Patents
Literature
1642results about "Engine control parameters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
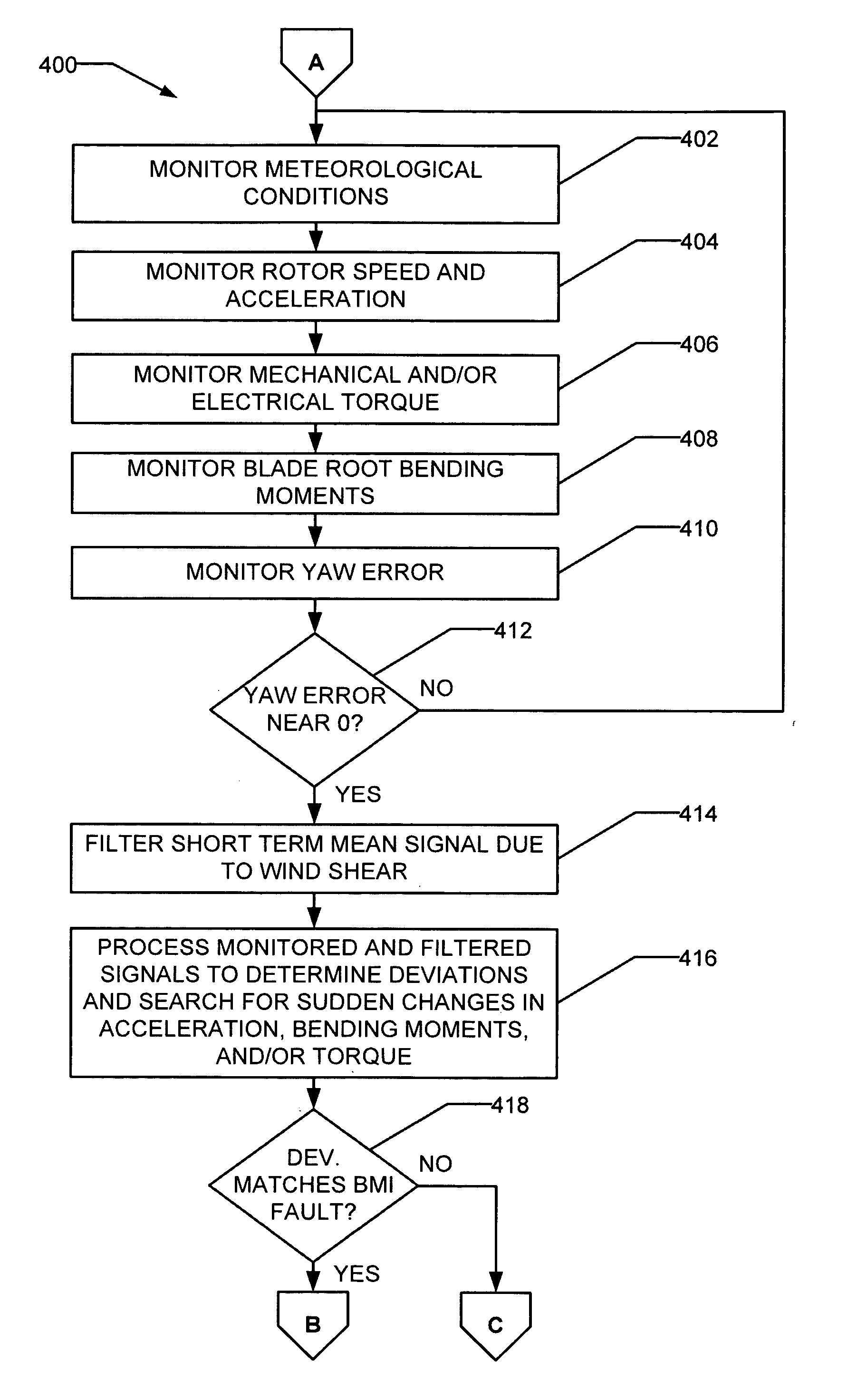
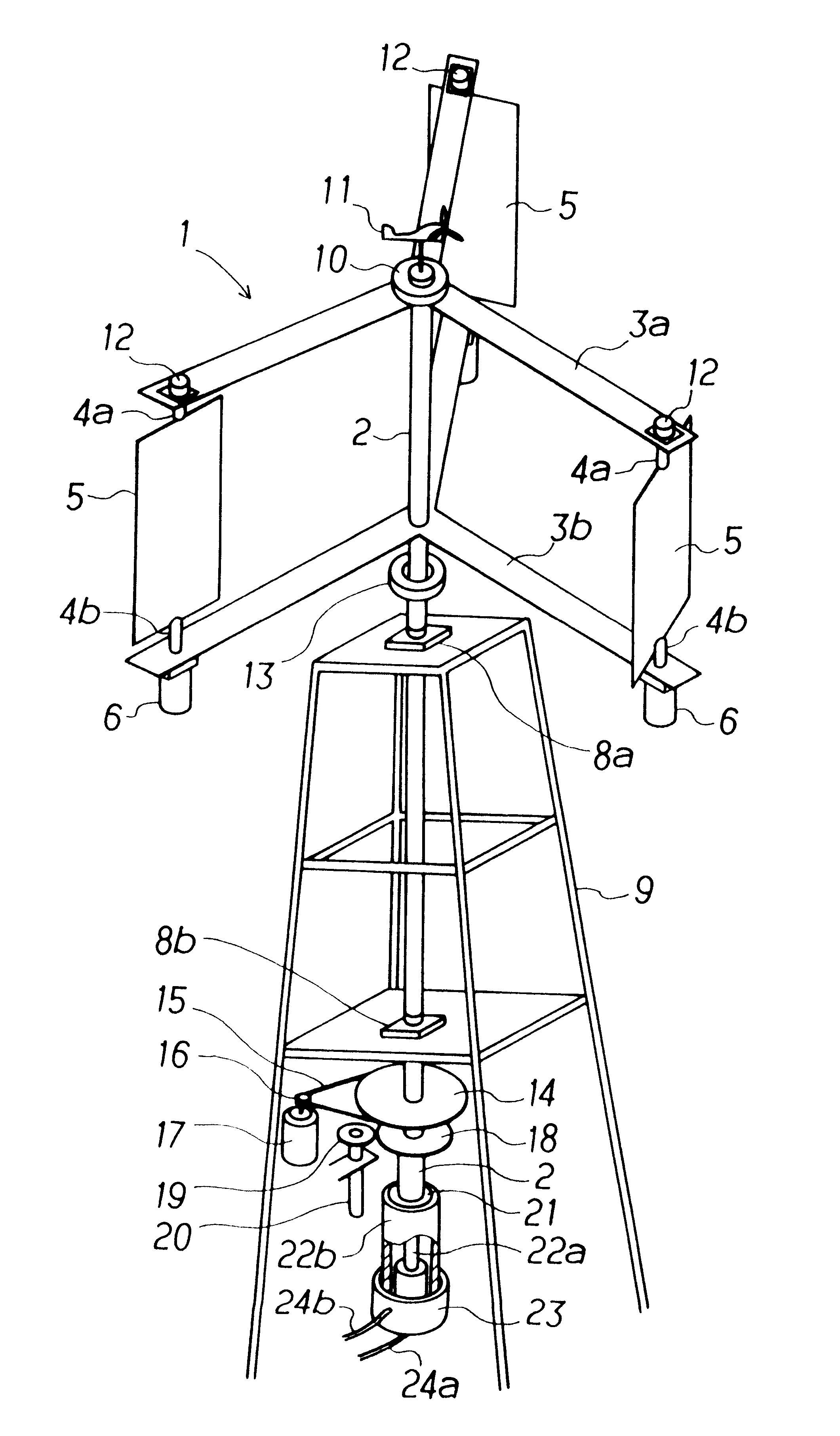
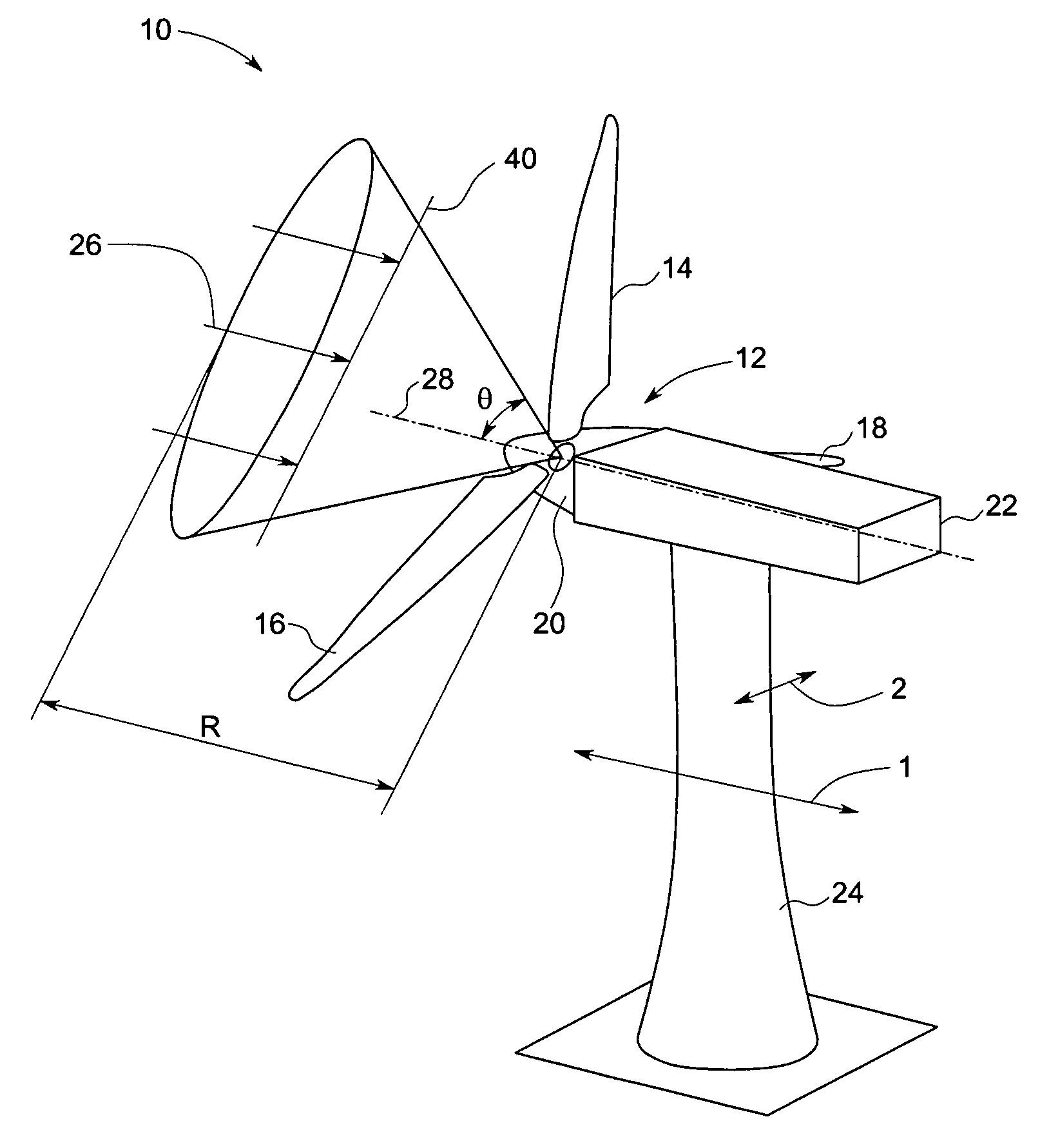
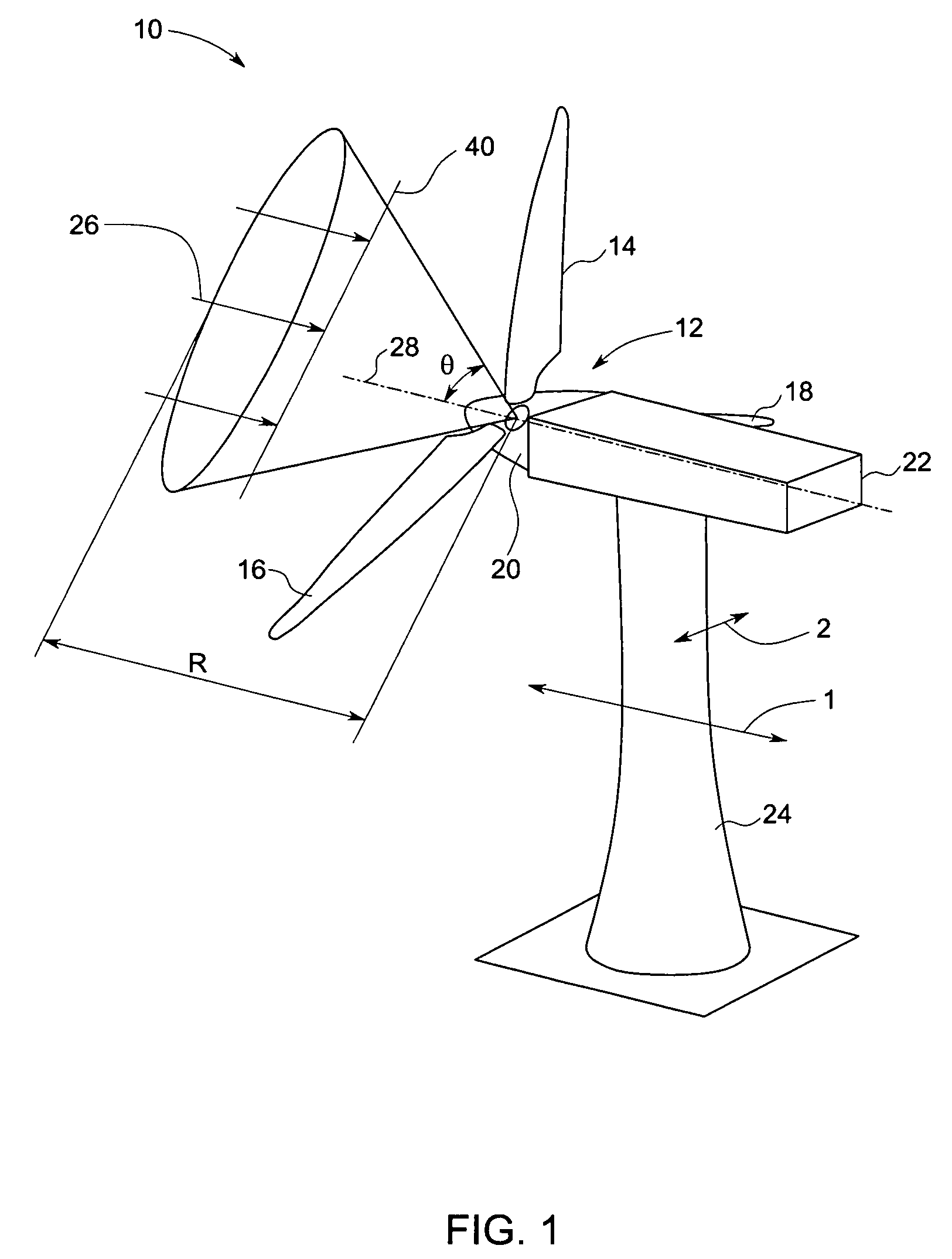
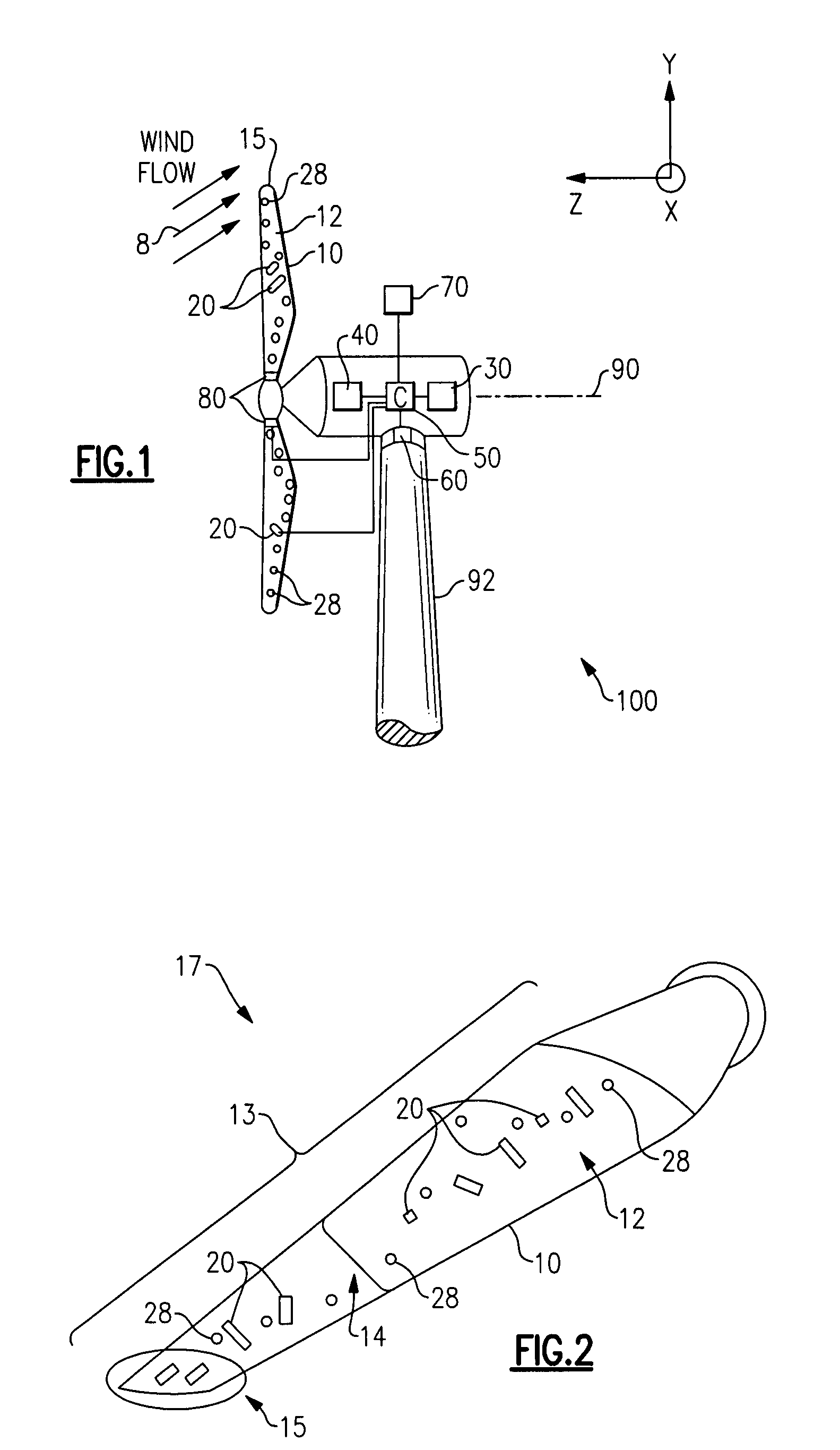
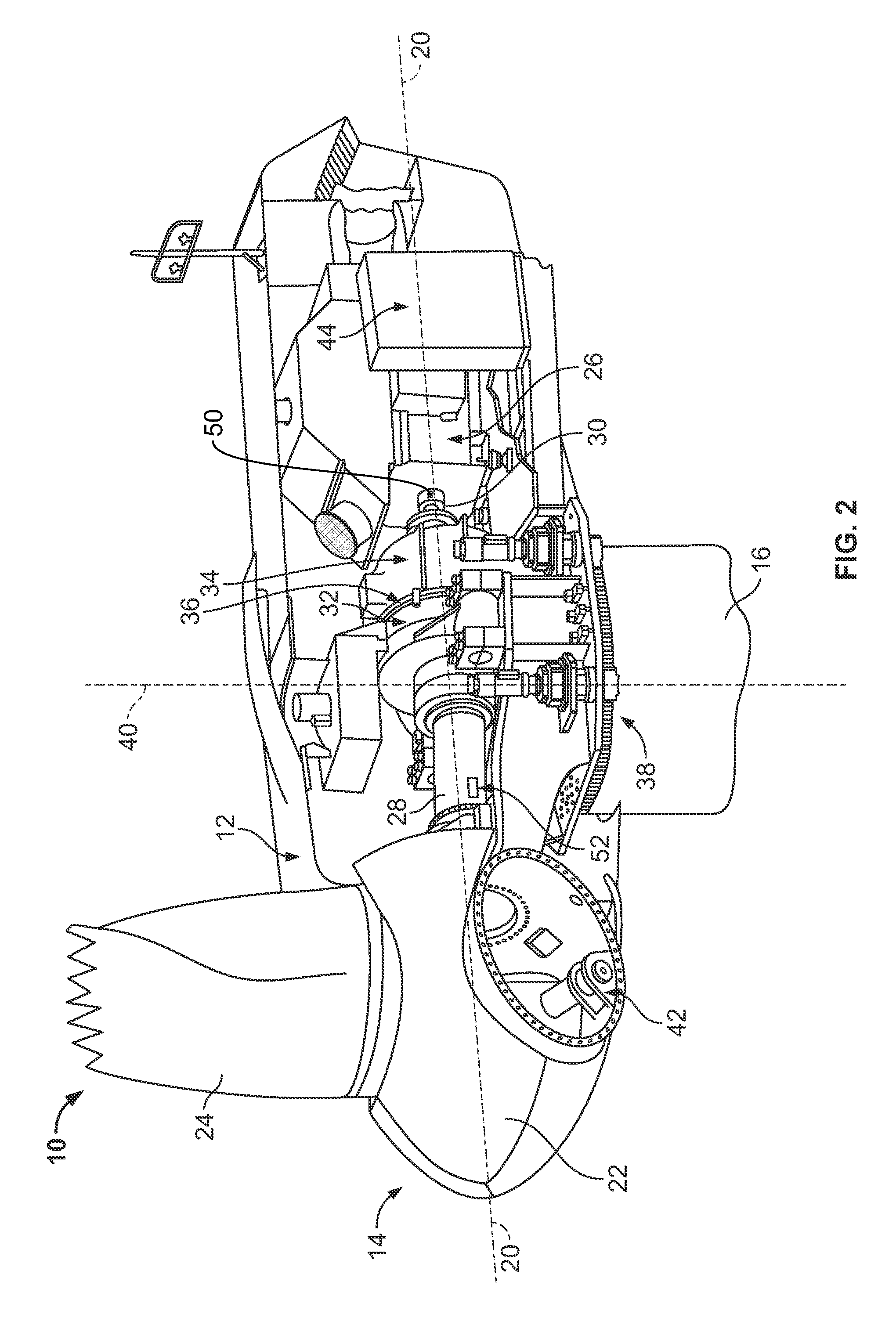
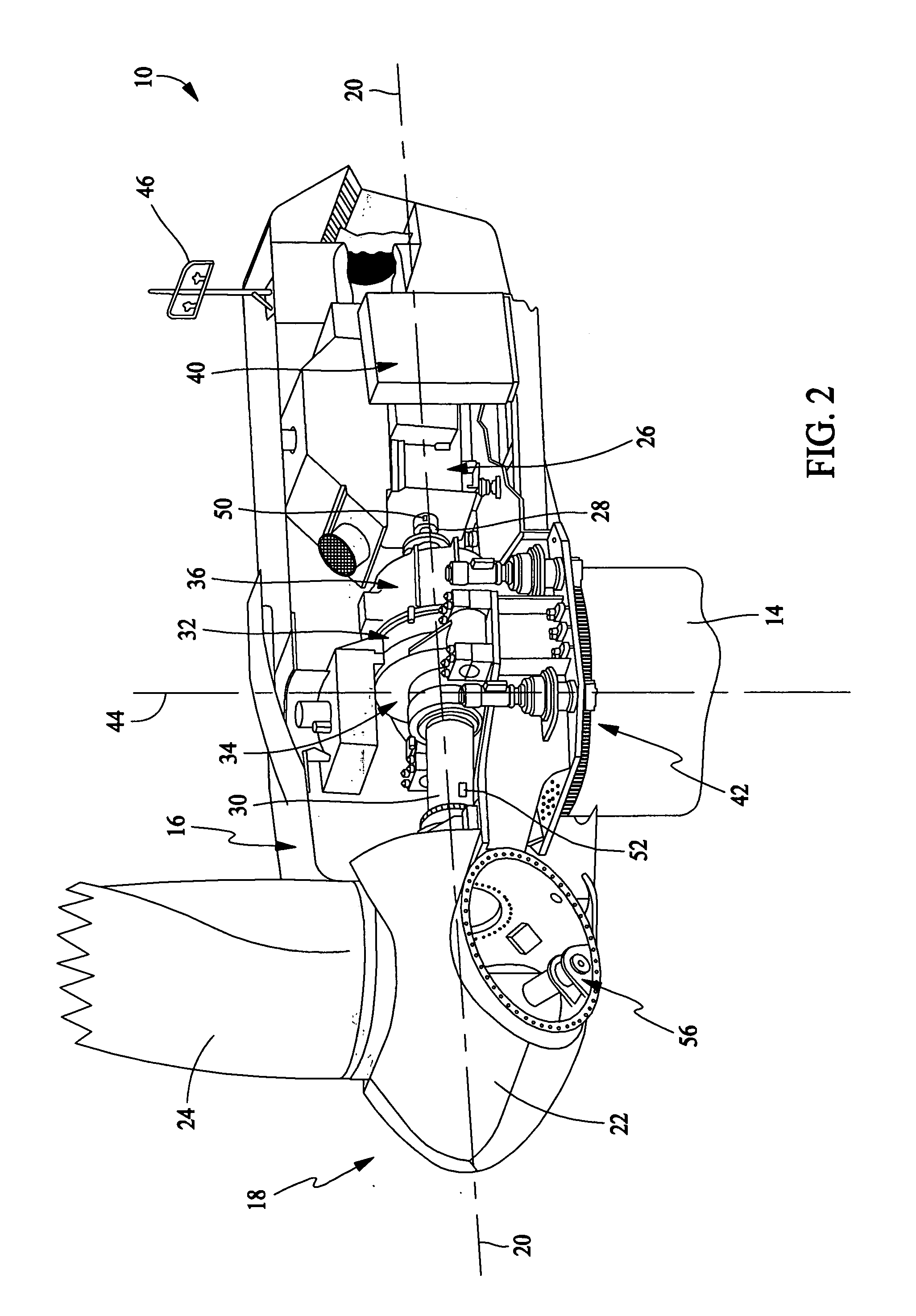
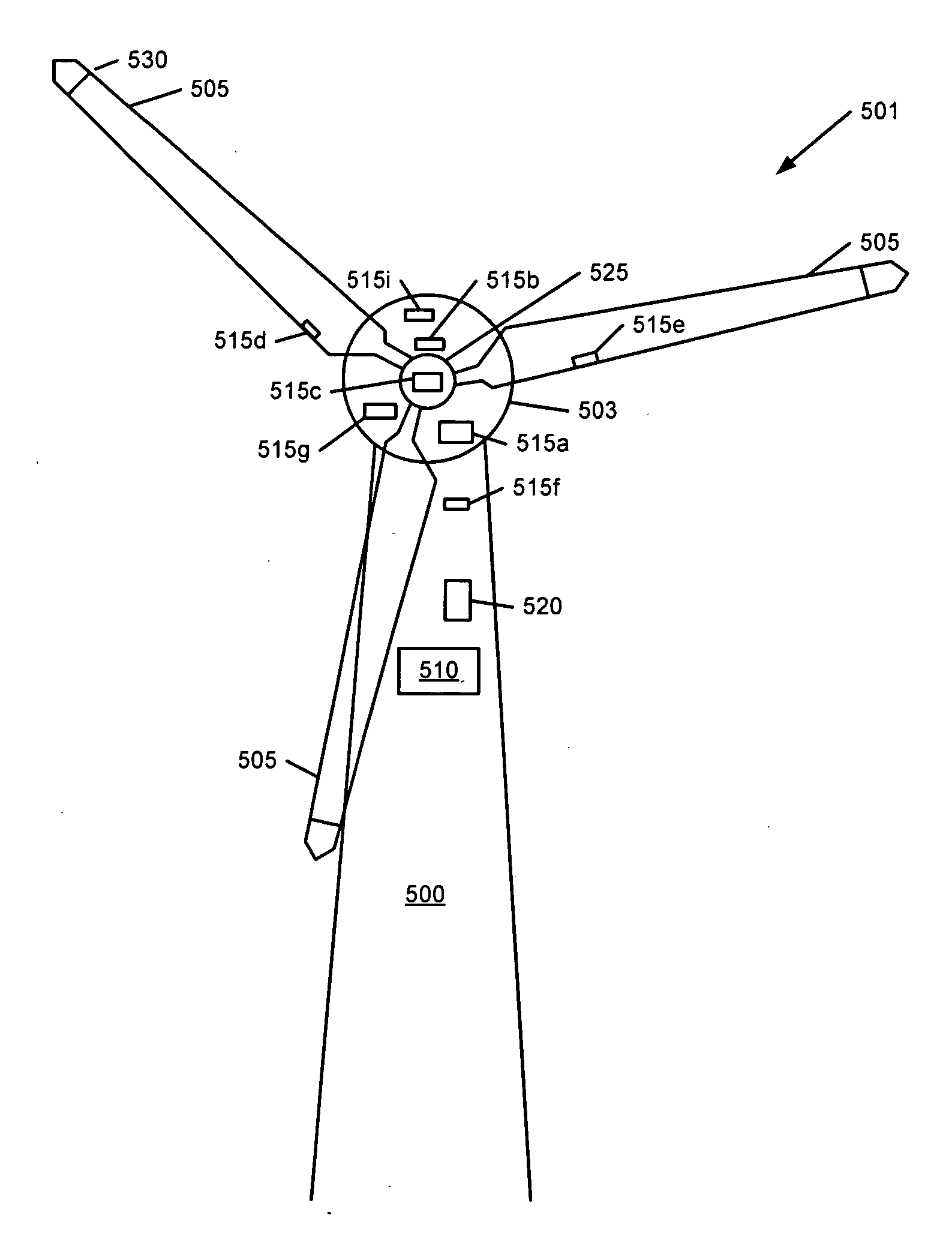
Methods and apparatus for rotor blade ice detection
ActiveUS20050276696A1Reduced lifting capabilityDiminished aerodynamic rotor blade performancePropellersWind motor controlIcing conditionsEngineering
A method for detecting ice on a wind turbine having a rotor and one or more rotor blades each having blade roots includes monitoring meteorological conditions relating to icing conditions and monitoring one or more physical characteristics of the wind turbine in operation that vary in accordance with at least one of the mass of the one or more rotor blades or a mass imbalance between the rotor blades. The method also includes using the one or more monitored physical characteristics to determine whether a blade mass anomaly exists, determining whether the monitored meteorological conditions are consistent with blade icing; and signaling an icing-related blade mass anomaly when a blade mass anomaly is determined to exist and the monitored meteorological conditions are determined to be consistent with icing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
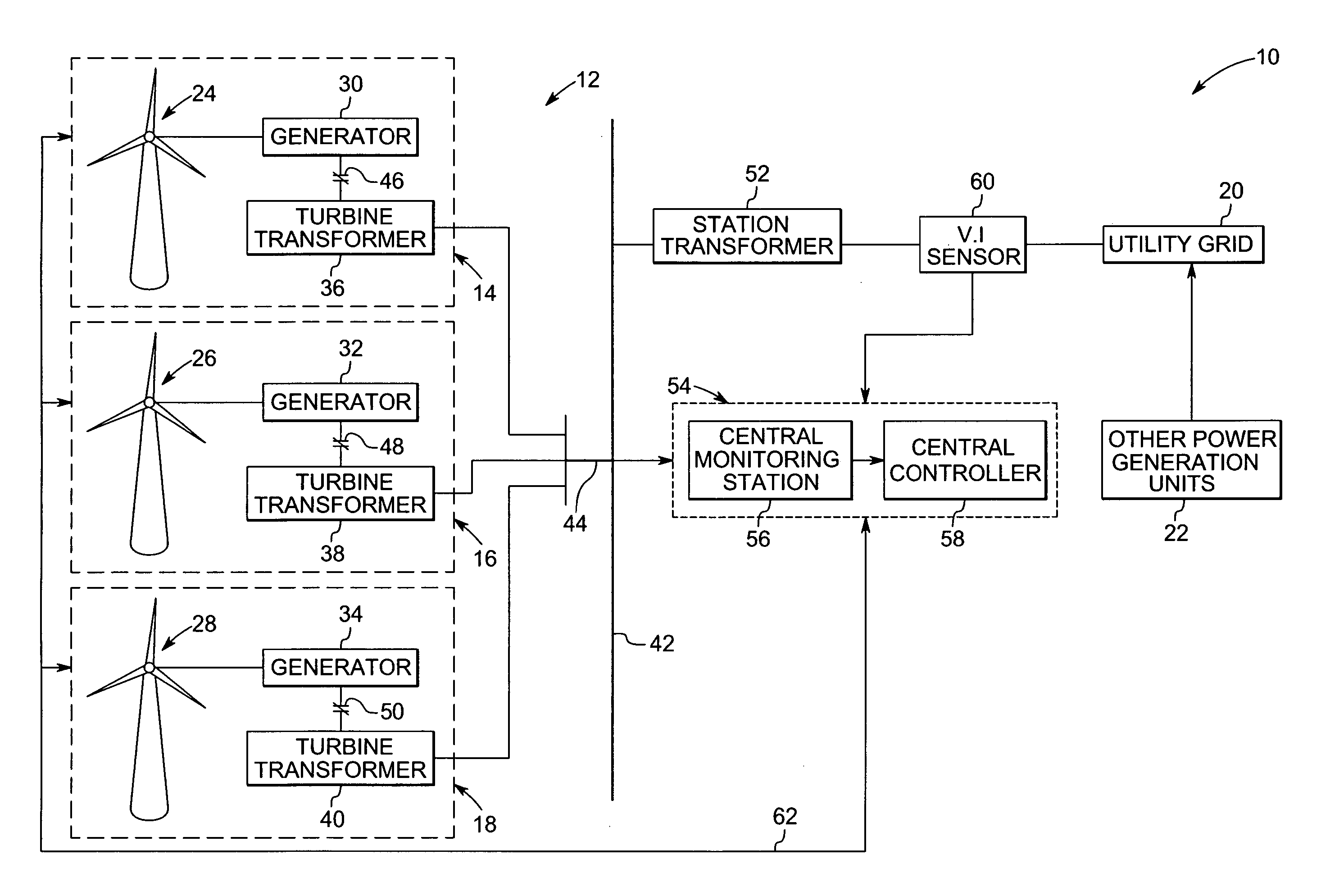
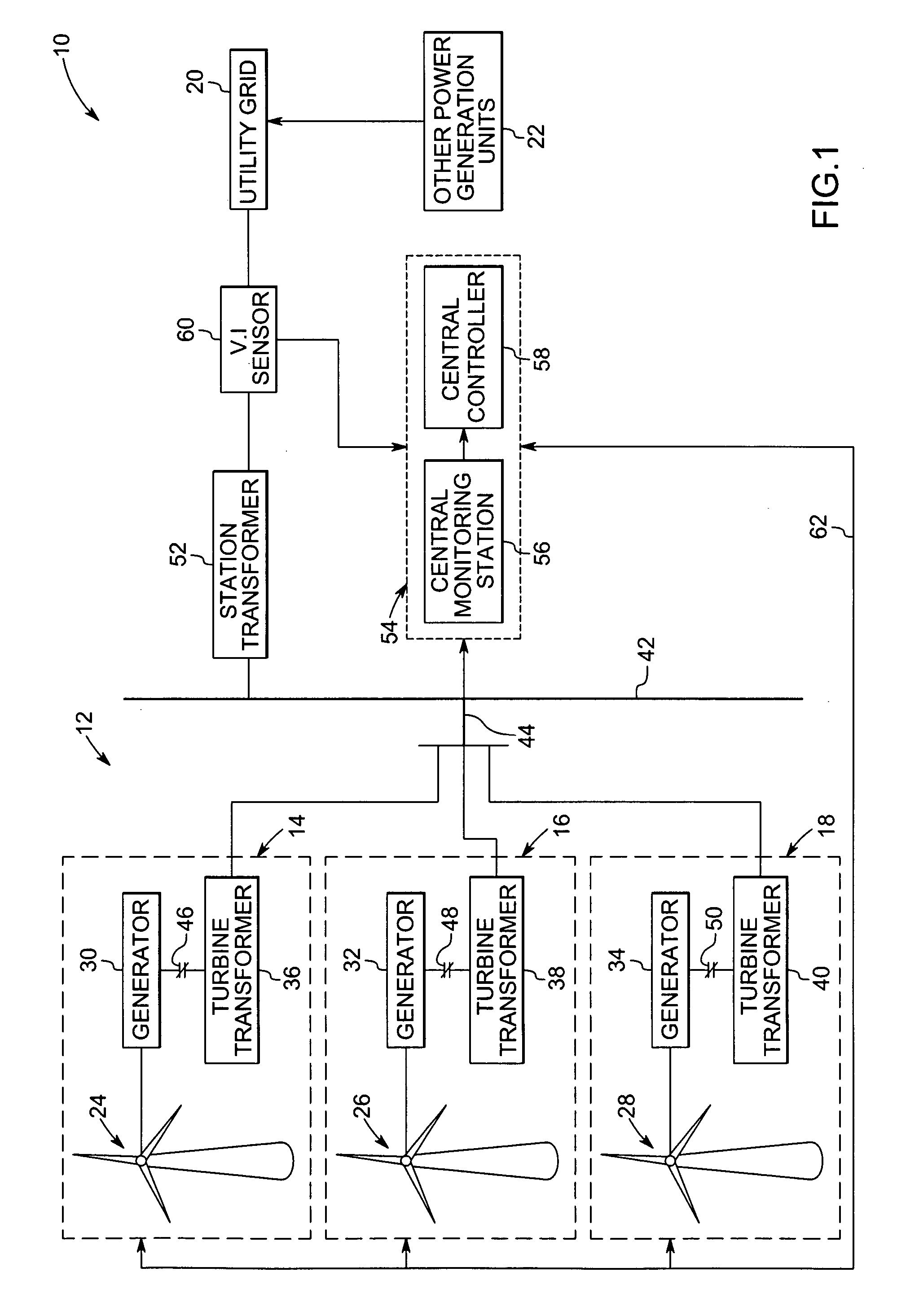
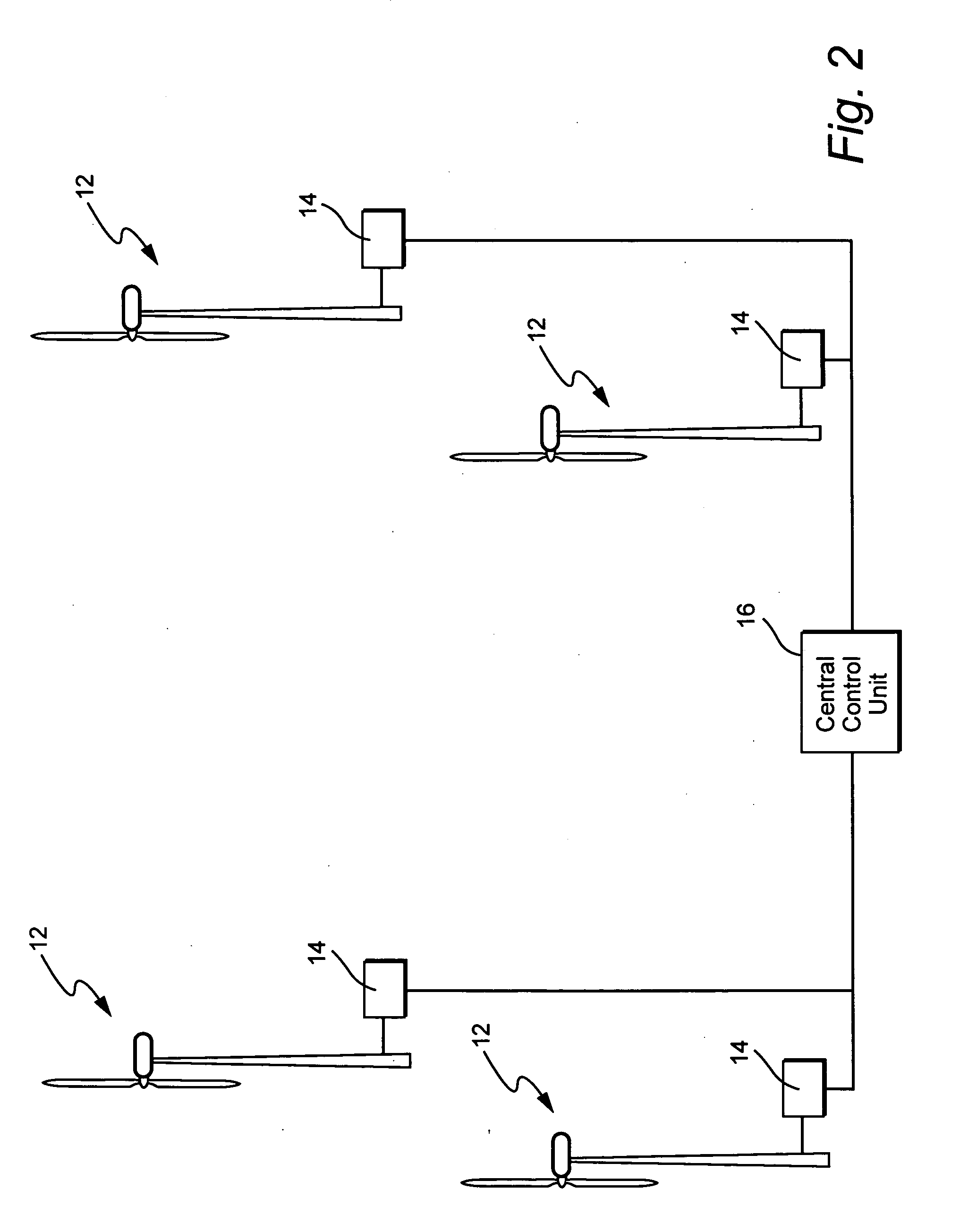
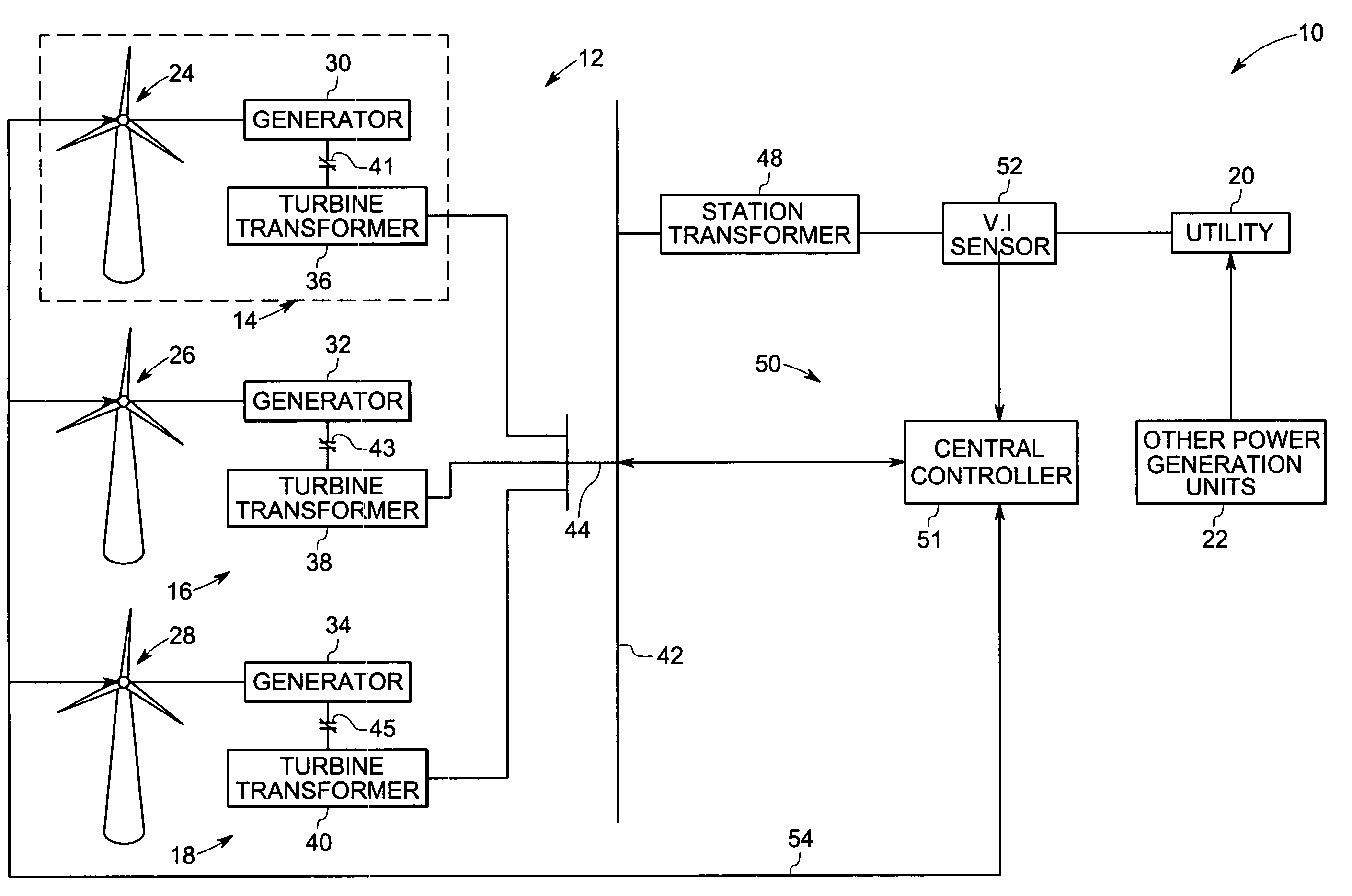
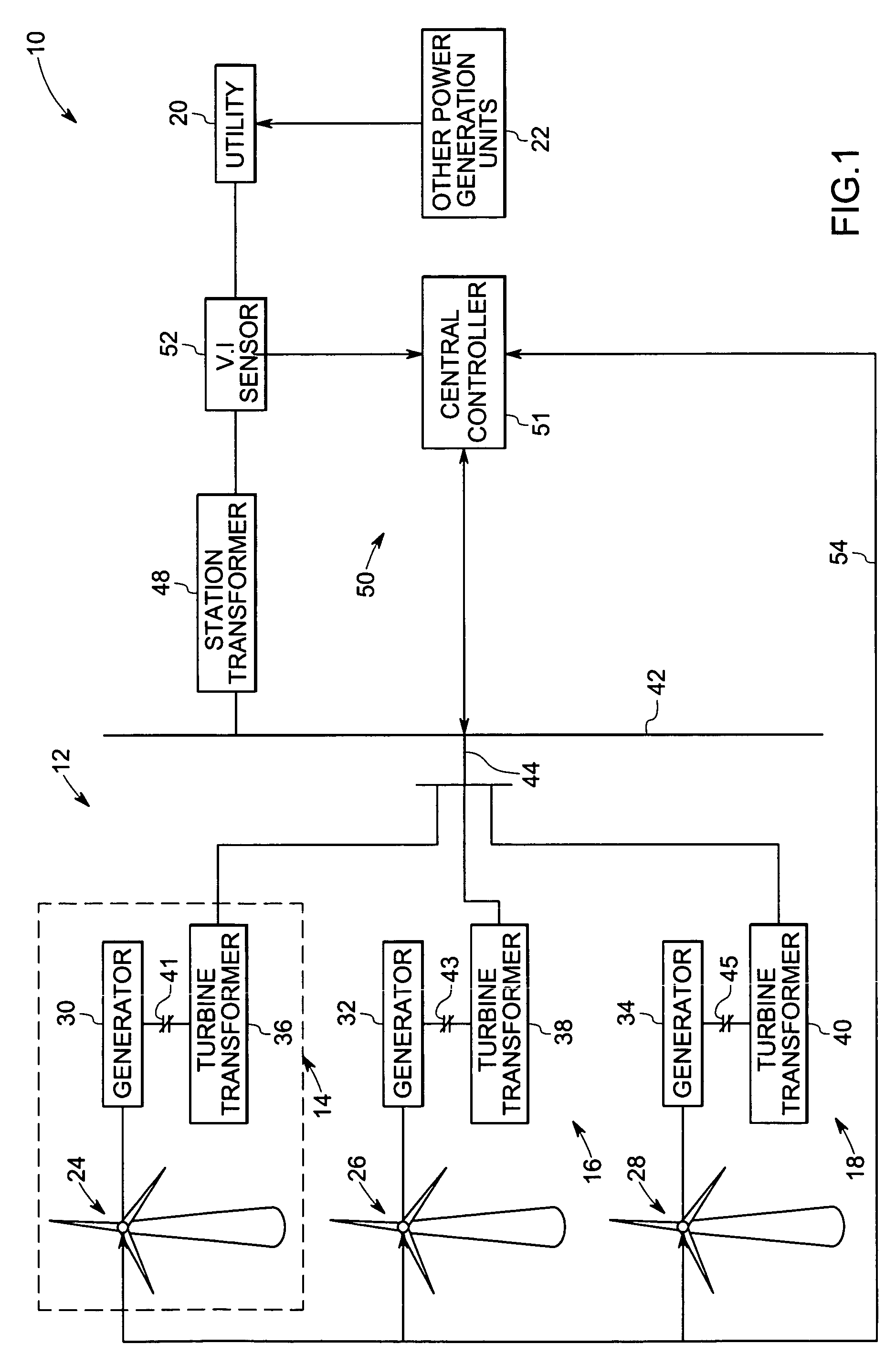
System and method for operating a wind farm under high wind speed conditions
ActiveUS20060273595A1Efficiently and cost-effectively harnessSimple designWind motor controlMachines/enginesTurbineWind force
A technique is provided for operating a wind farm at increased rated power output. The technique includes sensing a plurality of operating parameters of the wind turbine generator, assessing the plurality of operating parameters with respect to respective design ratings for the operating parameters, and intermittently increasing a rated power output of the wind turbine generator based upon the assessment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
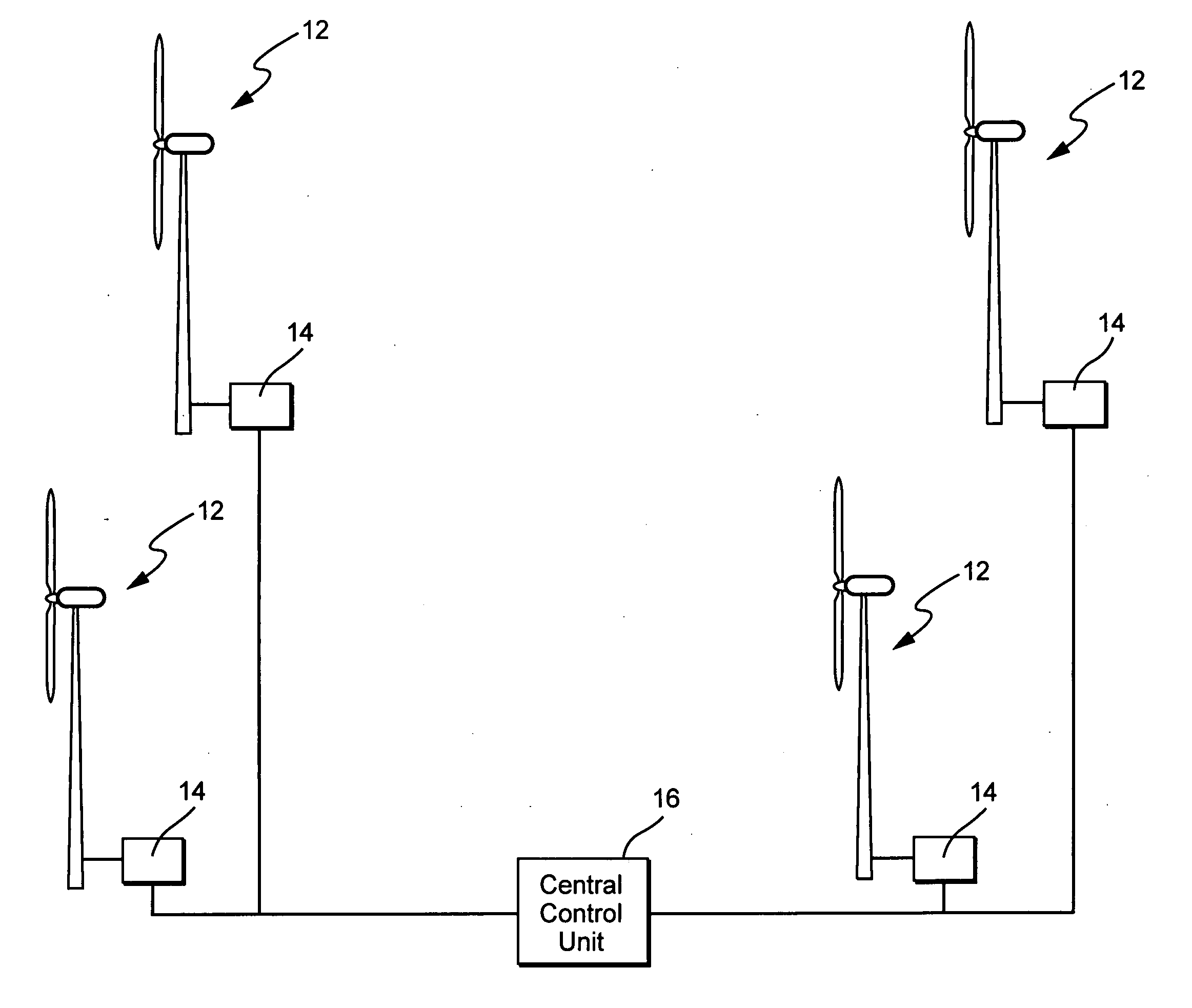
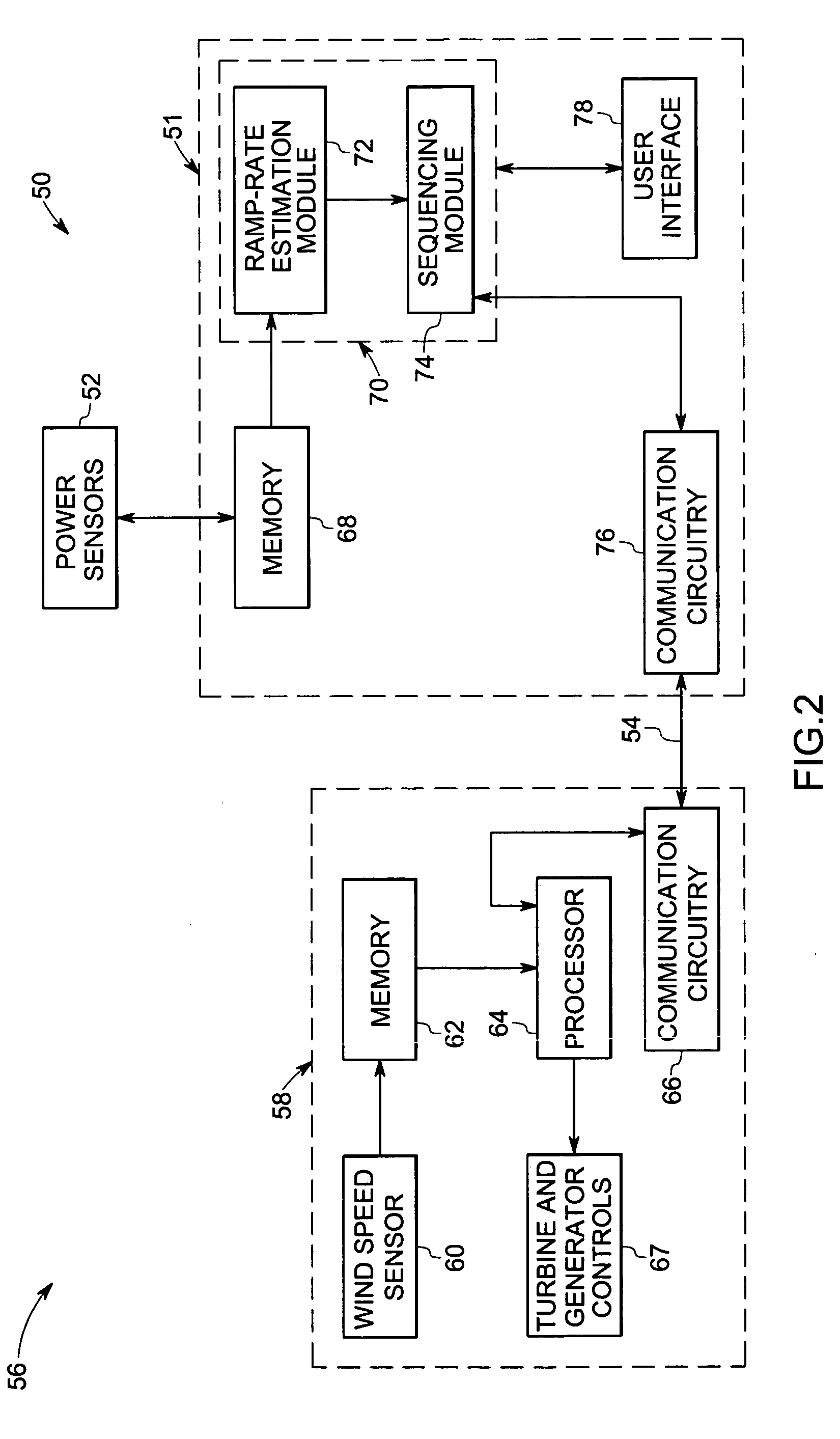
Windpark turbine control system and method for wind condition estimation and performance optimization
InactiveUS20070124025A1Minimize loading impactShorten speedLevel controlWind motor controlPower stationControl system
A method and system for controlling a windpark power plant includes a central processing and control unit operatively coupled to wind turbines in the windpark to receive data from and selectively transmit at least one of data and control signals to each wind turbine, to reduce fatigue loads and comply with power limits.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6933625B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
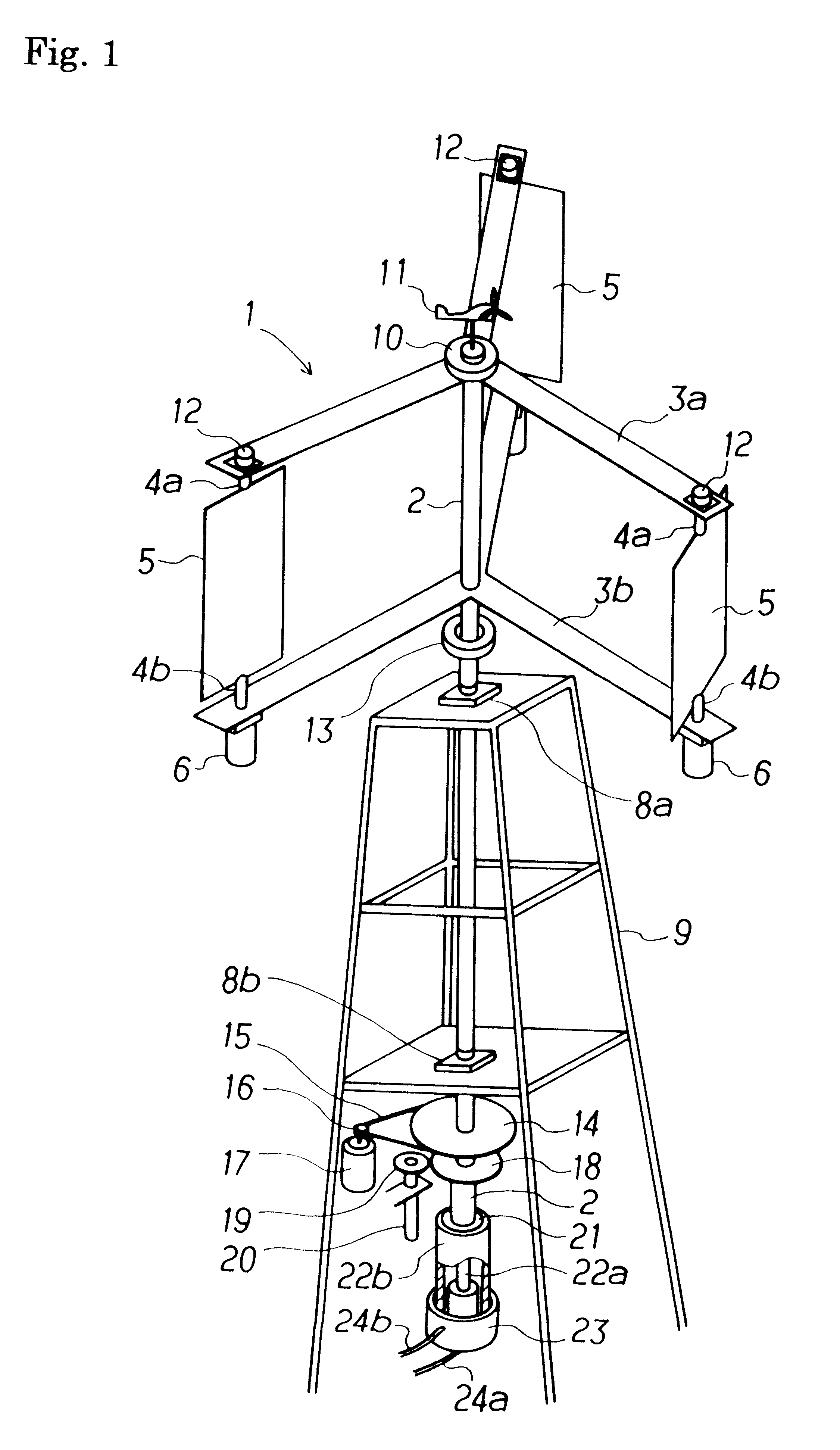
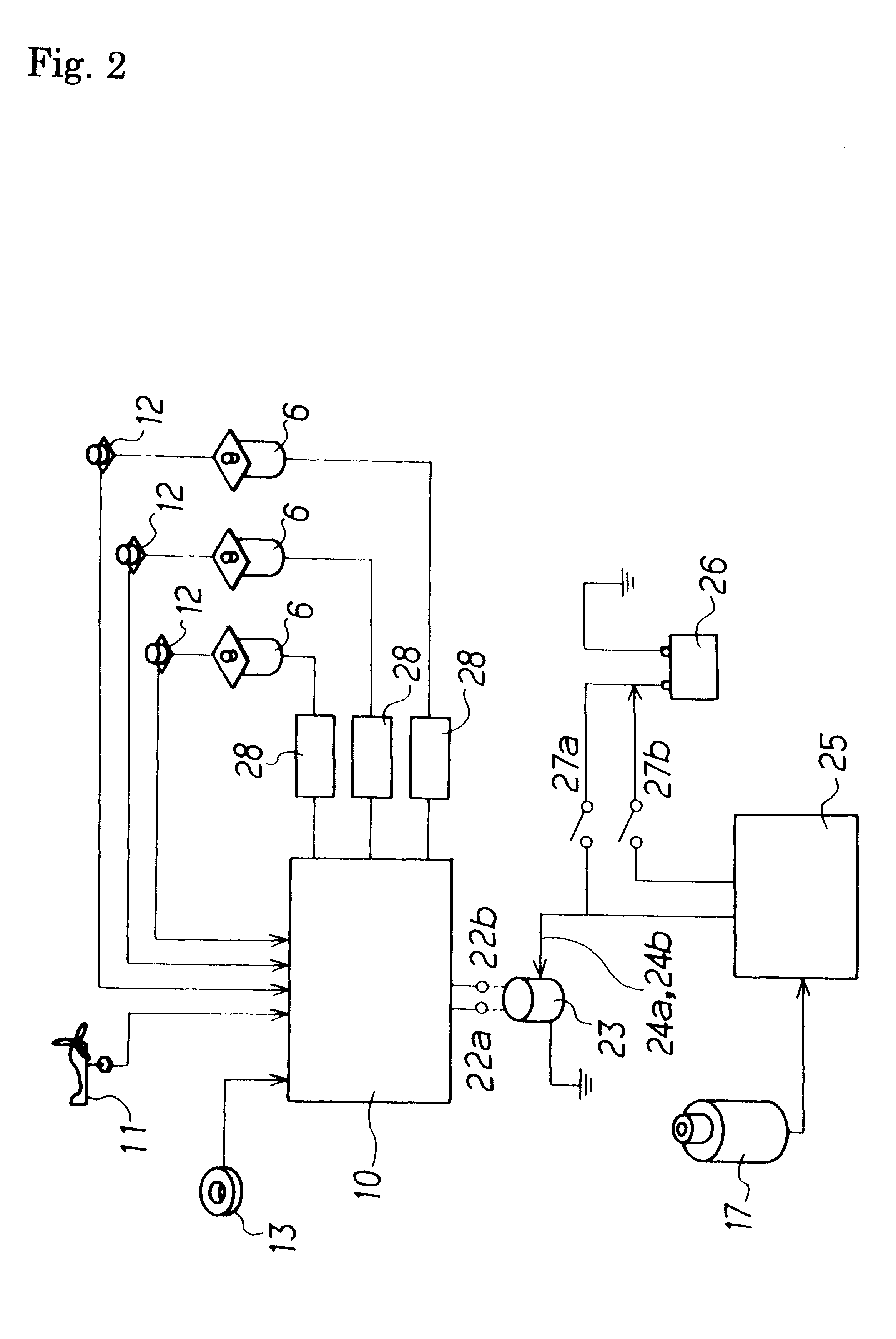
Windmill and windmill control method
A windmill includes a freely rotatable revolution shaft, a plurality of pairs of pivotal support rods provided at the revolution shaft, and wind receiving blades respectively and rotatably set between the pivotal support rods with wind receiving blade shafts. The windmill is applied to the driving of a lifting pump, a generator and the like by employing revolution driving force. An anemometer / anemoscope measures wind velocity and direction. A servo motor controls the direction of the wind receiving blades based on the detected velocity and direction. Various methods of control are also provided.
Owner:HIRAI TETSUO
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856040B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
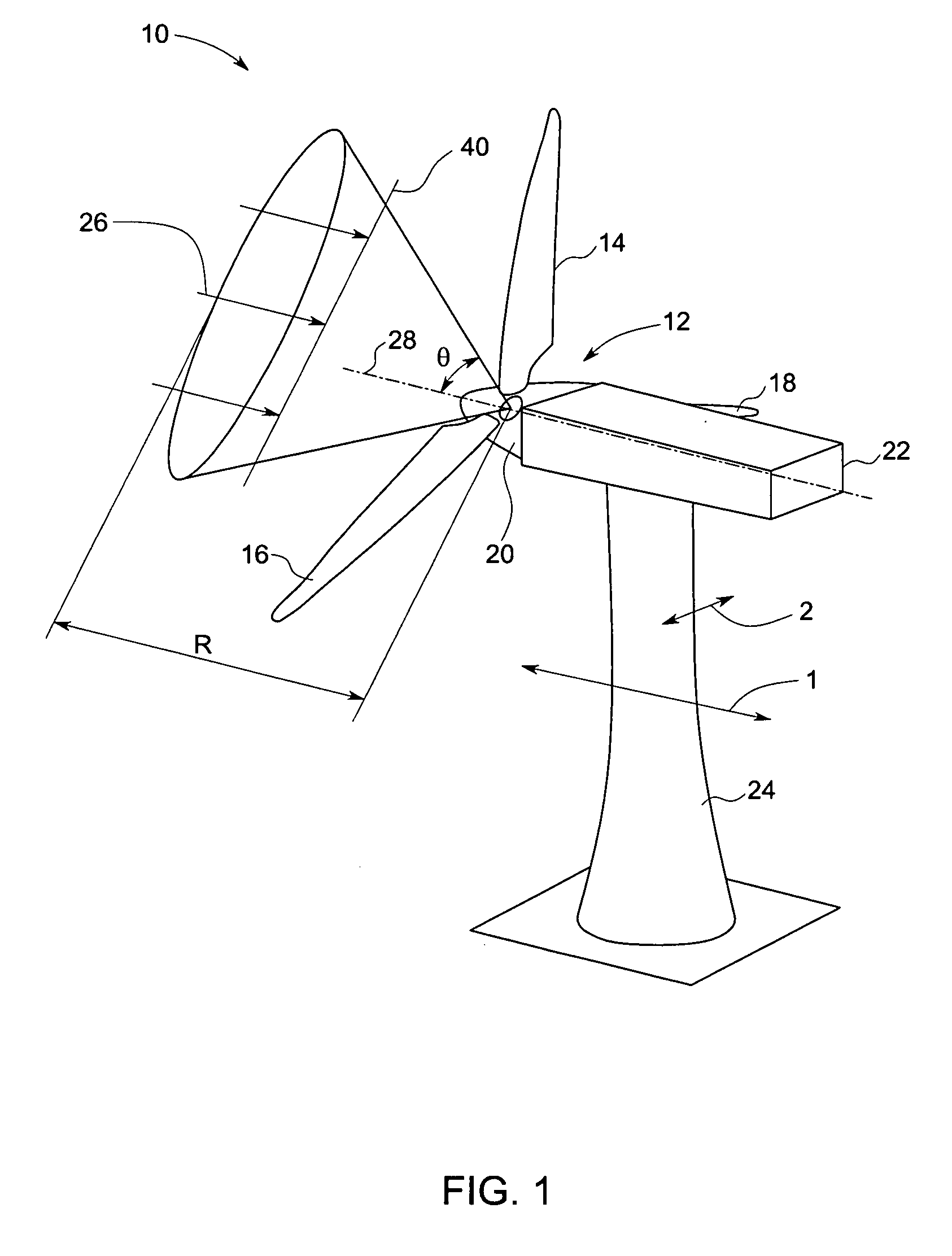
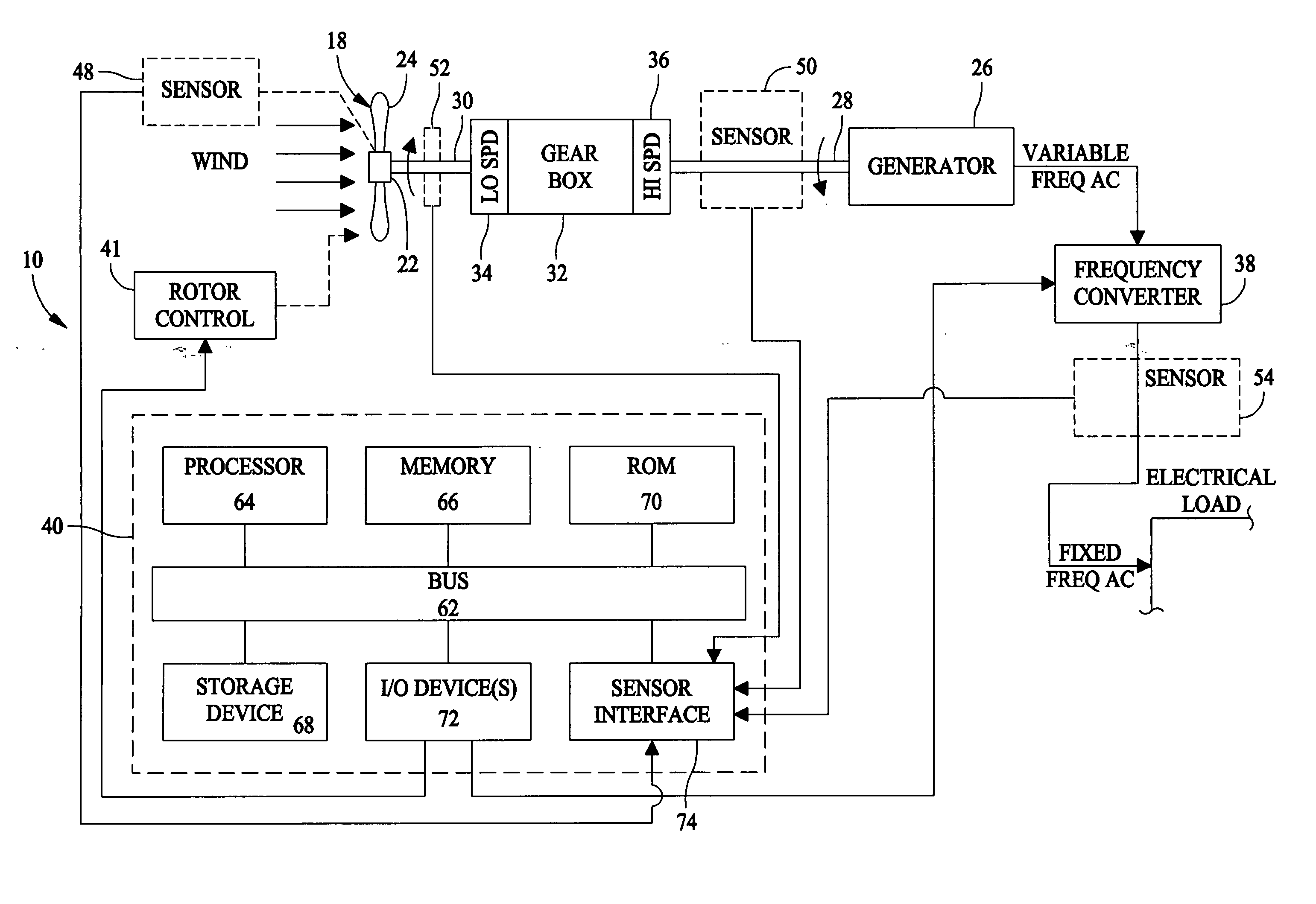
System and method for upwind speed based control of a wind turbine
A method for controlling power output of a wind turbine generator in response to an anticipated change in wind speed is provided. The method includes sensing wind speed at a desired distance from the wind turbine generator in a direction of the wind. The method further includes controlling pitch of a blade of the wind turbine generator based upon sensed transient wind speed in advance of a change in wind speed at the wind turbine generator.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Wind turbine load control method
InactiveUS20070057517A1Sufficient capabilityOperation loadPropellersWind motor controlEngineeringTurbine
A method for limiting loads in a wind turbine by using measured loads or wind speed to increase the minimum pitch angle for extended periods. The minimum pitch angle will be allowed to relax down to the default when load excursions diminish. The method will allow turbines to capture more energy by operating in higher wind speeds and / or utilizing larger rotors without additional loss of fatigue life.
Owner:MCNERNEY GERALD
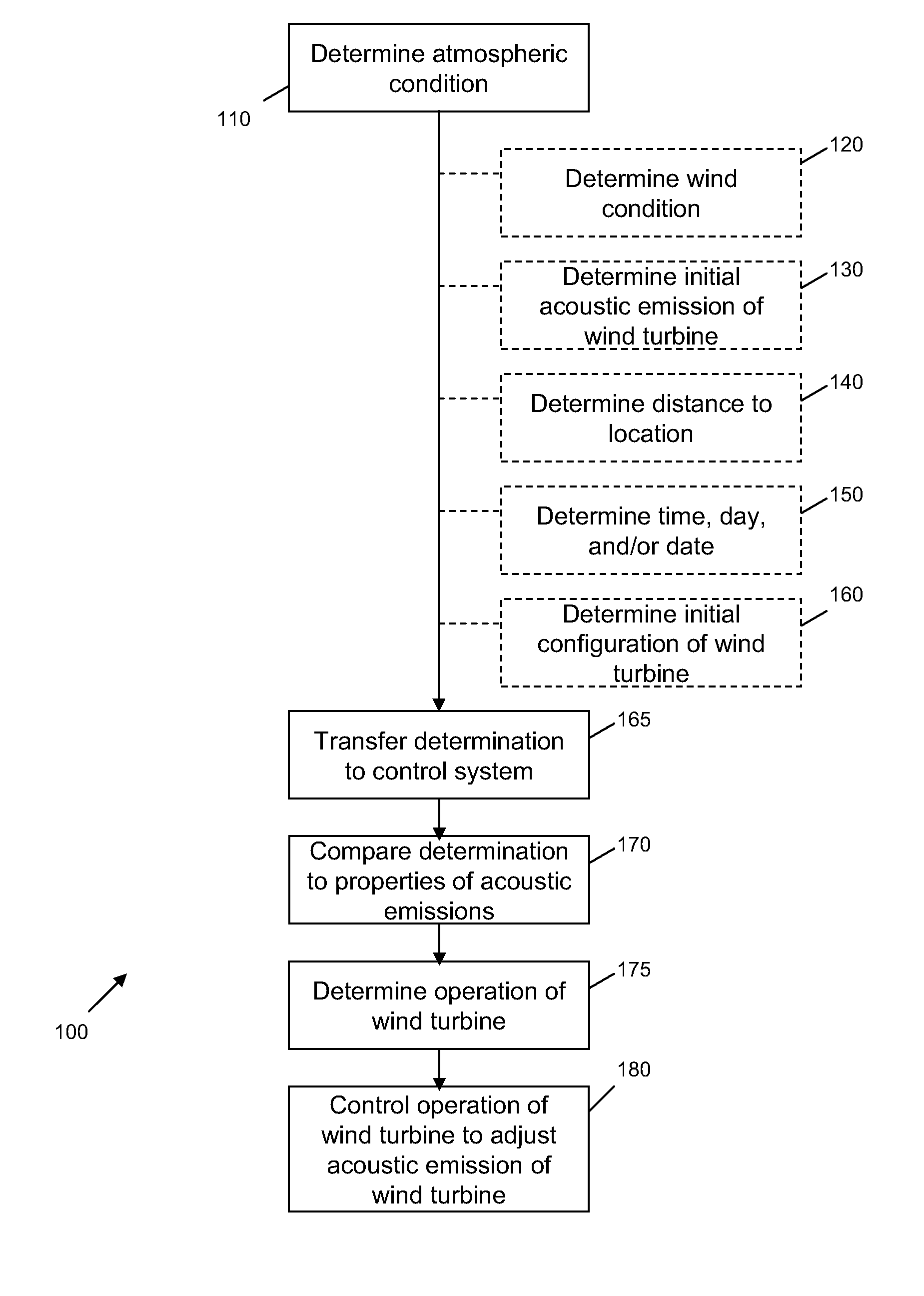
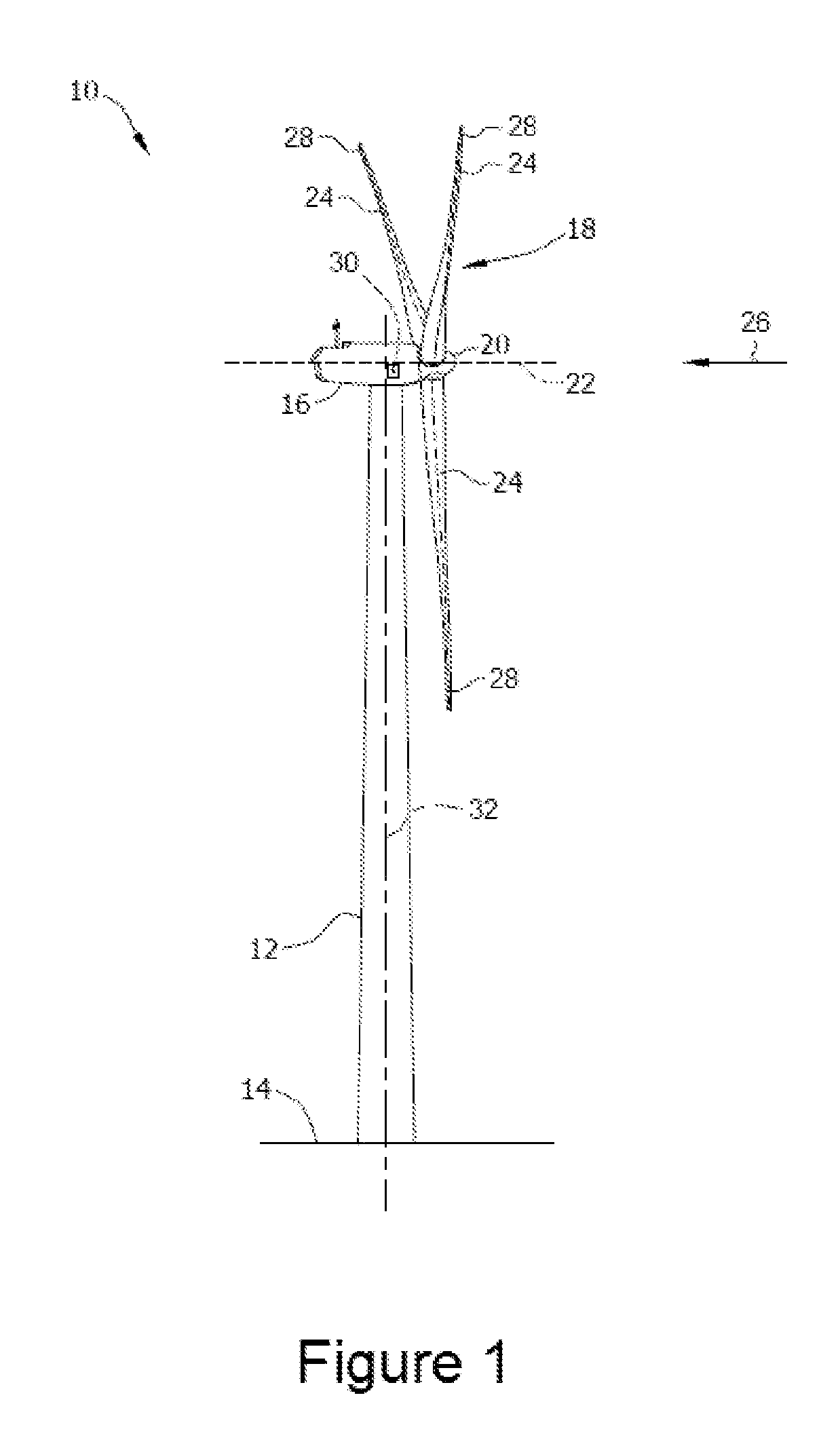
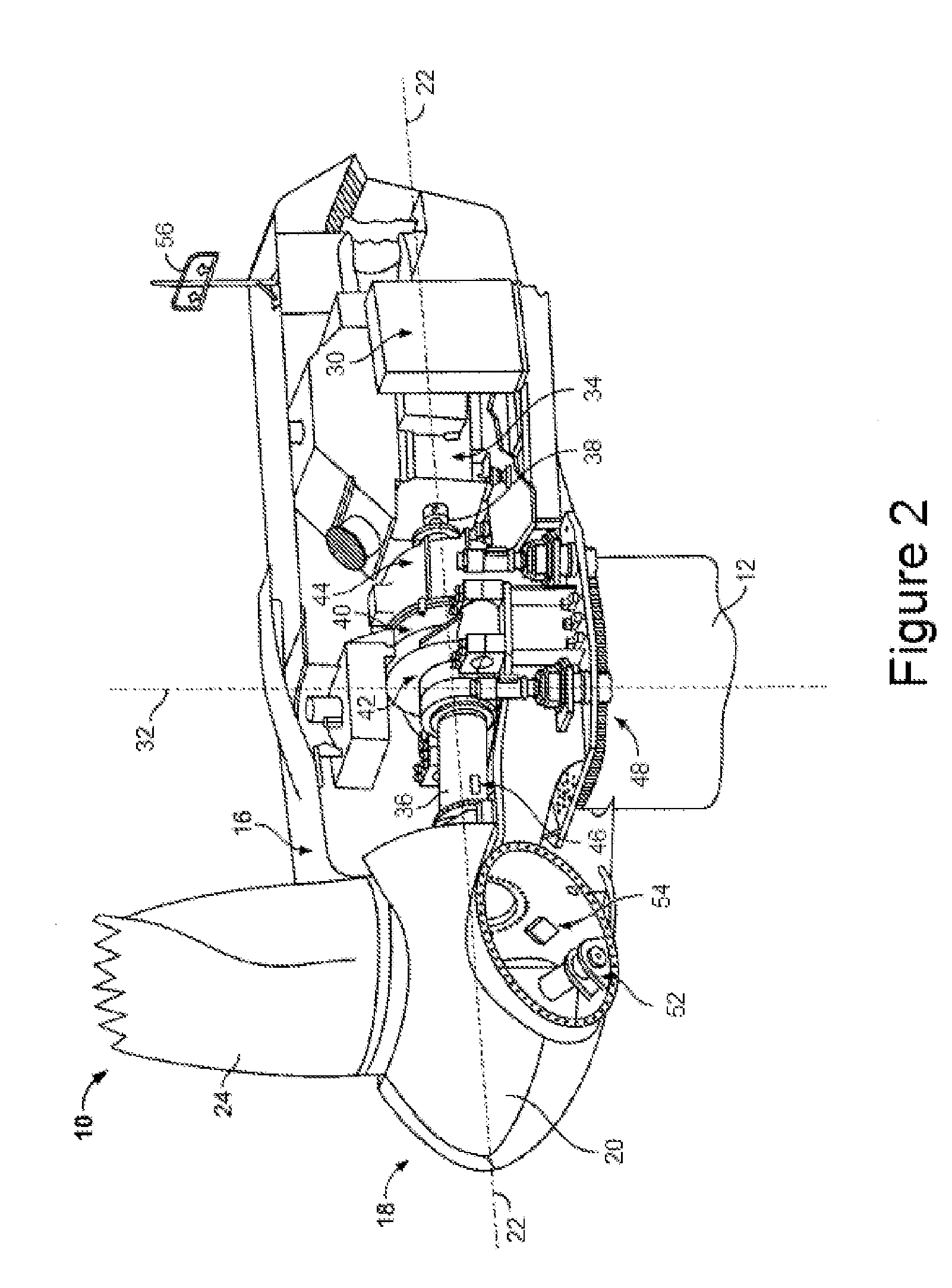
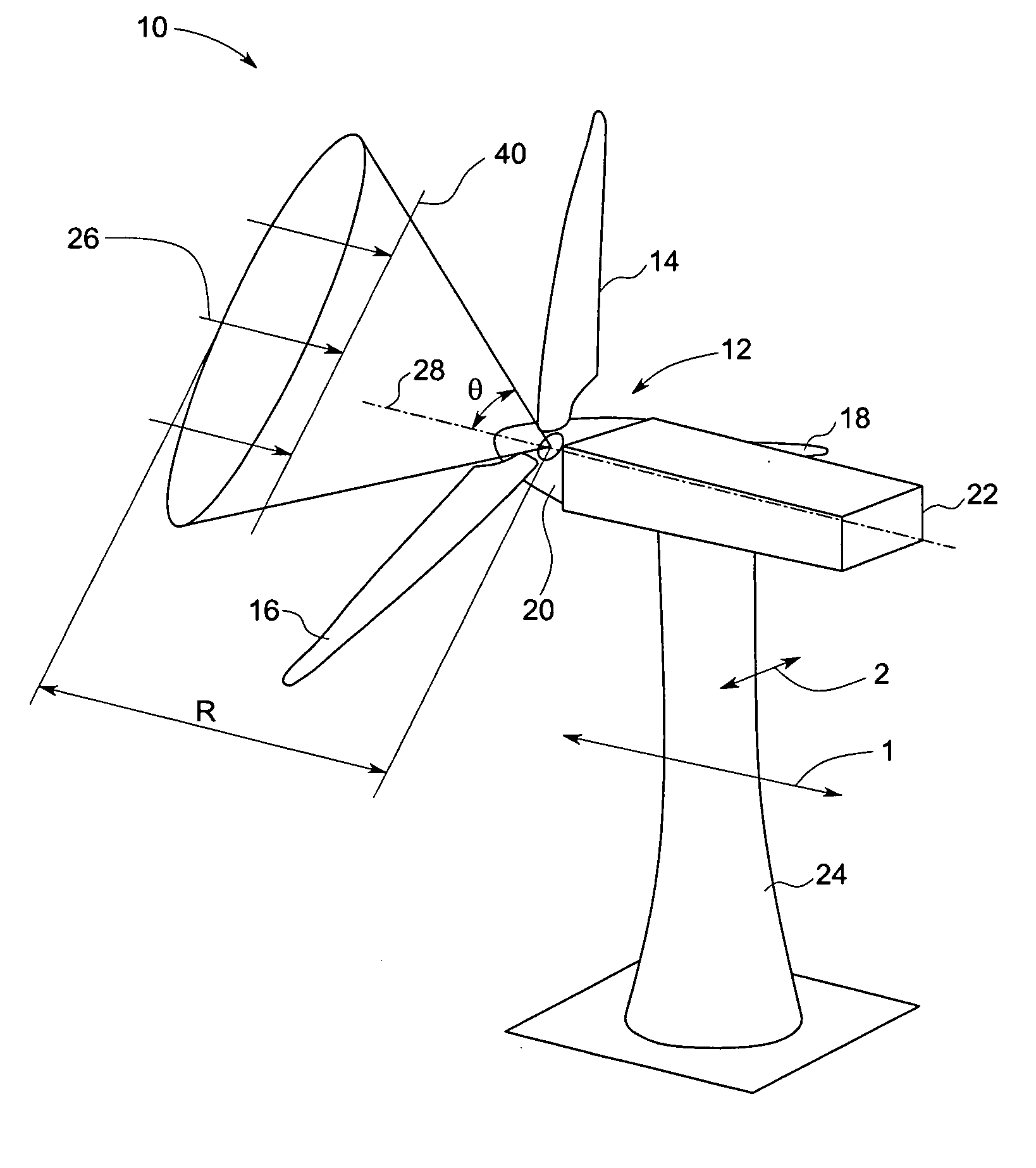
Method and apparatus for controlling acoustic emissions of a wind turbine
A method and an apparatus for monitoring an acoustic emission of a wind turbine that includes a rotor blade. The apparatus includes at least one sensor operatively coupled to the wind turbine. The sensor is configured to detect an atmospheric condition. A control system is communicatively coupled to the sensor, and configured to control operation of the wind turbine to adjust the acoustic emission of the wind turbine based on the atmospheric condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for upwind speed based control of a wind turbine
A method for controlling power output of a wind turbine generator in response to an anticipated change in wind speed is provided. The method includes sensing wind speed at a desired distance from the wind turbine generator in a direction of the wind. The method further includes controlling pitch of a blade of the wind turbine generator based upon sensed transient wind speed in advance of a change in wind speed at the wind turbine generator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
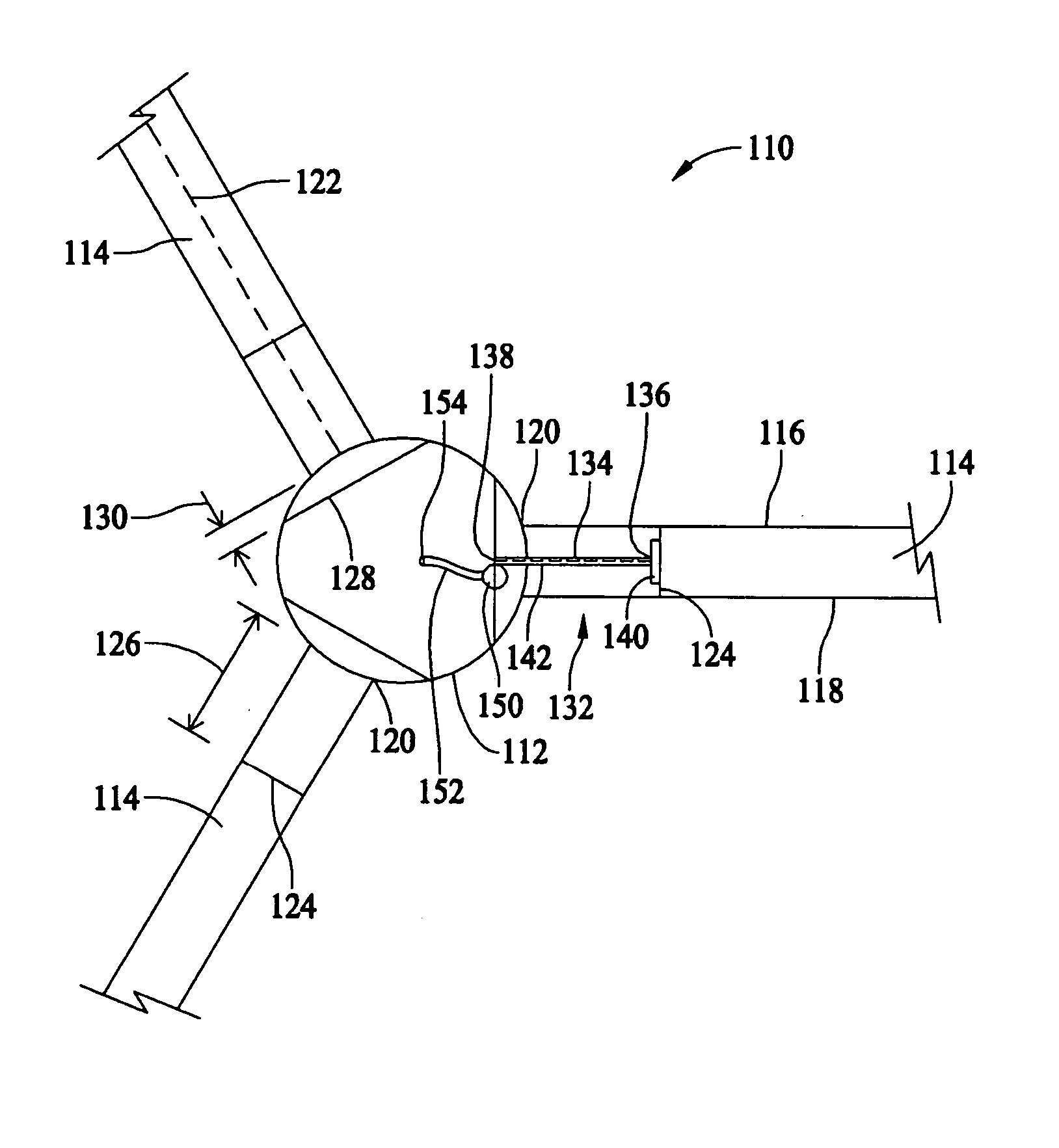
Methods and apparatus for measuring wind turbine blade deflection
A method for determining rotor blade deflection, wherein a rotor blade is coupled to a hub, includes coupling a first end of a beam to the rotor blade, positioning a second end of the beam adjacent the hub, measuring the deflection of the beam using at least one sensor, and determining the deflection of the blade based on the deflection of the beam.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
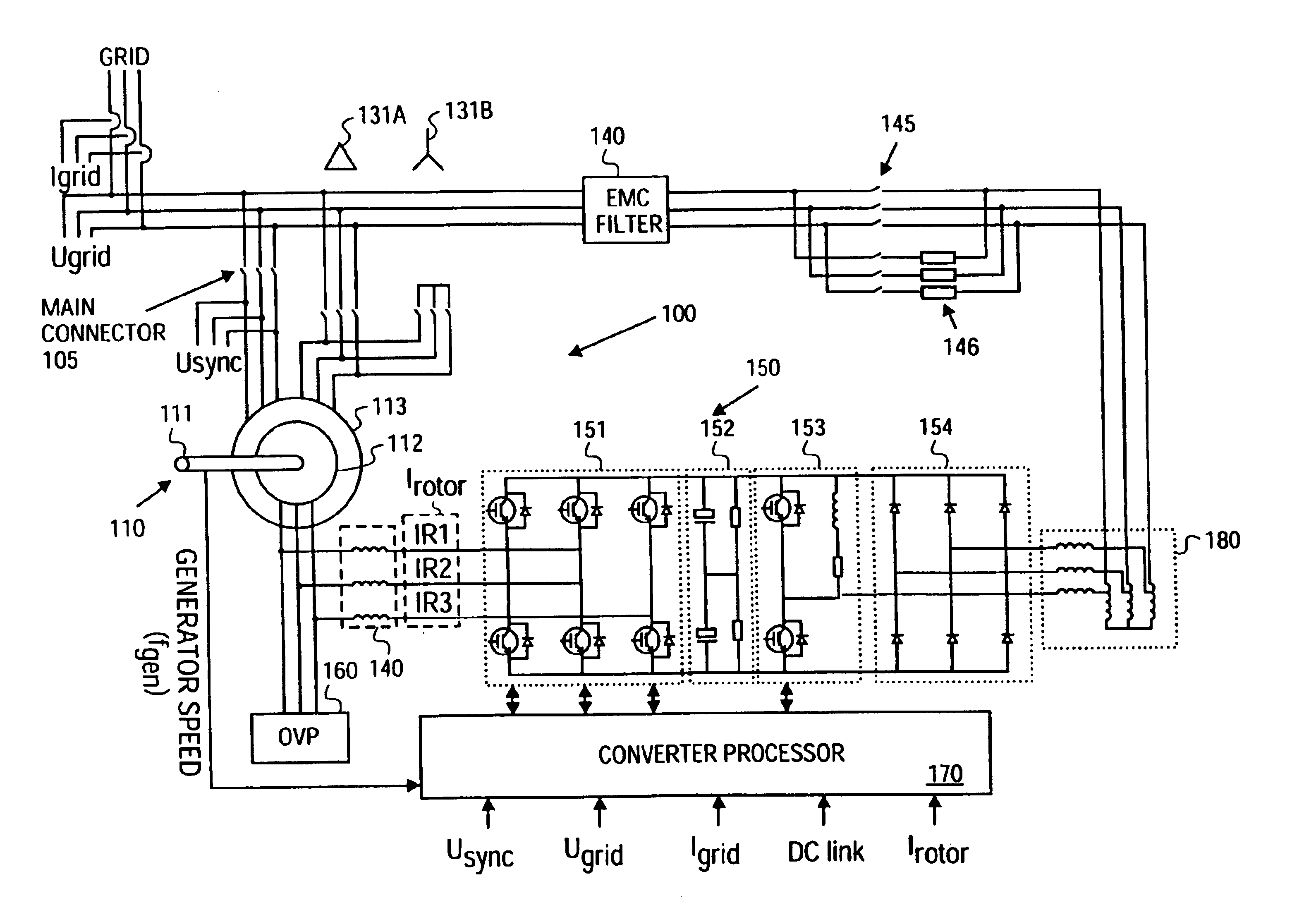
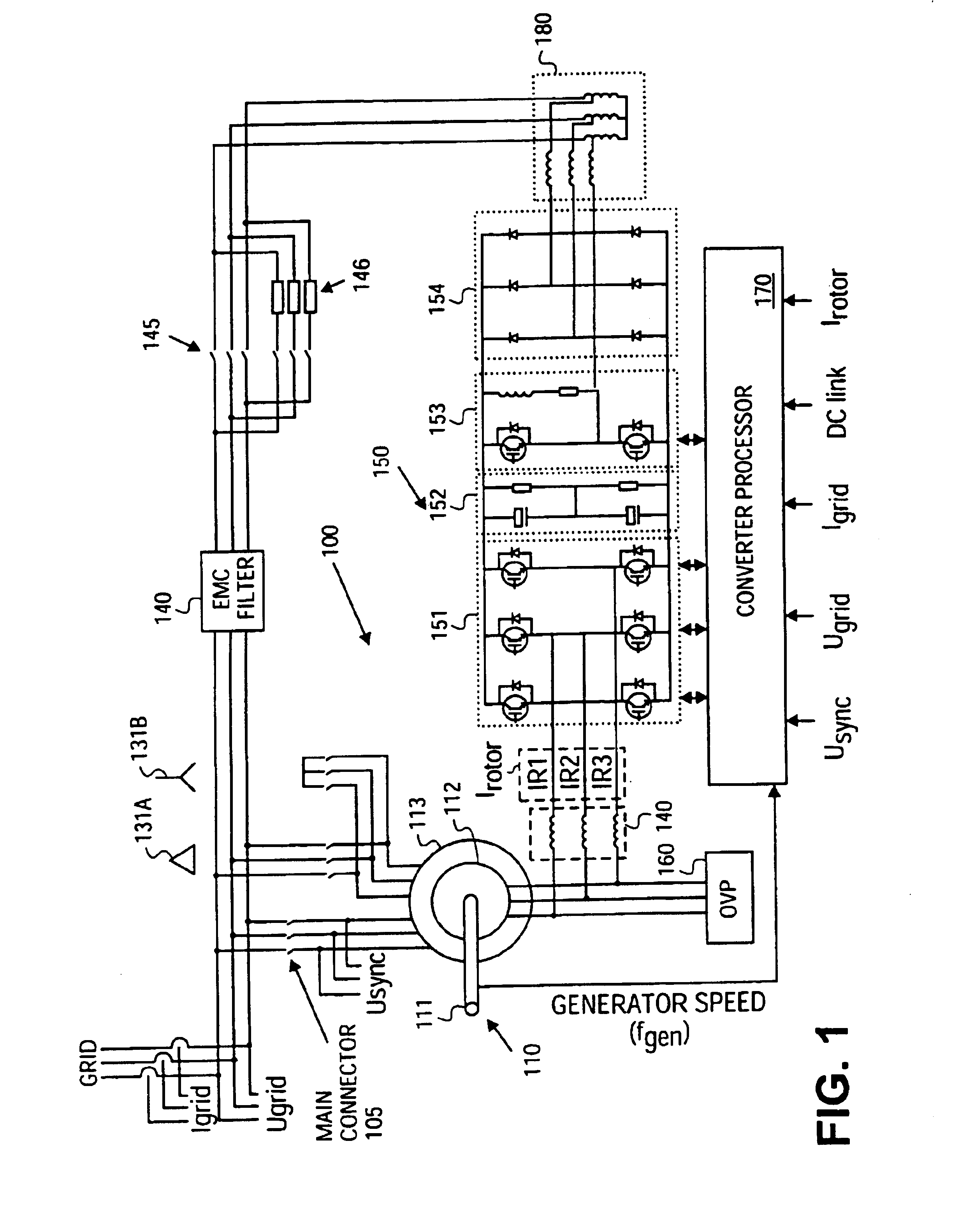
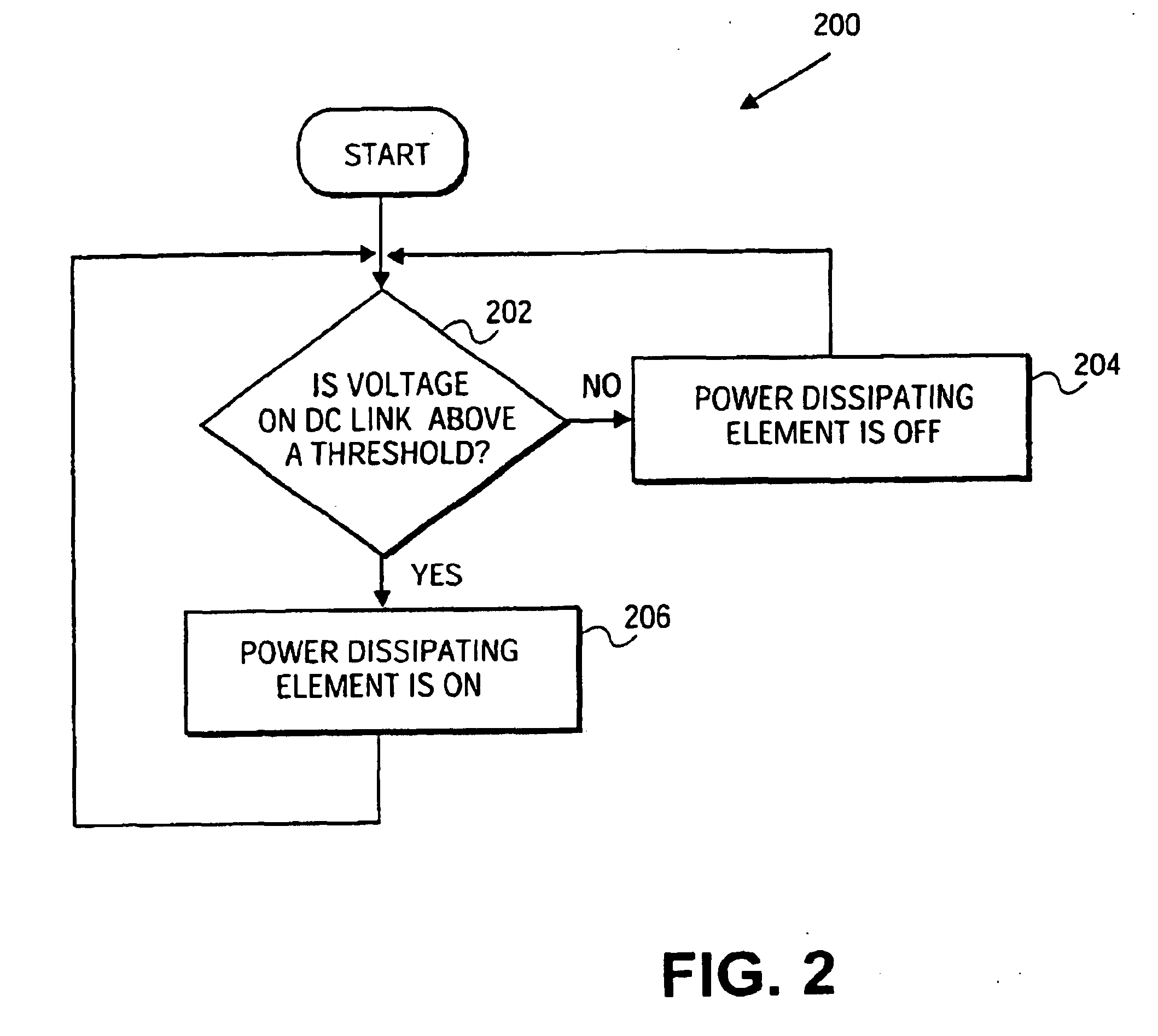
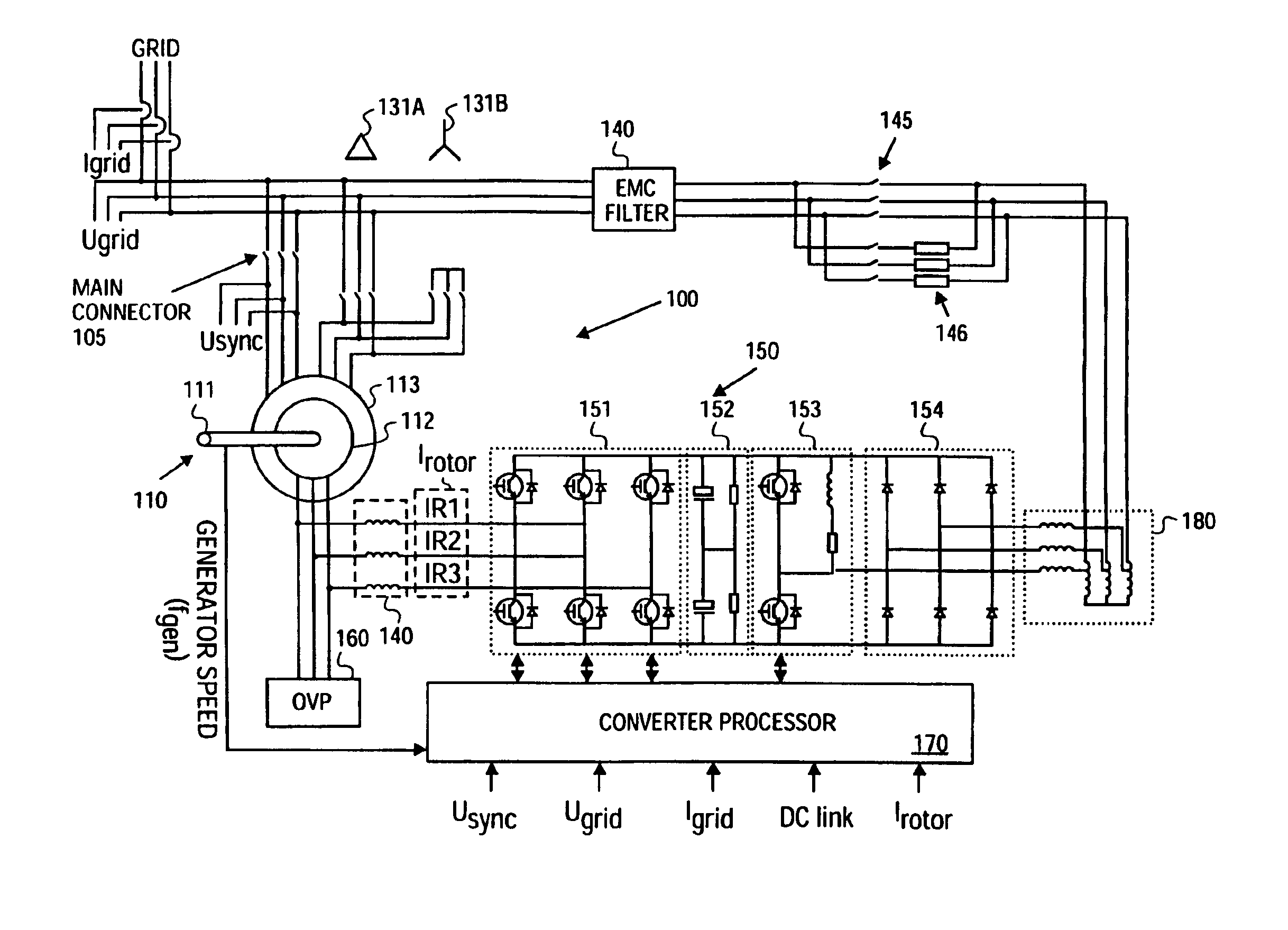
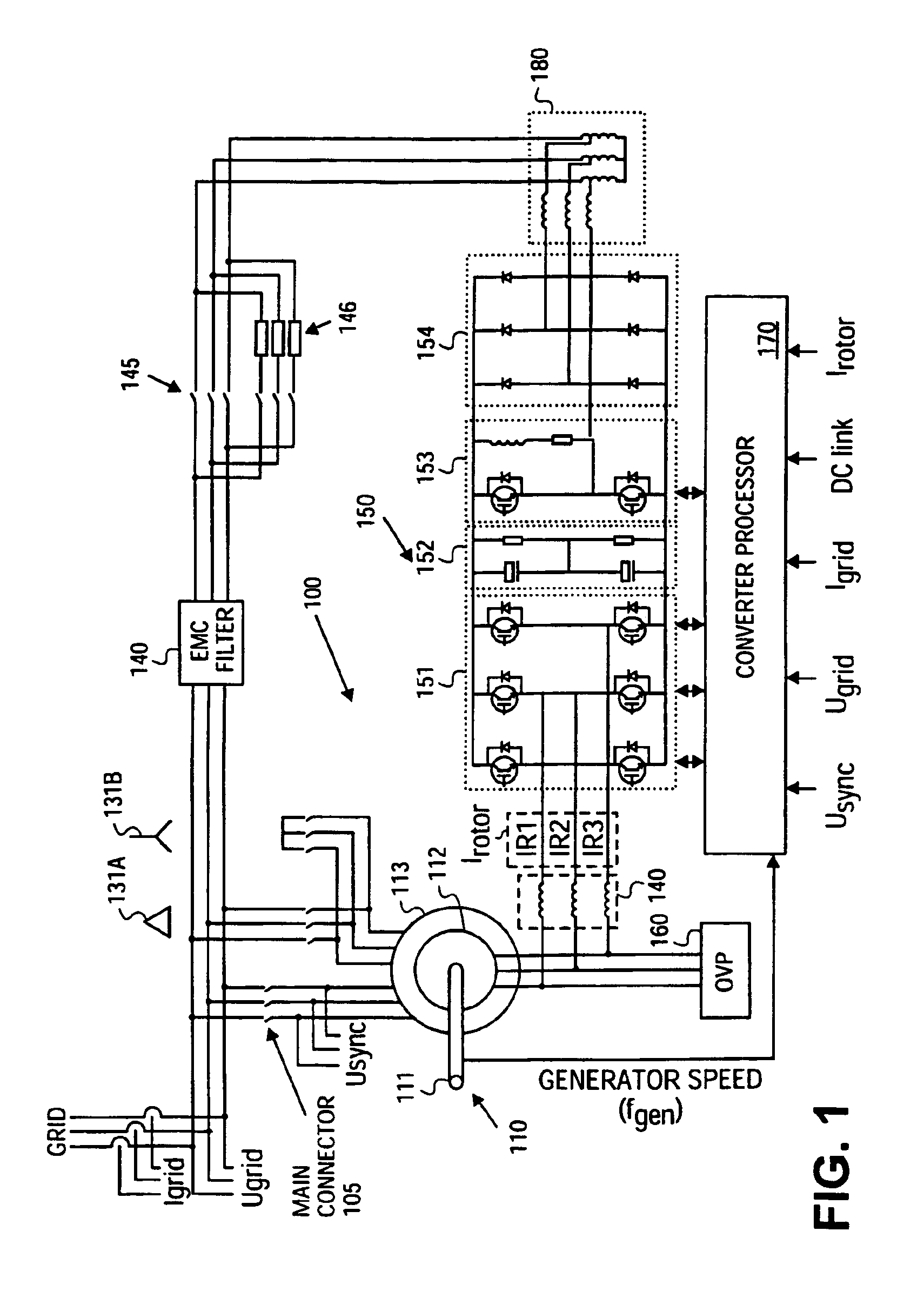
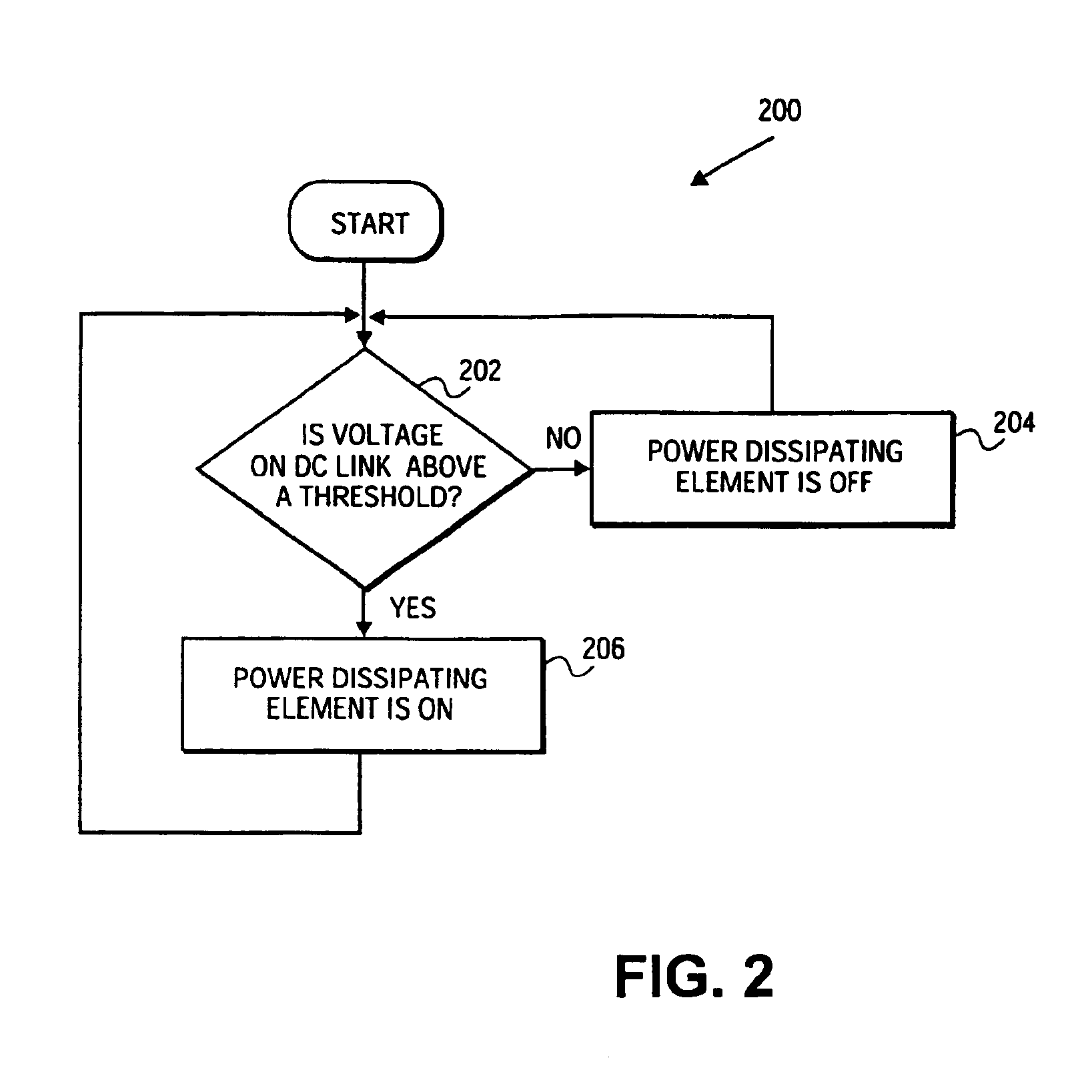
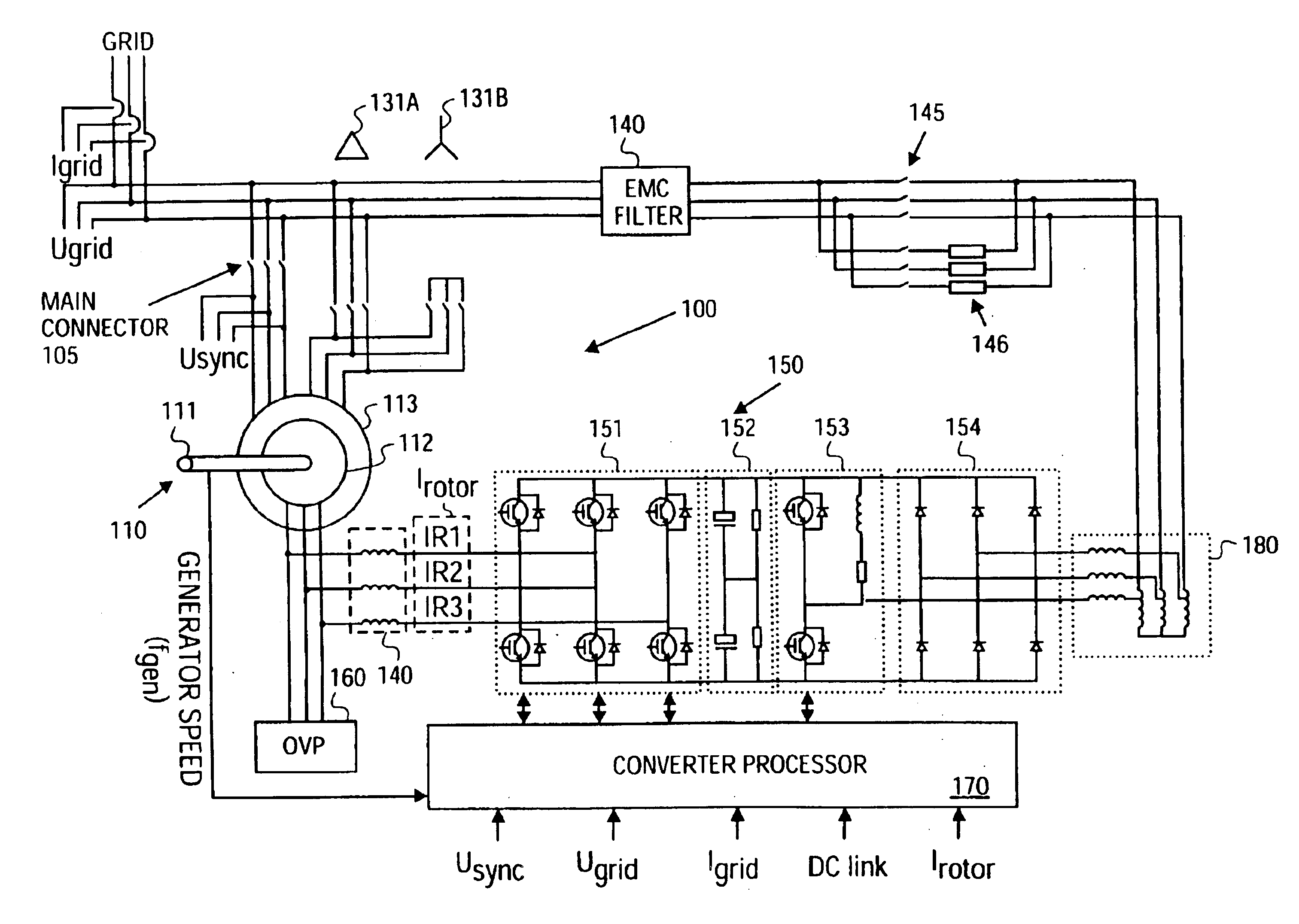
Doubly-controlled asynchronous generator
InactiveUS20080150285A1Avoid problemsReduce settingsGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlTransformerElectric power distribution
An electric power generator system or a motor comprising a doubly-fed asynchronous generator or motor comprising a stator and a rotor, a transformer having a first winding and a second winding, the first winding having a first end and a second end; and wherein the stator and the transformer are connectable in series with an electric power distribution grid.
Owner:WIND TO POWER SYST
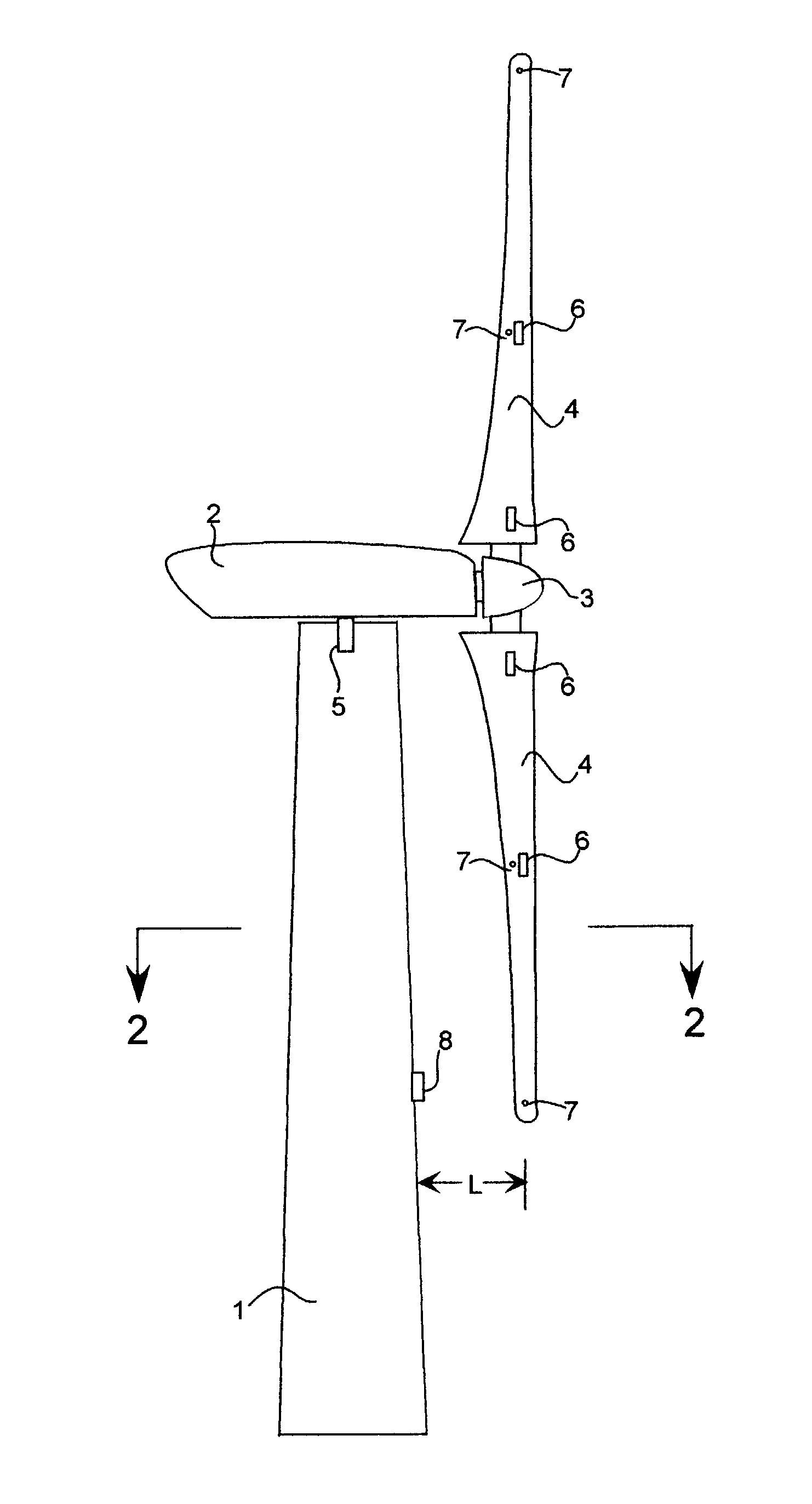
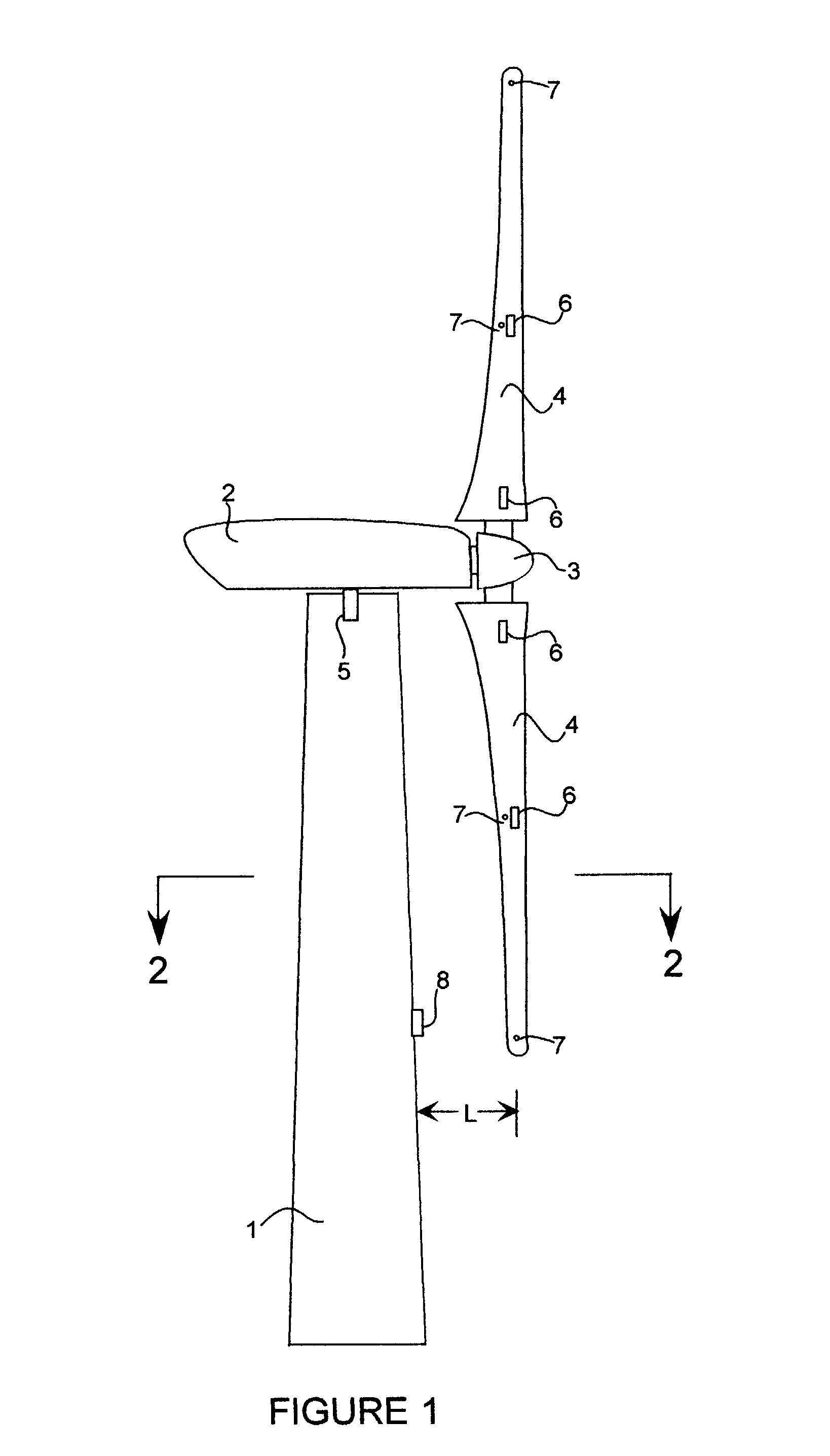
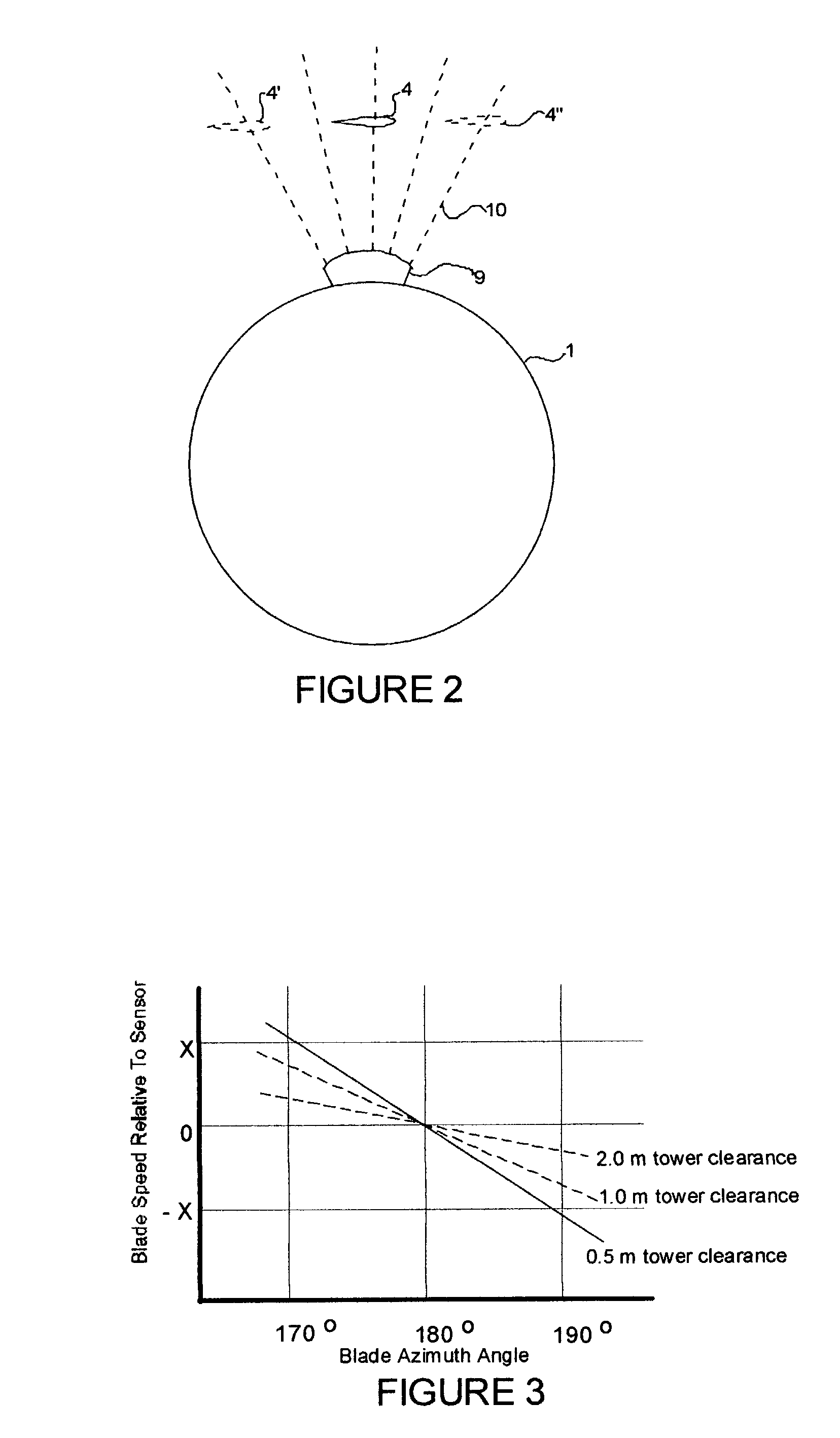
Wind turbine blade deflection control system
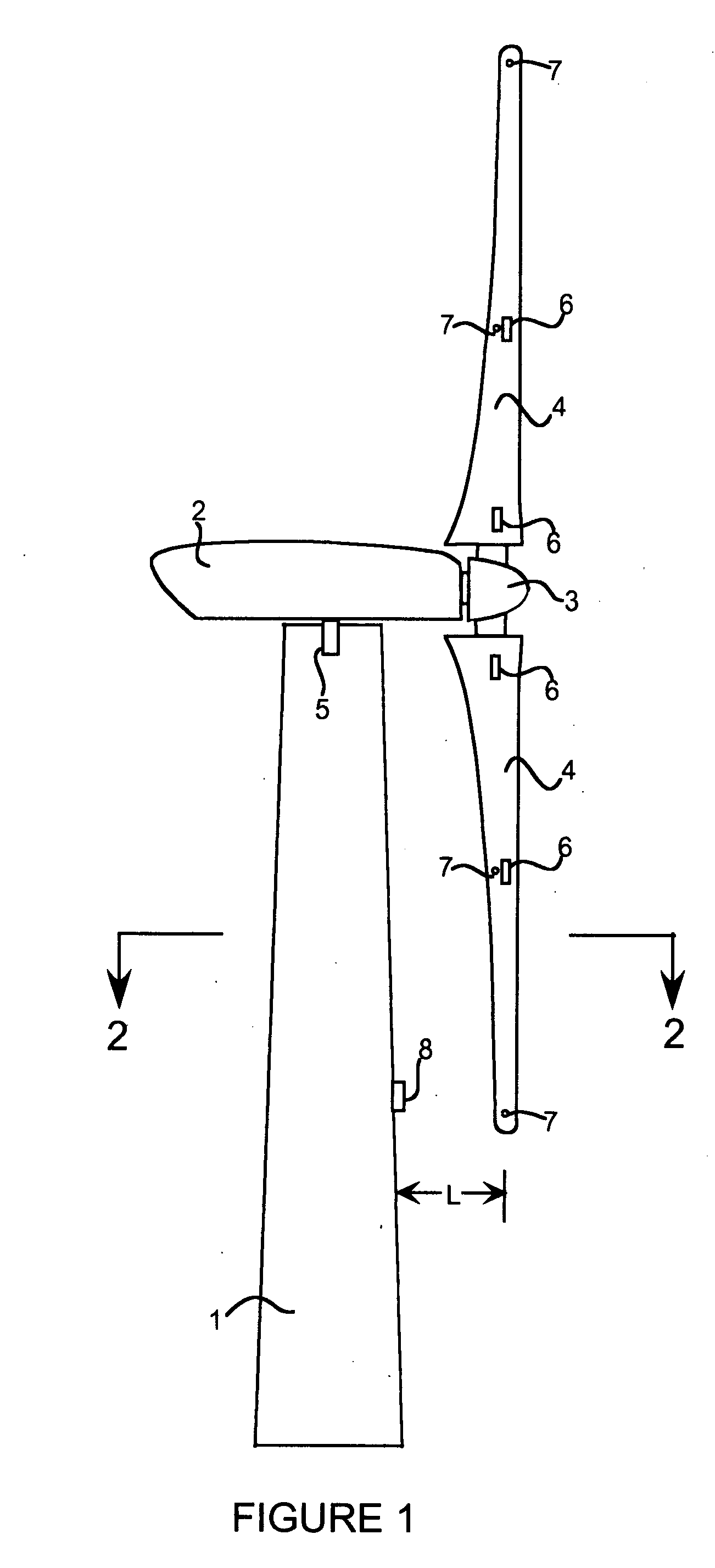
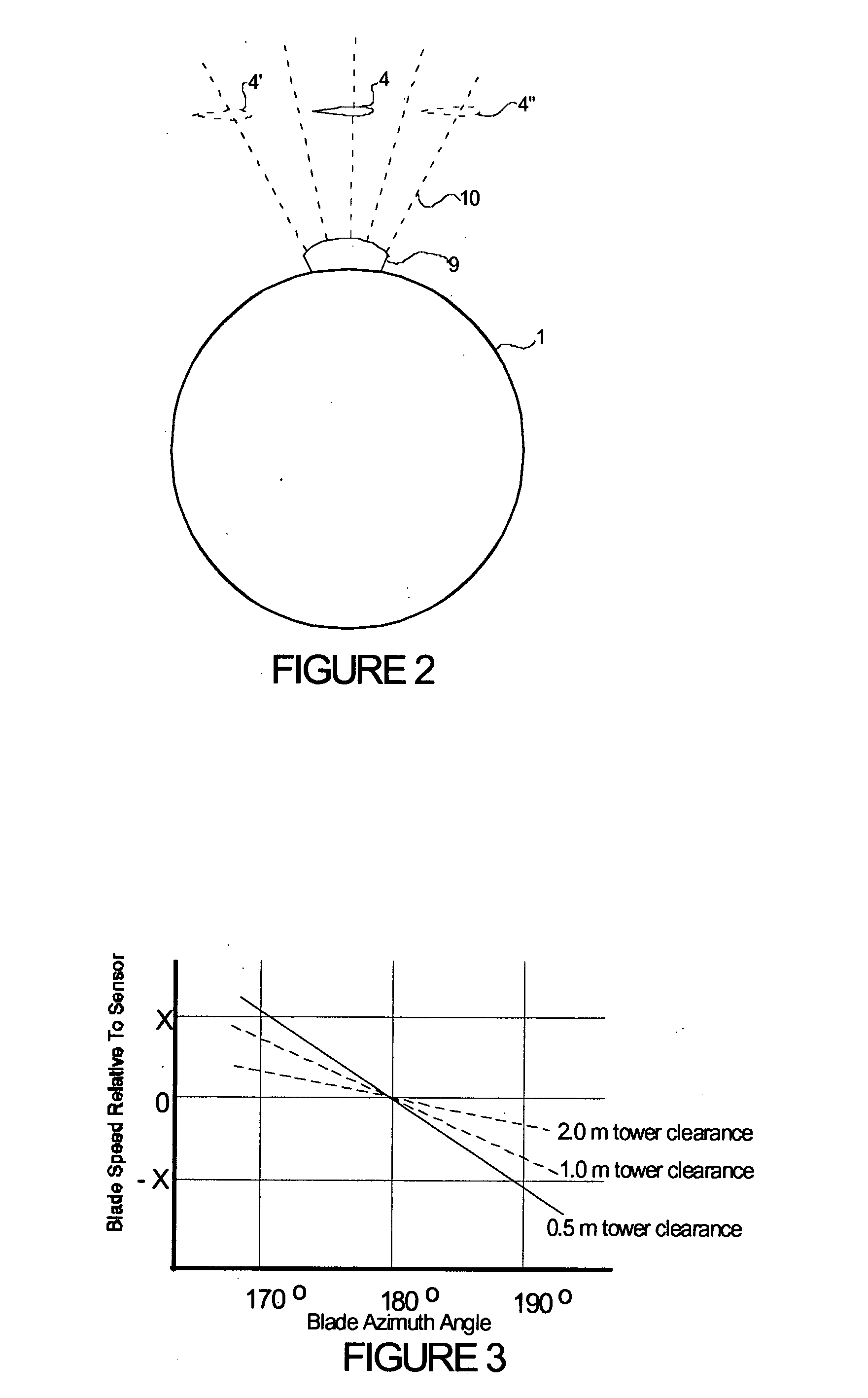
A wind turbine with a sensor that measures the out-of-plane deflection of the blades and a controller that uses the signal from the sensor to determine the risk of a tower strike. The controller takes any necessary action to prevent a tower strike when it determines that the risk of a strike is high. The sensor can include strain gages or accelerometers mounted on the blades or it can include a fixed sensor mounted on the side of the tower to measure tower clearance as the blade passes by. The control action taken can include pitching blades, yawing the nacelle, or stopping the turbine. The controller is preferably a fuzzy logic controller.
Owner:BOSCHE JOHN VANDEN
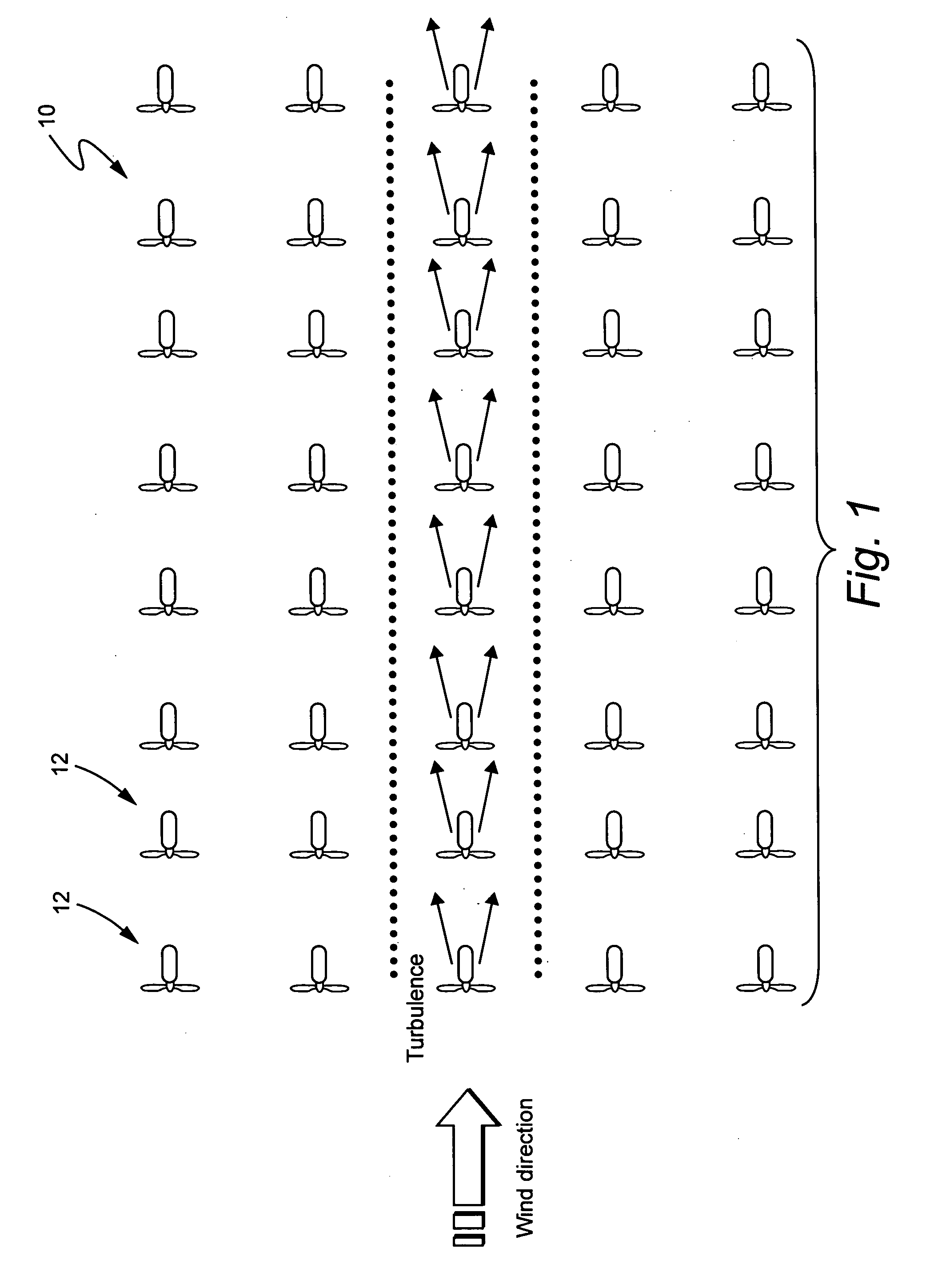
Power loss reduction in turbulent wind for a wind turbine using localized sensing and control
InactiveUS20080317598A1Reduce impactMinimize the differencePropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeAngle of attack
A wind turbine blade assembly includes at least one local load sensor disposed on and / or within a surface of the wind turbine blade and at least one active flow modification device disposed on and / or within a surface of the wind turbine blade and configured to alter the aerodynamics of the wind turbine blade in response to real time local load sensor measurements such that a difference between a current angle of attack and an optimum angle of attack on the wind turbine blade is substantially minimized.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
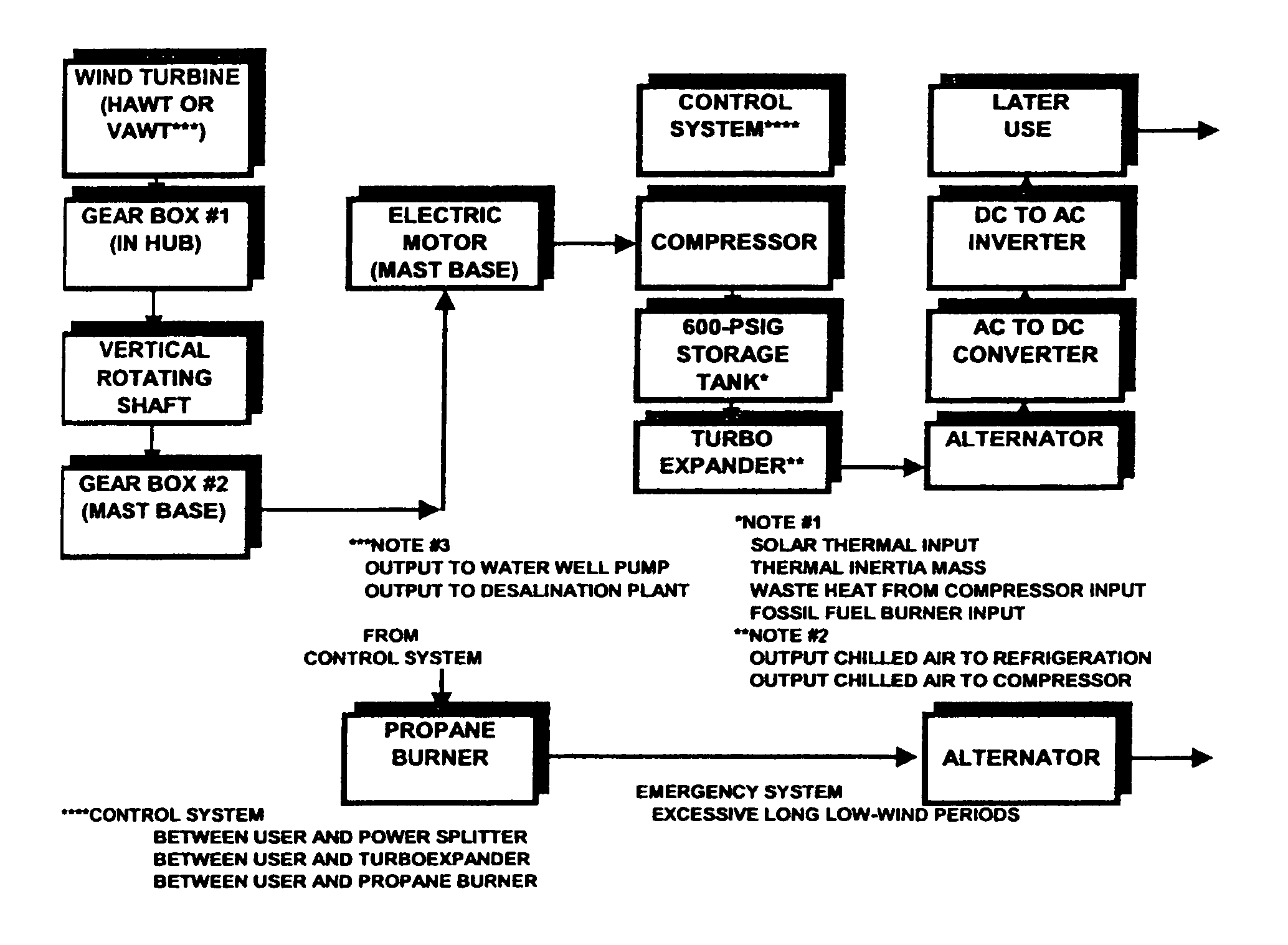
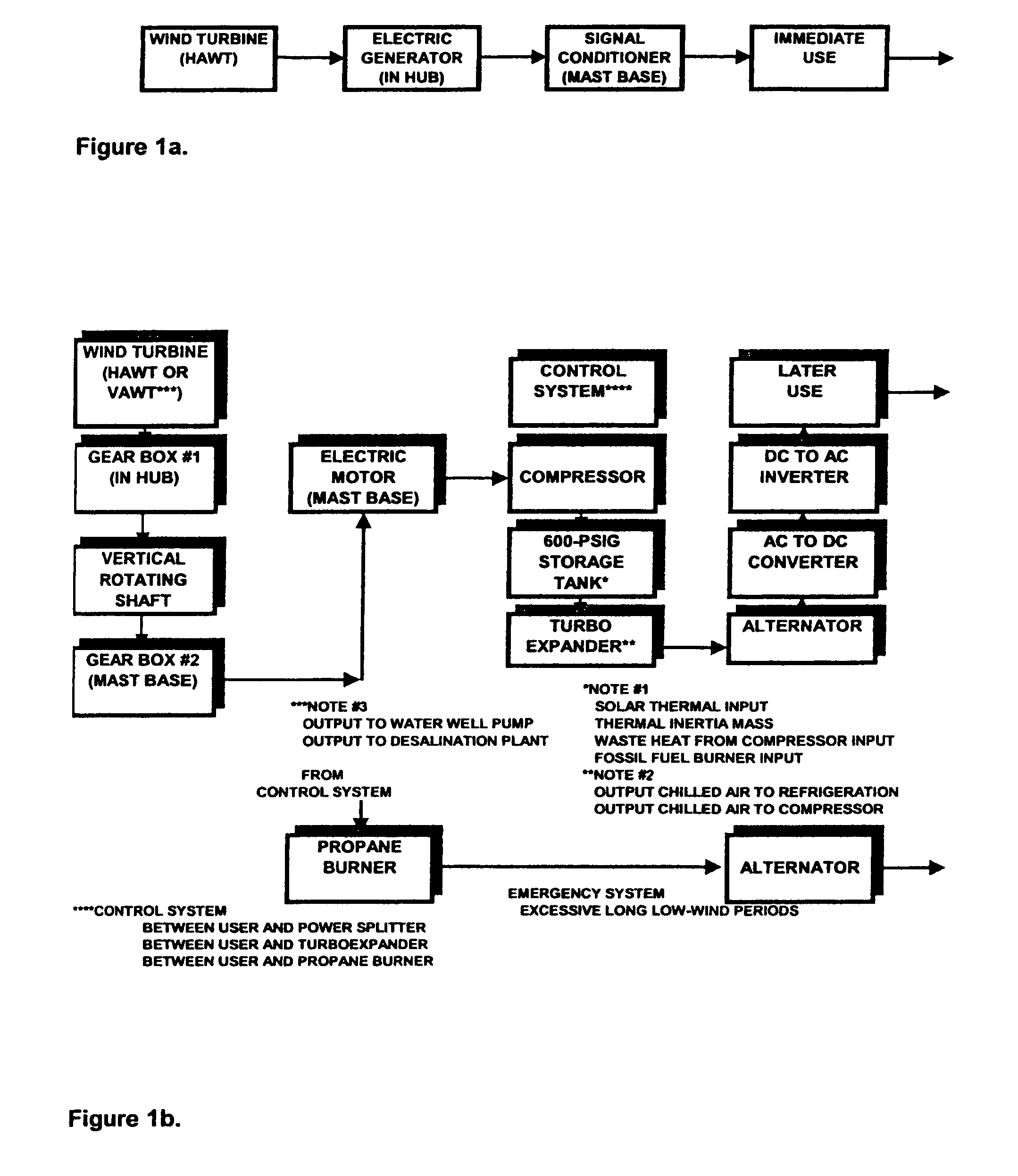
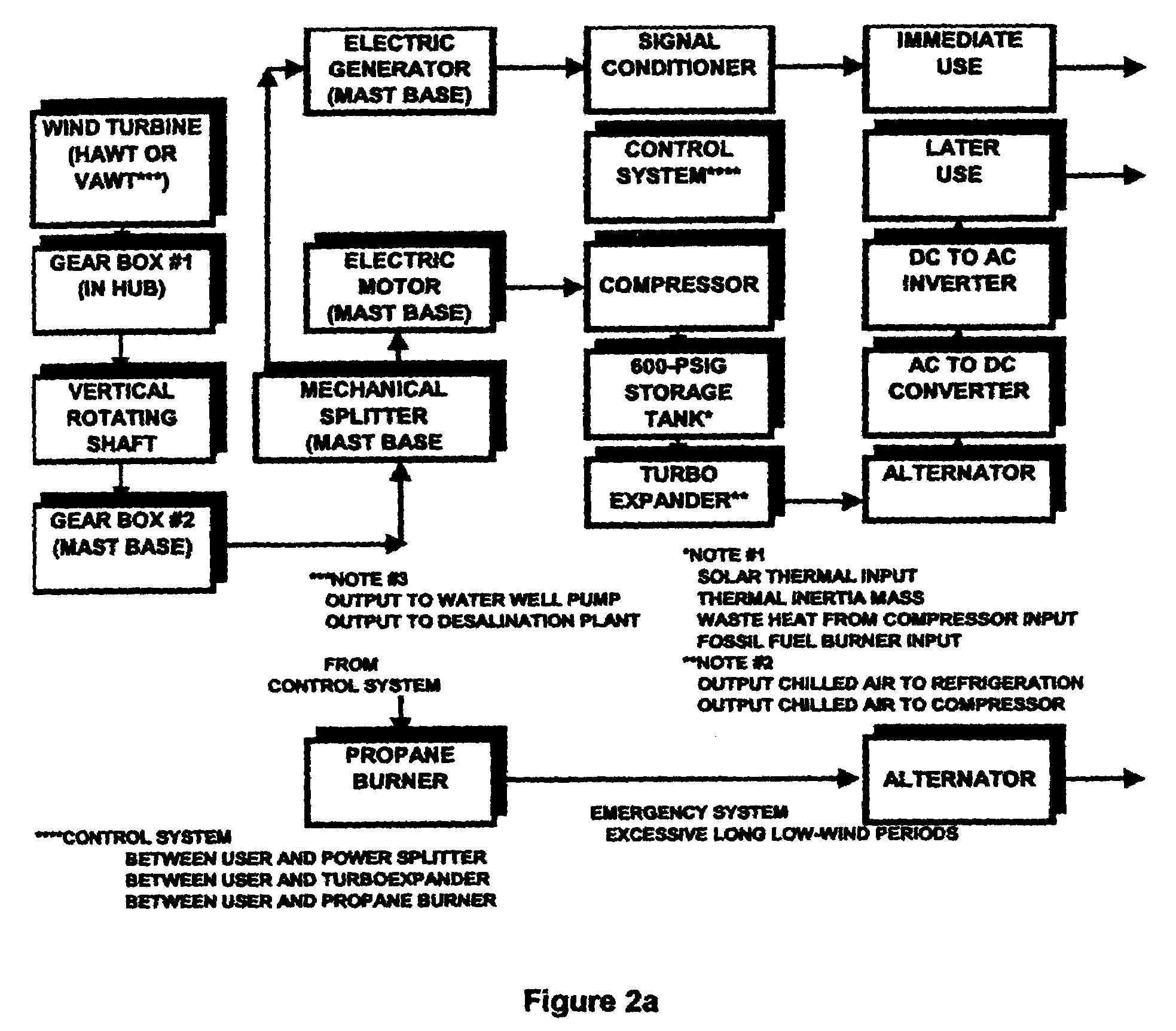
Method of coordinating and stabilizing the delivery of wind generated energy
ActiveUS6963802B2Oscillation be reduced and avoidedPower fluctuation can be reduced and avoidedGeneration forecast in ac networkWind motor controlConstant powerPower grid
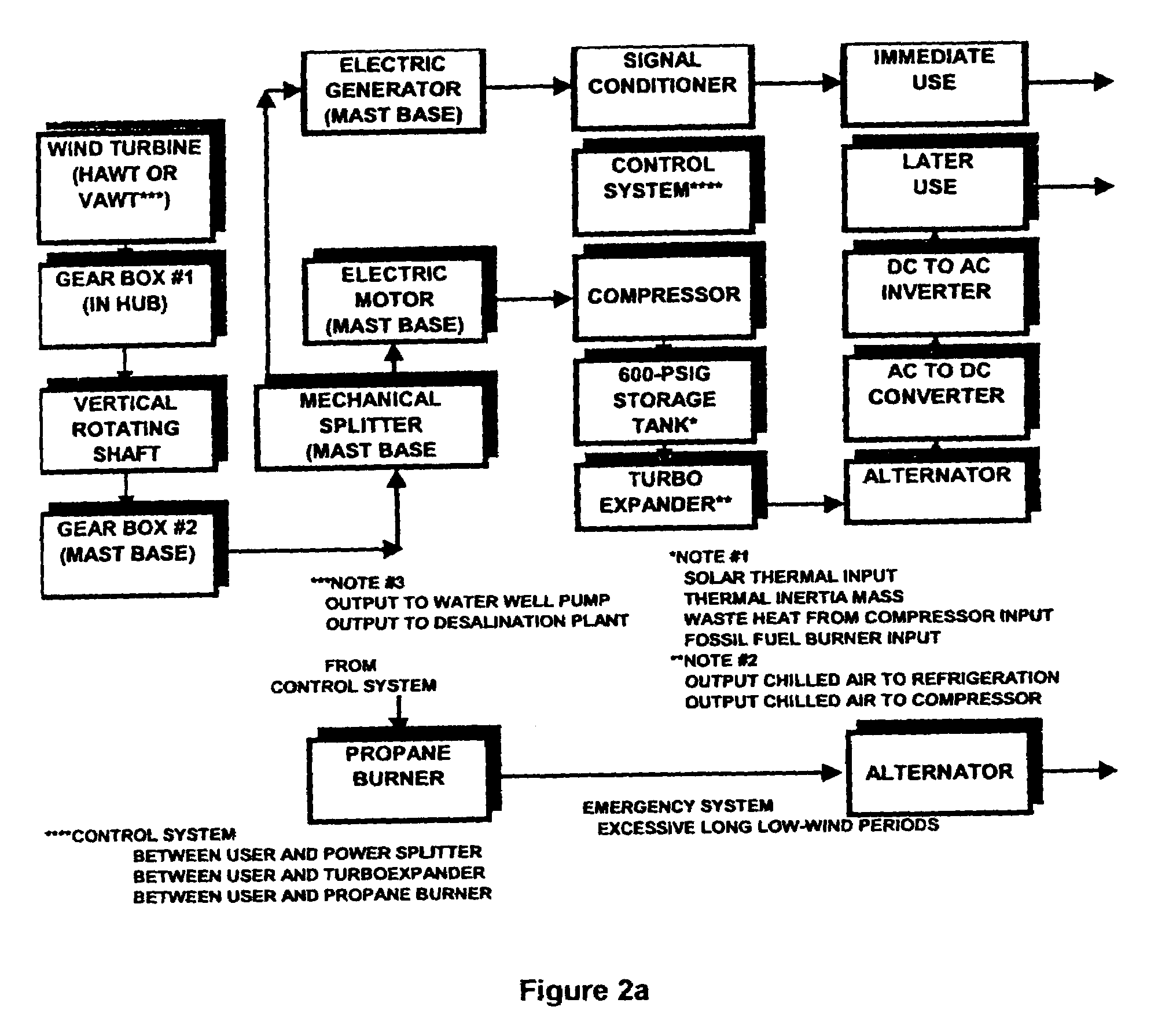
The invention relates to a method of coordinating and stabilizing the delivery of wind generated power, such as to a power grid, so as to avoid sudden surges and spikes, despite wind speed fluctuations and oscillations. The method preferably uses a plurality of windmill stations, including a number of immediate use stations, energy storage stations, and hybrid stations, wherein energy can be used directly by the power grid, and stored for later use when demand is high or wind availability is low. The method contemplates forming an energy delivery schedule, to coordinate the use of direct energy and energy from storage, based on daily wind speed forecasts, which help to predict the resulting wind power availability levels for the upcoming day. The schedule preferably sets a reduced number of constant power output periods during the day, during which time energy delivery levels remain substantially constant, despite fluctuations and oscillations in wind speed and wind power availability levels.
Owner:ENIS BEN M +1
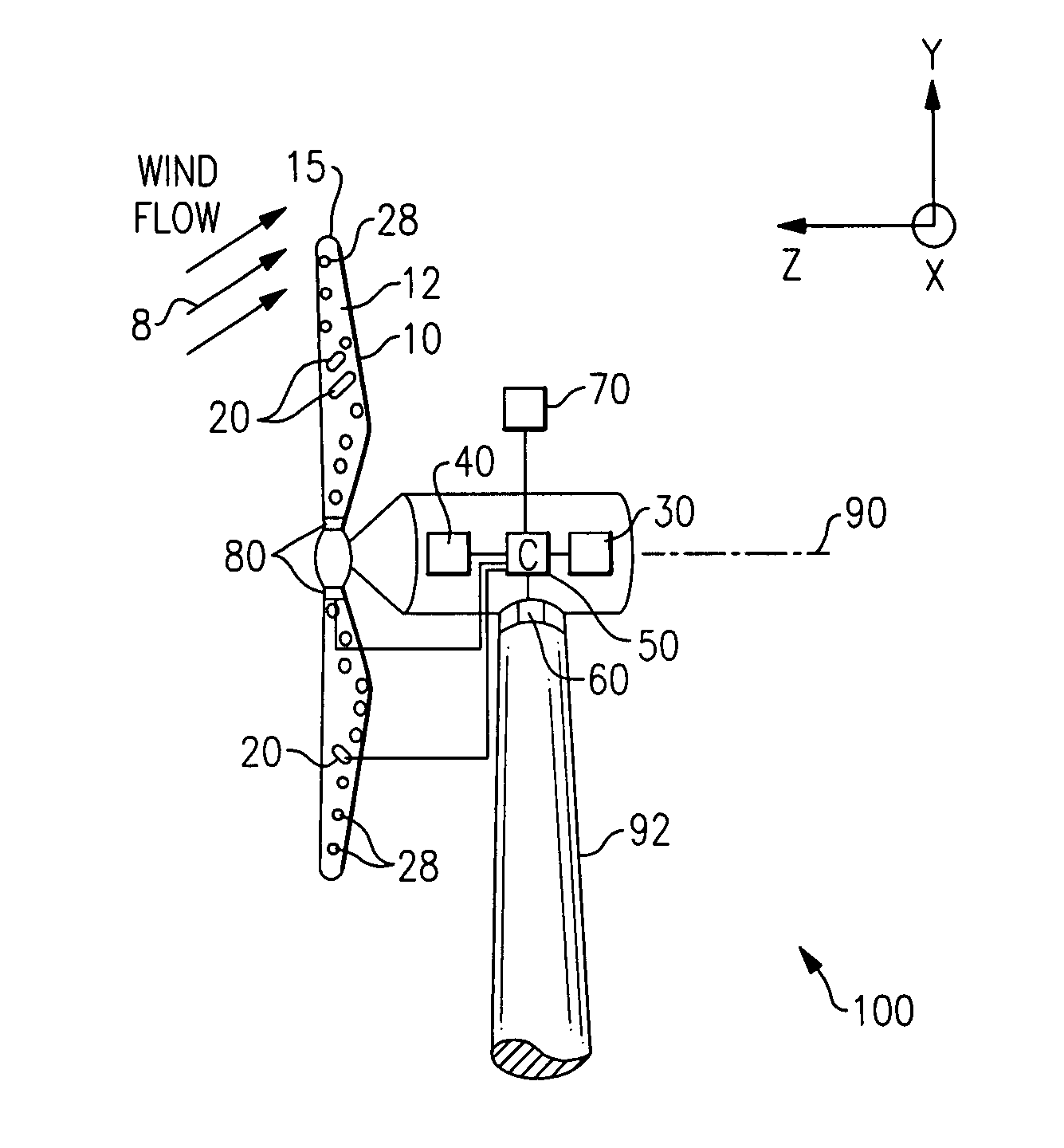
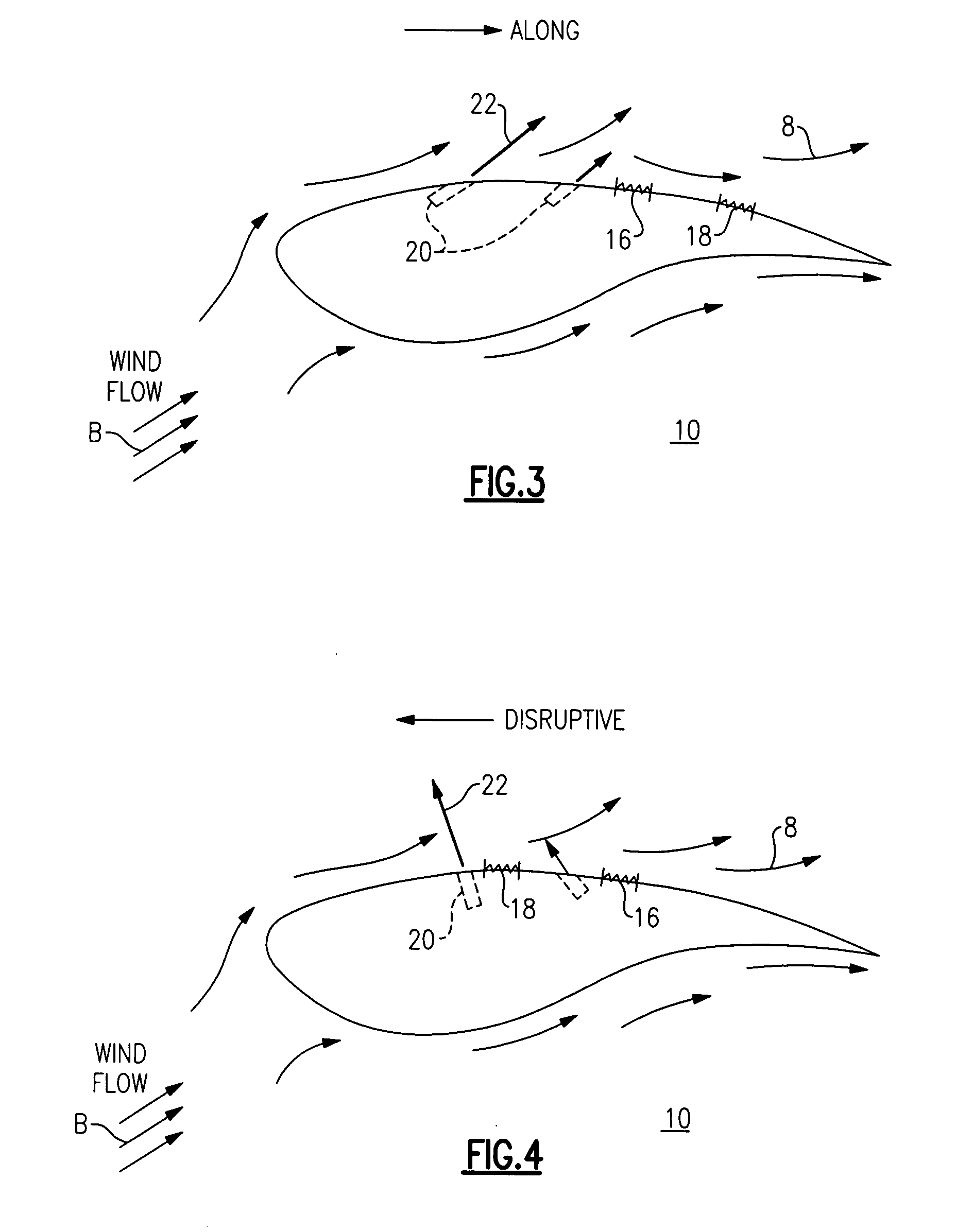
Method of controlling aerodynamic load of a wind turbine based on local blade flow measurement
The present invention relates to a method of controlling the aerodynamic load of a wind turbine's blades individually in such a way that the dynamic aerodynamic loads on the turbine are reduced and power production is optimised. In general the present invention will improve the overall stability of the turbine leading to reduce fatigue loads, reduced extreme loads during operation and reduced risk of blade-tower interaction. In particular preferred embodiment of the invention, flow properties are measured locally on the different blades or in front of the blades and from these measurements the pitch angle settings are changed, in other ways changing the aerodynamic properties, for the blades through a control unit.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Wind power generation evaluation system and predictive control service system for use with wind power generator
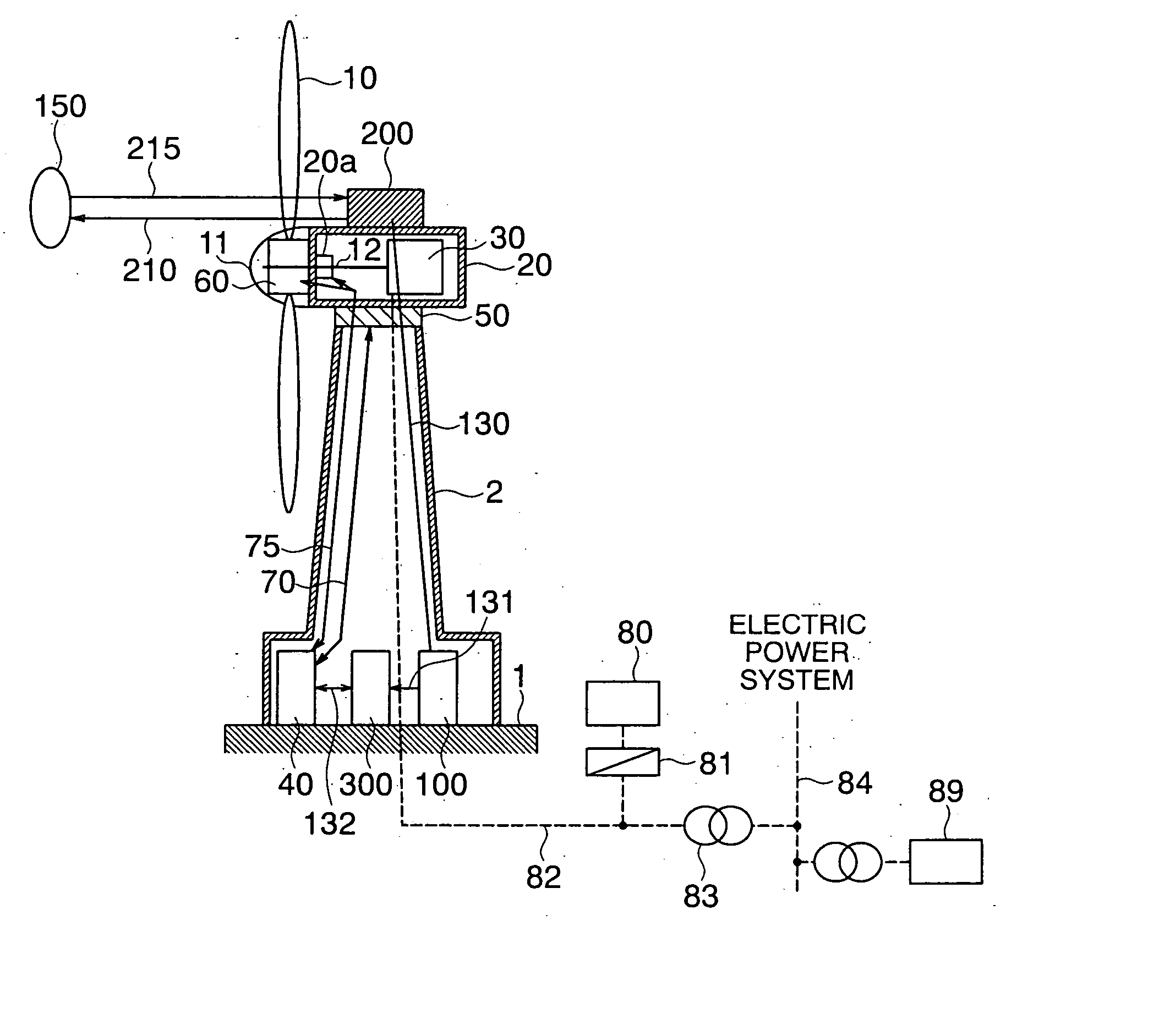
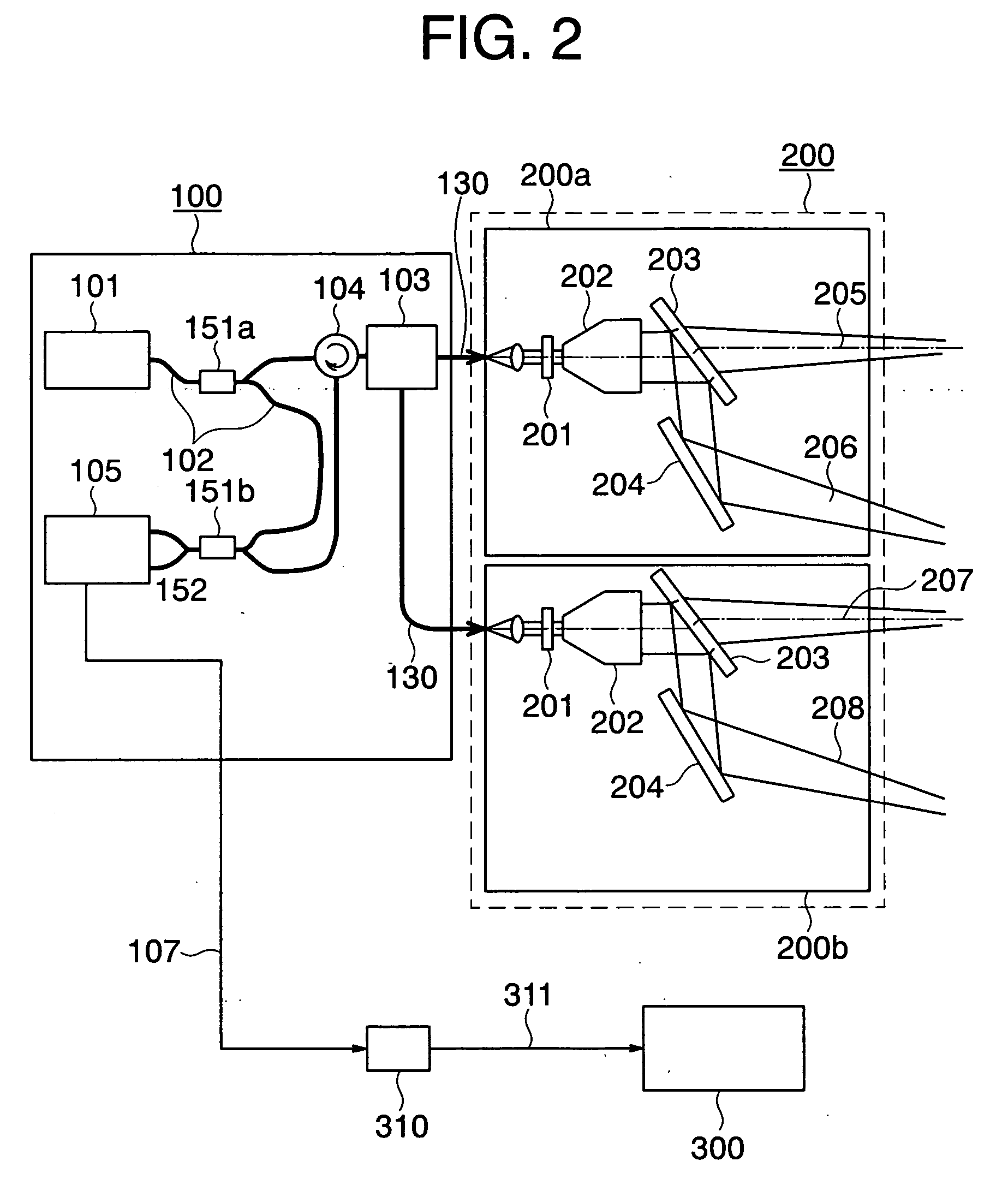
A wind power generation evaluation system includes: a laser aerovane that measures, with a laser, the direction and velocity of wind at a distance from a wind power generator' connected to an electric power system, to predict the direction and velocity of wind at the wind power generator; a second aerovane that measures the wind velocity and direction at the wind power generator; a wind power generation output calculation unit that integrates difference between power outputs calculated based on measurements by the laser aerovane and by the second aerovane, while referring to a windmill performance curve indicating output power characteristics of the wind power generator with respect to wind velocity, to produce a difference between the amounts of generated power; and an additional value calculation unit that calculates additional value of an influence on the environment based on the difference between the amounts of generated power produced by the calculation unit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
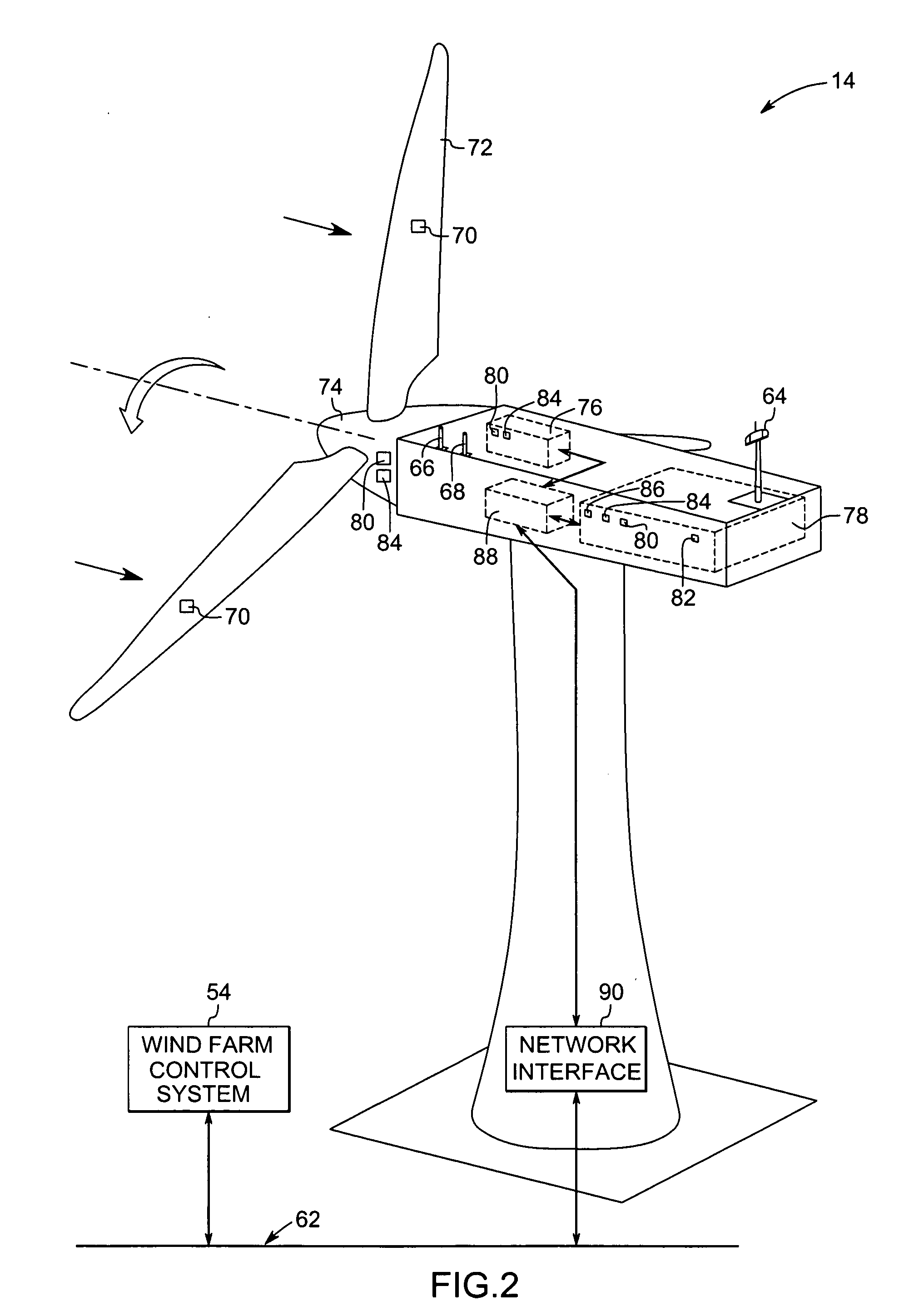
Method and apparatus to determine the wind speed and direction experienced by a wind turbine
ActiveUS20070086893A1Low costSimple and robust and low cost apparatusPropellersWind motor controlNacelleEngineering
An apparatus and a method used to determine the speed and direction of the wind experienced by a wind turbine are provided. The apparatus comprises at least one sensor fixed to the rotor of the wind turbine, an angular sensor to measure the angular position of the rotor of the wind turbine, and a circuit which converts the relationship between the output of the at least one sensor and the output of the angular sensor into the speed and direction of the wind experienced by the wind turbine. According to the invention, the sensing apparatus can measure the wind speed and direction in three dimensions. In addition, mounting the sensors directly to the rotor of the wind turbine results in a very simple and robust installation. Mounting the sensors directly to the rotor also eliminates the turbulence from the rotor and the nacelle of the wind turbine from affecting the sensors.
Owner:ROMO WIND AG
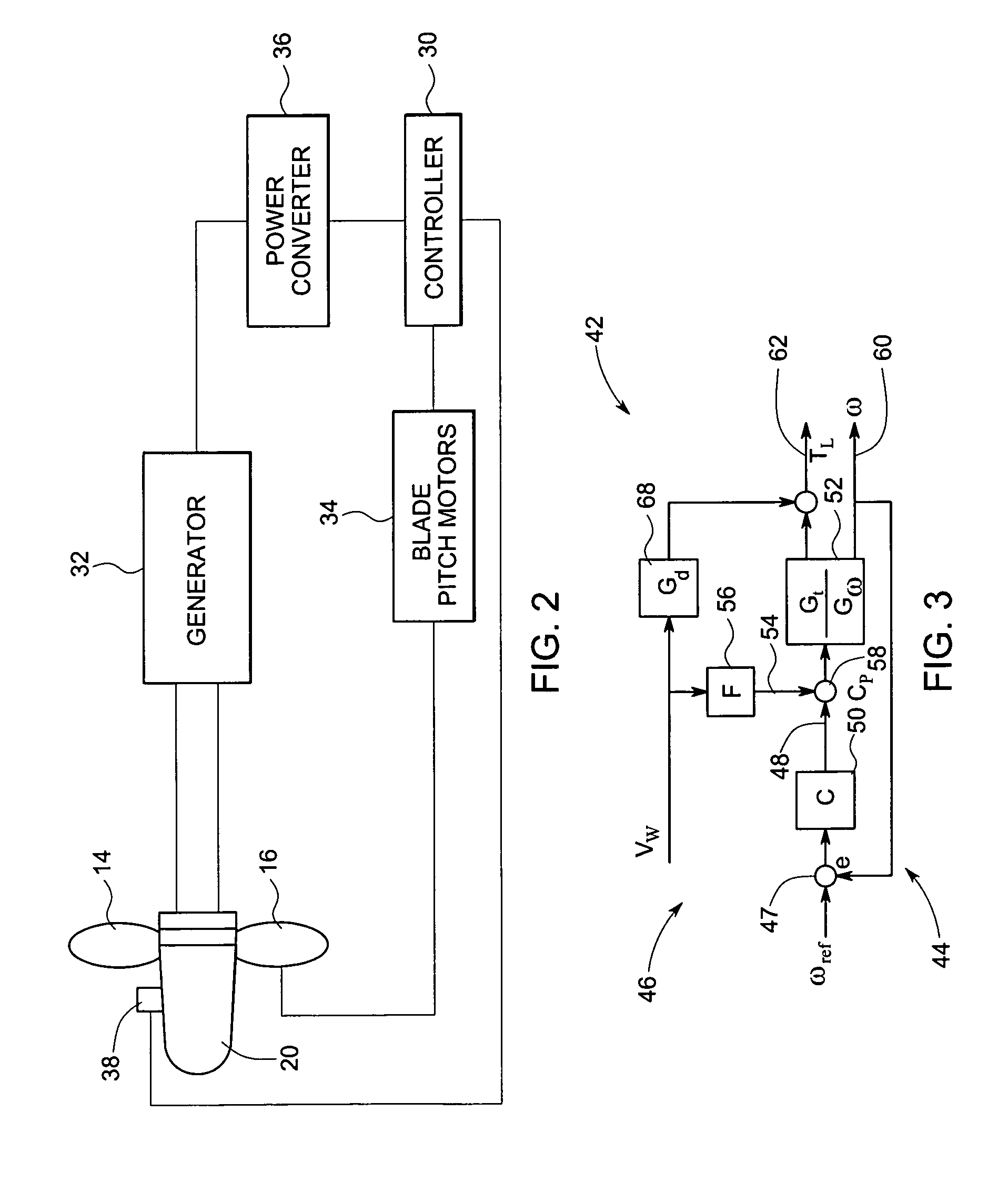
System and methods for controlling a wind turbine
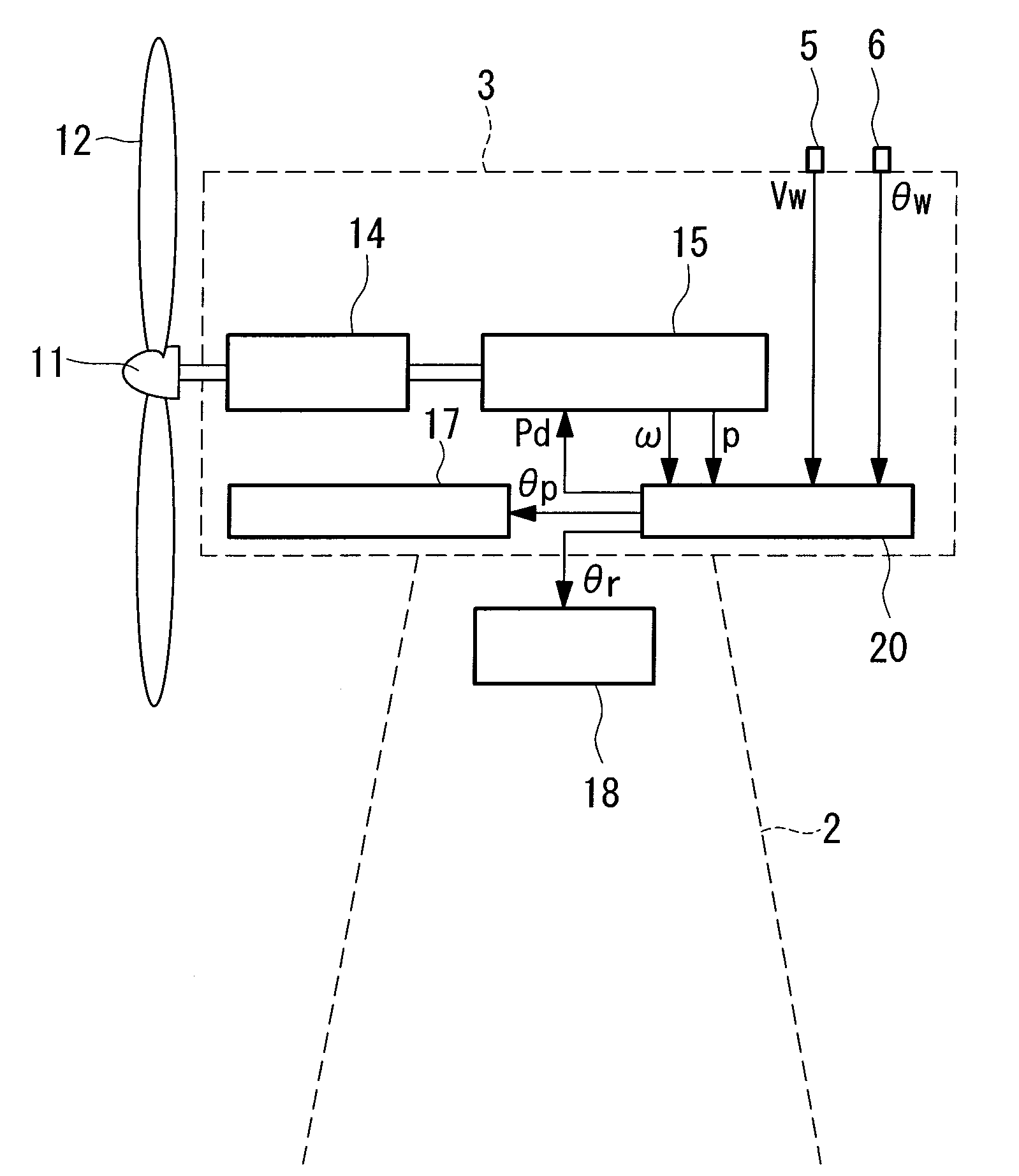
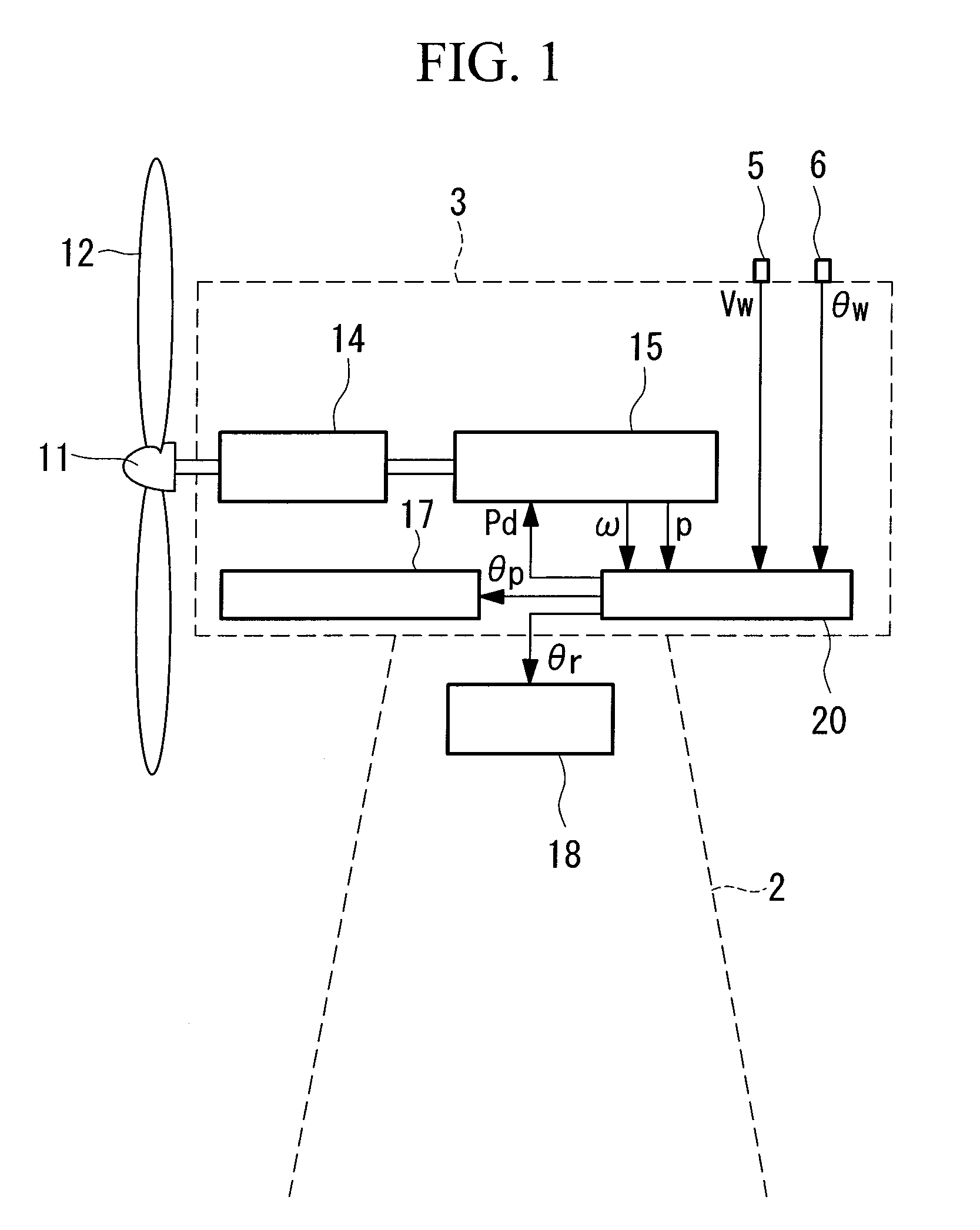
A method for controlling operation of a wind turbine is described. The wind turbine includes a rotor having a plurality of rotor blades and an upwind wind condition measurement device. The method includes measuring a wind condition upwind from the rotor using the upwind wind condition measurement device and providing the measured wind condition to a processor. The method also includes determining a control algorithm parameter, based at least partially on the measured wind condition, that controls at least one of a wind turbine response bandwidth, a wind turbine response speed, and a wind turbine control error range. The method also includes determining a wind turbine operating command based at least partially on the control algorithm parameter and applying the wind turbine operating command to operation of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for controlling rotational speed of a rotor
A method for controlling a rotational speed of a rotor having at least one rotor blade, a rotor shaft, and an electrical generator coupled thereto. The method includes controlling a torque of the rotor shaft by controlling a torque of the electrical generator, alternating between changing an angle of pitch of the at least one rotor blade and maintaining the angle of pitch of the at least one rotor blade substantially constant, and maintaining a substantially constant rotational speed of the rotor during variable wind speeds above a predetermined rated wind speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856041B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine blade deflection control system
A wind turbine with a sensor that measures the out-of-plane deflection of the blades and a controller that uses the signal from the sensor to determine the risk of a tower strike. The controller takes any necessary action to prevent a tower strike when it determines that the risk of a strike is high. The sensor can include strain gages or accelerometers mounted on the blades or it can include a fixed sensor mounted on the side of the tower to measure tower clearance as the blade passes by. The control action taken can include pitching blades, yawing the nacelle, or stopping the turbine. The controller is preferably a fuzzy logic controller.
Owner:BOSCHE JOHN VANDEN
Wind turbine generator, wind turbine generator system, and power generation control method of wind turbine generator
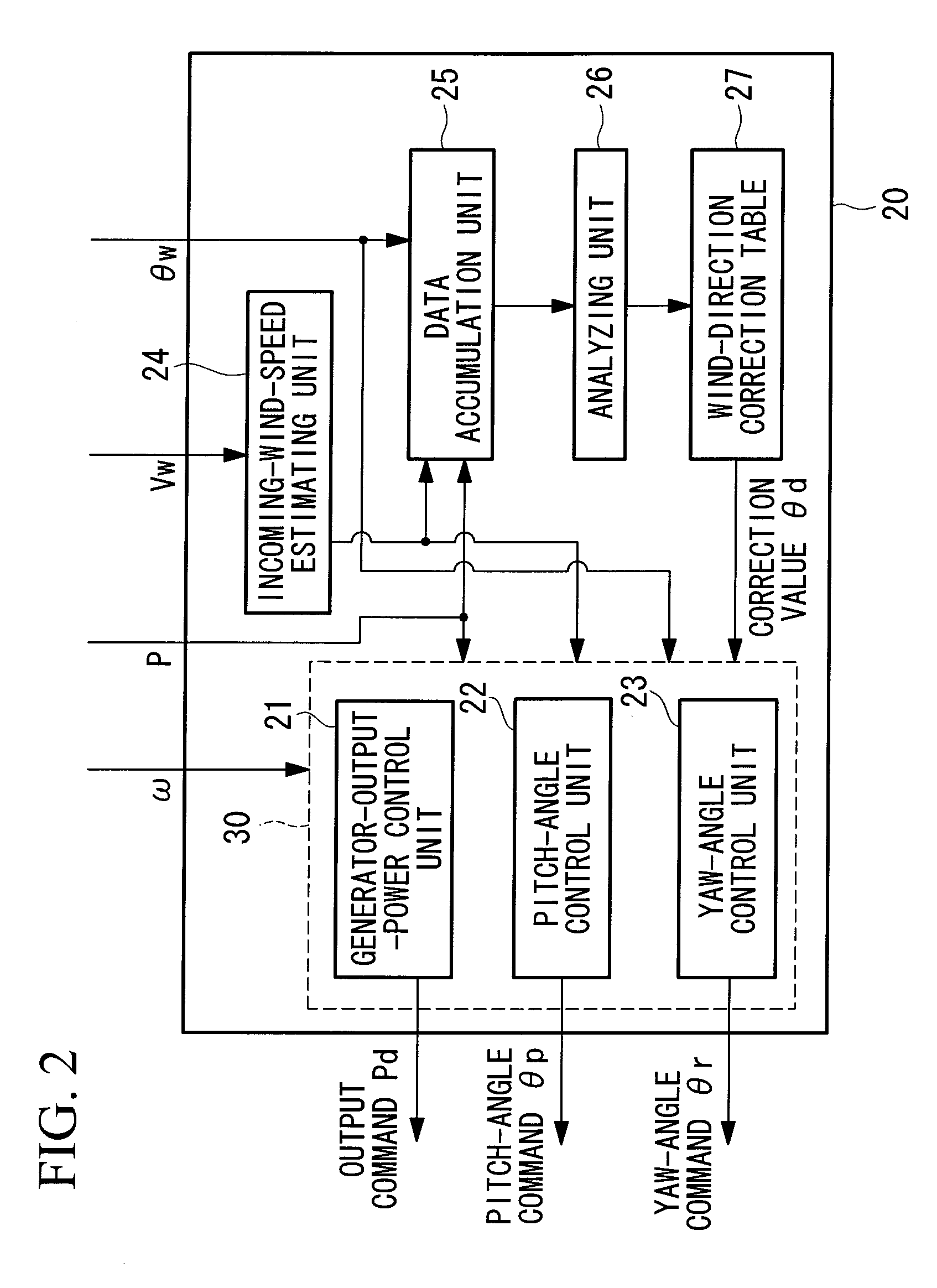
ActiveUS20100066087A1Accurate wind directionIncrease costElectric motor controlWind motor controlNacellePeak value
To provide a wind turbine generator, a wind turbine generator system, and a power-generation control method of a wind turbine generator that are capable of improving the power-generation capability and reducing the fatigue load on the windmill. A data accumulation unit 25 sequentially accumulates data sets of a generated output power P during operation of the wind turbine generator, an incoming wind speed Ws estimated on the basis of a wind speed measured at the anemometer, and a wind direction deviation, which is the difference between a wind direction θw measured at the anemoscope and the orientation of the nacelle; statistical analysis of the data accumulated is carried out by an analyzing unit 26; a distribution curve corresponding to the wind direction deviation of the generated output power at each incoming wind speed is determined; the wind direction deviation corresponding to the peak of the distribution curve is set as a correction value θd of the anemoscope; the correction value of the anemoscope for each incoming wind speed is stored in the wind-direction correction table 27; the wind direction Vw measured at the anemoscope is corrected with the correction value θd of the anemoscope for each incoming wind speed Ws; and power-generation control is carried out using the corrected wind direction as a control parameter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Methods and apparatus for controlling rotational speed of a rotor
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Control Modes for Extendable Rotor Blades
InactiveUS20100158687A1Maximize incomeReduce paymentPropellersRotary propellersAccelerometerEngineering
A wind turbine may be controlled in a variety of manners to optimize operating parameters. In one arrangement, for example, the length or the pitch of a wind turbine rotor blade may be adjusted to avoid harmonic resonance frequencies. In another example, the length of a rotor blade may be modified to reduce noise or to optimize profits or both. The controls may be based on data from various types of sensors including accelerometers, sound meters, strain gauges and the like. Actuation of extendable rotor blades can rotate wind turbine rotors without wind or generator pulsing affording multiple advantages. A battery test control may also be used to determine the operational readiness of a battery useful for a variety of purposes in a turbine.
Owner:FRONTIER WIND LLC
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6853094B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scaler power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method of coordinating and stabilizing the delivery of wind generated energy
InactiveUS7308361B2Smoothing and stabilizing delivery of powerStable deliveryGeneration forecast in ac networkWind motor controlConstant powerPower grid
The invention relates to a method of coordinating and stabilizing the delivery of wind generated power, such as to a power grid, so as to avoid sudden surges and spikes, despite wind speed fluctuations and oscillations. The method preferably uses a plurality of windmill stations, including a number of immediate use stations, energy storage stations, and hybrid stations, wherein energy can be used directly by the power grid, and stored for later use when demand is high or wind availability is low. The method contemplates forming an energy delivery schedule, to coordinate the use of direct energy and energy from storage, based on daily wind speed forecasts, which help to predict the resulting wind power availability levels for the upcoming day. The schedule preferably sets a reduced number of constant power output periods during the day, during which time energy delivery levels remain substantially constant, despite fluctuations and oscillations in wind speed and wind power availability levels.
Owner:ENIS BEN M +1
System and method for operating a wind farm under high wind speed conditions
A system and method of operating a wind farm, having multiple wind turbine generators, at high wind speeds is provided. Wind speeds at individual wind turbine generators are monitored and a signal is transmitted from the wind turbine generators to a wind farm control system based on the monitored wind speeds. Rate of change of collective power output of the wind farm is temporally monitored and is controlled by coordinating of operational states of the wind turbine generators based upon the signals transmitted by the one or more wind turbine generators, operating conditions of the wind turbine generators and the monitored rate of change of power output of the wind farm.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Method of operating a wind power plant
ActiveUS20130035798A1Reduce needUnbalanced loadLevel controlWind motor controlTime rangePower station
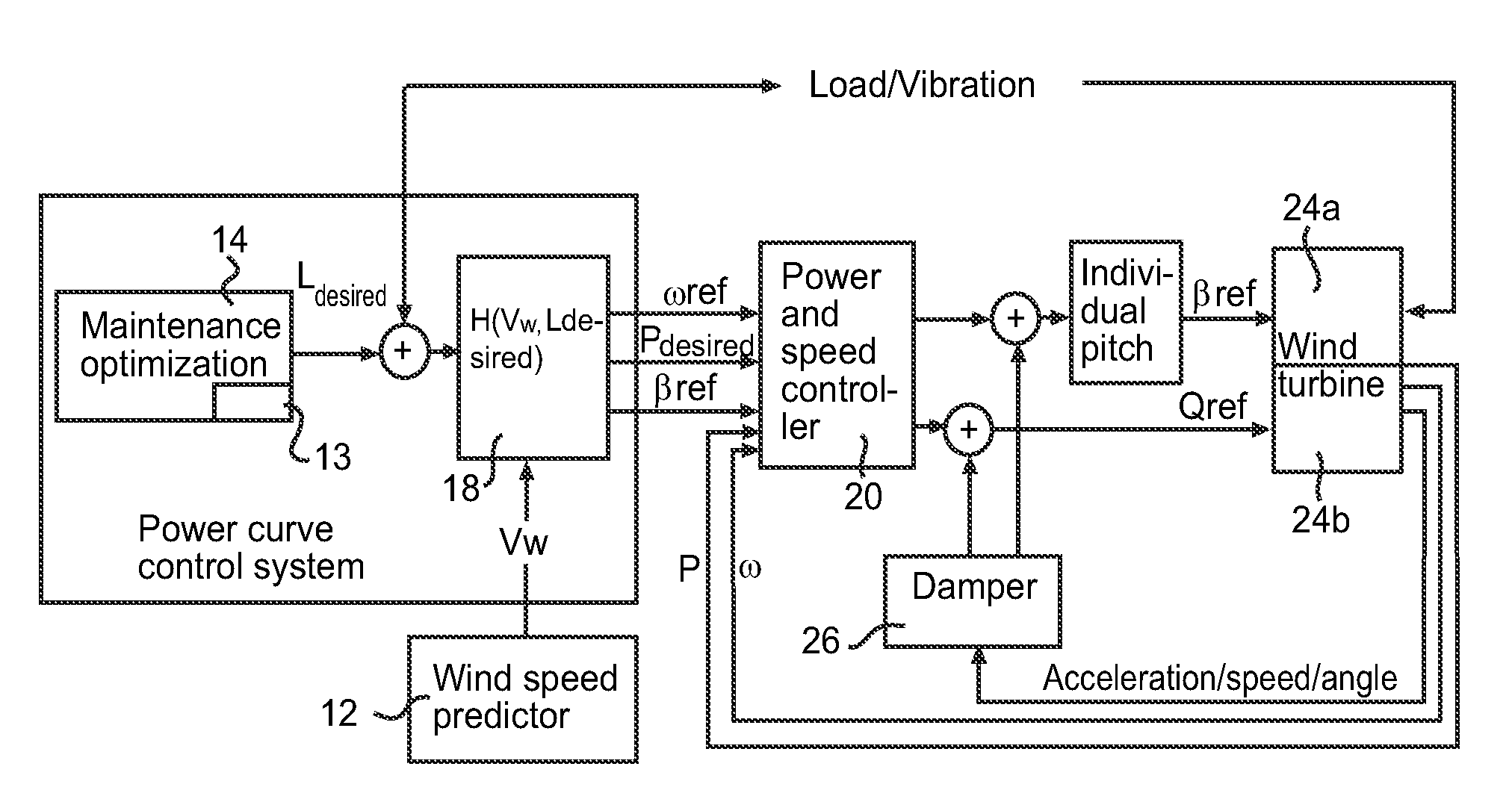
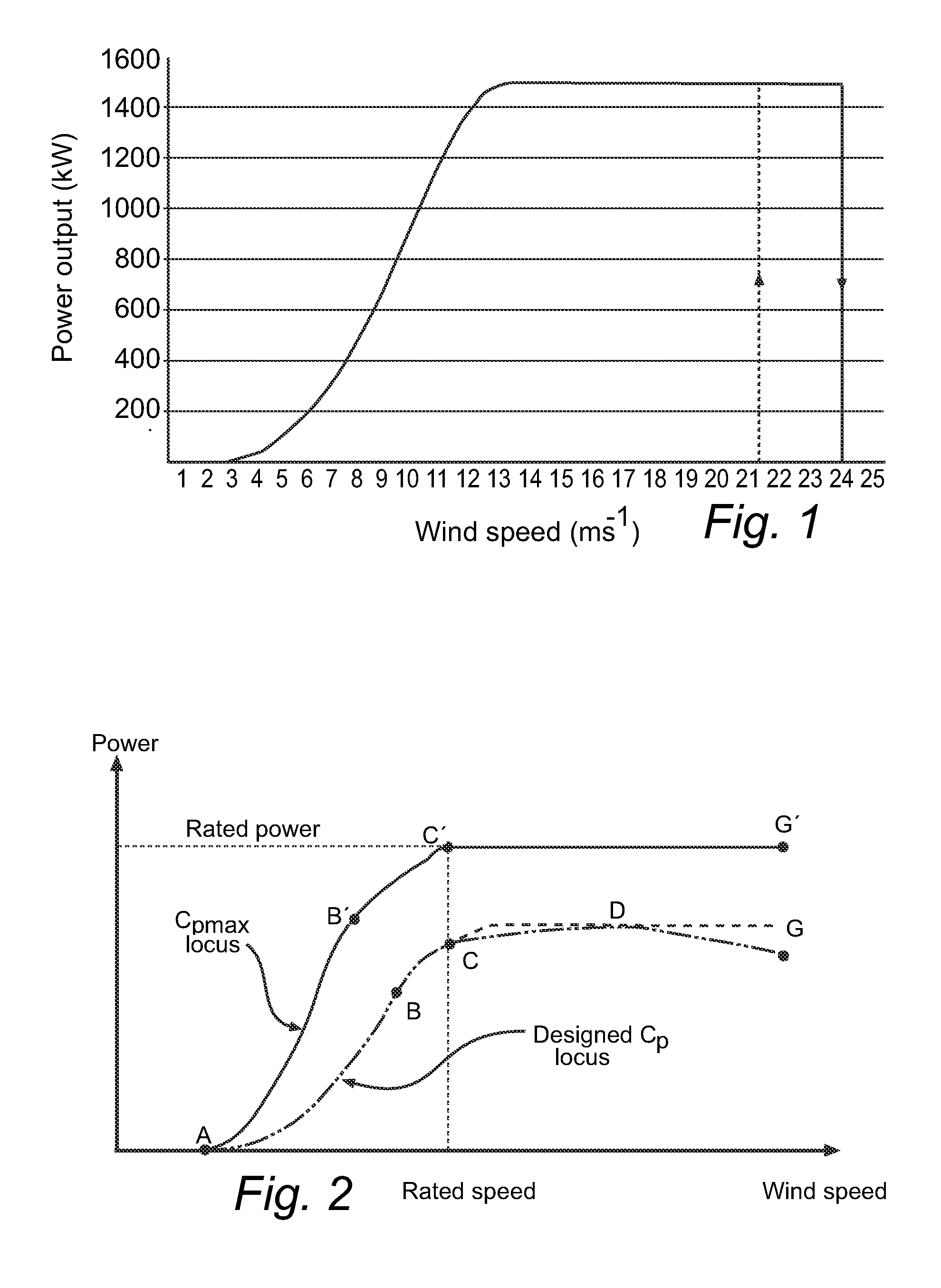
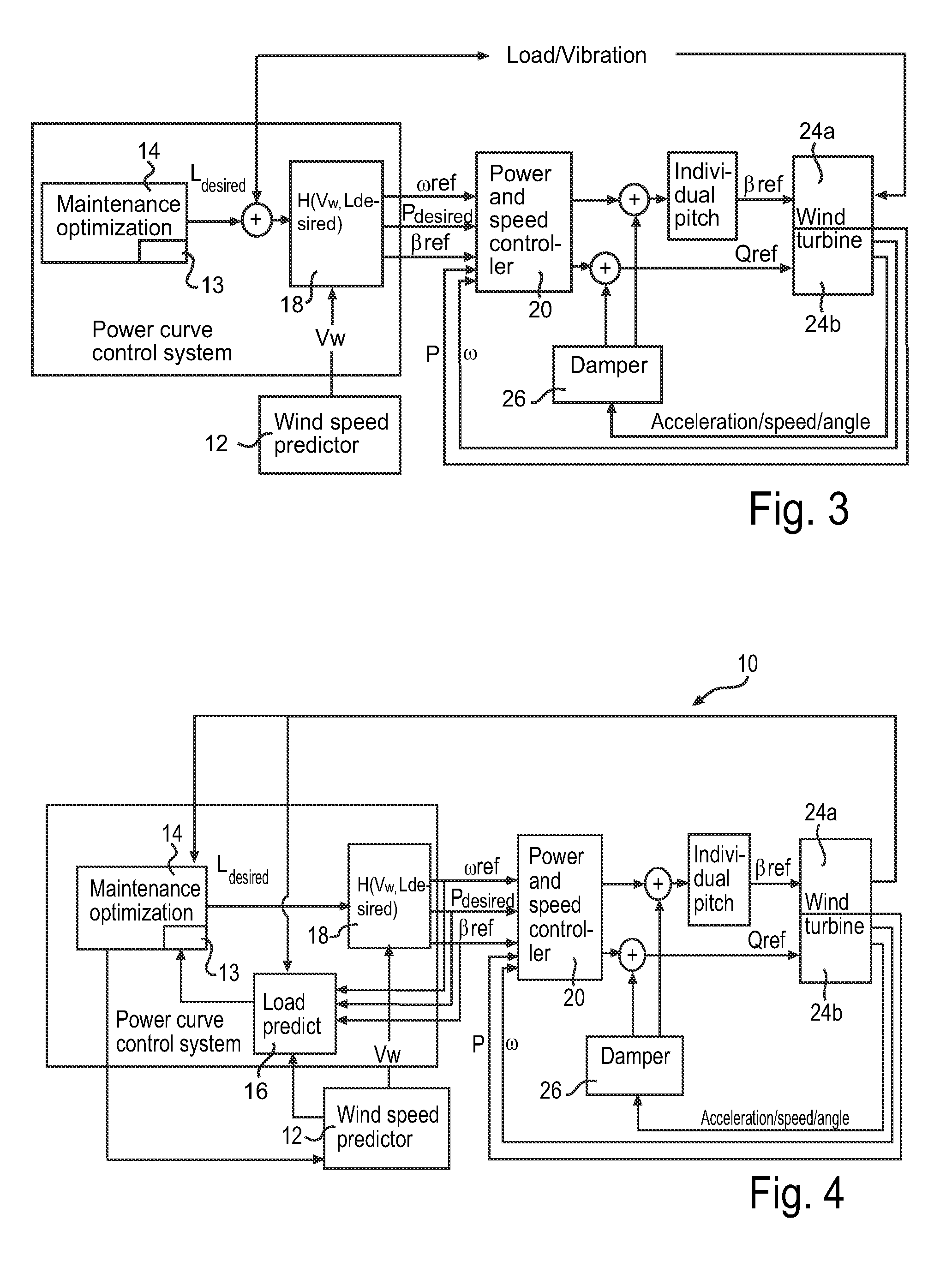
Method of operating a wind power plant including the steps of: operating the wind power plant at an current parameter schedule (Pcurrent(v)) performing a wind prediction of wind data (Vw) for a time frame (ΔT) extending to a future time T, determining a desired fatigue load level (Fdesired) of a wind power plant component at the future time T, and during operation of said wind power plant generating an updated parameter schedule (Pdesired(v)) to provide the desired fatigue load level (Fdesired) at time T if exposed to the predicted wind conditions (Vw(t)) during said time frame (ΔT)
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Control system for wind turbine
InactiveUS20080086281A1Maximize its energy outputMaintaining design lifeWind motor controlEngine fuctionsHorizonControl system
A control system for a wind turbine comprises: a sensor arrangement for capturing measures related to the turbine operation and fatigue accumulation; an upper level controller, which, on the basis of a statistical treatment of said measures, calculates optimized control settings at discrete points of time; a measurement module which processes said measures into instantaneous values; and a lower level controller that receives said control settings and said instantaneous values and calculates instantaneous optimal commands to control turbine actuators. The lower level controller comprises a continuous-time damage model which calculates the rate at which damage is accumulated at any time, and an optimal controller which controls operational states of the turbine, either by directly giving feedback of the instantaneous values to the actuators, or by generating a turbine performance objective function which is continuously optimized by repeatedly solving a receding horizon optimization problem.
Owner:ECOTECNIA ENERGIAS RENOVABLES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com