Modified factor IX polypeptides and uses thereof
A factor and amino acid technology, applied in the field of modified factor IX polypeptide, can solve problems such as defect coagulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0176] Example 1: Computer analysis
[0177] Implementation of solvent accessibility, known secondary structure, the location of known hemophilia B mutations, proximity to the predicted site of interaction with both FVIII and FX, and the prediction of the stability of the FIX protein for a given mutation Computer analysis of the FIX sequence on the impact to identify potential sites for the addition of a consensus sequence of new N-glycosylation sites.
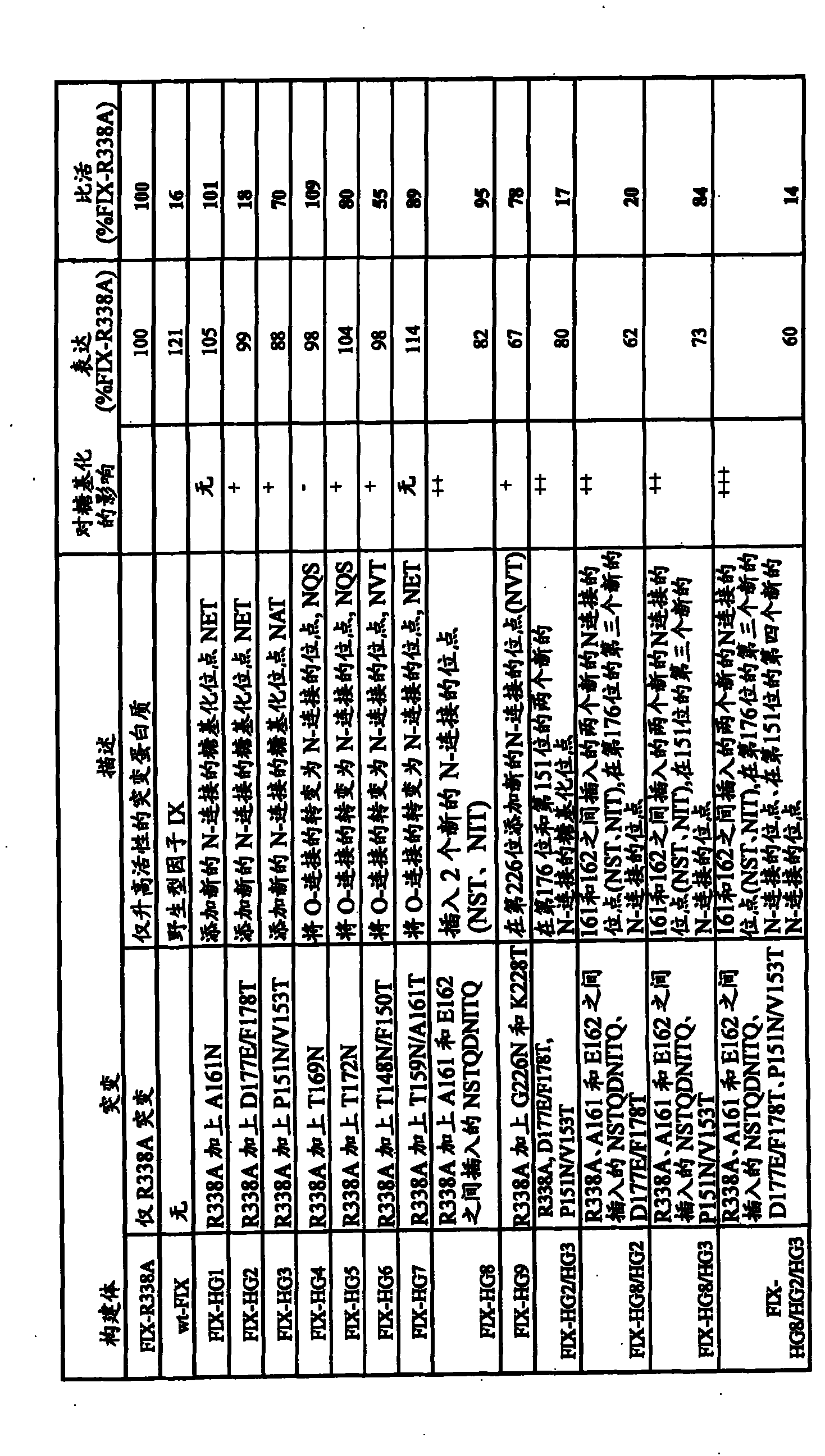
[0178] Based on this analysis, 5 sites were identified within the catalytic domain to create new N-linked glycosylation sites. Table 2 shows the selected site design and the changed amino acid sequence.
[0179] Table 2
[0180]
Embodiment 2
[0181] Example 2: Sequence alignment of activation peptides
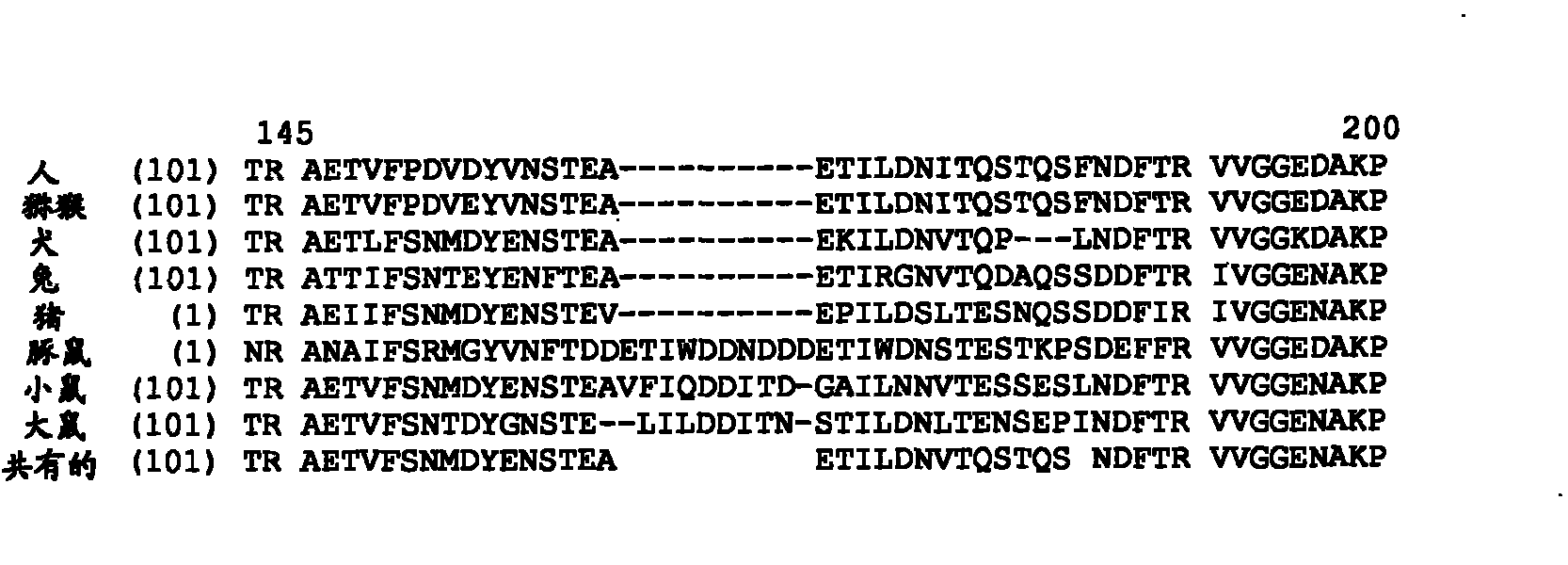
[0182] Identify the conserved and non-conserved residues in the activation peptide by multi-species sequence alignment, such as figure 1 Shown in.
[0183] The consensus sequence for the N-linked glycosylation site is Asn-X-Ser / Thr (where X is any amino acid except proline or aspartic acid (which may also not be advantageous)). In order to design new N-linked glycosylation sites in the FIX activation peptide, avoid the consensus sequence of amino acids that are conserved among species in the activation peptide and the consensus sequence of other N-linked sites and the consensus sequence of tyrosine sulfation. These post-translational modifications are not disrupted, as these can be important for the pharmacokinetics of FIX. Using these criteria, three sites for adding new N-linked glycosylation sites within the activation peptide were identified, as shown in Table 3.
[0184] table 3
[0185] name
[0186] HG2
Embodiment 3
[0187] Example 3: Insertion of amino acids to create N-linked glycosylation sites
[0188] Multiple sequence alignment ( figure 1 ) Also revealed that mice, rats, and guinea pigs have additional amino acids between residues A161 and E162 relative to human, macaque, pig, dog, and rabbit FIX. These extra amino acids vary in size from 7 to 10 across the three species, and contain an overrepresentation of Asp and to some extent Ile residues. This observation indicates that 7-10 additional residues are tolerated at this site in rats, mice, and guinea pigs, and have no significant effect on FIX activity. According to the criteria used to perform multiple sequence alignments among FIXs from 8 species, the apparent sites for finding extra amino acids in rats, mice, and guinea pigs can vary so that the sites can be Between E160 and A161, between A161 and E162, between E162 and T163, or between T163 and I164 of human FIX.
[0189] In the activation peptide, 9 additional amino acids with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com