Method for rapidly identifying fibers
A fiber and fast technology, applied in the field of rapid fiber identification, can solve the problems of accumulation of experience, inappropriate judgment, and difficulty in distinguishing synthetic fibers, etc., and achieve the effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
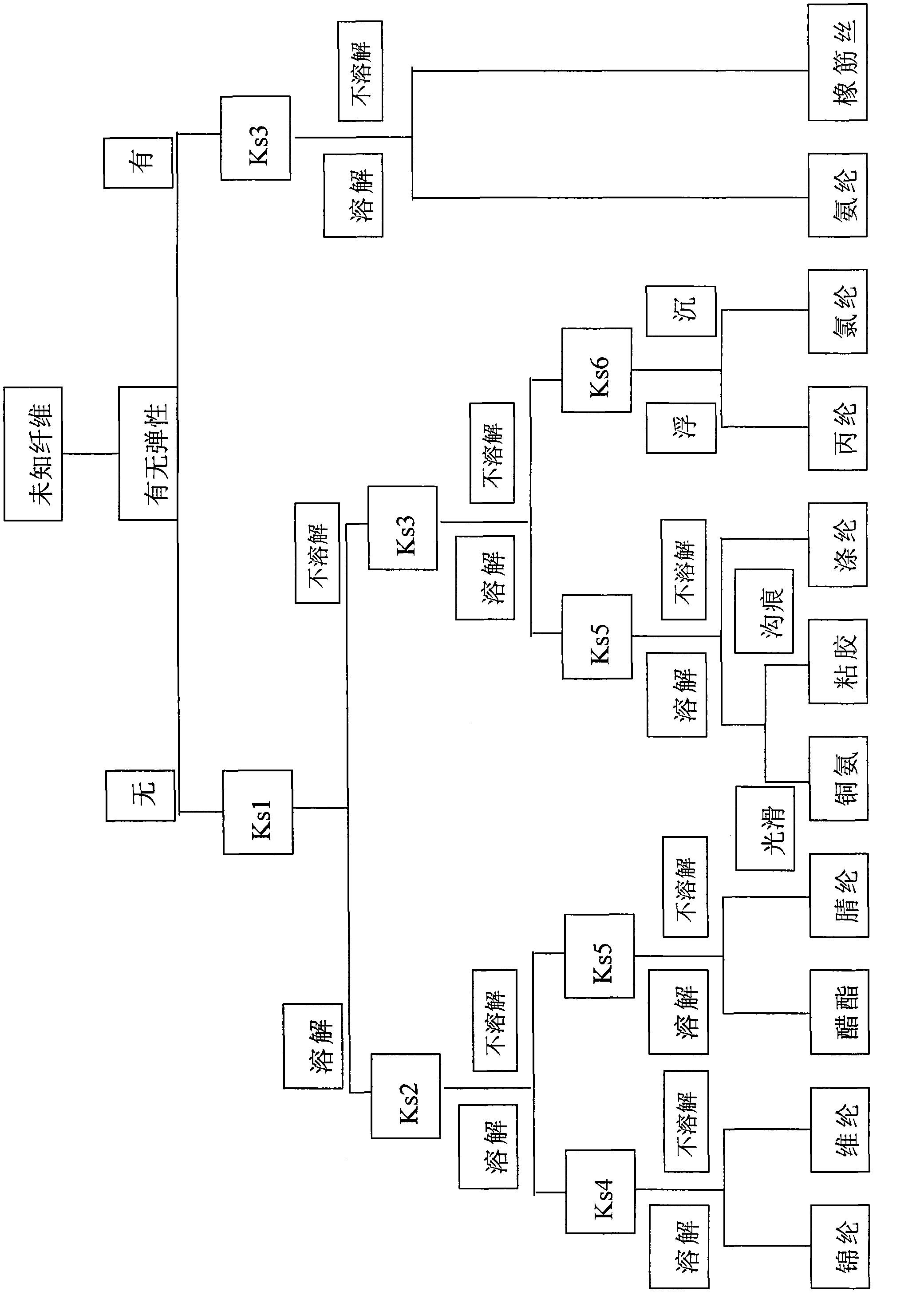
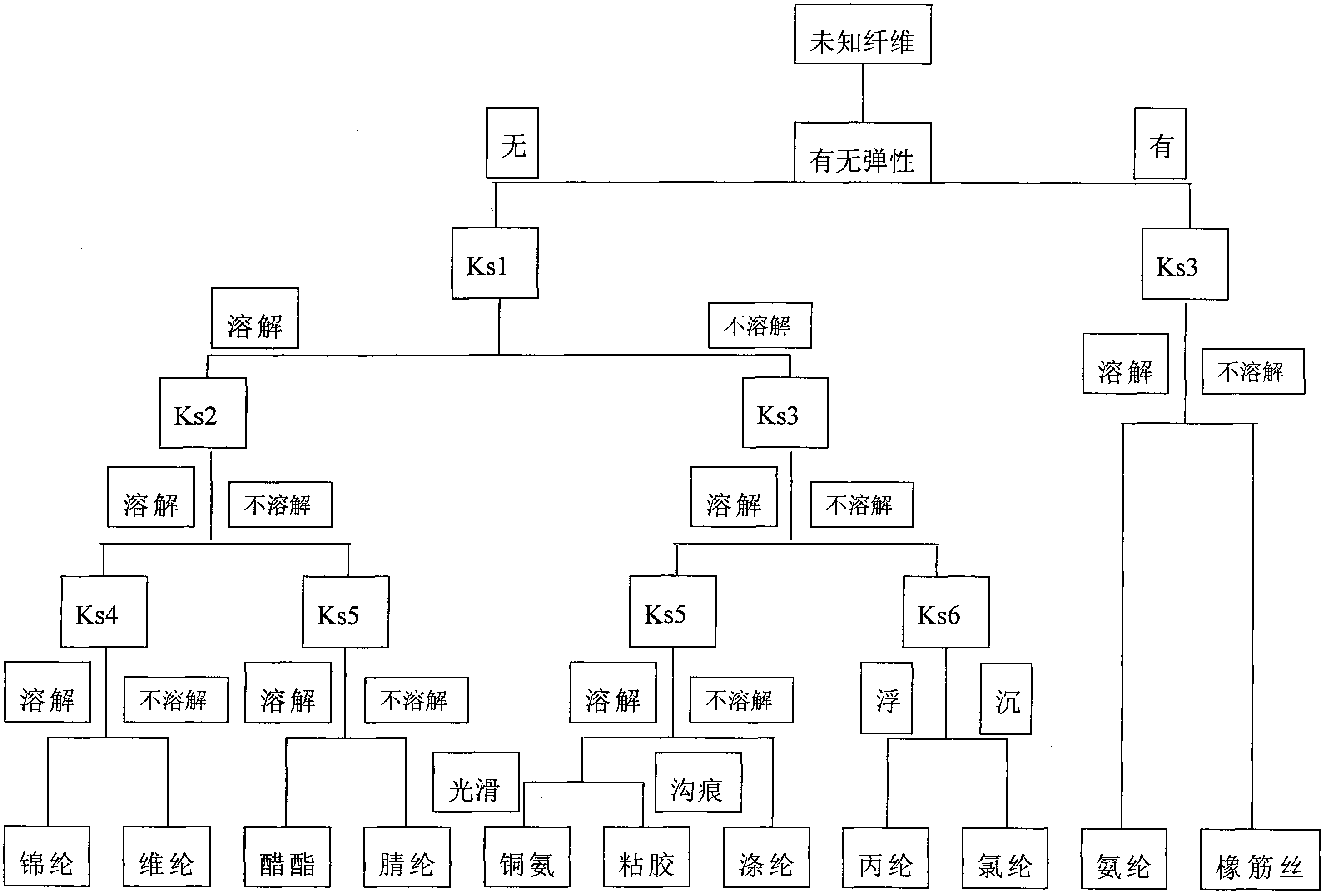
[0032] Tensile test of unknown fibers, elastic, confirmed with KS3, KS3 is 98% concentrated sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 (density 1.84g / cm 3 ), the result was dissolved, and the result was that the fiber was identified as spandex.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Tensile test of unknown fiber, no elasticity, confirmed by KS1, KS1 is 65% concentrated nitric acid HNO 3 (density 1.39g / cm 3 ), the result was dissolved, and then confirmed with KS2, the result was dissolved, and then dissolved with KS4, the result was insoluble, and it was determined to be Velen fiber.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Tensile test of unknown fiber, no elasticity, confirmed by KS1, the result is not dissolved, then confirmed by KS3, the result is not dissolved, then confirmed by KS6, floating on the liquid surface, so the fiber is confirmed to be polypropylene.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com