Positioning method for fixing T steel through magnetic force
A technology of magnetic fixing and positioning method, which is applied in the processing of building materials, the preparation of building components on site, the connection of formwork/template/work frame, etc. Complicated problems, to achieve the effect of preventing slurry leakage, facilitating mold removal, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
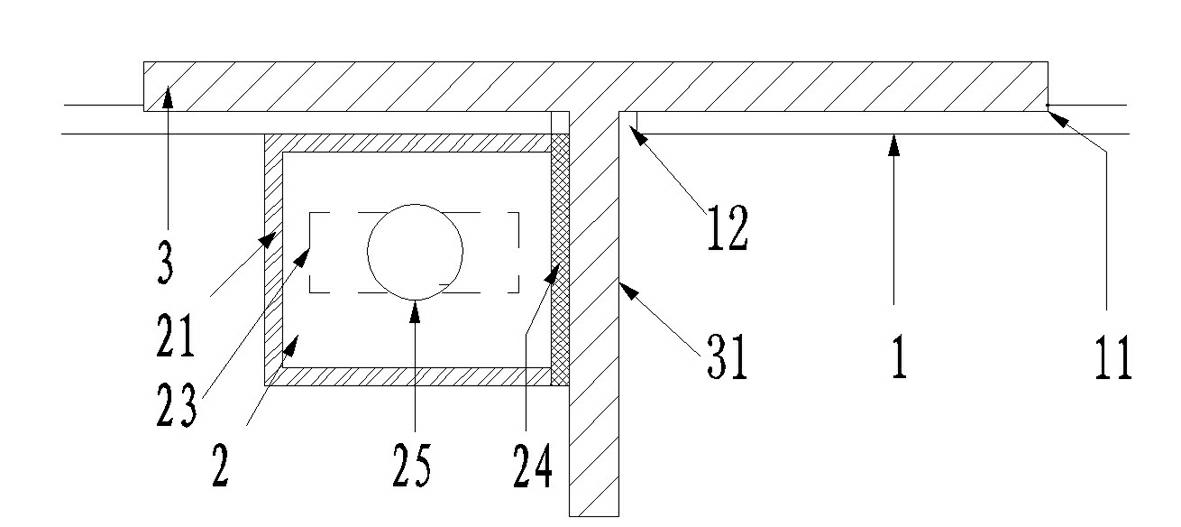
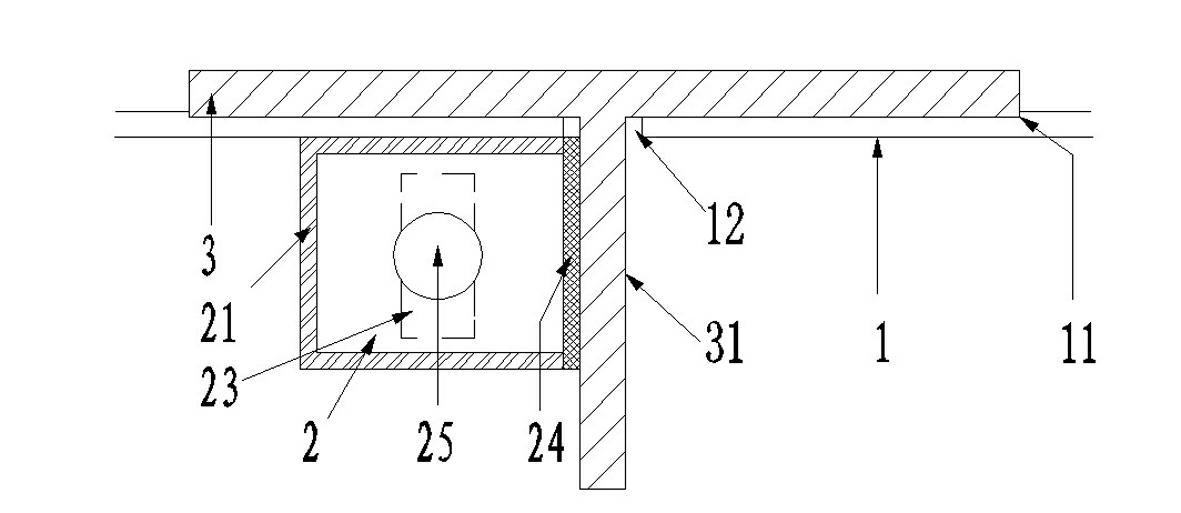
[0027] see Figure 1-2 , in the first embodiment, the magnetic fixing device is a magnetic box 2 . The magnetic box 2 is composed of a box body 21 , a rotating fixture 22 , a magnet 23 and a magnetic switch 25 . Wherein, the magnet 23 may be a bar-shaped or cylindrical permanent magnet. The box body 21 is fixedly welded on the outer side of the T steel 3 near the hole 12. When the T steel 3 is inserted into the steel mold 1, one side of the box body 21 is attached to the web 31 of the T steel 3, and the box body 21 is connected to the T steel 3 The attached side is the base 24 of the magnetic box 2 . The material of the base 24 is a soft magnetic material. The so-called soft magnetic material is a magnetic material with low coercivity for magnetic induction and magnetic polarization. It can achieve maximum magnetization with the smallest external magnetic field, and is easy to magnetize and demagnetize. Such as iron-silicon alloy (silicon steel sheet) and various soft ferri...
Embodiment 2
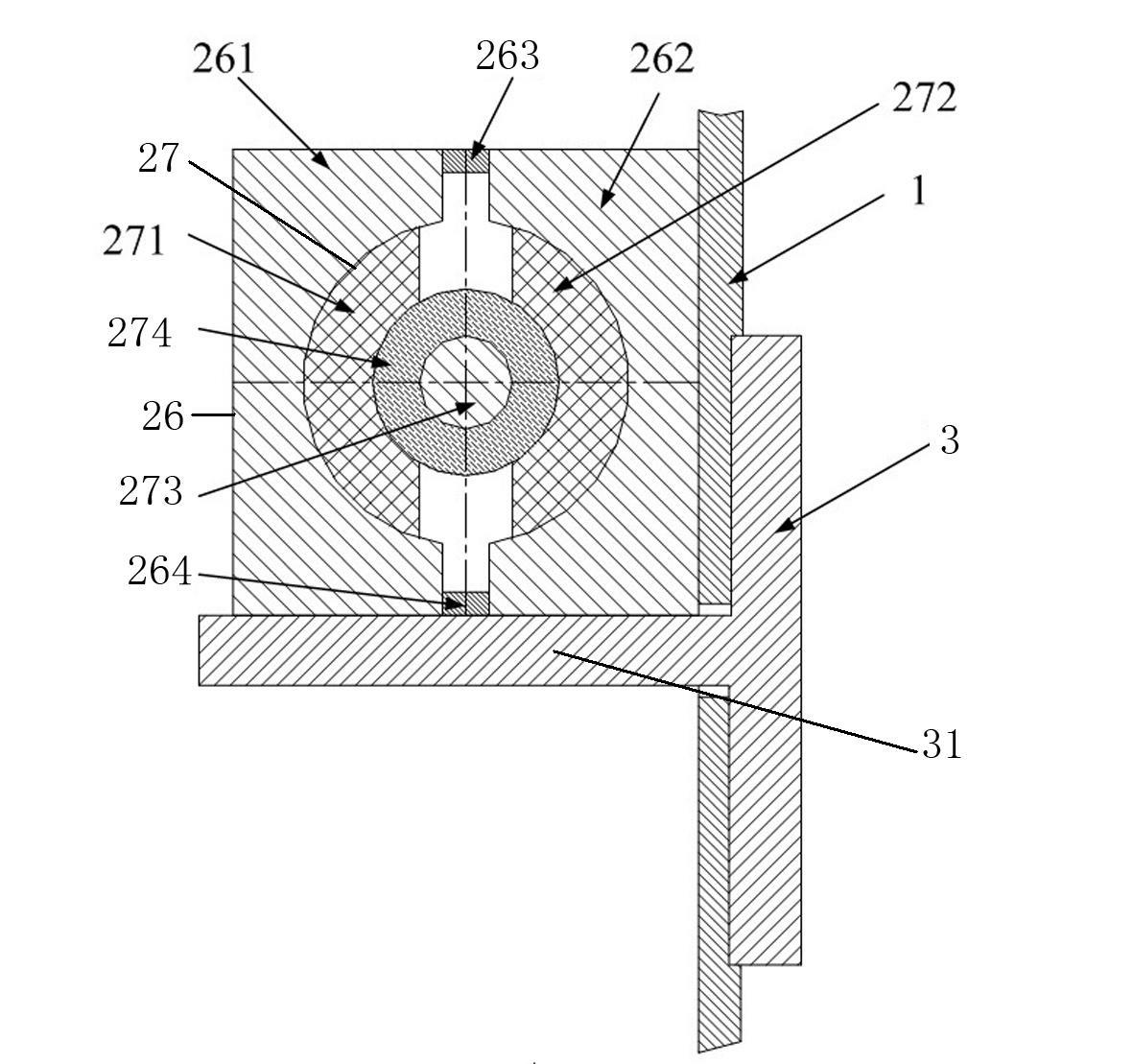
[0032] see Figure 3-4 As shown, in the second embodiment, the magnetic box 2 is composed of a shell 26 with a cylindrical cavity inside and a core 27 movably fitted in the shell 26 . Wherein, the housing 26 is a rectangular parallelepiped-shaped Hafur structure, which is composed of magnetically permeable half bodies 261 , 262 and two non-magnetically permeable bodies 263 , 264 . The inner sides of the two magnetically conductive halves 261, 262 have arc-shaped grooves. The upper and lower raised ends of the grooves are the end faces in the usual Hafur structure. The ends of the two magnetically conductive halves 261, 262 are Two non-magnetic conductors 263, 264 are fixedly connected to form a whole. The split plane of the Harfur structure is perpendicular to the web 31 of the T-steel 3 . The core 27 is composed of a magnet 273 and magnetically conductive rotors 271, 272 symmetrically fixed on the outside of the two magnetic poles of the magnet 273. The two rotors 271, 272 ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] see Figure 5 In this embodiment, the structure of the magnetic box 2 is basically the same as that of the first embodiment, and it also has a base 24 that is easily magnetized. The difference is that the permanent magnet and the rotating device are replaced by an electromagnet 275, and the electromagnet 275 is fixed in the box body 21 , by starting the switching power supply 276 to generate a magnetic field to magnetize or demagnetize the base 24, the effect of magnetic attraction and positioning of the above-mentioned magnet 23 can also be achieved. This kind of structure can be mainly applied in large steel components, especially when the permanent magnet cannot meet the magnetic force requirements.
[0038] For the connection positioning structures of the above three embodiments, the calculation of the connection strength is as follows:
[0039] During the pouring process, T-steel 3 is mainly subjected to three forces, namely, the vibration force of the vibrating r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Remanence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturation magnetic induction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com