Permanent-magnet synchronous motor adopting concentrated winding
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, centralized technology, applied in the direction of synchronous motors with stationary armature and rotating magnets, synchronous machine parts, magnetic circuit rotating parts, etc., can solve the problem of electromagnetic power and electromagnetic rotation of permanent magnet synchronous motors Small torque, difficulty in off-line of distributed windings, long ends of distributed windings, etc., to achieve high electromagnetic power and electromagnetic torque, weaken armature reaction, and light weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be explained in detail below in conjunction with the drawings.
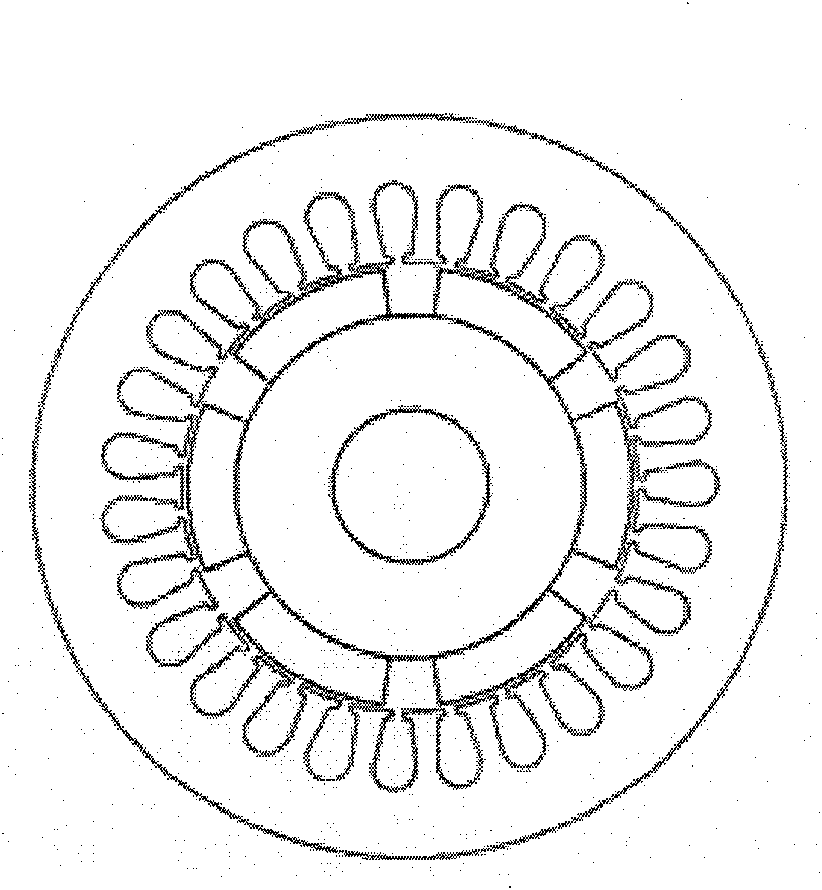
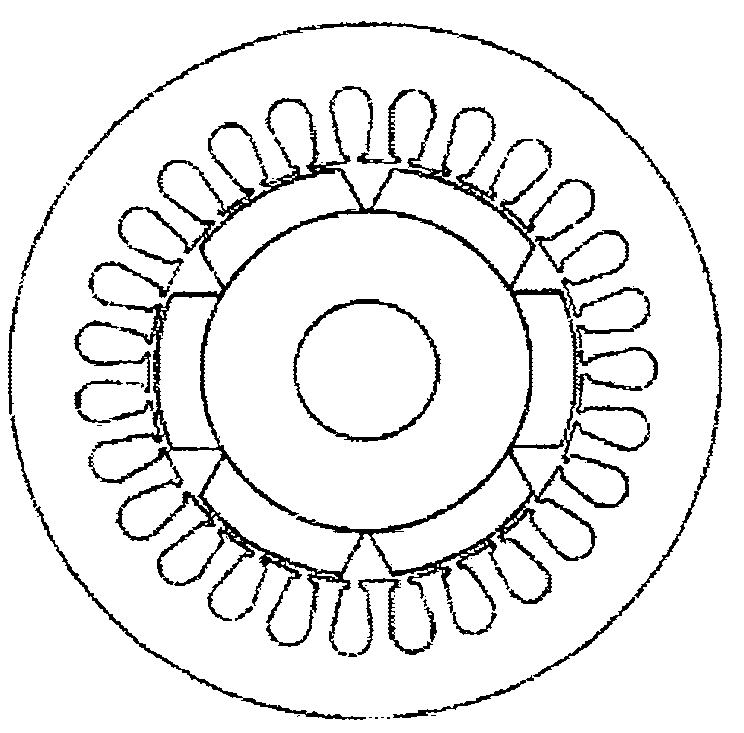
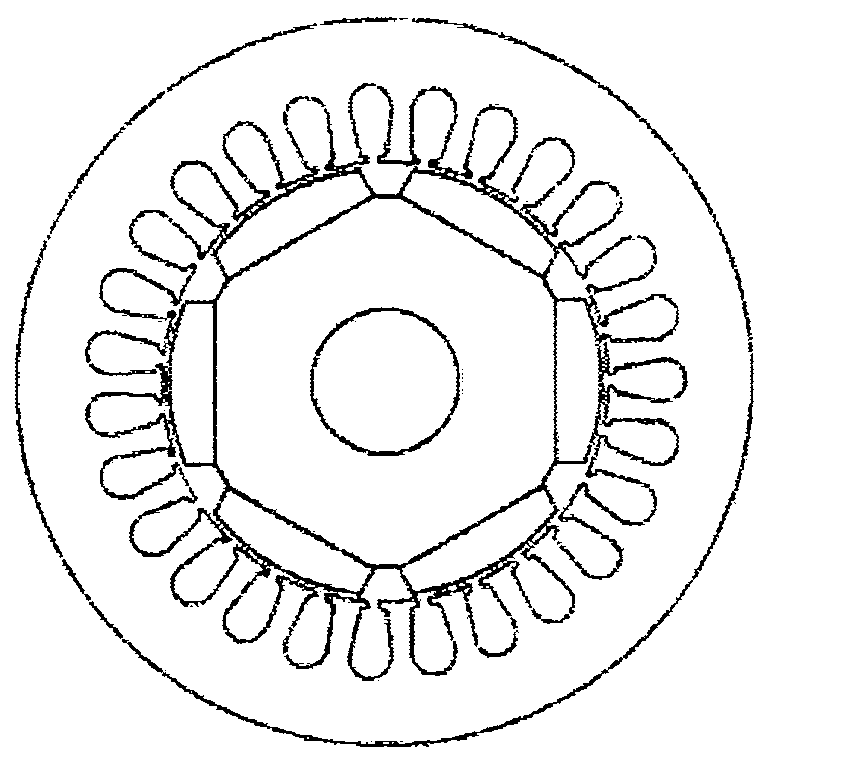
[0028] Reference attachment figure 2 , The present invention uses a concentrated winding permanent magnet synchronous motor, including a stator 10 and a rotor 20, there is an air gap 30 between the stator 10 and the rotor 20, the stator 10 includes a stator core 11 and a stator winding 12, the rotor 20 includes a rotor The iron core 21, the rotating shaft 22, and the permanent magnet steel 23, the stator winding 12 is a concentrated winding, the rotor 20 is an eccentric rotor, and the air gap 30 between the stator 10 and the rotor 20 is non-uniform air Gap. The permanent magnetic steel 23 is a radial magnetic steel.
[0029] Reference attachment image 3 The center of the rotor 20 of the present invention deviates from the center of the stator 10. As shown in the figure, the center 0 of the stator 10 does not coincide with the center 0'of the arc formed by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com