Method for the operative monitoring of track brakes
A track brake and operation monitoring technology, applied in the direction of brakes, brake components and track interaction brakes, brake components, etc., can solve the problem of inaccurate and wrong signals of sensors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
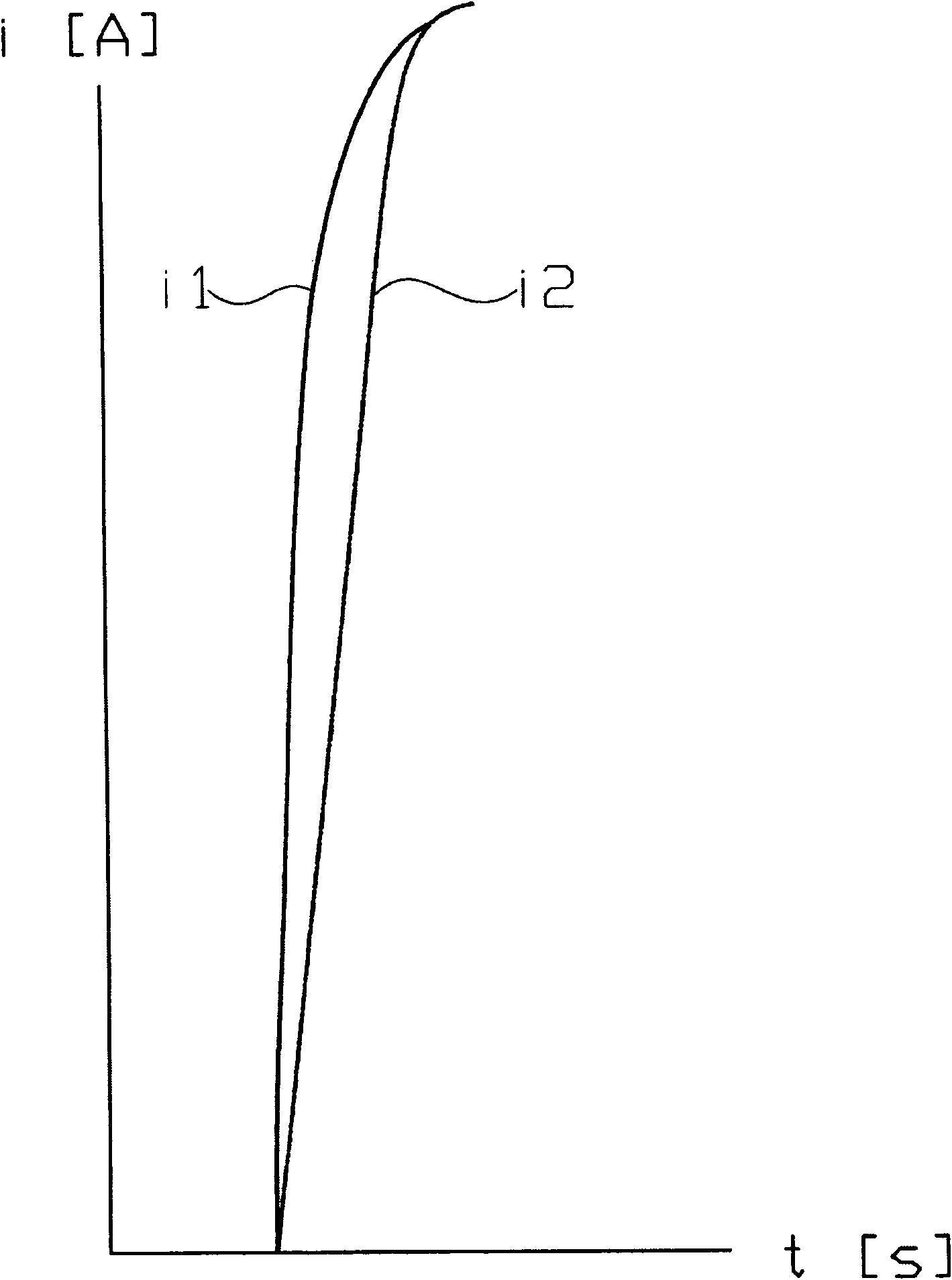
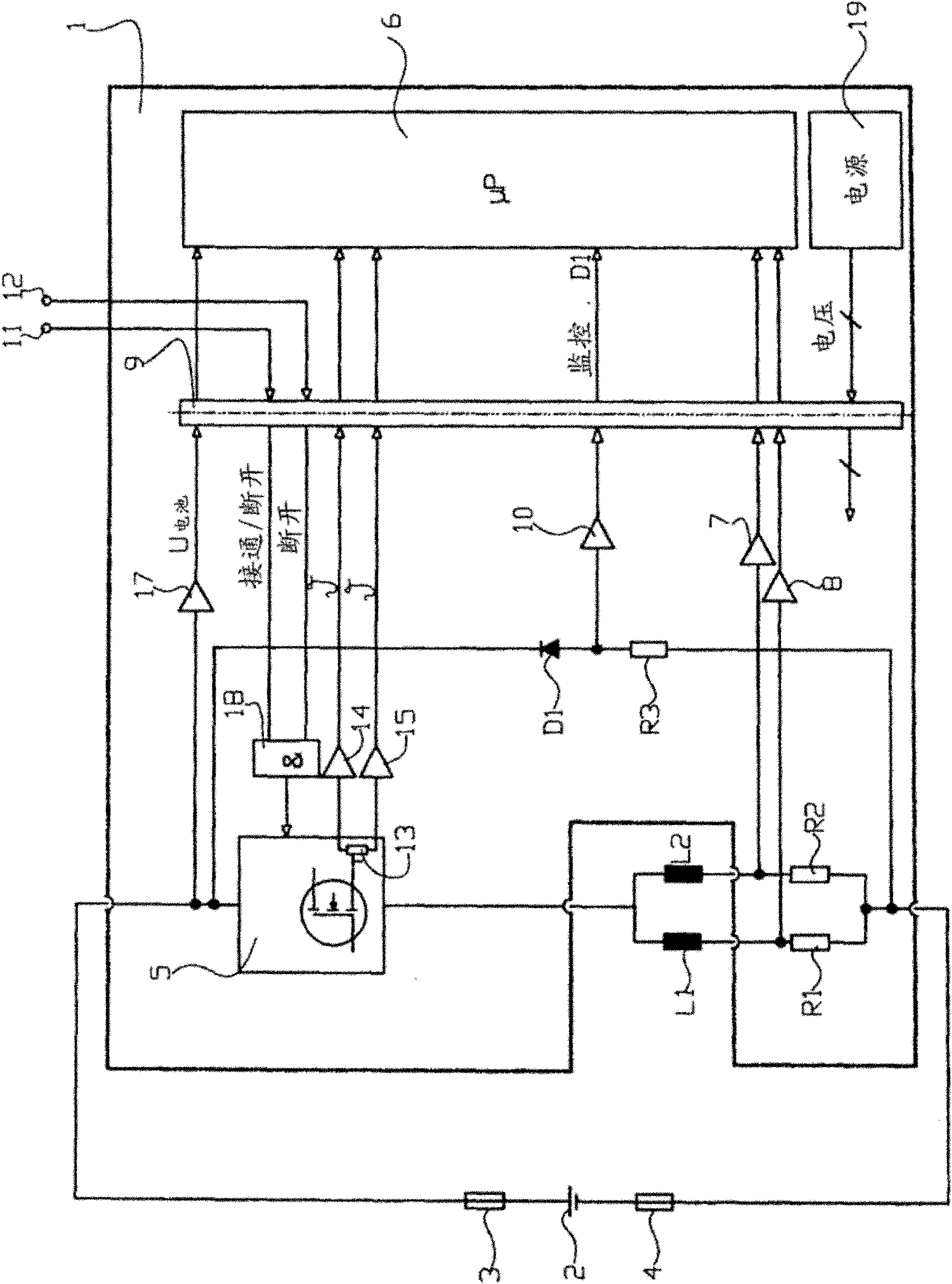
[0024] figure 1 A control device 1 is shown for controlling the braking electromagnets, which are represented as inductances L1 and L2 in the figure 1 circuit diagram.
[0025] The control device 1 is supplied with electrical energy from the vehicle electrical system, for example a battery 2 , the control device being connected to the poles of the battery via a fuse 3 or 4 .
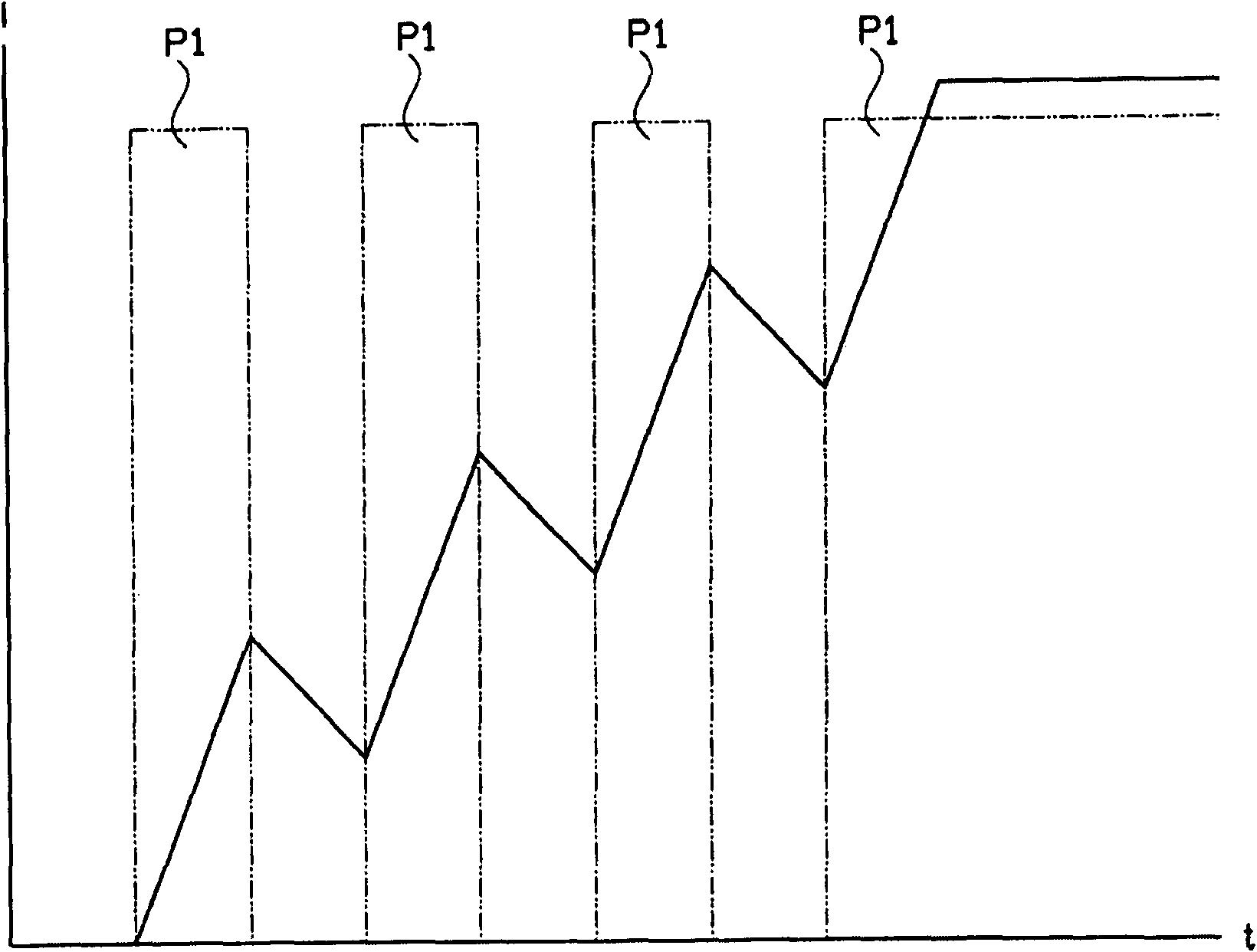
[0026] The two inductors L1 and L2 are in a circuit comprising a power switch 5 controlled by a microprocessor 6 and the inductors L1 and L2 are connected to the battery voltage of the battery 2 . Two inductors L1 and L2 are connected in series with shunt resistors R1 or R2 respectively, and the voltage drop of these shunt resistors is proportional to the current flowing through the inductors L1 or L2. The voltage is tapped at a common connection point between inductances L1 and L2 and shunt resistors R1 and R2 and passed on to microprocessor 6 via measuring amplifier 7 or 8 . The microprocessor 6 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com