Vertically taking off and landing small unmanned aerial vehicle
A small unmanned aerial vehicle, vertical take-off and landing technology, applied in the direction of rotorcraft, motor vehicles, aircraft control, etc., can solve the problems of small flight range, poor take-off and landing conditions, low flight speed, etc., and meet the requirements of reducing the take-off and landing space , Expand the scope of use, and the effect of good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example
[0042] The embodiment of the present invention is described below by two kinds of examples:
example 1
[0043] Example 1: Conversion between vertical take-off and landing and horizontal flight
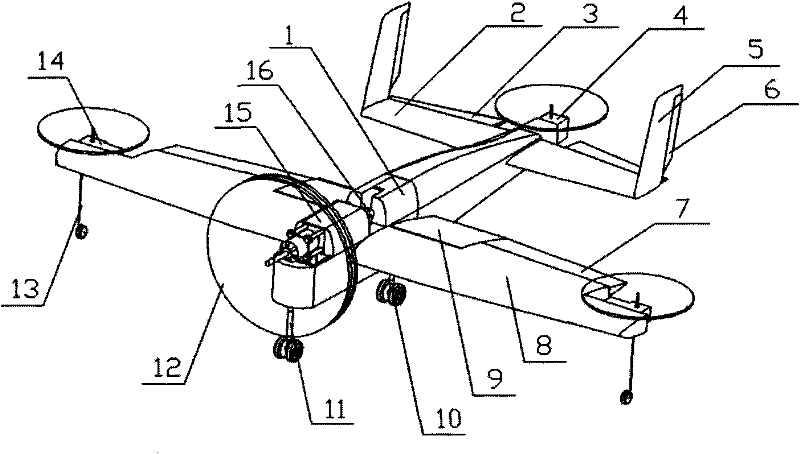
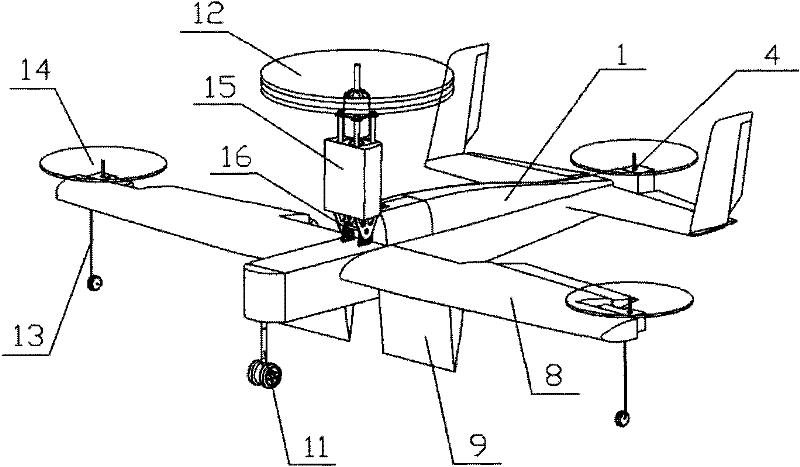
[0044] When the take-off and landing conditions are good, carry out horizontal taxi take-off and landing. When the take-off and landing environment is too bad to take off and land horizontally, the power cabin of the nose is tilted to a vertical state, the attitude adjustment system is turned on, and the vertical take-off is carried out. After reaching a certain height, the power cabin of the nose slowly turns to a horizontal state. After the horizontal flight speed accumulates to a certain flight speed, turn off the attitude adjustment system and switch to normal horizontal flight. After completing the flight mission, reach the sky above the landing area, turn on the attitude adjustment system, and the power cabin of the nose will slowly tilt to a vertical state, and after the flight speed drops to zero, it will land vertically.
example 2
[0045] Example 2, horizontal flight and hovering in the air conversion
[0046] When performing tasks that require hovering in the air, such as aerial photography, after the aircraft flies horizontally to the sky above the target, the attitude adjustment system is turned on, and the power cabin of the nose is tilted to be perpendicular to the ground, and it is converted into a hovering state in the air. Carry out fixed-point aerial photography and detection. After completing the mission, the power cabin of the nose is tilted to a horizontal state. After accumulating to a certain flight speed, the attitude adjustment system is turned off, converted to a horizontal flight state, and flies away from the target.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com