Methods for detecting and modulating the sensitivity of tumour cells to anti-mitotic agents
A tumor cell, sensitive technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, antineoplastic drugs, etc., can solve the problem that the efficacy of βIII tubulin has not yet been determined
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0175] Example 1. Cell culture and siRNA transfection
[0176] Human NSCLC cell lines Calu-6 and H460 (ATCC: Calu6 Cat. No. HTB-56, NCI-H460 Cat. No. HTB-177) were maintained as monolayer cultures in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) and RPMI, respectively, The medium was supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) and 2 mM L-glutamine. Cells at 37°C with 5% CO 2 grow in a moist atmosphere.
[0177] Various siRNAs or shRNAs were used in the Examples described herein.
[0178] class III beta-tubulin
[0179] (formal code: TUBB3), also known as MCIR; TUBB4; β-4SMARTpool, human TUBB4, NM_006086 (class III β-tubulin) Dharmacon RNA Technologies
[0180] class III beta-tubulin sequence 1
[0181] Sense sequence: GGGCGGAGCUGGUGGAUUCUU (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0182] (bits 327 to 245, mismatches at bits 346 to 347)
[0183] Antisense sequence: 5Phos-GAAUCCACCAGCUCCGCCCUU (SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0184] class III beta-tubulin sequence 2
[0185] Sense sequence: GUACGUGCCUCGAGCCAUUUU (S...
Embodiment 2
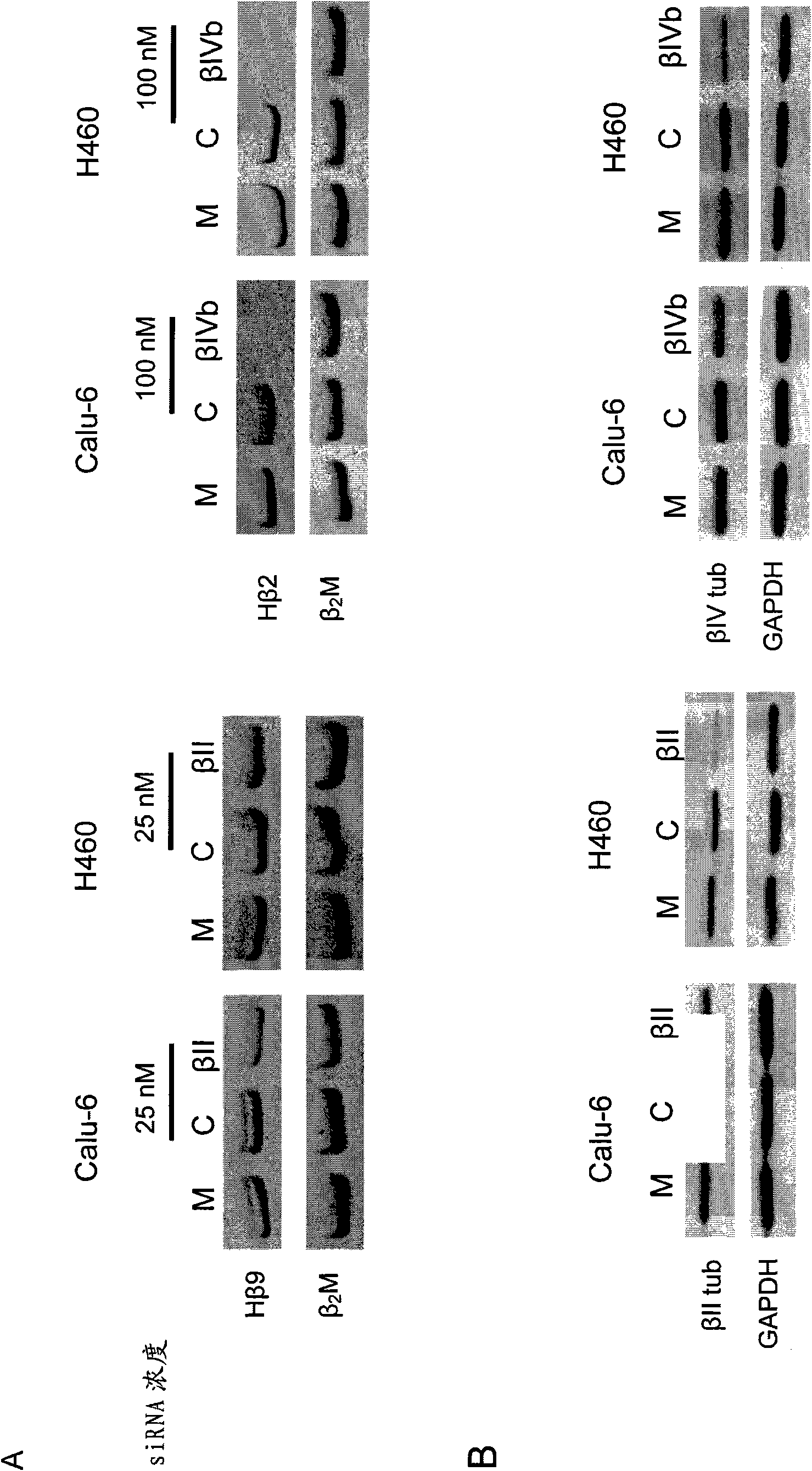
[0244] Example 2: Analysis of β-tubulin isoforms
[0245] The effect of siRNA transcription on the expression of β-tubulin isoforms was assessed using reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) analysis of β-tubulin isoforms and by Western blotting. For reverse transcription analysis, total RNA was isolated using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNA samples were treated with DNase and reverse-transcribed for RT-PCR analysis using the method and specific primers described in Kavallaris et al. (1997) J ClinInvest 100, 1282-1293, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference. For the Hβ9 (class II), H5β (class IVa), and Hβ2 (class IVb) genes, semiquantitative PCR-based testing involves setting up two separate PCR tubes for the target (beta tubulin) and control (beta 2 Microglobulin) gene sequence. Amplification products were resolved on a 12.5% polyacrylamide gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining with a GelDoc 100...
Embodiment 3
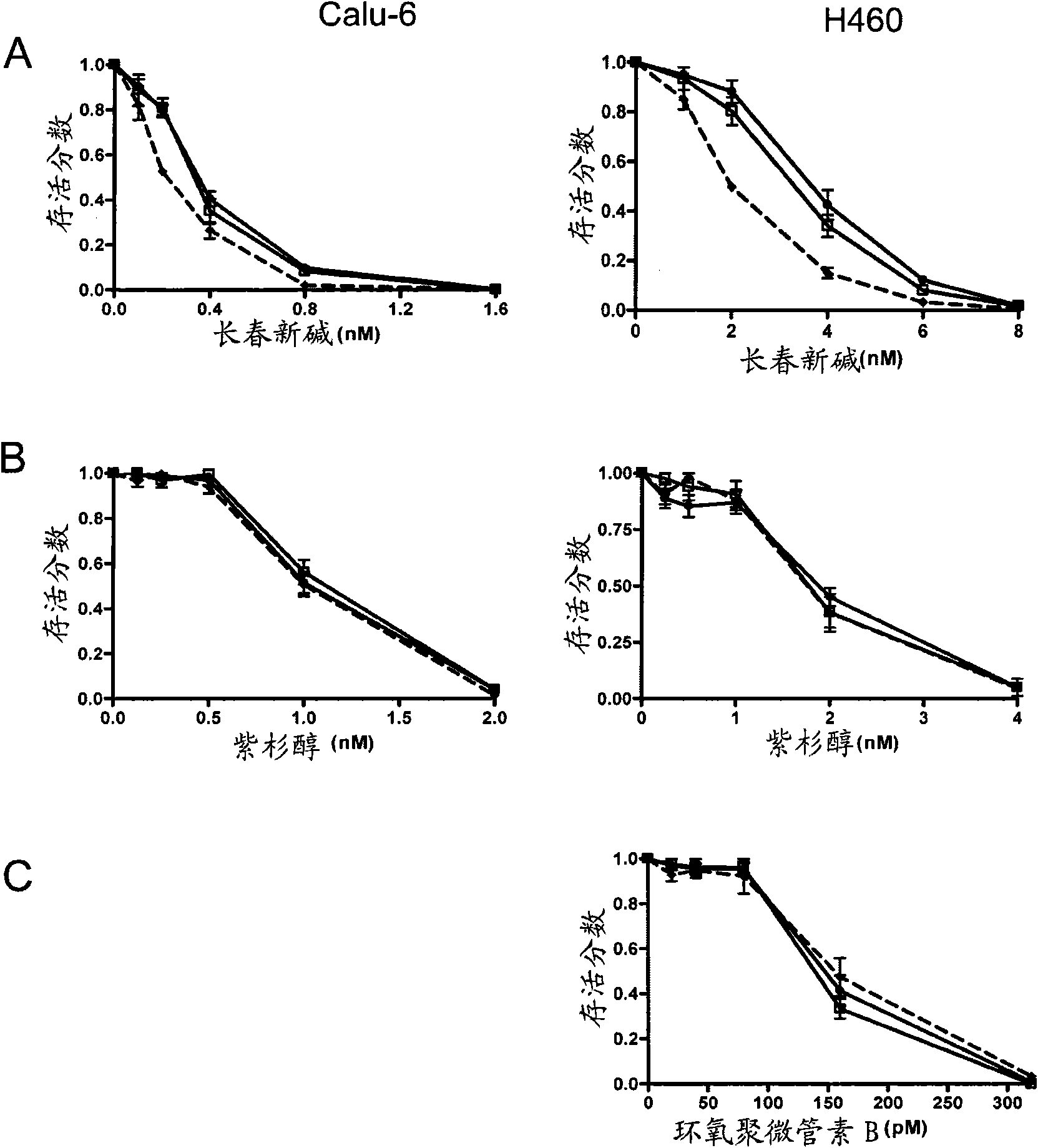
[0248] Example 3: Drug-resistant clone testing
[0249] Cells were transfected for 24h and approximately 600 cells (for Calu-6) or 150 cells (for H460) were seeded into each well of a 6-well plate and allowed to attach for 4-6h. The cell lines used in this study did not undergo prior drug selection and tended to exhibit the intrinsic drug resistance observed in lung cancer.
[0250] Cells were then treated with increasing concentrations of various anti-mitotic drugs. After 3 days of incubation at 37°C, the drug-containing medium was removed and replaced with fresh complete medium. The medium was changed every 3 to 4 days for 7 to 10 days until visible colonies were formed. Control cells were treated identically with similar media changes. Surviving colonies were simultaneously fixed and stained with 0.5% crystal violet in methanol, washed with water to remove excess staining and air dried overnight.
[0251] The colonies in each well were manually counted, and the results ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com