Microscopic image fusing method based on two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition
An empirical mode decomposition, microscopic image technology, applied in the field of image fusion, can solve the problems of block effect, fusion result influence, unsatisfactory effect, etc., to achieve the effect of expanding the depth of field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0079] In order to better understand the technical solutions of the present invention, the implementation manners of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
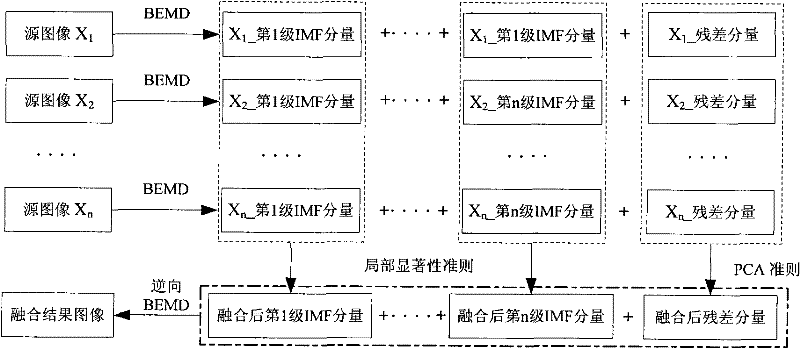
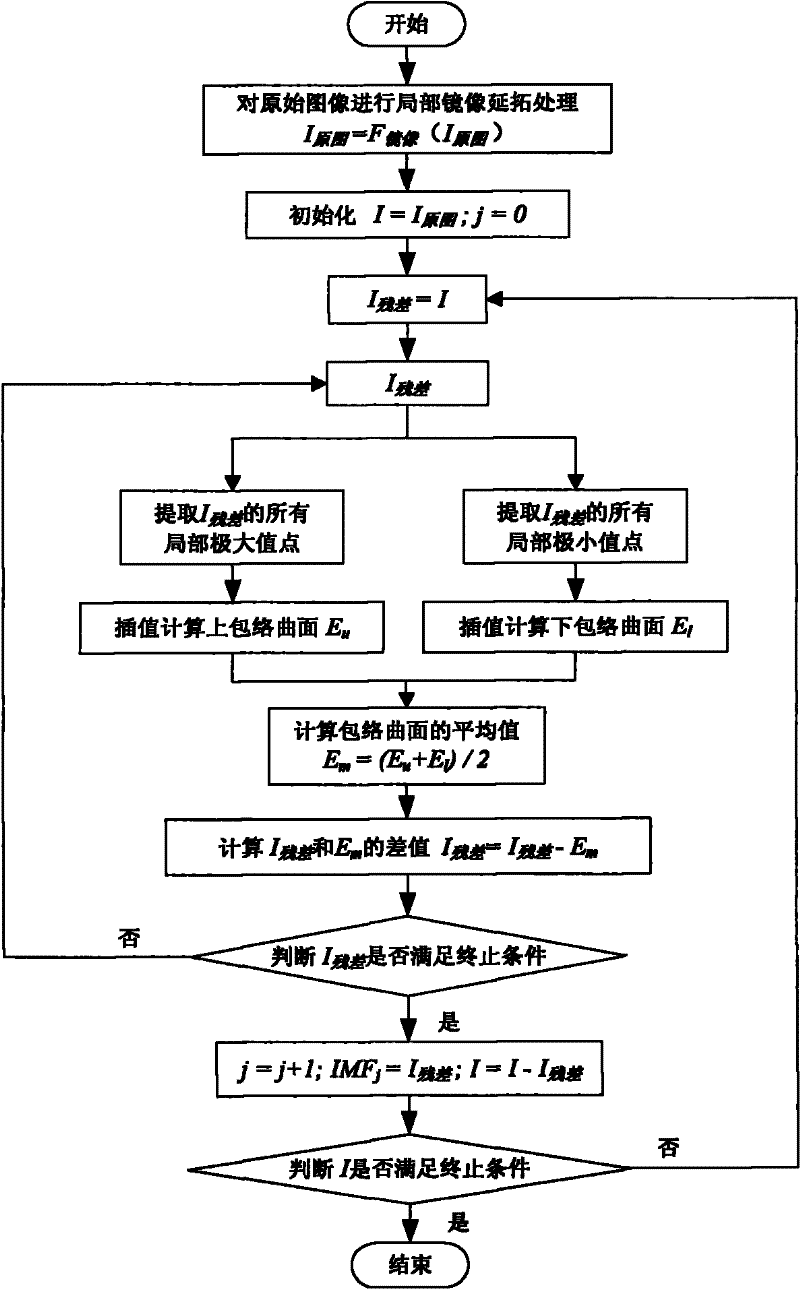
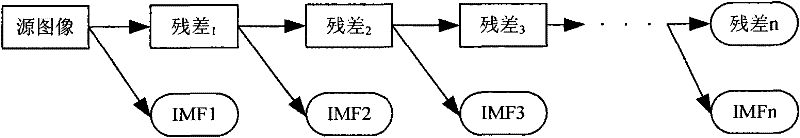
[0080] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention first processes the source image X 1 , X 2 ,...,X n Carry out two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition separately to obtain n-level IMF components and a residual component of each source image; perform fusion processing on all levels of IMF components according to the local significance criterion; use PCA method to perform fusion processing on the residual components; The fused IMF components and residual components of all levels are reversely reconstructed to obtain the final fused image.
[0081] The concrete implementation of the present invention is as follows:
[0082] 1. Perform two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition processing on multiple collected microscopic images
[0083] The BE...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com