Genetic variations associated with drug resistance
A resistance and anti-mitotic agent technology, applied in the field of genetic variation, can solve problems such as increased resistance to Paclitaxel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0162] Example 1 - Techniques and Assays
[0163] Cell Lines and Viability Assays
[0164] Breast cancer cell lines AU565, BT-474, BT-549, CAMA-1, DU4475, HCC1143, HCC1419, HCC1428, HCC2218, HCC70, Hs578T, KPL-1, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB- 435S, MDA-MB-436, MDA-MB-453, MDA-MB-468, T-47D, UACC-812, ZR-75-1 and ZR-75-30 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (American Type Culture Collection, ATCC, Manassas, VA). Cell lines CAL-120, CAL-148, CAL-51, CAL-85-1, EFM-19, EFM-192A, EVSA-T, and MT-3 were obtained from the German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures (Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH, DSMZ, Braunschweig, Germany). All cell lines were maintained in DMEM or RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sigma, St. Louis, MO), non-essential amino acids, and 2 mmol / L L-glutamine. Although annotated as mammary, MDA-MB-435S may actually be of melanoma origin and MT-3 may actually be of colorectal origin based on m...
Embodiment 2
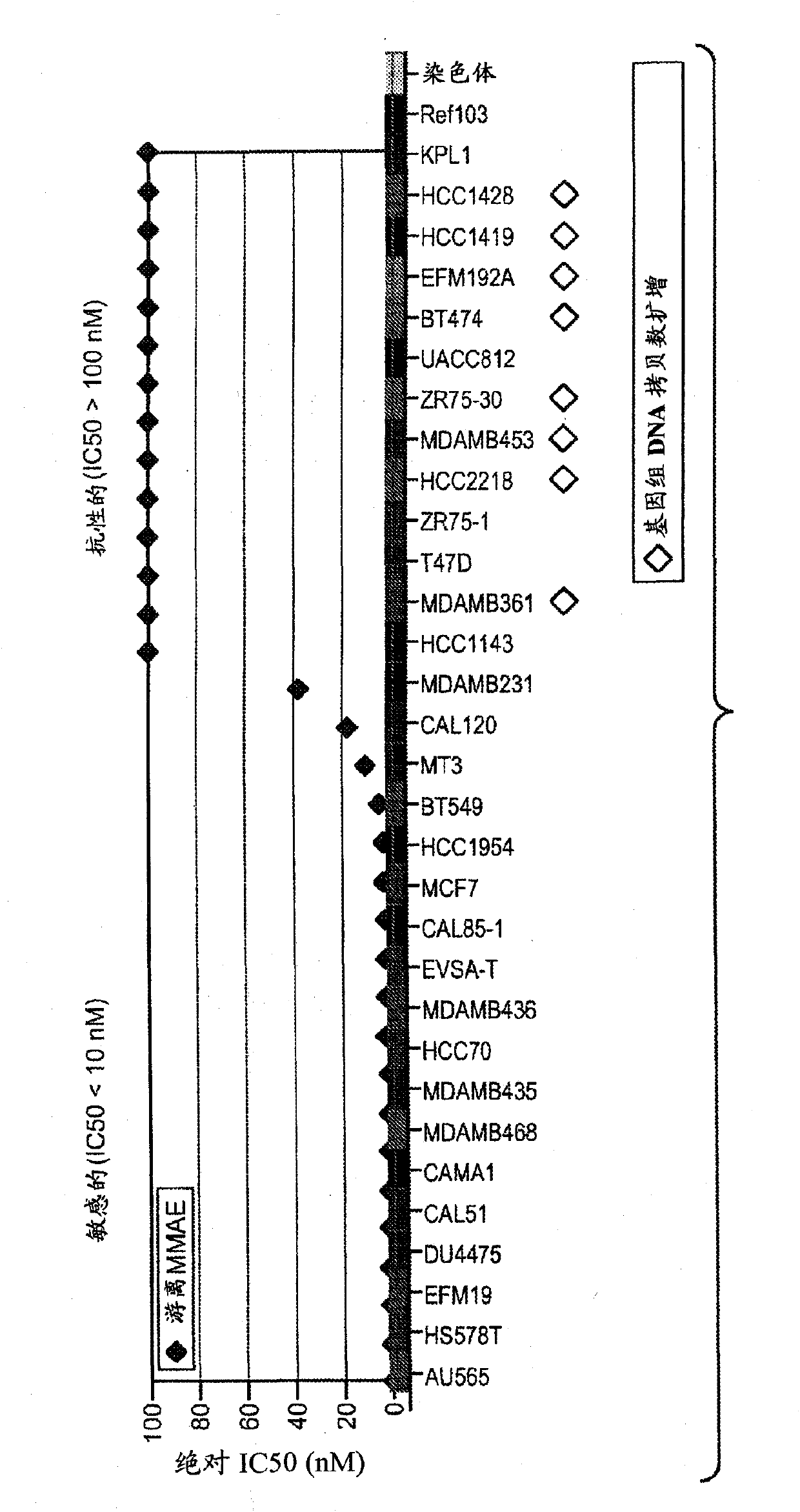
[0187] Example 2 - Molecular Characterization of Cell Lines
[0188] Affymetrix gene expression profiling was performed on cDNA prepared from total mRNA and Affymetrix 100K SNP array profiling was performed on DNA from 44 breast cancer cell lines. Cell lines were classified into luminal and basal-like subtypes based on gene expression using an unsupervised analysis of the 11,000 most differentially expressed genes between cell line groups ( Figure 11 ). Cell lines classified as luminal expressed high levels of estrogen receptor alpha (ER) and many target genes regulated by ER, including GATA3, HNF3A, IGF1R, and XBP1. Cell lines classified as basal express high levels of some or all of the well-documented basal markers vimentin, caveolin, MFGE8 and basal cytokines such as KRT5 (31). Because amplification of the HER2 oncogene clearly defined a discrete disease subtype that was not clearly grouped according to overall gene expression in the cell lines (14), HER2 copies were de...
Embodiment 3
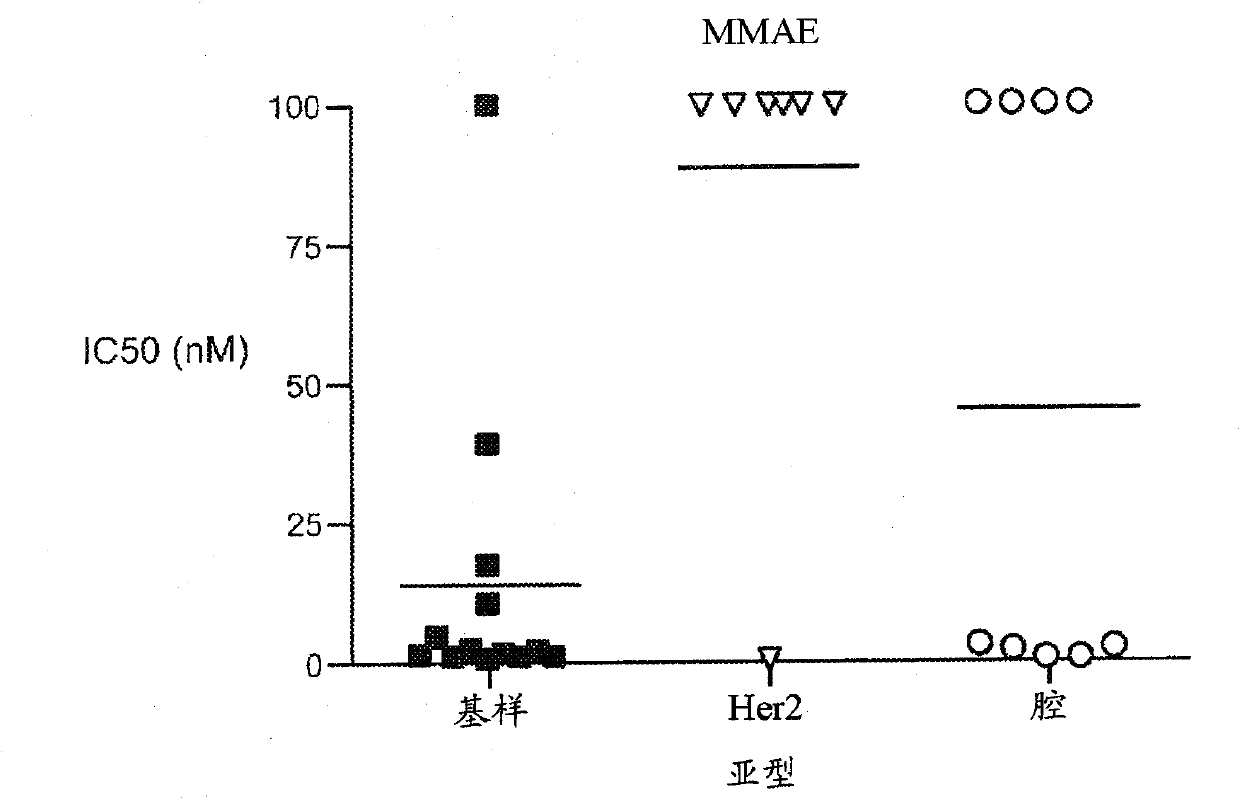
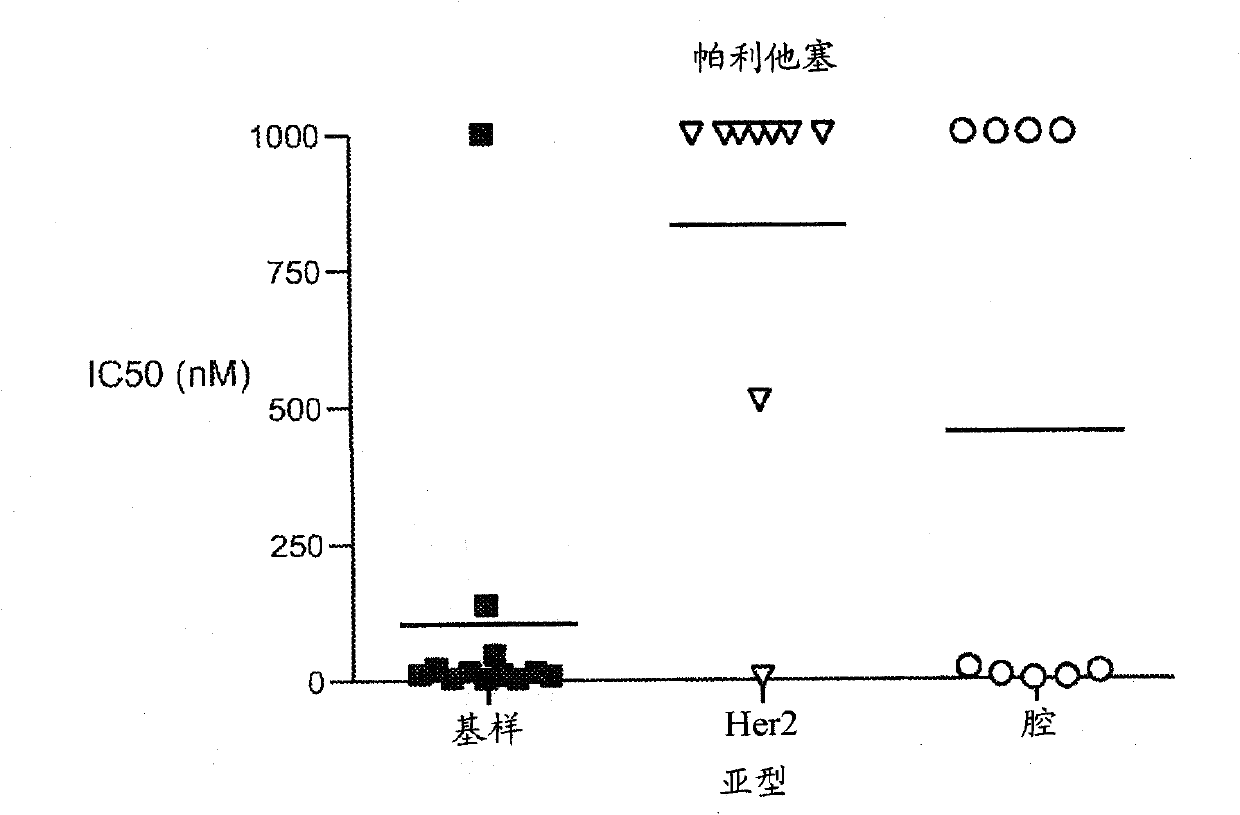
[0189] Example 3 - Sensitivity to anti-mitotic drugs in vitro
[0190] Thirty-one breast cancer cell lines were screened for sensitivity to paclitaxel and MMAE in vitro. Figure 11 IC50 values are shown for each compound in all cell lines, defined as the concentration required for 50% inhibition of cell viability in a standard luciferin-based viability assay. Notably, there was a significant correlation between the relative sensitivity to each agent between the cell line groups (Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient, rs=0.55). In addition, Figure 1 shows that compared with luminal or HER2-amplified cell lines, cells with basal-like gene Cell lines expressing the signature had lower mean IC50 values and were more sensitive to each agent.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com