Heat exchanger for improving drainage performance
A drainage performance and heat exchanger technology, applied in heat exchange equipment, evaporator/condenser, lighting and heating equipment, etc., can solve the problems of deteriorating defrosting, difficult defrosting, thick frosting, etc., and achieve improved drainage performance , Improve the effect of heat transfer performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
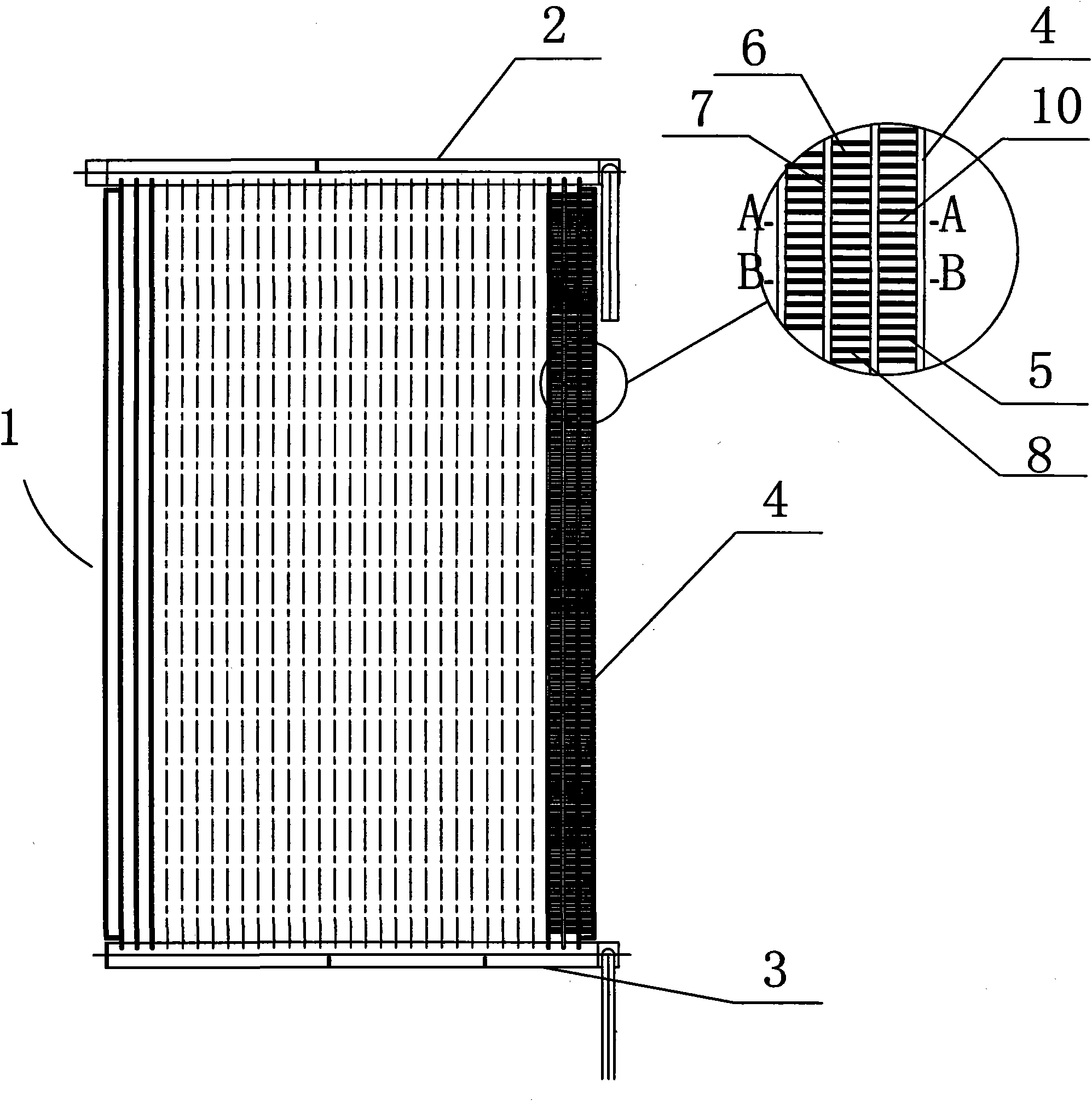
[0025] The parallel flow heat exchanger involved in the present invention can be applied to indoor and outdoor units of an air conditioner as a refrigerant heat exchanger for cooling and heating. Since the main purpose of the present invention is to optimize the drainage of parallel flow heat exchangers, only discuss its use as an evaporator in this patent, such as figure 1 As shown, the heat exchanger 1 is a flat plate type, including an upper header 2 on the upper part, a lower header 3 on the lower part, and a plurality of connecting flat tubes 4 between the upper and lower headers 2 and 3, Between the flat tubes 4, there are rectangular arrangements (as attached) Figure 9d Shown) fin 5. Air enters one side of the heat exchanger and exits the other, at figure 1 The middle is the blowing direction from the surface of the paper. In Example 1, the projection line of the working section of the water-permeable fin on the flat tube is perpendicular to the edge of the air inlet...
Embodiment 2
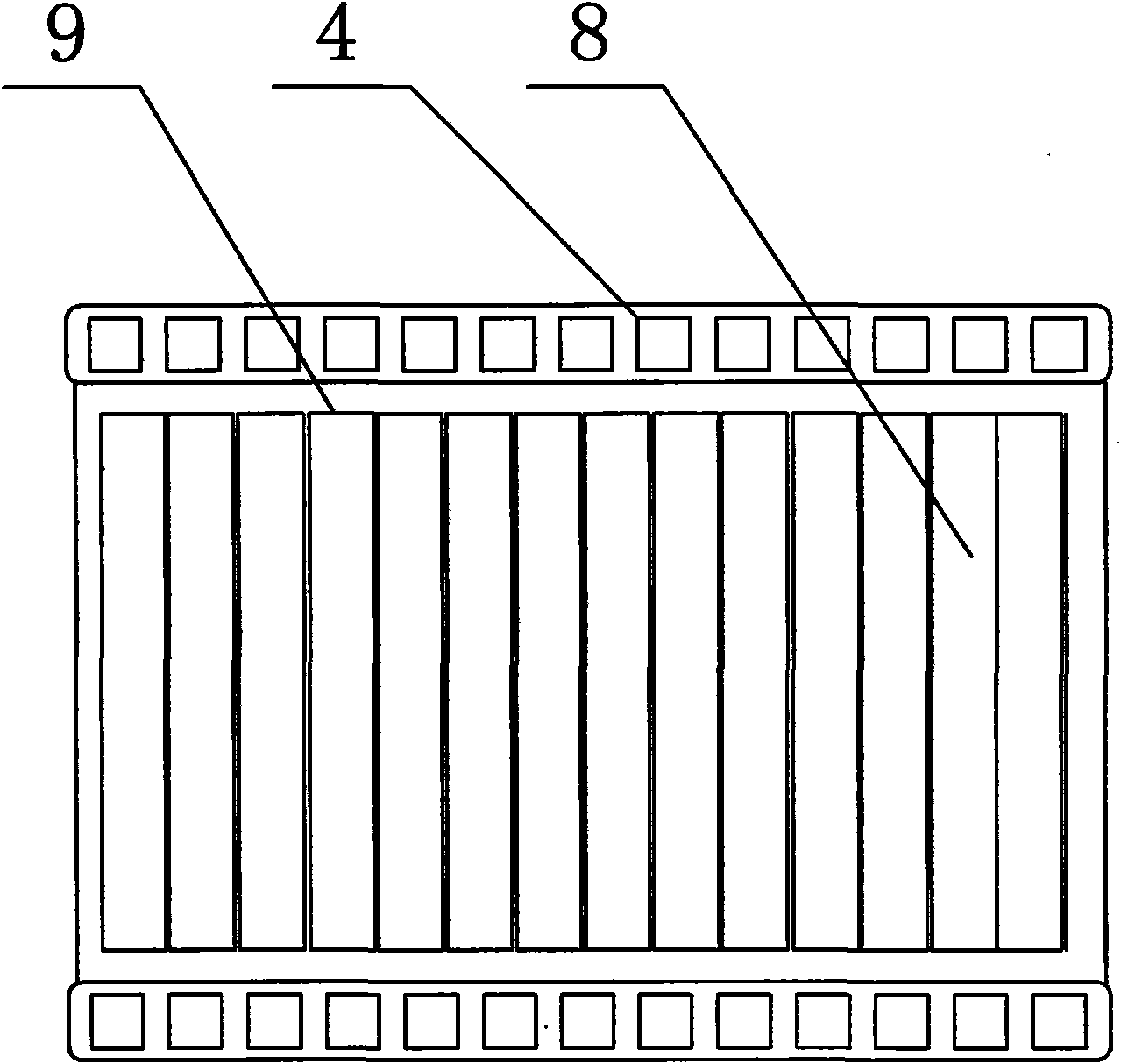
[0030] The main difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the number of fins in the impermeable section is more than one. The numerical value of the punched sheet of each group in the embodiment two is 8, namely Figure 4 The water-permeable section 14 includes 8 punched sheets, and the water-impermeable section 15 below it includes 2 water-impermeable fins 10 . The second water-impermeable fin 10 is to avoid the damage of the single water-impermeable fin in the first embodiment and make the drainage function invalid, so each water-impermeable section 15 can be provided with 2-3 water-impermeable fins, Together to complete the task of draining condensate.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The main difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that the number of perforated pieces in the permeable section of the third embodiment is changed. Such as Figure 5 As shown, when the number of water-permeable fins in the water-permeable section is different, set n1, n2, n3..., n1=445 of the uppermost layer in Embodiment 3, according to each passing through a water-permeable fin segment, The ratio n is reduced by 40, then n2=405, n3=365. An impermeable fin section is arranged under each water-permeable fin section, and the water-impermeable wing section includes 1 to 3 fins. The number of working sections of the total fins in Example 3 is 2282, and n7 is 205. Due to the high temperature in the upper part of the heat exchanger, the amount of condensed water produced is less than that in the lower part of the heat exchanger with a lower temperature. If the number of punched plates in each permeable section is consistent, the amount of condens...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com