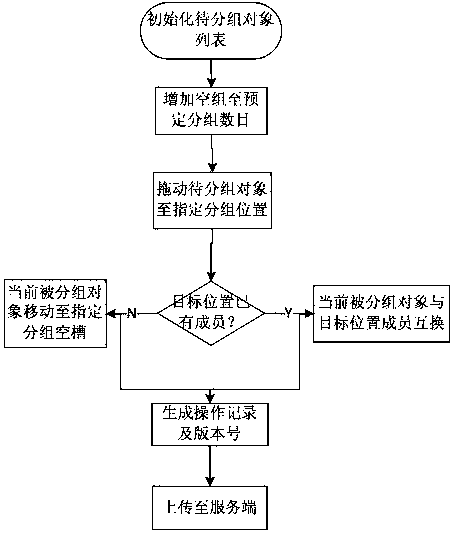
The invention provides a multi-client cooperative grouping and displaying method. When a plurality of clients perform grouping operation on a plurality of to-be-grouped objects, each client stores an operation record, each operation record corresponds to a version number, and the operation records and the corresponding version numbers are uploaded to a server; and the server receives the operation record and the corresponding version number, updates the version number of the server to the received version number, stores the operation record and pushes a new grouping result to the other clients, and the other clients receive the new grouping result and display newest grouping result information in a home page. The method solves the problem of conflict when the clients display newest grouping data mutually during simultaneous grouping of the to-be-grouped objects. According to the method, the server receives the newest grouping operation record of each client and pushes the operation record to each client, the multi-client cooperative grouping is orderly and effectively carried out, and the clients can obtain the newest grouping information data from one another in time.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIUYUN INFORMATION TECH
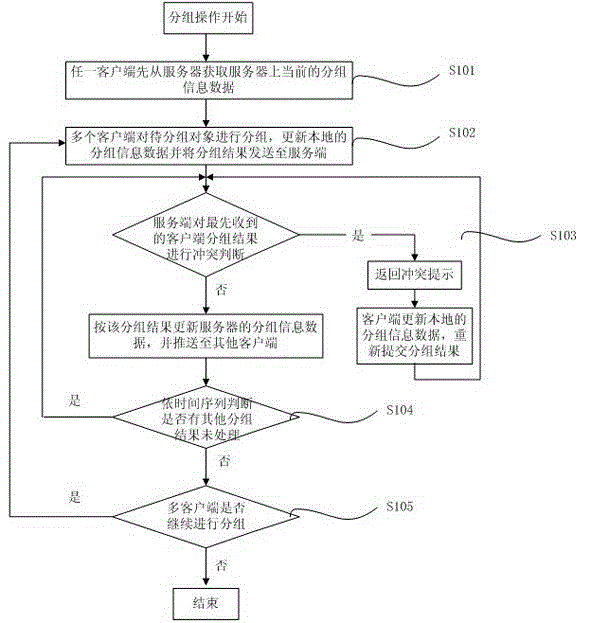
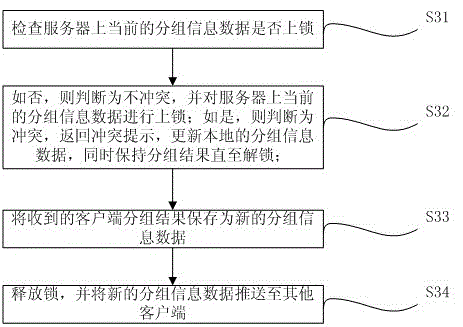
Concurrent conflict and permission processing method for cooperative grouping through multiple clients
The invention provides a concurrent conflict and permission processing method for cooperative grouping through multiple clients, comprising the following steps: any client acquires current grouping information data of a server from the server each time the client starts grouping operation; the multiple clients group a plurality of objects to be grouped, and send grouping results to the server; the server makes conflict judgment on the first received client's grouping result, updates the grouping information data of the server according to the grouping result and pushes the grouping information data to the other clients if there is no conflict, and returns a conflict prompt if there is conflict; and the server processes the received grouping results of the other clients according to the time sequence, and the process continues until the grouping operations of all the clients end if multiple grouping operations can be performed. By adopting the concurrent conflict and permission processing method, grouping can be carried out synchronously at multiple clients, multiple users can operate grouping objects synchronously without influencing one another, and the grouping results can be shared through the server.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIUYUN INFORMATION TECH
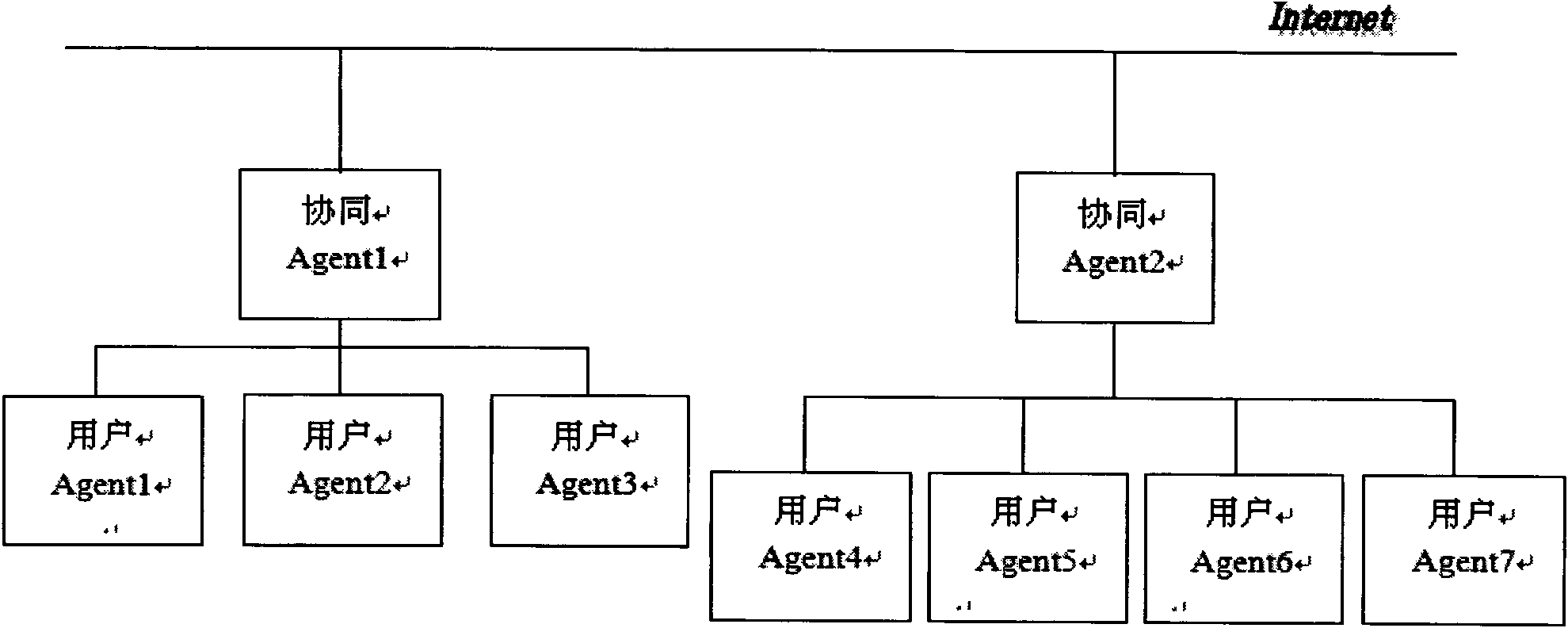
Dynamic group establishment-based cooperative control method
The invention relates to the technical field of cooperative control, in particular to a dynamic group establishment-based cooperative control method. The method comprises the following steps that: a cooperative agent receives a cooperative request of a master user agent terminal; the cooperative agent selects one or more slave user agent terminals from a group user list; the cooperative agent sends the cooperative requests to one or more slave user agent terminals; the cooperative agent receives the responses of one or more slave user agent terminals; and the cooperative agent establishes the master user agent terminal and one or more slave user agent terminals into a dynamic group. By the method, a dynamic group establishment-based cooperative control system is realized, the dynamic requirement of a cooperative group in practical work is met, and the adaptability of the group to environment is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
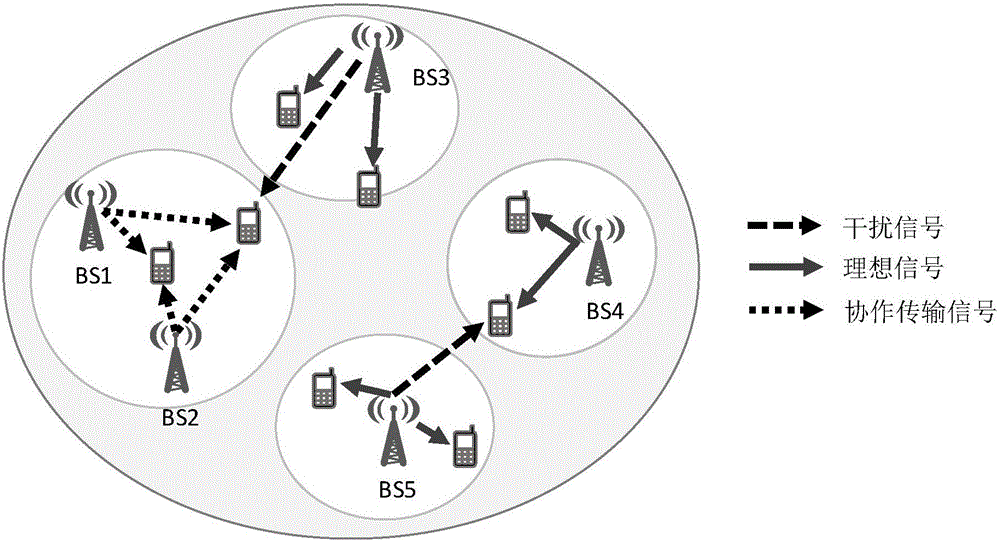
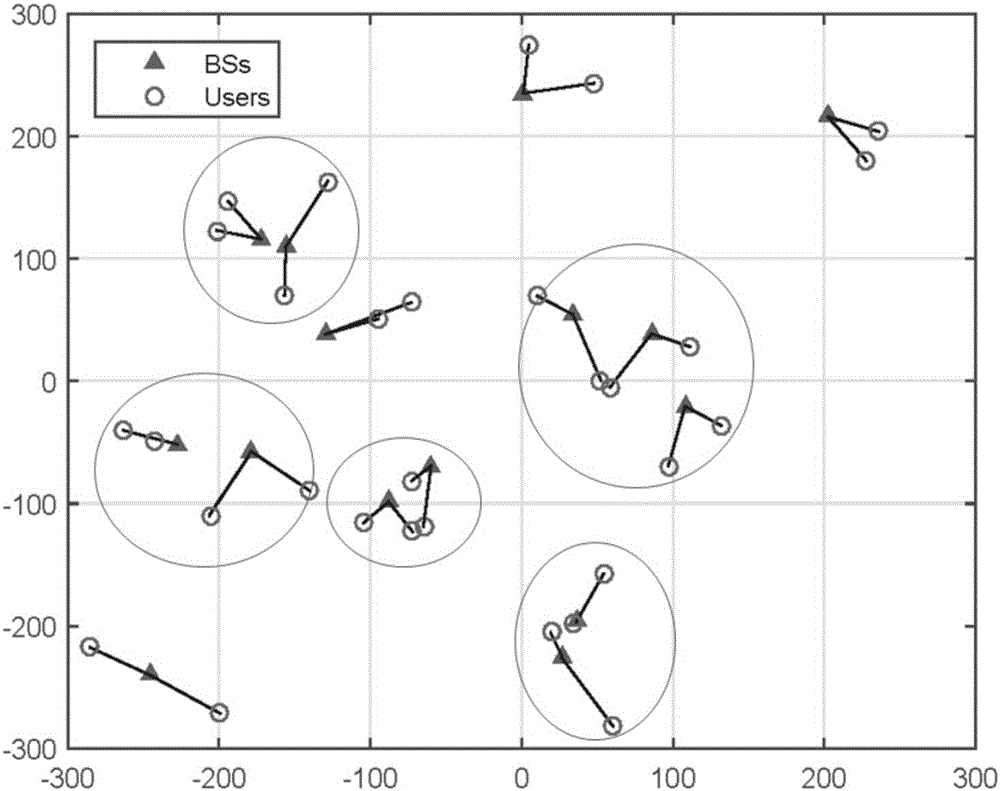
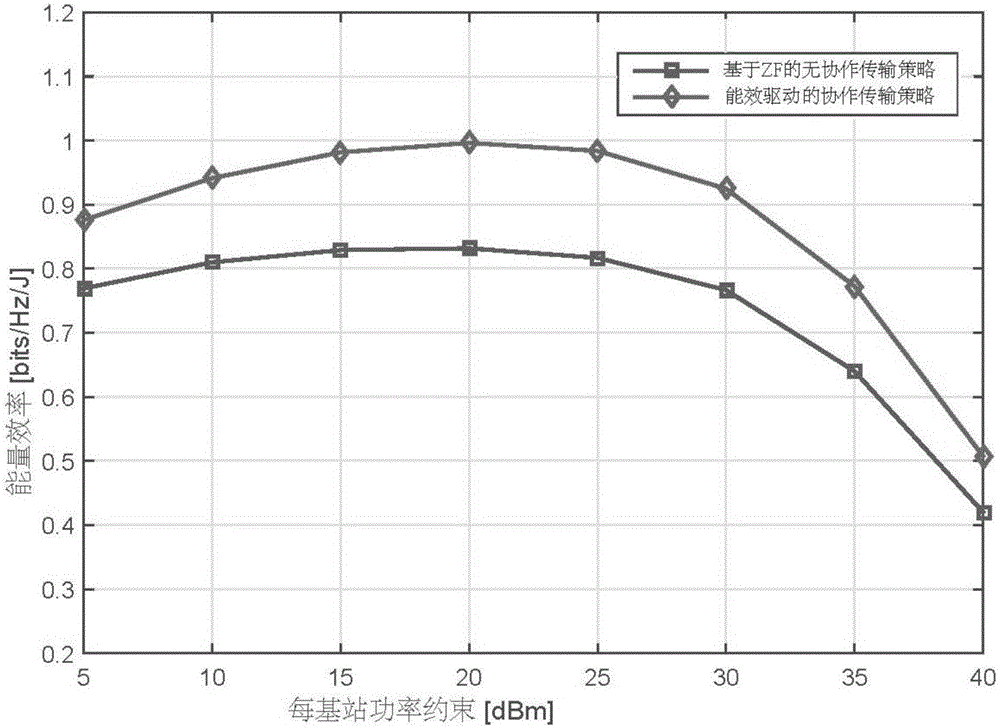
Multi-base station cooperative transmission strategy in energy efficiency drive
ActiveCN105959043AFix build issuesFast convergenceSite diversitySpatial transmit diversitySimulationTrade offs
The invention discloses a multi-base station cooperative transmission strategy in energy efficiency drive, and belongs to the technical field of energy efficiency optimization in wireless networks. The transmission strategy adopts the technical means of coalition formation game; the base station cooperative group problem is modeled as the coalition formation game, a merge-split algorithm is used for enabling the base station to always add in a cooperative cluster capable of promoting self energy efficiency, thereby implementing the optimal network clustering. The network clustering is performed based on the energy efficiency index to optimize the trade-off relation between the throughput promotion and energy consumption increment caused by the network cooperation. The technical means of coalition formation game is used for solving the cooperation cluster construction problem based on the energy efficiency so as to fast converge to an equilibrium point. Through the limitation on the base station and the interference on the cooperation of adjacent regions, and the adoption of the historic clustering data in the merge-split operation process, the purposed coalition formation game can obtain the unique stable solution.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
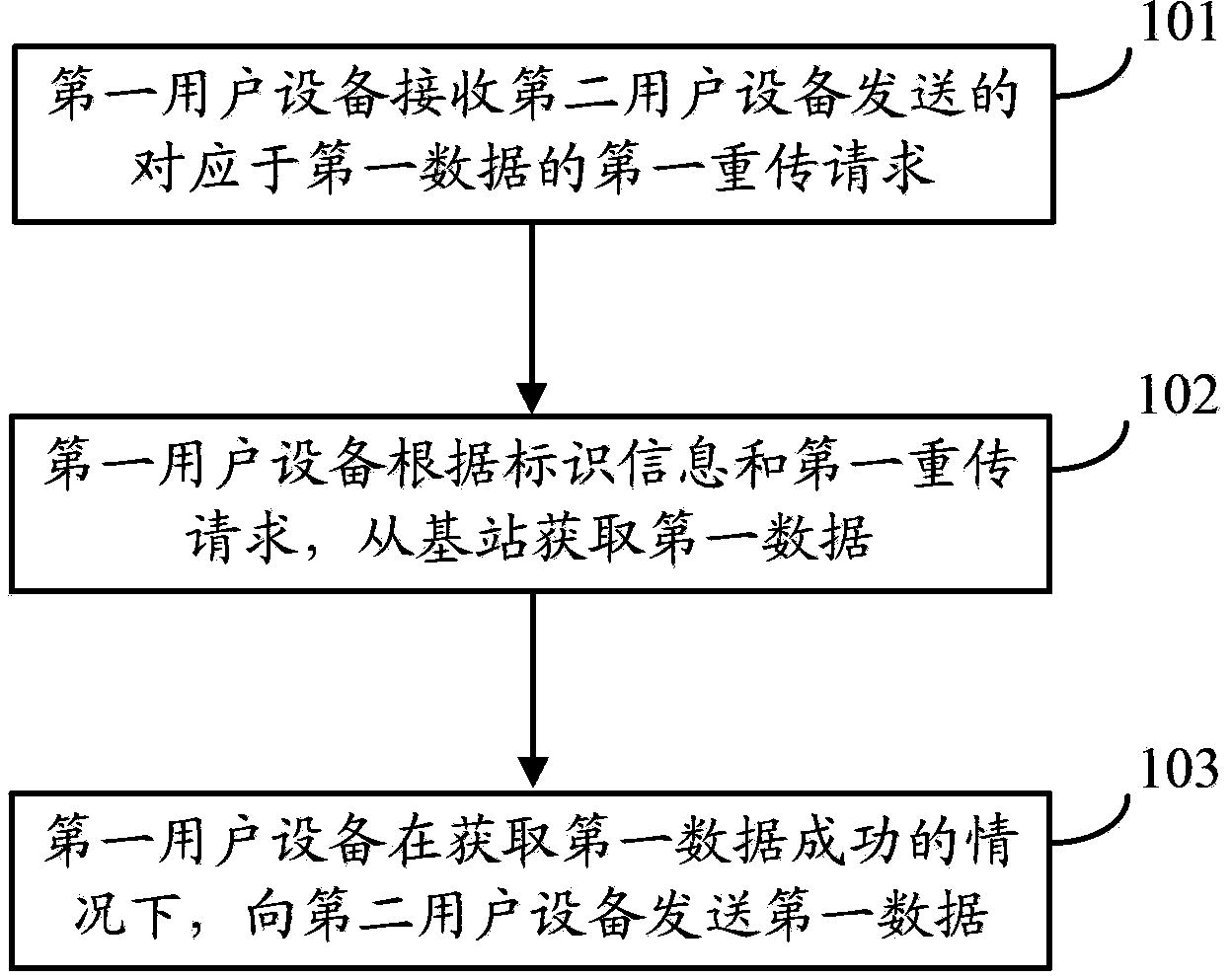
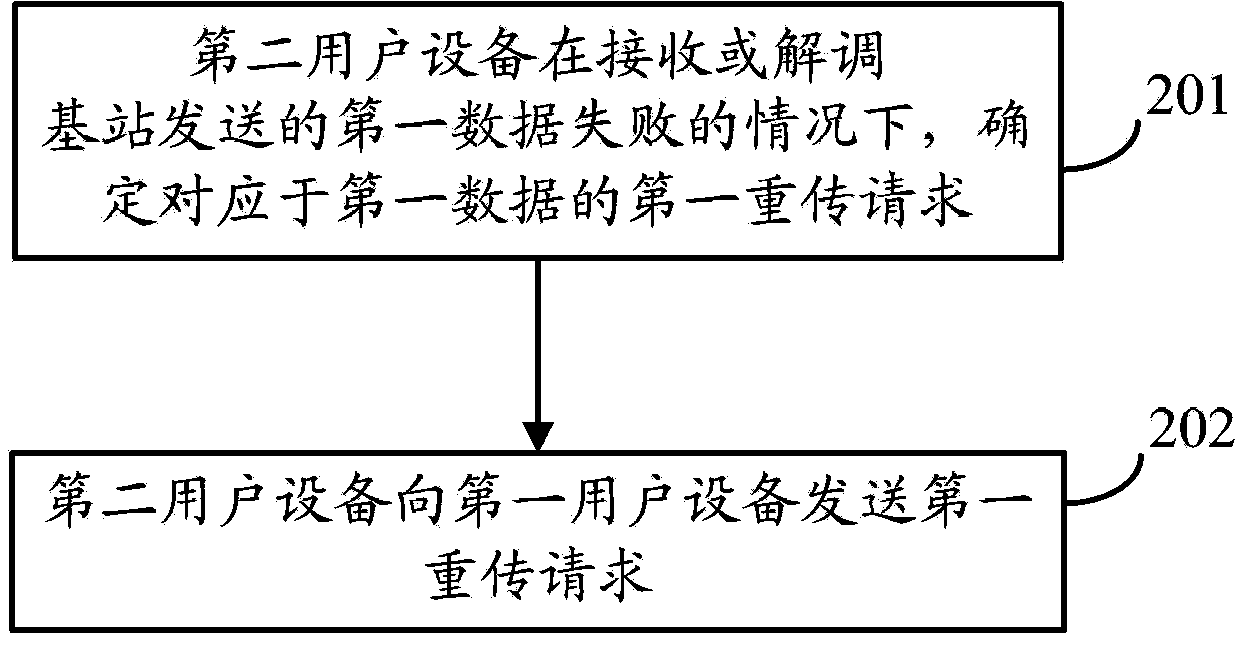
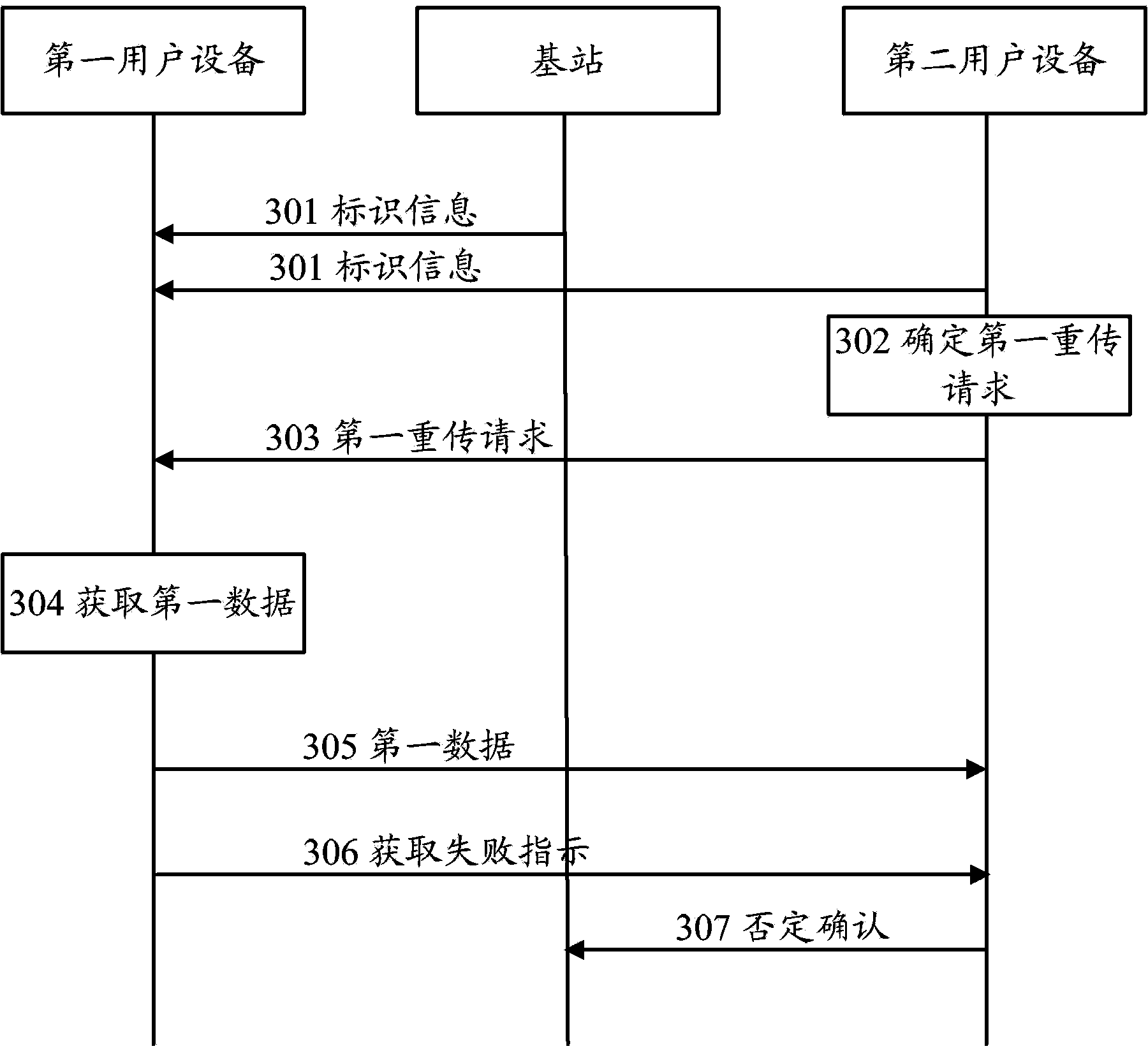
Method for data retransmission in end-to-end communication and user devices
The invention provides a method and device for data retransmission in end-to-end communication. The method comprises the steps of utilizing a first user device in an end-to-end cooperative group to receive a first retransmission request corresponding to first data and sent by a second user device in the end-to-end cooperative group, utilizing the first user device to obtain the first data according to identification information and the first retransmission request, and utilizing the first user device to send the first data to the second user device on the conditions that the first user device obtains the first data successively. The first user device can obtain the first data, the second user device directly requests the first user device to retransmit the first data on the conditions of failing in receiving or demodulation of the first data fails, the second user device does not need to request a base station to perform retransmission, so that expenses of system time-frequency resources are reduced, and power consumption of the base station and the user devices is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for cancelling interference
ActiveUS20150016293A1Site diversityError preventionInterference eliminationElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ZTE CORP
Numerical optimization method based on cooperative group decision mechanism
InactiveCN104036138AImprove convenienceMeet needsSpecial data processing applicationsOptimization problemGlobal optimal
The invention relates to a numerical optimization method based on a cooperative group decision mechanism. The method includes: first, establishing an individual position coordination item mainly used for keeping spacing of individuals and allowing a group to explore large search space; second, establishing an individual speed coordination item, mainly whereby uniform speed of the individuals is kept, the speeds of the individuals are coordinated in the speed uniformization process and the direction of the uniform speed accordingly can point to a position of a global optimum; third, establishing a direction coordination item mainly used for keeping motion directions of the individuals and motion directions obtained by individual decisions uniform. The motion directions obtained by the individual decisions are obtained in such a manner that the individuals judge the direction of a global optimal position by making full use of ambient information. The numerical optimization method has the advantages that problems in the existing numerical optimization method can be solved and good optimization results can also be obtained with regard to other types of numerical optimization problems.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
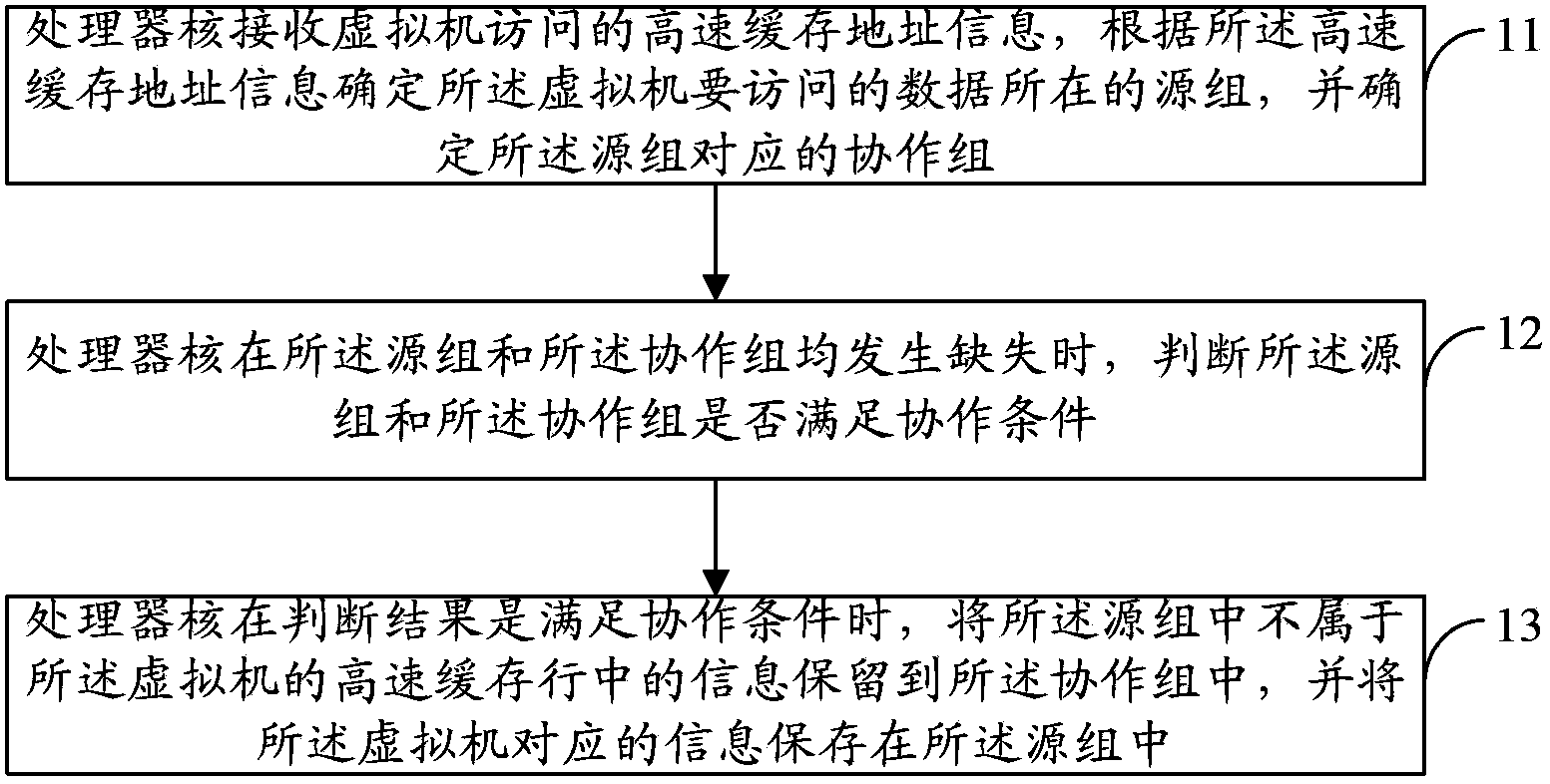
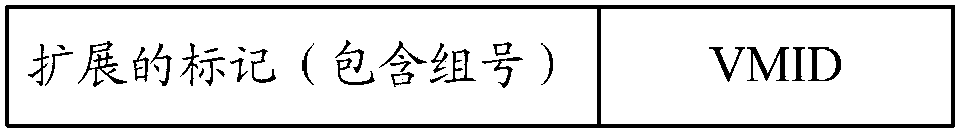
Processing method and equipment during virtual machine scheduling
ActiveCN104077171AProlong survival timeLower latencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtual machine schedulingVirtual machine
The invention provides a processing method and equipment during virtual machine scheduling. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a cache address message accessed by a virtual machine; according to the cache address message, determining a source group where data to be accessed by the virtual machine is positioned; confirming a cooperative group corresponding to the source group; when both the source group and the cooperative group miss, judging whether the source group and the cooperative group meet a cooperative condition; when the source group and the cooperative group meet the cooperative condition, storing a message which does not belong to a cache line of the virtual machine into the cooperative group; and storing the message corresponding to the virtual machine into the source group. The embodiment of the invention can be used for reducing an access delay.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Method of Incentive Distribution For Cross Client Referral
InactiveUS20090259546A1No costMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsDistribution methodComputer science
The present invention relates generally to methods of generating business by providing incentives for clients to obtain goods and / or services from goods and service providers, wherein said providers refer clients to other providers and as said providers have incentives provided within the method to make said referrals. The method involves one central manager serving as a communications conduit among goods and service providers pooling their services into one joint goods and services cross-client referral cooperative group. The method provides an incentive system among group members for referring clients to other group members.
Owner:DRAPER ALLEN
Distributed media access control method based on analog network coding
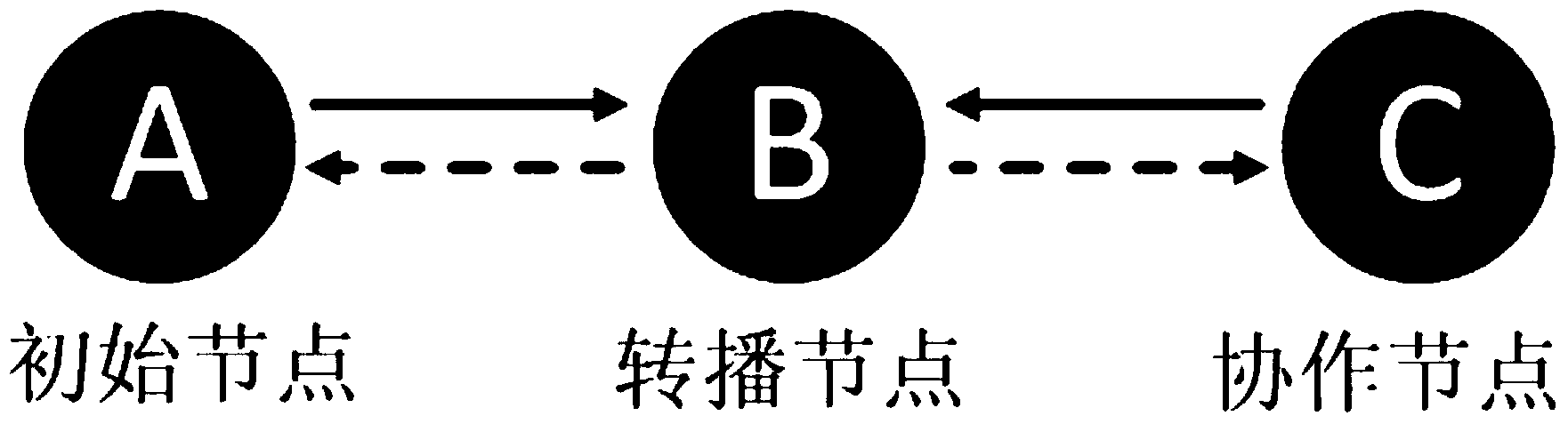
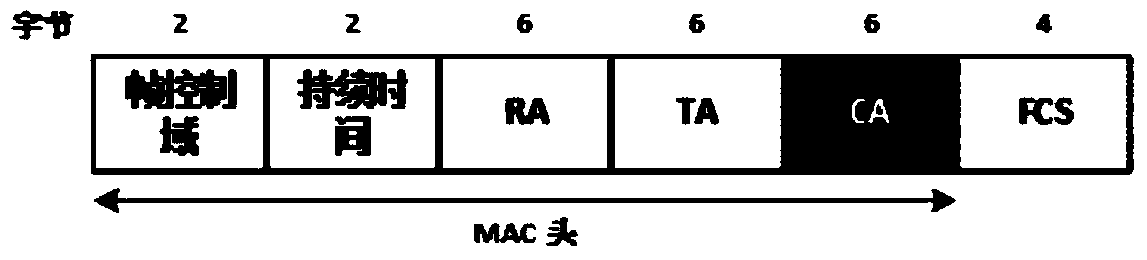
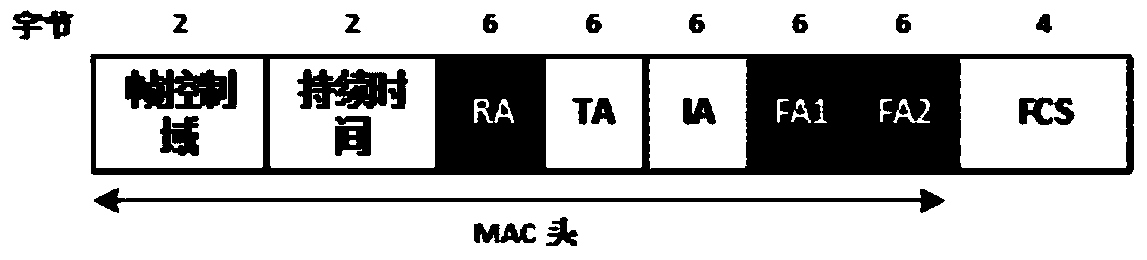
ActiveCN104378181ARetain propertiesLow costError prevention/detection by using return channelForward error control useNetwork codeData needs
The invention discloses a distributed media access control method based on analog network coding. The method includes the following steps that (1) a rebroadcasting node sends RTC control frames to a cooperation node after receiving RTS control frames sent by an initial node; (2) after receiving the RTC control frames, the cooperation node sends ATC control frames to a forwarding node if data need to be sent to the initial node; (3) when receiving the ATC control frames before waiting time is up, the rebroadcasting node sends CTS control frames; (4) after the initial node and the cooperation node receive the CTS control frames, a cooperative group is established successfully, and data sending can be started; (5) after data transmission is finished, the initial node and the cooperation node send ACK signals for confirmation in an analog network coding mode. According to the distributed media access control method based on analog network coding, dynamic establishment of the cooperative group in a wireless network is achieved through control frame exchanging, and complex parameter obtaining in traditional scheduling algorithms is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
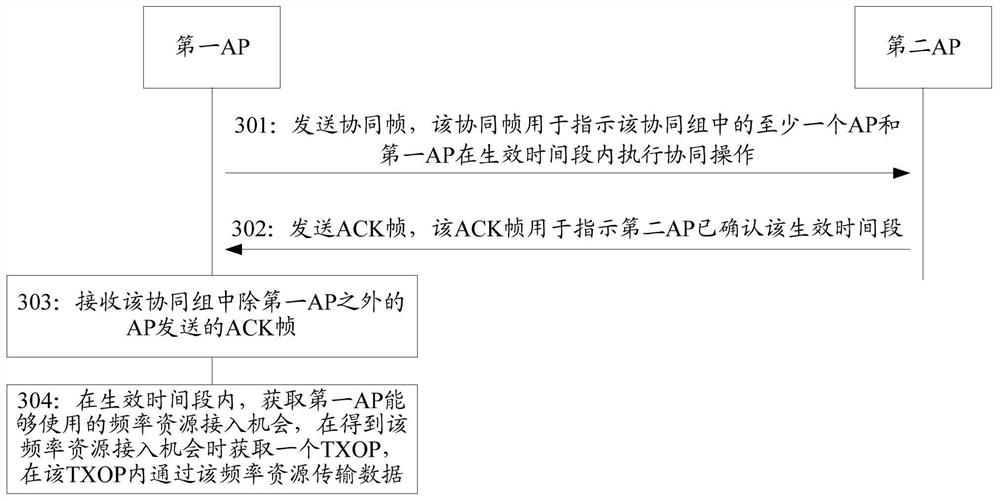
Method and device for cooperative communication of multiple access points
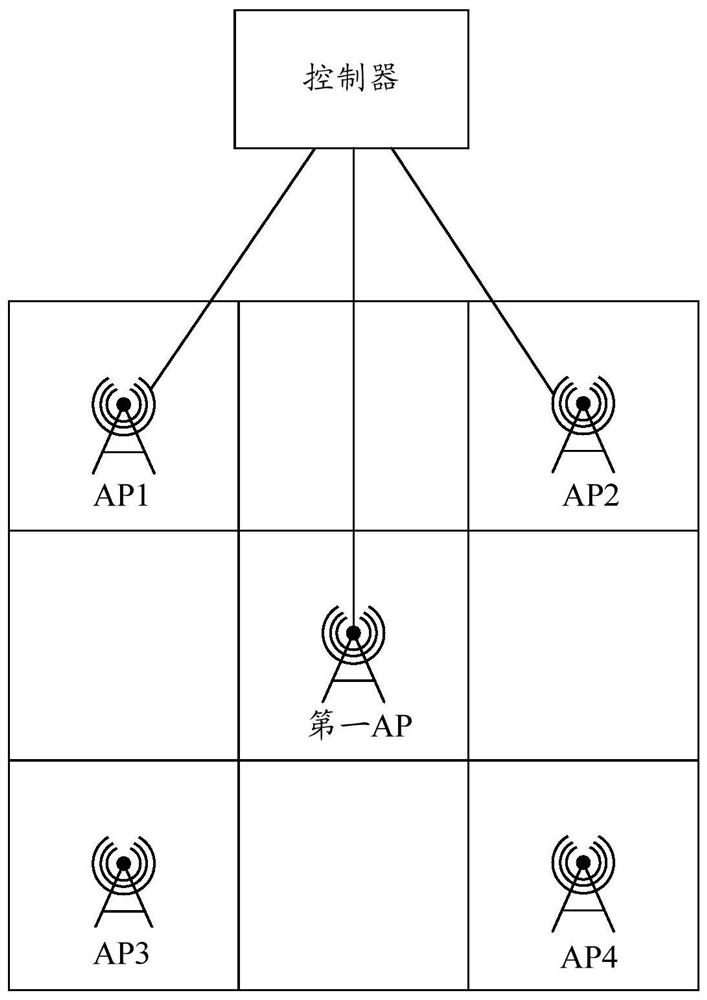
PendingCN114124324ANetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesComputer networkTelecommunications
The invention discloses a method and device for cooperative communication of multiple access points, and belongs to the field of communication. The method comprises: a first access point (AP) sends a collaboration frame to APs in a collaboration group, the collaboration frame instructing at least one AP in the collaboration group and the first AP to perform collaboration operation within an effective time period, the collaboration group comprising a plurality of APs working on the same channel, and the first AP operating on the same channel; the first AP is the AP acquiring the channel access opportunity in the cooperative group, and the time length of the effective time period exceeds the time length of one transmission opportunity TXOP. The application can improve the channel utilization rate.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Neighbor discovery method based on node cooperation
InactiveCN111901811AIntegrity guaranteedAwakening time slot reductionNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesLine sensorNeighbour discovery
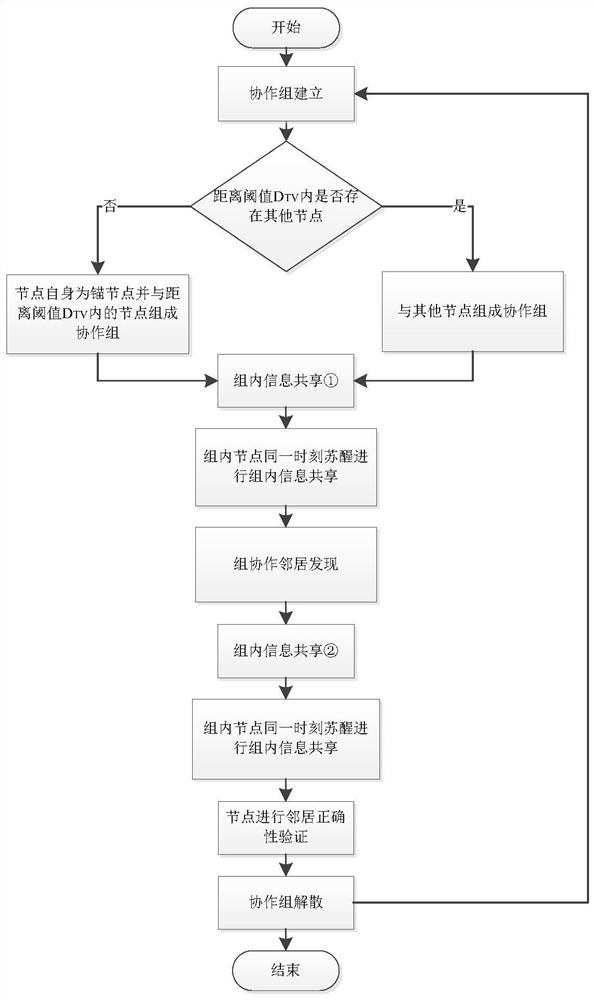
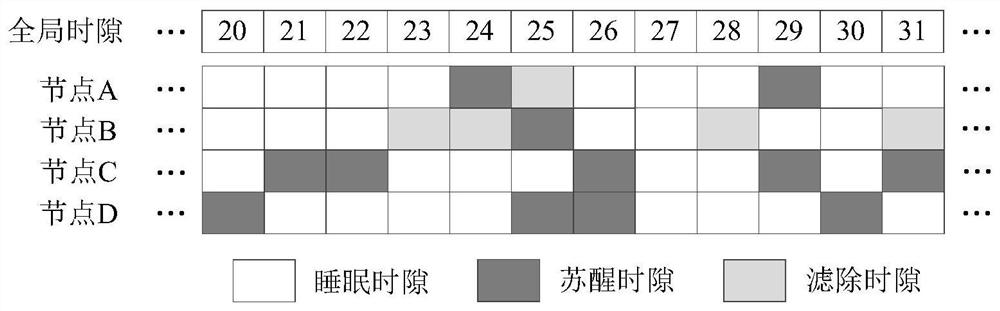
The invention discloses a neighbor discovery method based on node cooperation. The invention designs a neighbor discovery method based on node cooperation according to the characteristics of a low-duty-ratio wireless sensor network. According to the method, nodes within a specific distance threshold value are regarded as a cooperative group based on the receiving intensity of signals, and awakening time slots of all the nodes in the group are replanned, so that the nodes in the group are jointly responsible for an awakening task of an awakening time table of the cooperative group. Meanwhile, the optimal group scale capable of maximizing the energy efficiency of the cooperative group is researched, factors which cannot be ignored on the energy efficiency of the cooperative group are quantitatively analyzed, and the optimal values of all parameters which enable the energy efficiency of the cooperative group to be optimal are derived. Correspondingly, a set of cooperative group managementmechanism is designed in the method, and the whole life cycle of the cooperative group comprises group establishment, group information sharing, group cooperation and group dissociation. According tothe neighbor discovery method, the integrity of the node awakening time table is ensured, and meanwhile, the awakening time slot with low energy efficiency can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Aircraft control method and control terminal
ActiveCN105892476BEnsure safetyEasy to controlAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsComputer terminalCooperative group
The embodiment of the invention discloses a control method of an aircraft. The method is applied to at least one aircraft cooperative group which comprises a control terminal, a master unit and at least one slave unit. The method comprises the following steps: when the aircraft is in a flying state, receiving current flying information transmitted by the master unit and the slave units; determining a flying error value of each slave unit according to the current flying information of the master unit and the slave units; generating a first control instruction of the master unit according to the current flying information of the master unit, and generating a second control instruction of the slave units according to the current flying information and the flying error value of the slave units; transmitting the first control instruction to the master unit, and transmitting the second control instruction to the slave units. The embodiment of the invention further provides the control terminal. One control terminal can be used for simultaneously controlling a plurality of aircrafts to fly under a condition of no mutual collision, to guarantee the safety during flying and keep a formation during flying; the control terminal is favorable for letting an operator control the aircraft.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
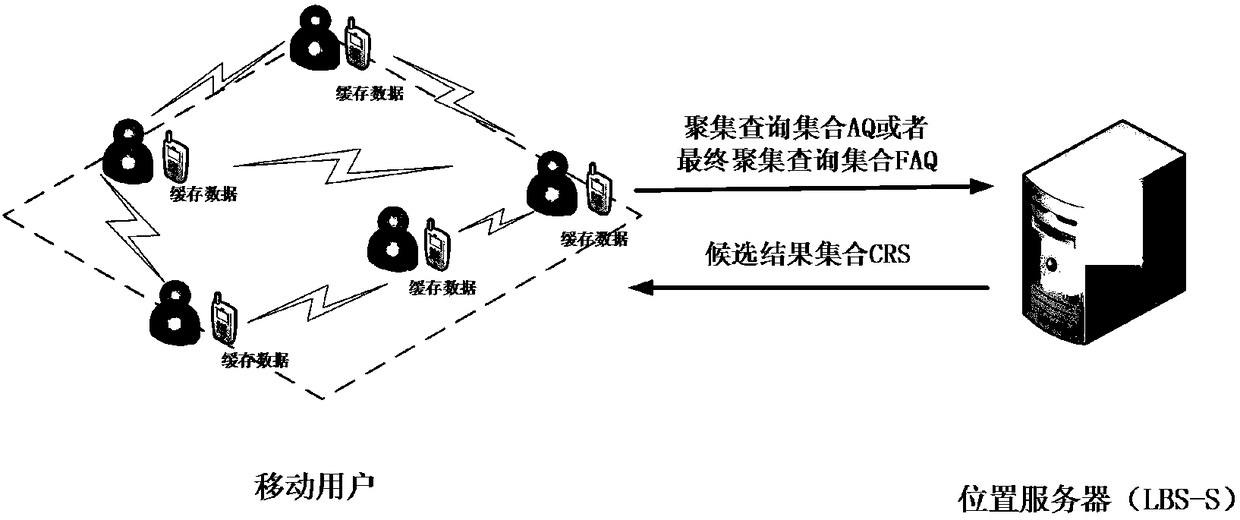
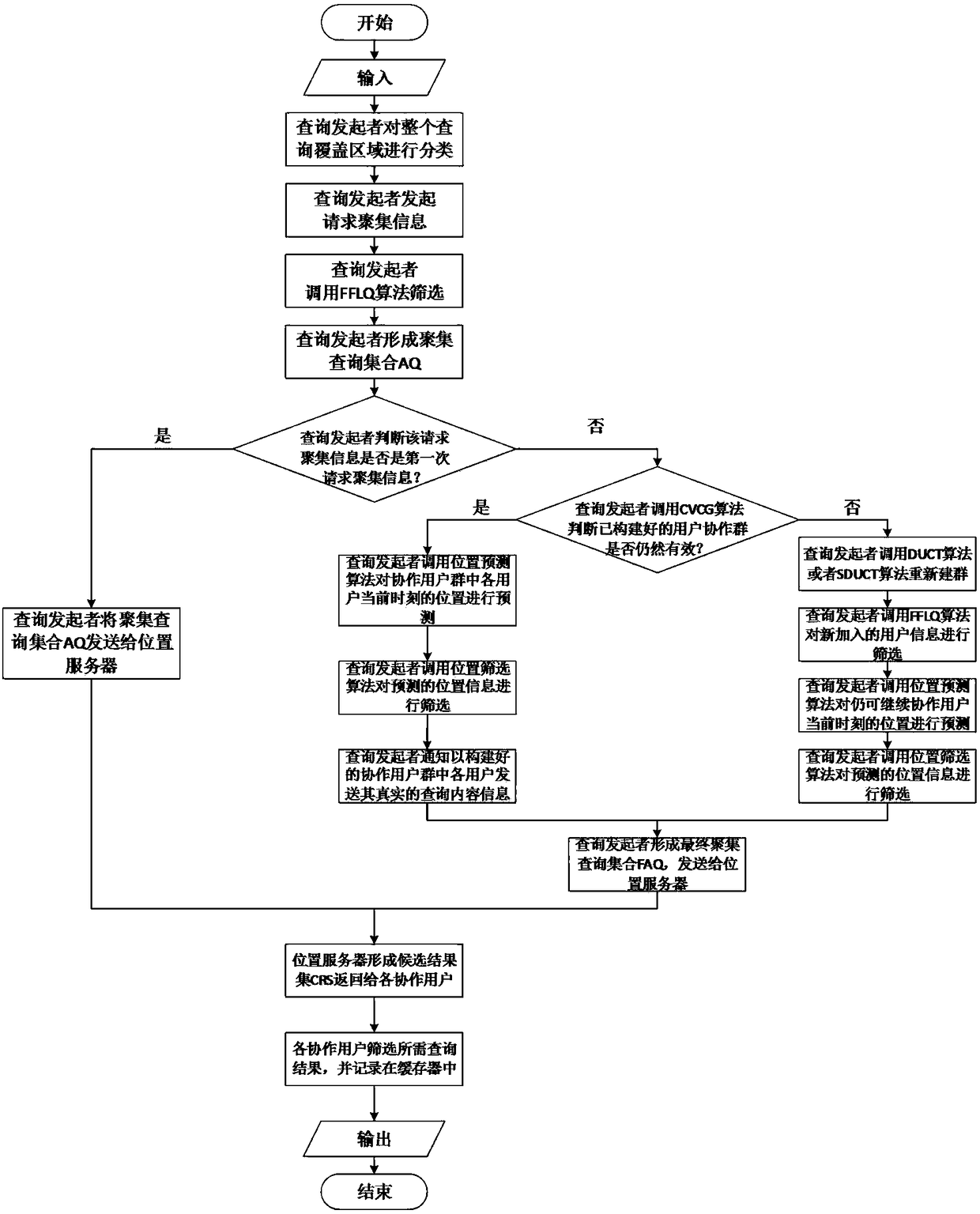
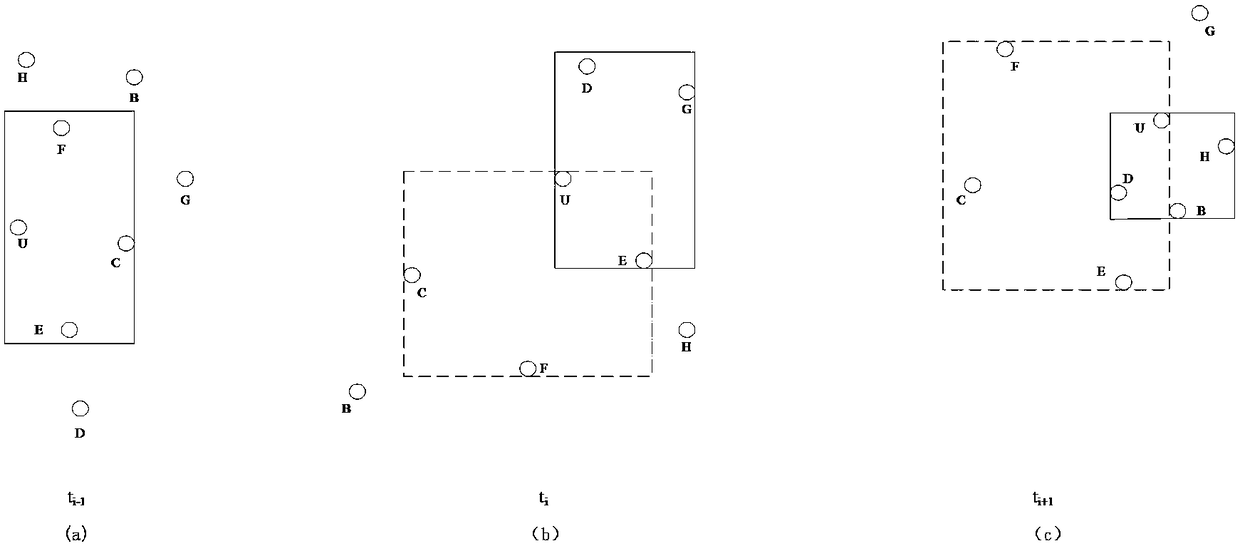
Privacy protection method based on user cooperation
ActiveCN108282745ARaise the possibilityHigh feasibilityBroadcast service distributionTransmissionPrivacy protectionUser privacy
The invention discloses a privacy protection method based on user cooperation, which mainly solves the problem of leakage of user privacy in the prior art. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a query initiator classifies query regions and issues a cooperative group building request; when the request is received, other users answer a message to the query initiator; the query initiator only predicts and screens user location information according to a current query number and a privacy protection request; the user location information forms an aggregation query set ora final aggregation query set together with a current real and concrete query content and the query set is sent to a location server; after the location server receives the information, a look-up database forms a candidate result set, which is returned to each cooperative user; and each cooperative user screens the required query result, which is stored to a buffer. According to the method, not only are the accuracy and the usability of the prediction information and the query result improved, but also a location correlation attack and a track attack can be resisted at the same time; and the method can be applied to various continuous query location services.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
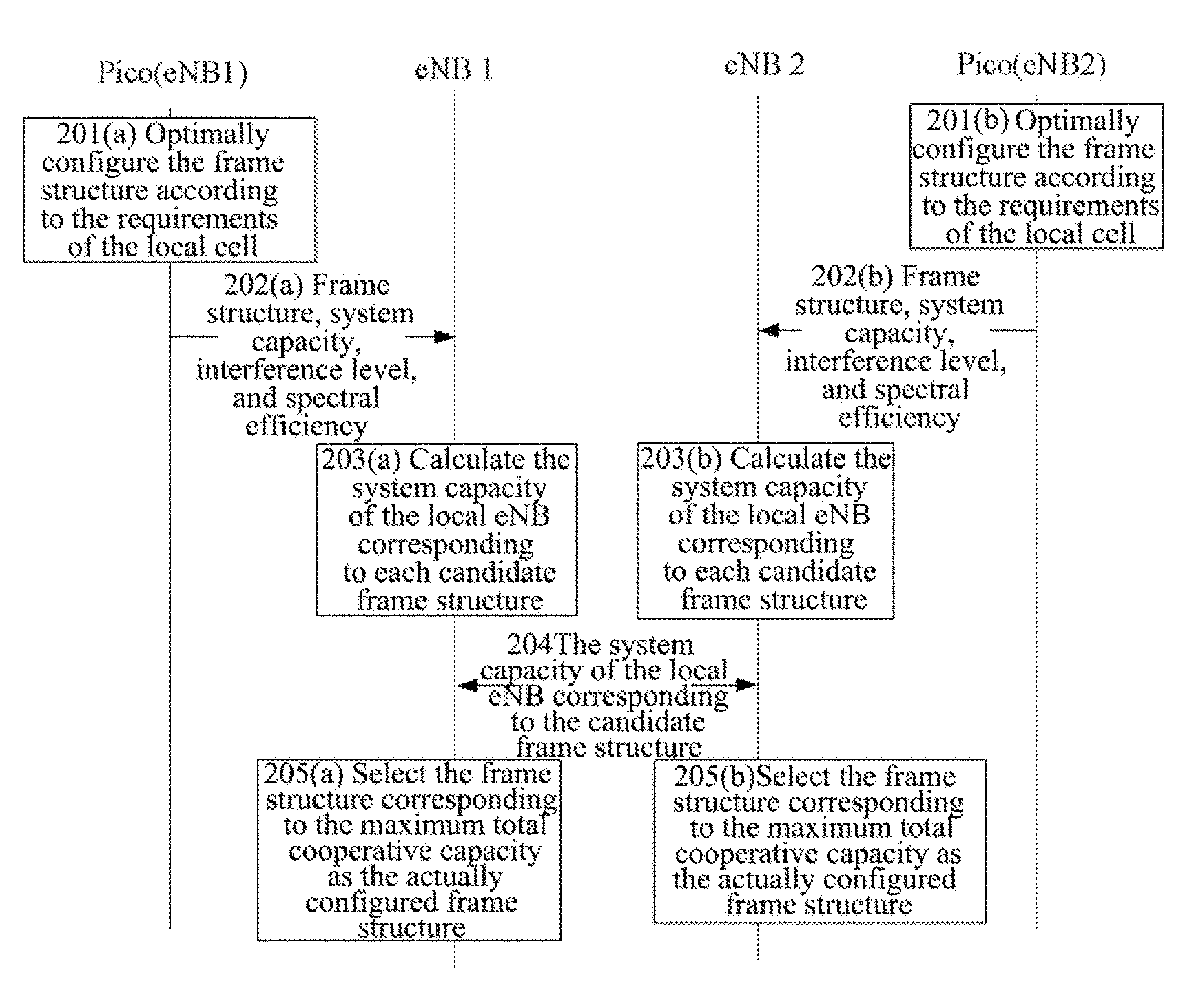
Method and apparatus for cancelling interference
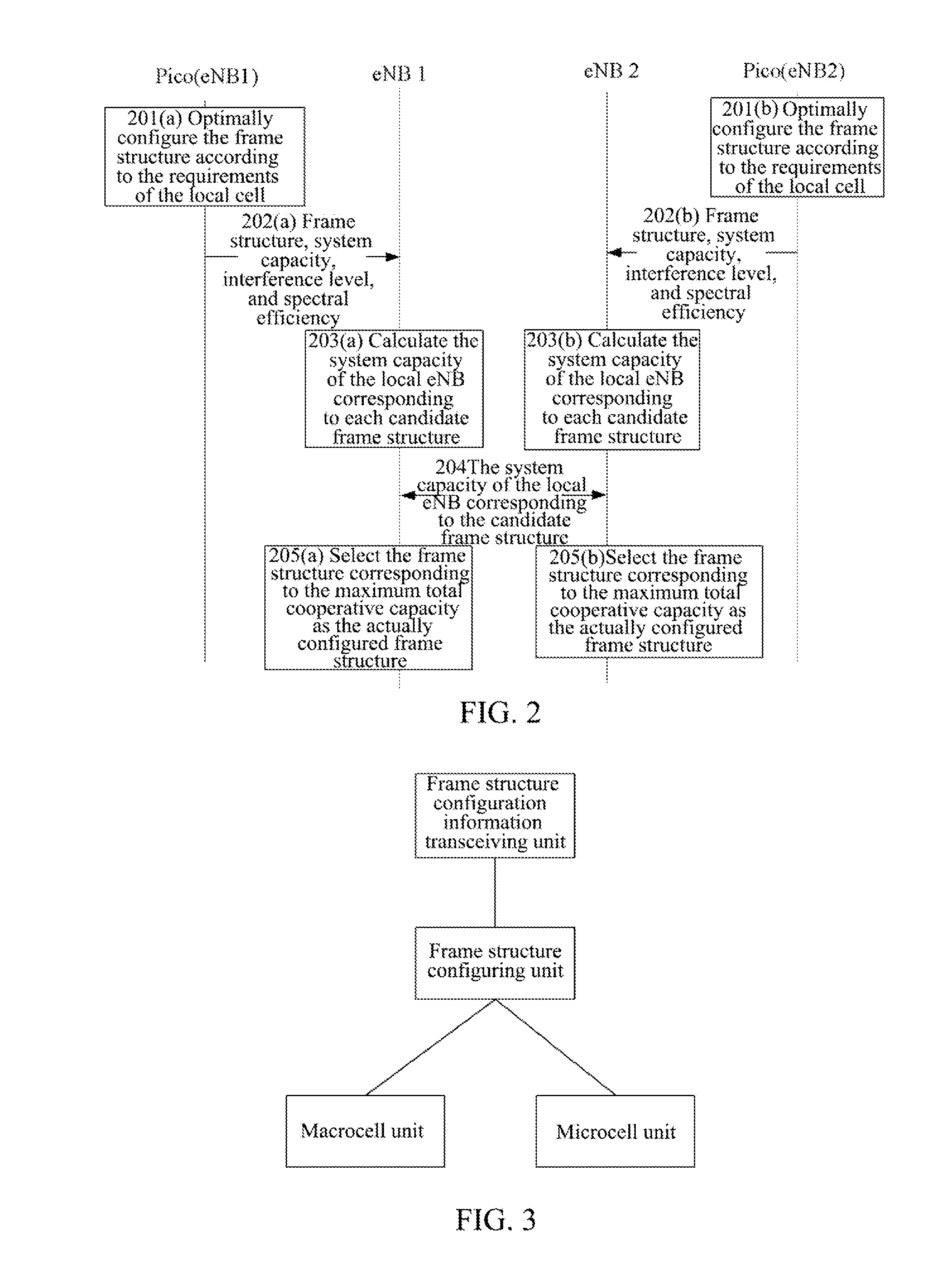
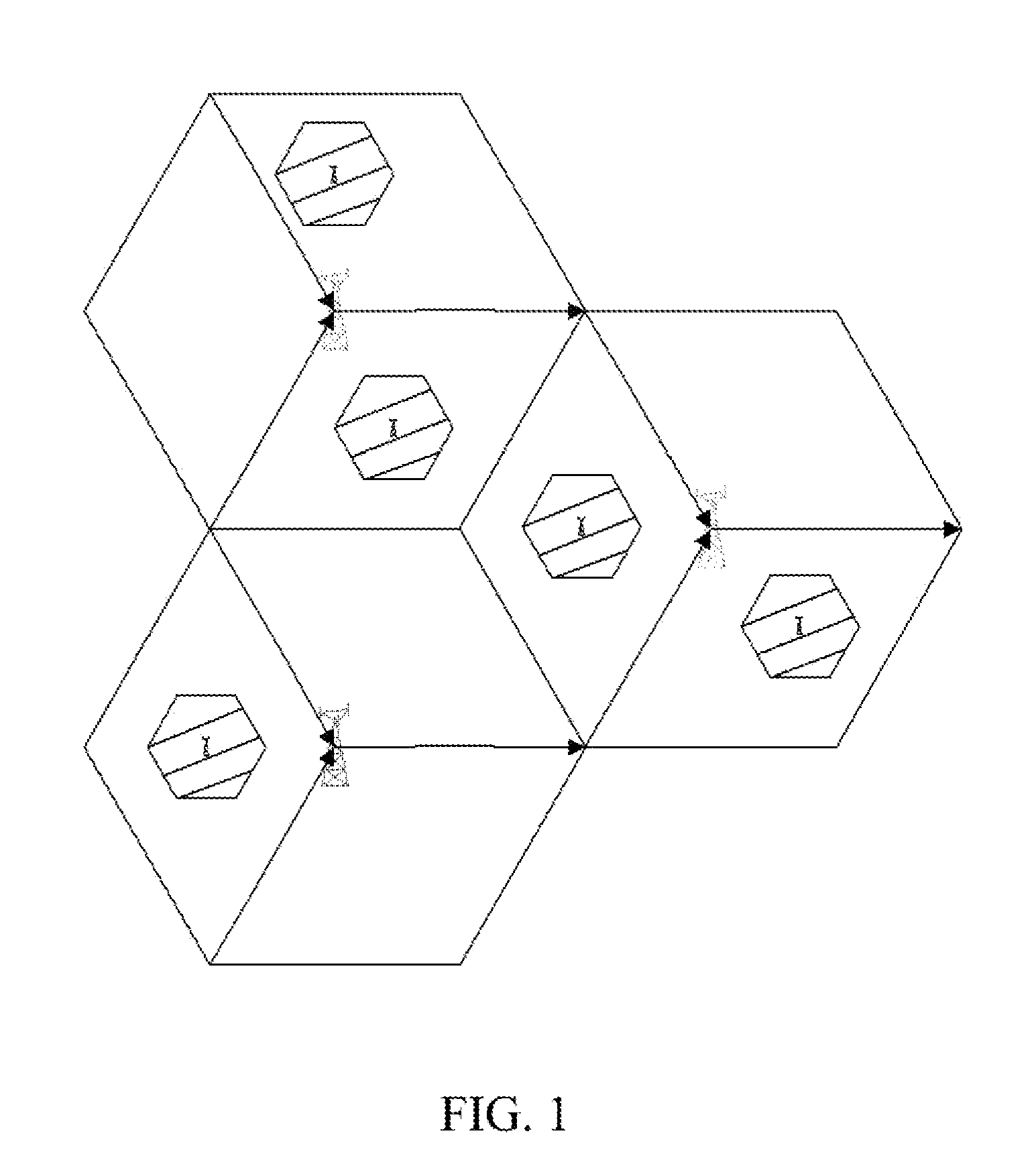
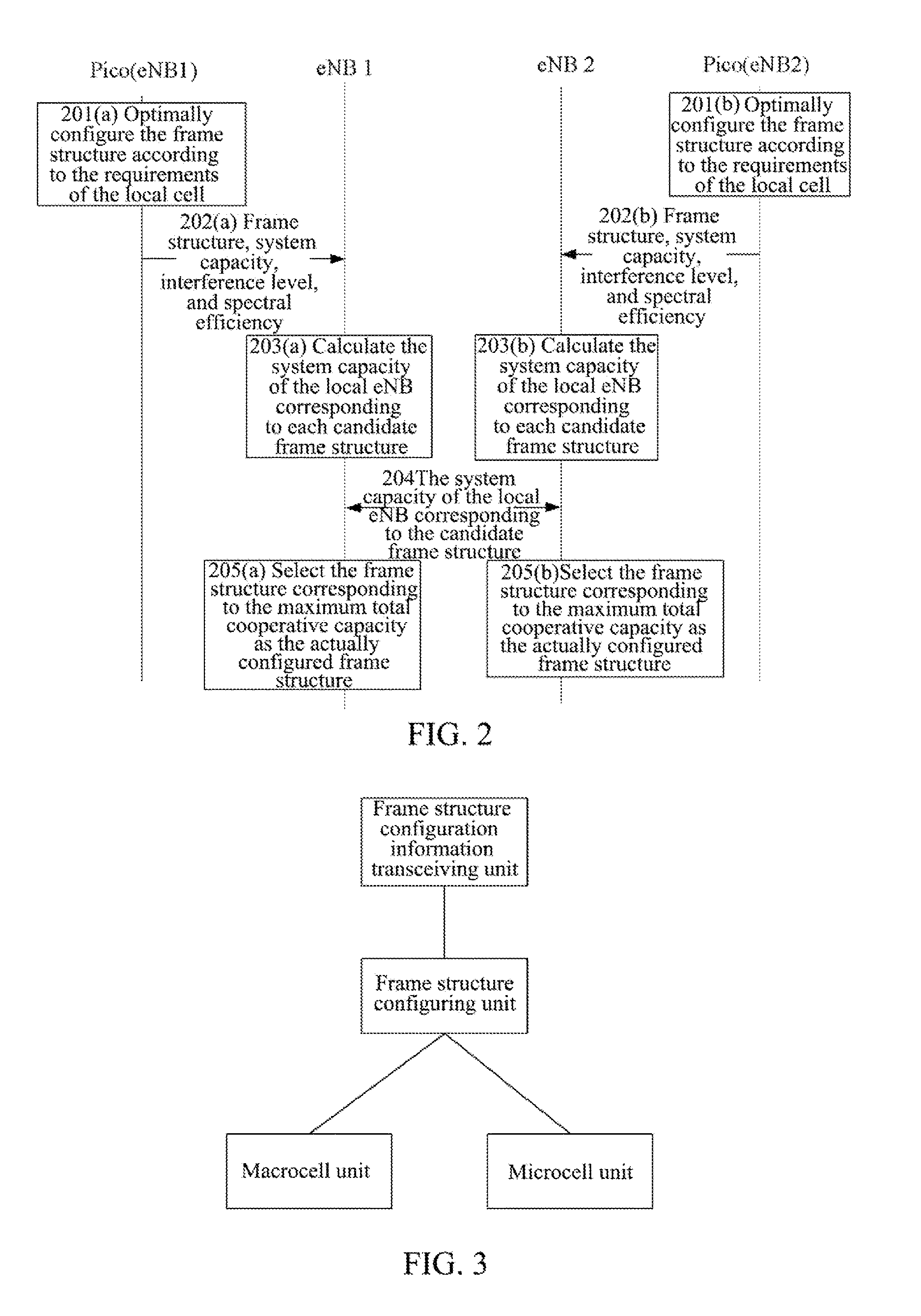
A method and apparatus are disclosed for canceling interference. The method includes: composing a cooperative group with multiple adjacent evolved NodeB (eNB); each eNB in the cooperative group sending frame structure configuration information to each eNB other than itself in the cooperative group every other frame structure change cycle; and each eNB in the cooperative group configuring a frame structure to be used in a next frame structure change cycle according to the received frame structure configuration information. With introducing 10 ms-dynamic frame structure switching, this method and apparatus can cancel the mutual interference of uplink and downlink, especially the mutual interference of uplink and downlink between the eNBs at the system side.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multi-client cooperative grouping and display method
InactiveCN105005499BCollaborative grouping is orderly and effectiveVersion controlMultiprogramming arrangementsHome pageClient-side
The invention provides a multi-client cooperative grouping and displaying method. When a plurality of clients perform grouping operation on a plurality of to-be-grouped objects, each client stores an operation record, each operation record corresponds to a version number, and the operation records and the corresponding version numbers are uploaded to a server; and the server receives the operation record and the corresponding version number, updates the version number of the server to the received version number, stores the operation record and pushes a new grouping result to the other clients, and the other clients receive the new grouping result and display newest grouping result information in a home page. The method solves the problem of conflict when the clients display newest grouping data mutually during simultaneous grouping of the to-be-grouped objects. According to the method, the server receives the newest grouping operation record of each client and pushes the operation record to each client, the multi-client cooperative grouping is orderly and effectively carried out, and the clients can obtain the newest grouping information data from one another in time.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIUYUN INFORMATION TECH
Stochastic access method based on user side cooperative grouping in collaboration cellular network
InactiveCN101365220BAvoid collisionReduce the probability of collisionEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesGroup controllerAccess method
A random access method based on the cooperation and the grouping of user ends of a collaborative cellular network comprises the following steps: the user end is determined as a cooperation group leader; each user end is accommodated by the cooperation group leader into a group to form a corresponding cooperation group; and each user end in the cooperation group sends a corresponding signal of request for base station access to a base station in an established cooperation mode. When the base station conducts the initial allocation of resources according to the detected signal of request for base station access, each user end in the cooperation group occupies a resource block initially allocated by the base station in sequence, and sends a concrete message of request for access to the base station independently. At last, the base station dispatches the resource blocks again to satisfy the actual operational requirements of each user end. Through the cooperation and the grouping of each user end during the random access process, the method can reduce the probability of collision and conflict between the user ends and reduce the energy consumption thereof, thus further improving the random access performance of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
A virtual mimo communication strategy for wireless sensor networks based on cooperative groups
InactiveCN104010344BReduce the number of retweetsReduce energy consumptionPower managementNetwork topologiesMimo transmissionMimo communication
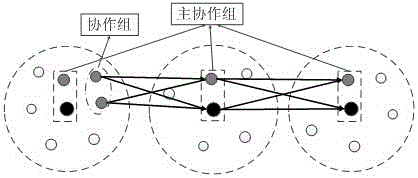
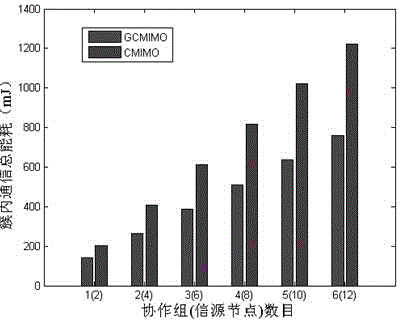
A wireless sensor network virtual MIMO communication strategy based on cooperative groups is called as group collaboration MIMO (GCMIMO). A method similar to the CMIMO is adopted to carrying out clustering on a network for the GCMIMO, and each cluster is managed by two cluster heads, namely a main cluster head and a secondary cluster head. The main cluster heads are used for dividing information source nodes in the corresponding clusters into a plurality of cooperative groups, each cooperative group is composed of two adjacent information nodes, is equivalent to a virtual double-antenna sending end and is used for sending information source data of the cooperative groups, the secondary cluster heads and the main cluster heads are considered as one cooperation group which is called as a main cooperative group and used for receiving and forwarding the data of other cooperative groups, and therefore multi-hop virtual MIMO transmission is achieved. Different from an existing virtual MIMO communication strategy, the GCMIMO does not need to collect information source data through the cluster heads and directly sends the information source data through the cooperative groups, so that the forwarding frequency of the information source data is reduced and the energy efficiency of intra-cluster communication stages is improved. In a simulation experiment, energy consumption analysis of each communication stage of the GCMIMO proves that the GCMIMO effectively lowers the energy consumption of intra-cluster communication and network maintenance frequency, and improves energy efficiency.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
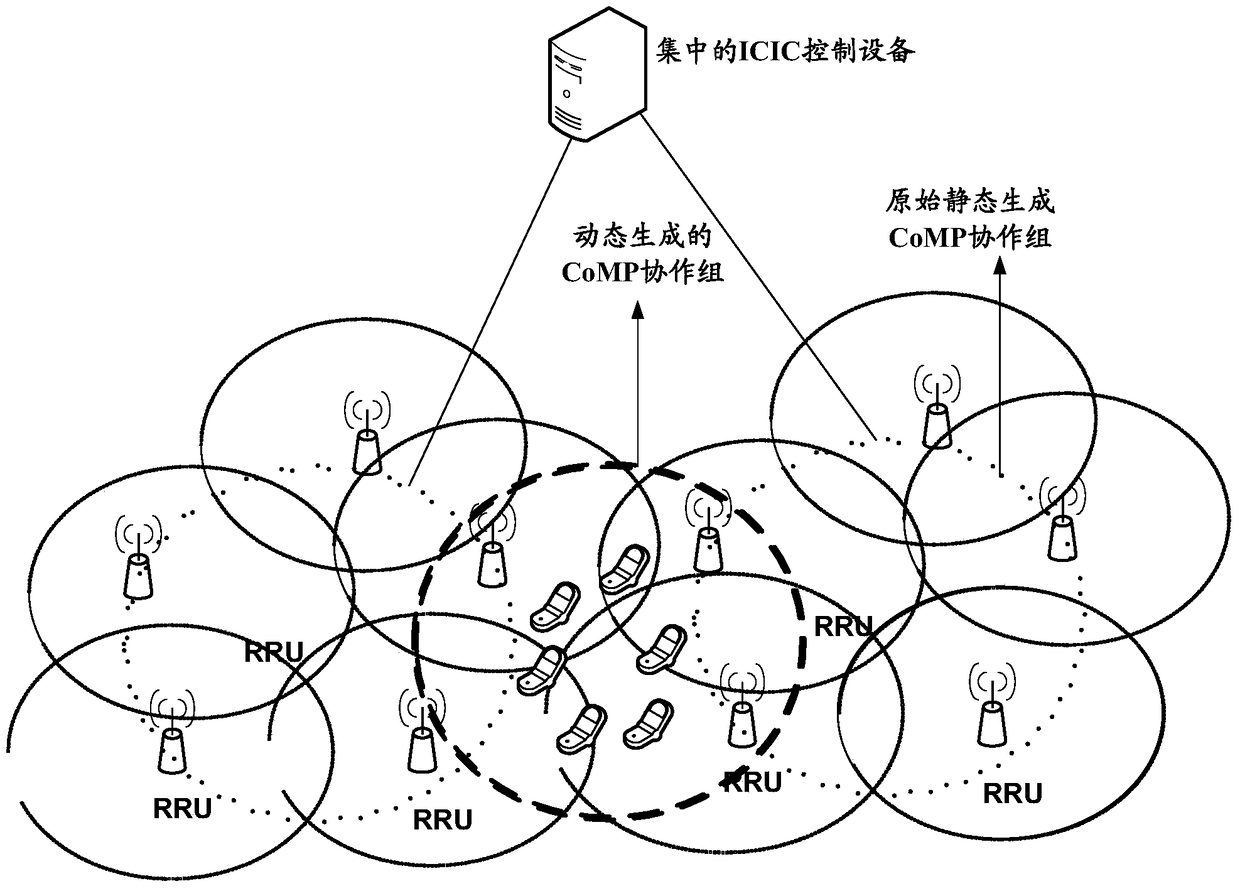
A cell user processing method, device and centralized icic equipment
ActiveCN105323766BImprove spectral efficiencyFast coordinated interferenceSite diversityNetwork planningFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
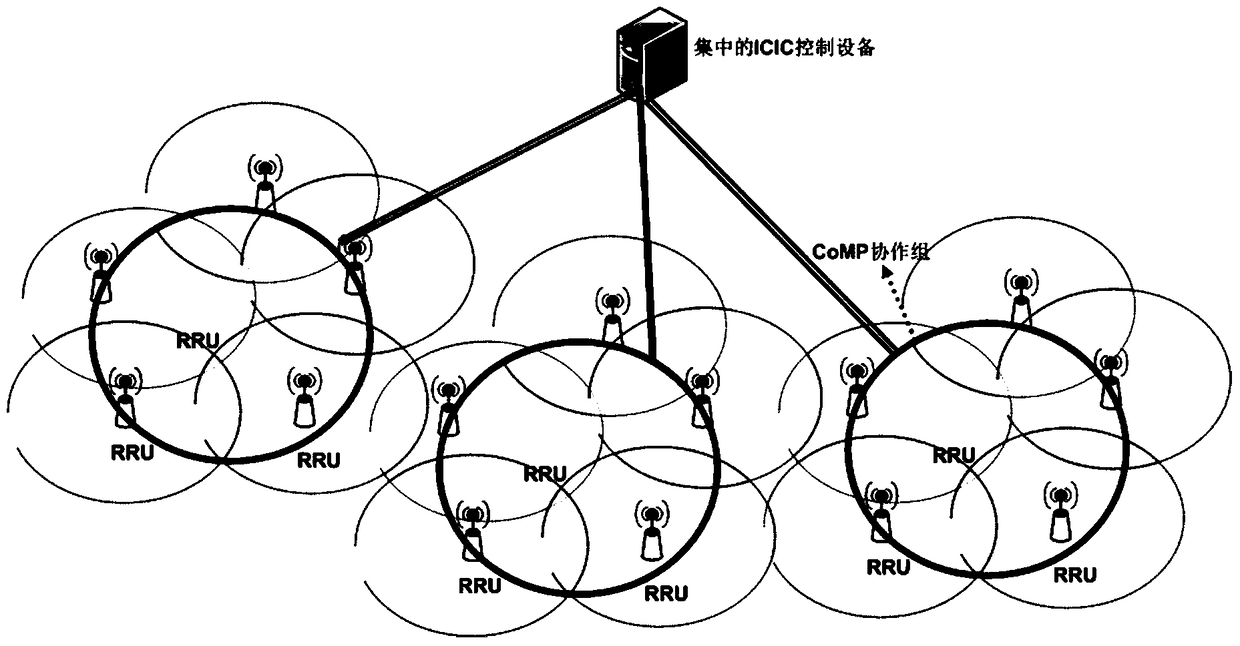
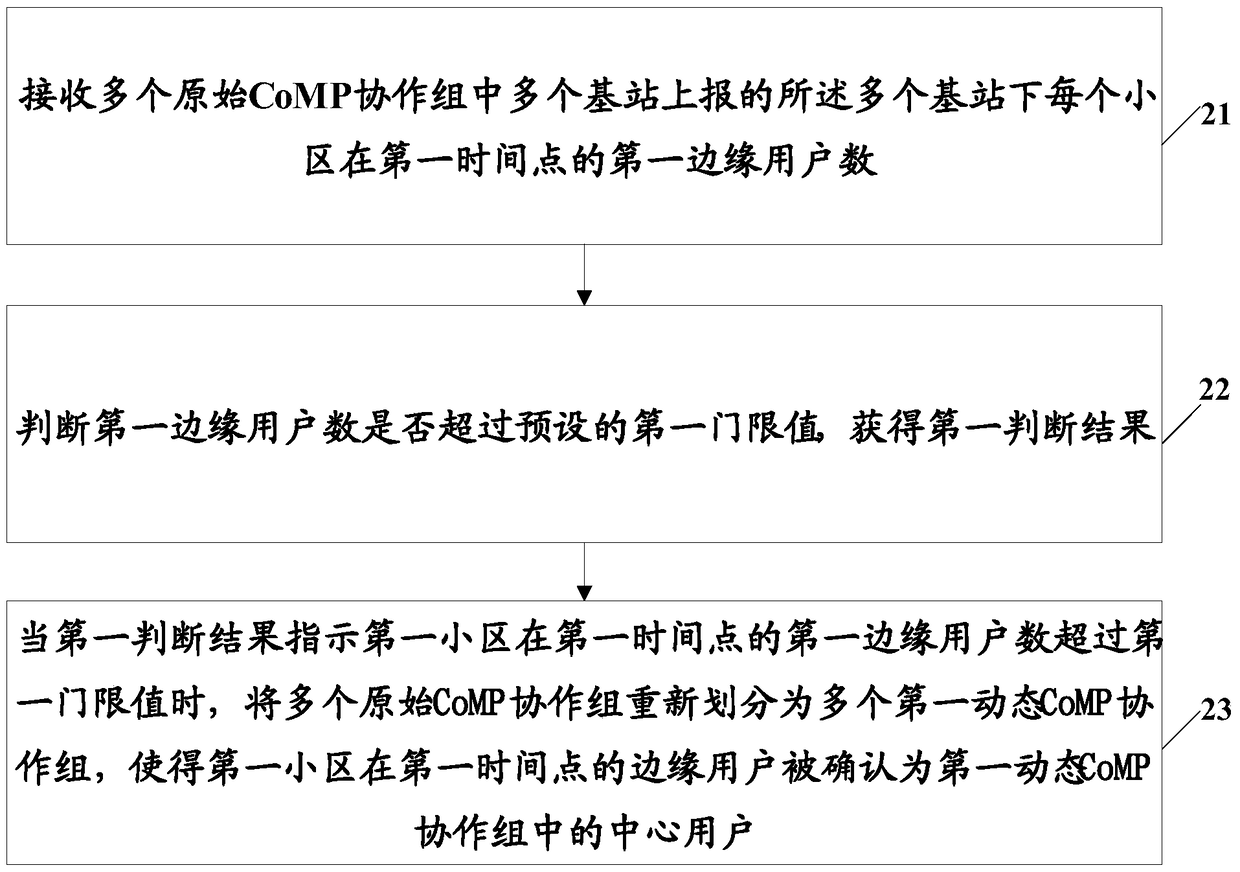
The invention provides a cell user processing method and device, and centralized ICIC (Inter-Cell Interference Coordination) equipment. The method comprises the following steps of receiving a first edge user number of each cell at a first point under a plurality of base stations reported by a plurality of base stations in a plurality of original CoMP (Coordinated Multiple Points Transmission / Reception) cooperative groups; judging whether the first edge user number exceeds a preset first threshold value to obtain a first judging result; and when the first judging result indicates that the first edge user number of a first cell at the first point exceeds the first threshold value, re-dividing the original CoMP cooperative groups to a plurality of first dynamic CoMP cooperative groups in order to affirm edge users of the first cell at the first time point as central users in the first dynamic CoMP cooperative groups. Through detecting the gathering degree of the users at the cell edge, the edge users of the first cell at the first time point are re-divided to the central users in the first dynamic CoMP cooperative groups, so that a CoMP technology can be guaranteed to coordinate interference quickly, and the spectrum effectiveness of the cell edge is improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
A Video Processing System Based on Cooperative Group Mechanism
ActiveCN107241577BAchieving Detection AccuracyReduce computational complexityNetwork topologiesClosed circuit television systemsBlock schedulingEdge node
The invention discloses a video processing system based on a cooperative group mechanism, which belongs to the field of video wireless communication. The system of the present invention includes a camera node, an edge node, and a server node; the control module of the server node utilizes the edge node based on the relationship between the average video code rate and the object detection accuracy through the received channel state and computing capability information of the edge node. The cooperative processing of nodes, that is, the formation of cooperative groups and the construction of a video block scheduling mechanism, effectively improves the accuracy of object detection. Subtask scheduling problems caused by the transmission delay, the waste of computing resources of redundant edge nodes in the non-cooperative processing mechanism, and the difference in transmission rate.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com