Static latch
A latching and static technology, applied in the latching field, can solve the problems of shortening the maintenance time of the frequency signal level and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
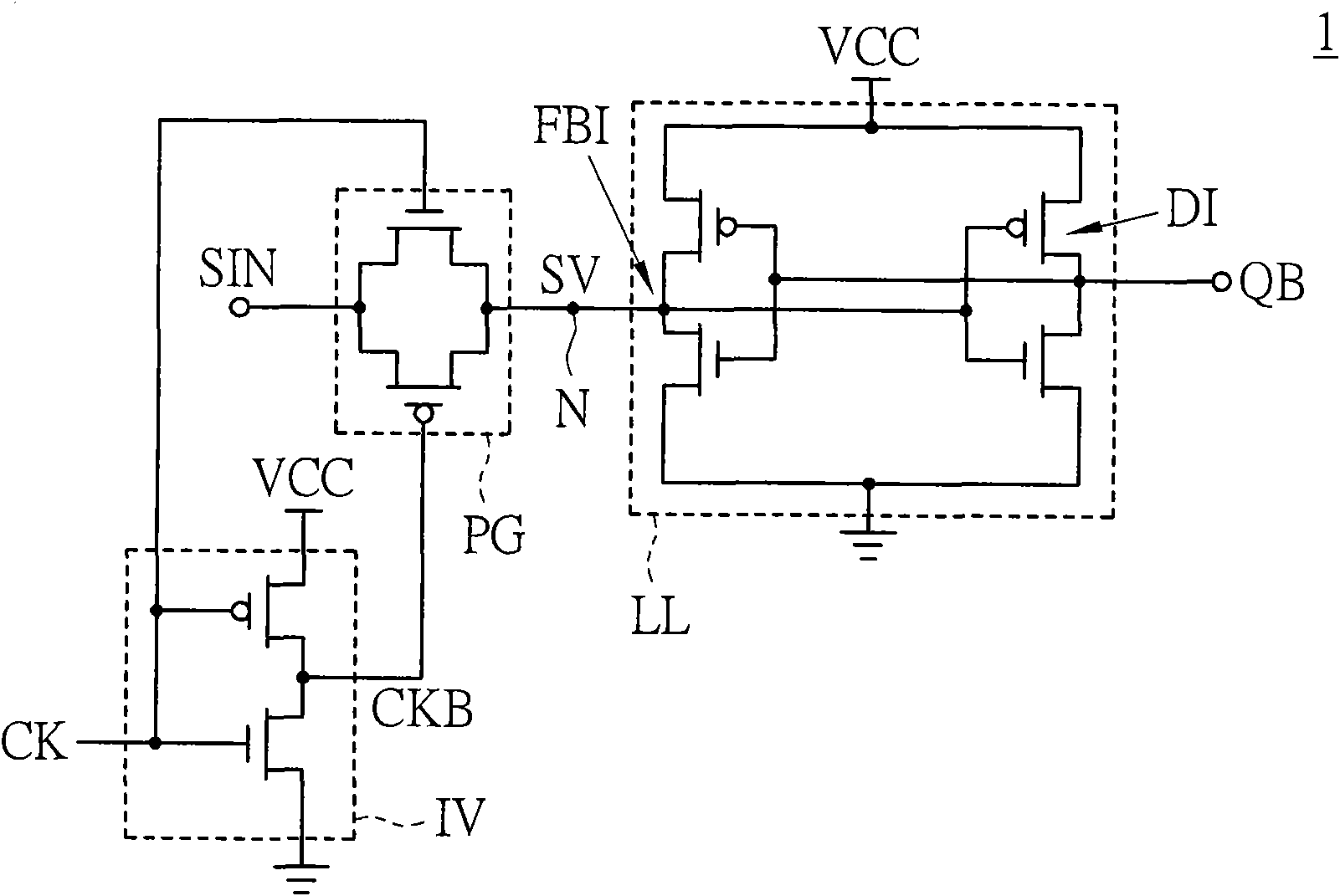
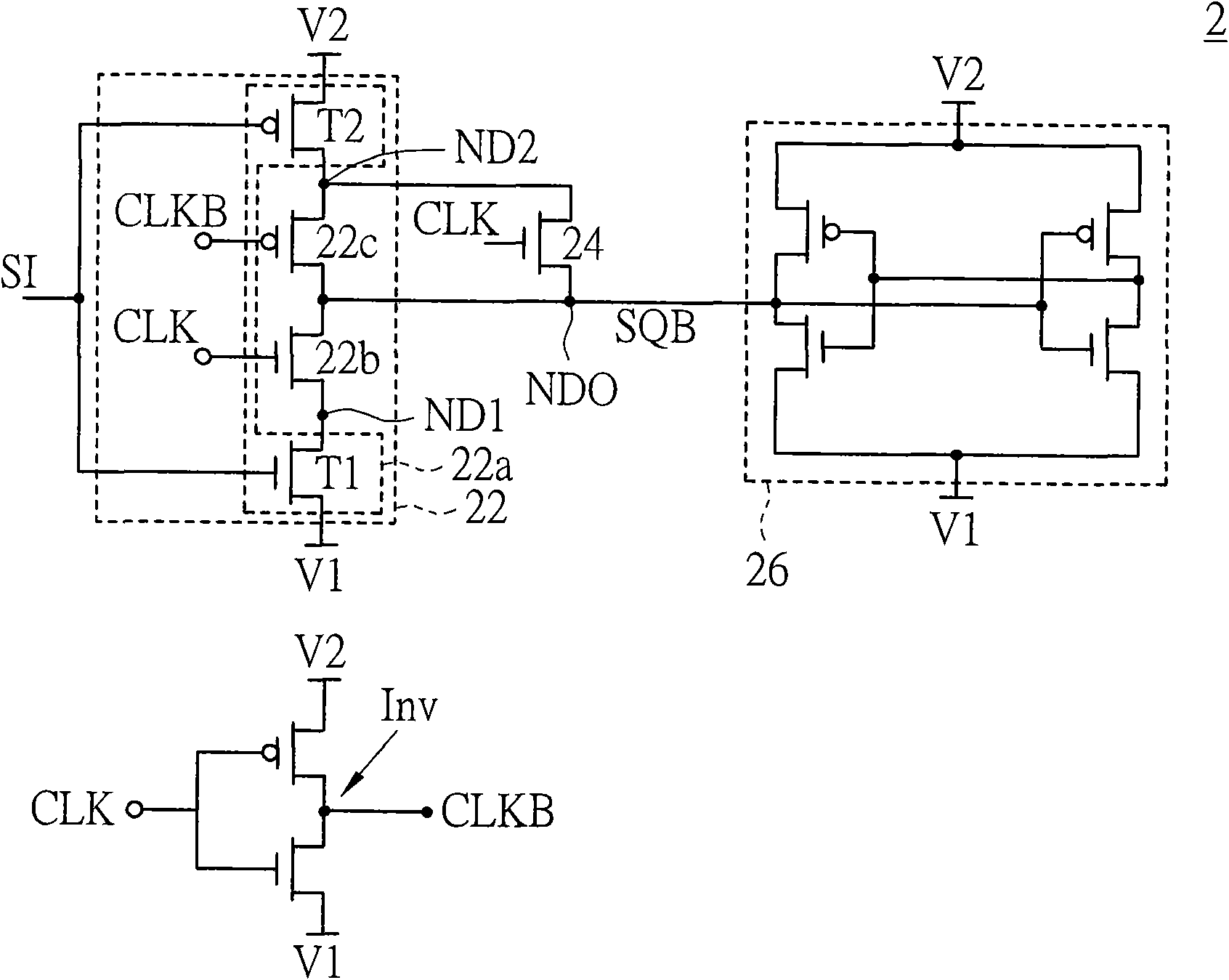
[0031] refer to figure 2 , which shows a circuit diagram of the static latch according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The static latch 2 is controlled by the clock signal CLK and the inverted clock signal CLKB, and is used for storing the latch signal SQB on the output node NDO in response to the input signal SI. For example, the static latch 2 includes an inverter Inv for generating an inverted clock signal CLKB according to the clock signal CLK. The static latch 2 includes a clock-based driver 22 , a trigger circuit or flip-flop 24 and a weak latch unit 26 . The frequency driven driver 22 , the driving circuit 24 and the low driving force latch unit 26 are all coupled to the output node NDO.
[0032] The frequency-driven driver 22 includes nodes ND1, ND2, a driving unit 22a, and switches 22b and 22c. The driving unit 22a and the switch 22b are coupled to the node ND1. The driving unit 22a and the switch 22c are coupled to the node ND2.
[0033] The d...
no. 2 example
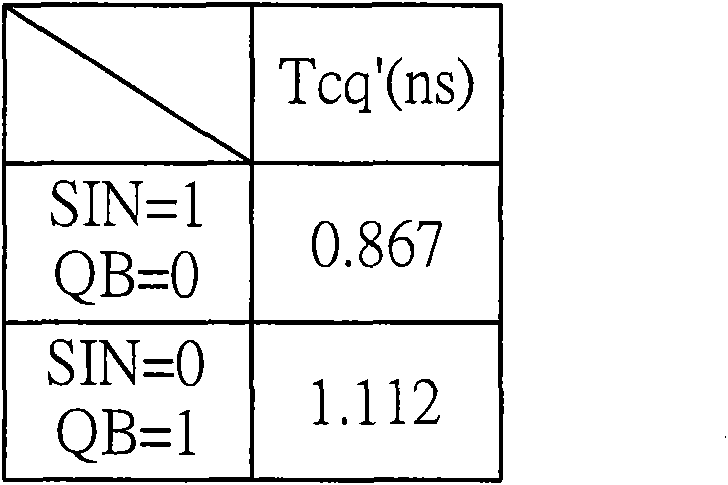
[0045] refer to Figure 4 , which shows a circuit diagram of the static latch according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Figure 4 The static latch 3 shown with the figure 2 The difference between the illustrated static latch 2 is that the static latch 3 further includes a trigger circuit 34', which includes a PMOS transistor for responding to the inverted frequency signal CLKB, and provides the switch 32b on the node ND1 together with the switch 32b. voltage to output NDO. In this way, because the trigger circuit 34' and the switch 32b are provided in parallel, the equivalent resistance between the node ND1 and the output terminal NDO can be effectively reduced. In this way, the time required for the latch signal SQB to be discharged to the voltage V1 can be effectively shortened.
no. 3 example
[0047] refer to Figure 5 , which shows a circuit diagram of a static latch according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Figure 5 The static latch 4 shown with the Figure 4 The difference of the static latch 3 shown is that the static latch 4 only includes a trigger circuit 44 having substantially the same circuit connection relationship and function as the trigger circuit 34 ′, and the trigger circuit 44 is used to respond to the anti-phase frequency signal CLKB, together with the switch 42b, provides the voltage on the node ND1 to the output terminal NDO. The trigger circuits corresponding to the trigger circuits 24 and 34 in the static latches 2 and 3 are omitted in the static latch 4 . Since the trigger circuit 44' and the switch 42b are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance between the node ND1 and the output terminal NDO can be effectively reduced. In this way, the time required for the latch signal SQB to be powered up to the voltage V1 can ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com