Preparation and application of latent nonionic self-emulsifying epoxy curing agent
A self-emulsifying epoxy and non-ionic technology, which is applied in the preparation of imino compounds, epoxy resin coatings, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of gel and curing agent with short storage period, and achieve excellent bonding performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
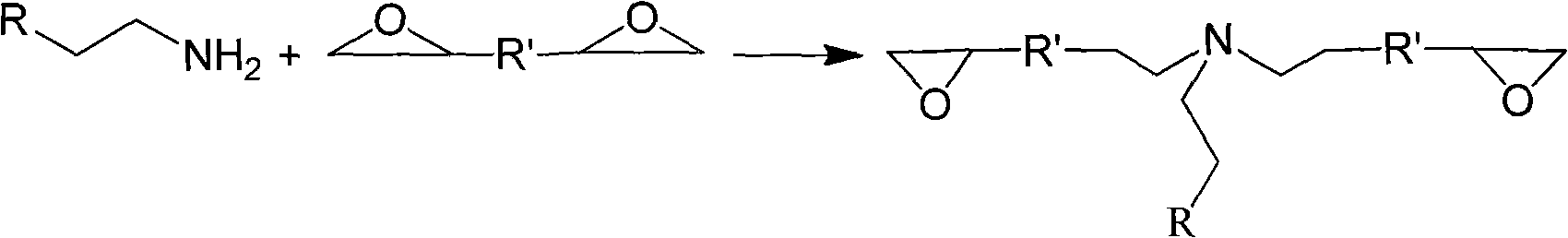
[0033] 1. Preparation of epoxy-terminated adducts:
[0034] In a four-neck flask filled with nitrogen, equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, and a reflux condenser, add 0.24 moles of ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, raise the temperature to 70 ° C, and add solid octadecylamine in batches, controlled at The addition is completed within 1 to 1.5 hours. After the addition, the reaction was continued for about 4 to 6 hours, and the end point of the reaction was determined by the hydrochloric acid acetone method. The product was taken out, cooled, and sealed for storage.
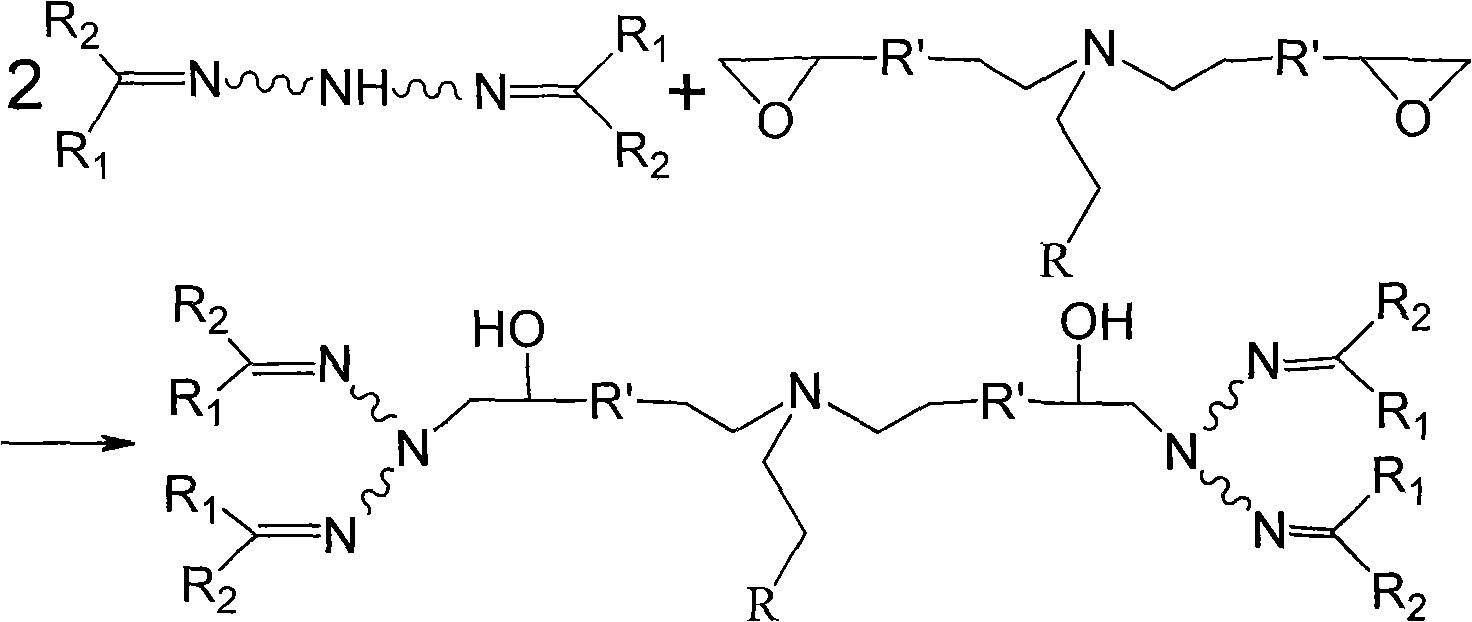
[0035] 2. Preparation of ketimine
[0036] Add 51.68 grams of diethylenetriamine, 105 grams of methyl isobutyl ketone, 0.3 grams of 723 cation exchange resin and 50 milliliters of benzene solution into a three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer, a water separator, and a condenser tube. Under the condition of reflux water separation. When the quality of the separated water is close to the theoretical valu...
Embodiment example 2
[0044] 1. Preparation of epoxy-terminated adducts
[0045] In a four-neck flask filled with nitrogen, equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, and a reflux condenser, add 0.24 moles of ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, raise the temperature to 70 ° C, and add solid octadecylamine in batches, controlled at The addition is completed within 1 to 1.5 hours. After the addition, the reaction was continued for about 4 to 6 hours, and the end point of the reaction was determined by the hydrochloric acid acetone method. The product was taken out, cooled, and sealed for storage.
[0046] 2. Preparation of ketimine
[0047] Add 74.62 grams of triethylenetetramine, 61 grams of acetone, 0.3 grams of 723 cation exchange resin, and 50 milliliters of cyclohexane solution into a three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer, water separator, and condenser, and reflux at a temperature of 80°C Divide water. When the quality of the separated water is close to the theoretical value of 18 grams, in...
Embodiment example 3
[0054] 1. Preparation of epoxy-terminated adducts:
[0055] In a four-neck flask filled with nitrogen, equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, and a reflux condenser, add 0.24 moles of ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, raise the temperature to 70 ° C, and add solid octadecylamine in batches, controlled at The addition is completed within 1 to 1.5 hours. After the addition, the reaction was continued for about 4 to 6 hours, and the end point of the reaction was determined by the hydrochloric acid acetone method. The product was taken out, cooled, and sealed for storage.
[0056] 2. Preparation of ketimine
[0057] Add 51.68 grams of diethylenetriamine, 61 grams of acetone, 0.3 grams of 723 cation exchange resin, and 50 milliliters of cyclohexane solution into a three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer, water separator, and condenser, and reflux at a temperature of 80°C Divide water. When the quality of the separated water is very close to the theoretical value of 18 grams...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com