Wind sensor system using blade signals
A sensor signal, blade technology, applied in the field of wind speed field measurement system, can solve problems such as being too expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
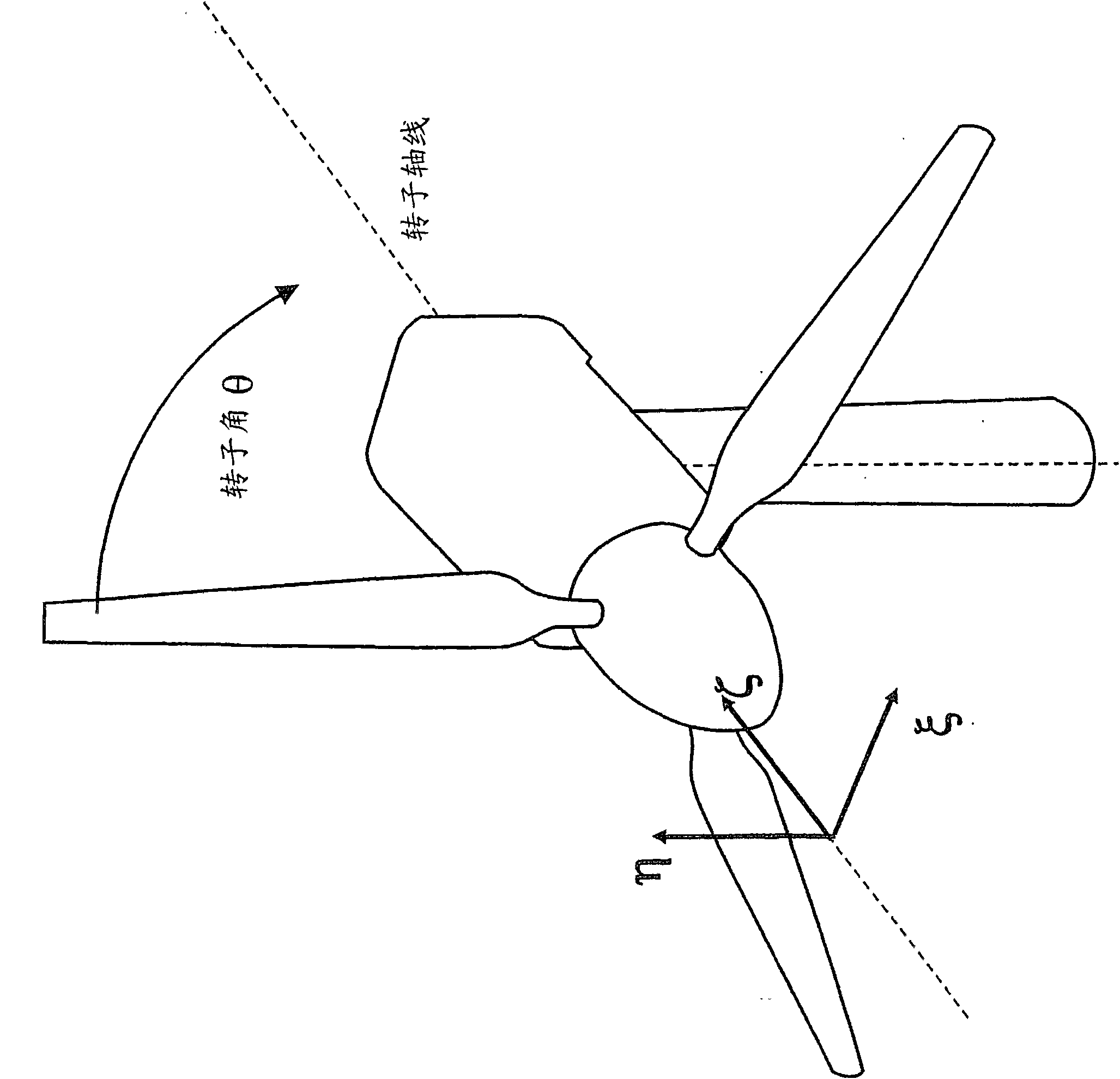
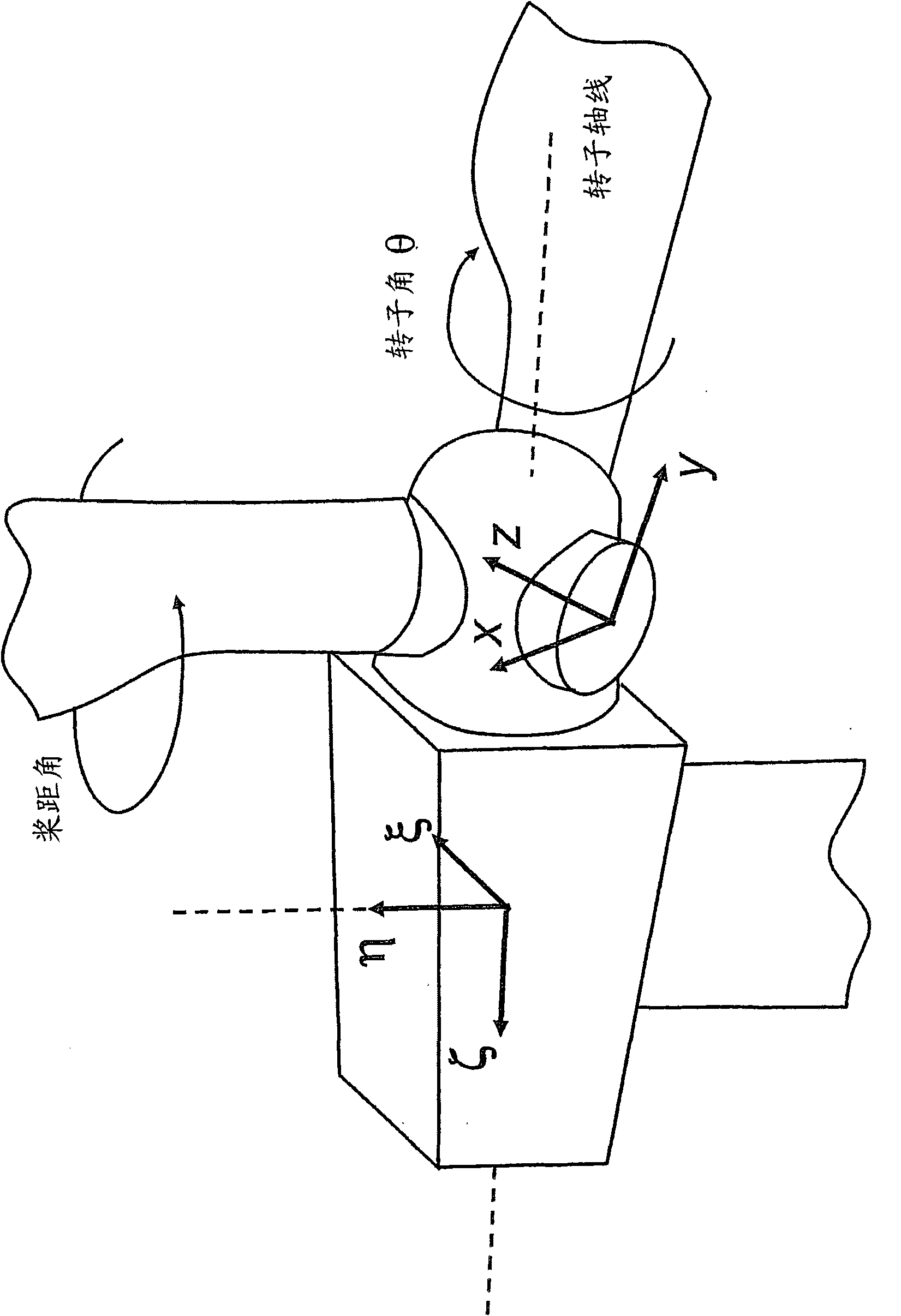
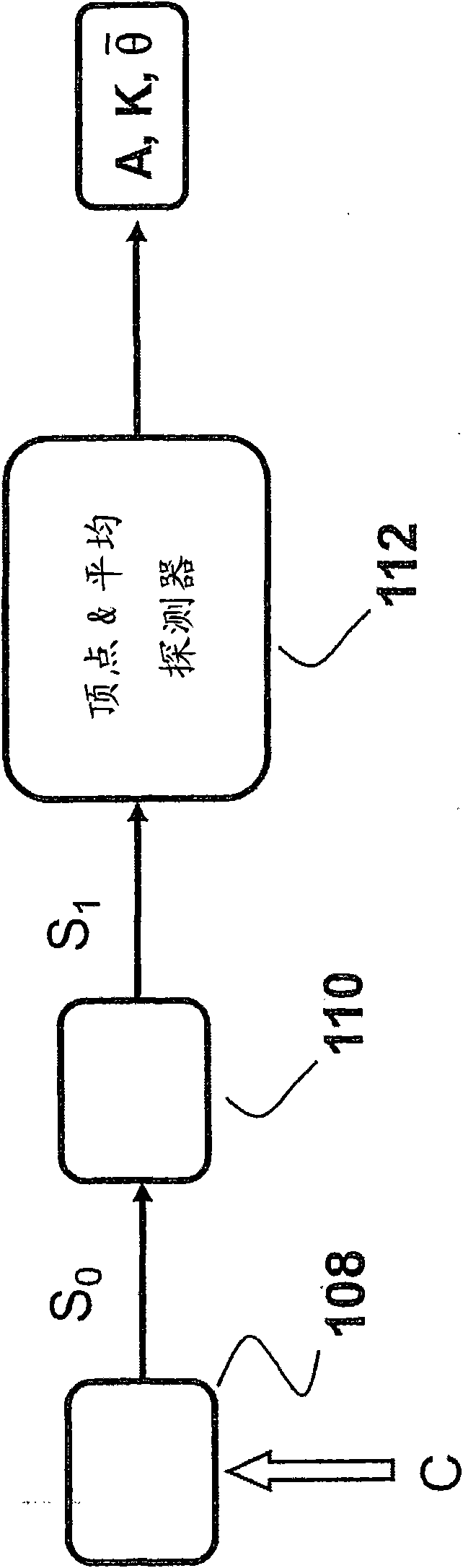
[0056] refer to image 3 , with S 0 Denotes sensor signals from sensors 108 positioned on the rotor hub or blades, where sensor signal S corresponds to at least one wind velocity field characteristic denoted by C. The sensor signal S passes through a calibration arrangement 110 which provides variable gain and offset to the sensor signal so as to always substantially calibrate the sensor signal, thus producing a balanced sensor signal S 1 . If there is noise in the sensor signal, a low-pass filter can be incorporated in the correction device to attenuate or remove this noise.
[0057] In the case of misalignment between the rotor axis and the wind direction, or in the presence of wind shear, the rotation of the rotor (turned angle θ) within the sensor signal S 1 produces a cyclic change added to a constant value. Let A represent the amplitude of the cyclic change, and use Denotes the angle θ at which the maximum value occurs, and denote the sensor signal S by K 1 consta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com