Vertical shaft wind turbine with lifting power and resistance complementary adjustment
A vertical axis, wind turbine technology, applied in the direction of wind turbines at right angles to the wind direction, wind turbines, control of wind turbines, etc., can solve problems such as mechanical damage of fans, low wind speed, and generator output power decline, and achieve wind energy utilization The effect of increasing the wind speed, widening the wind speed range, and increasing the upper limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
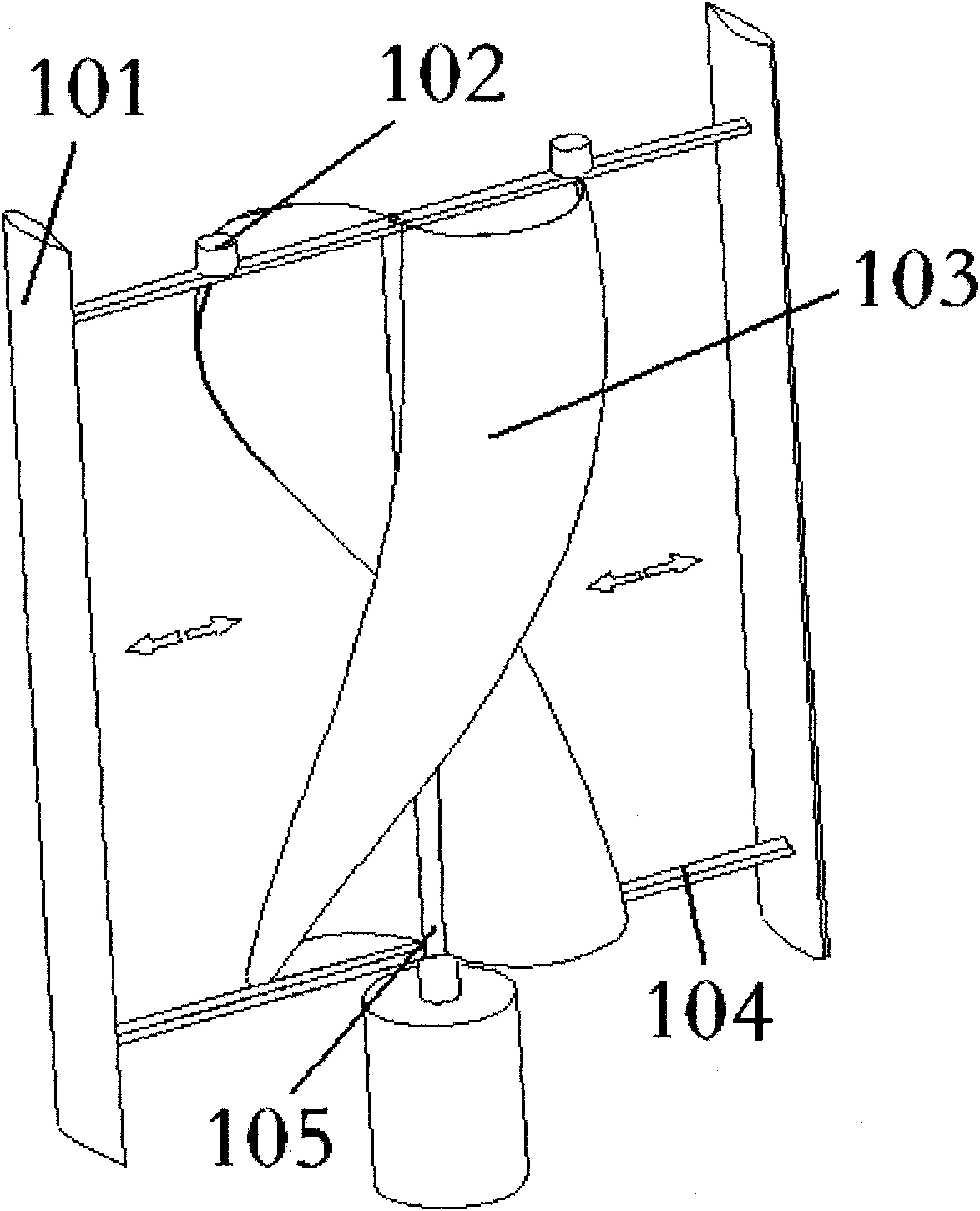
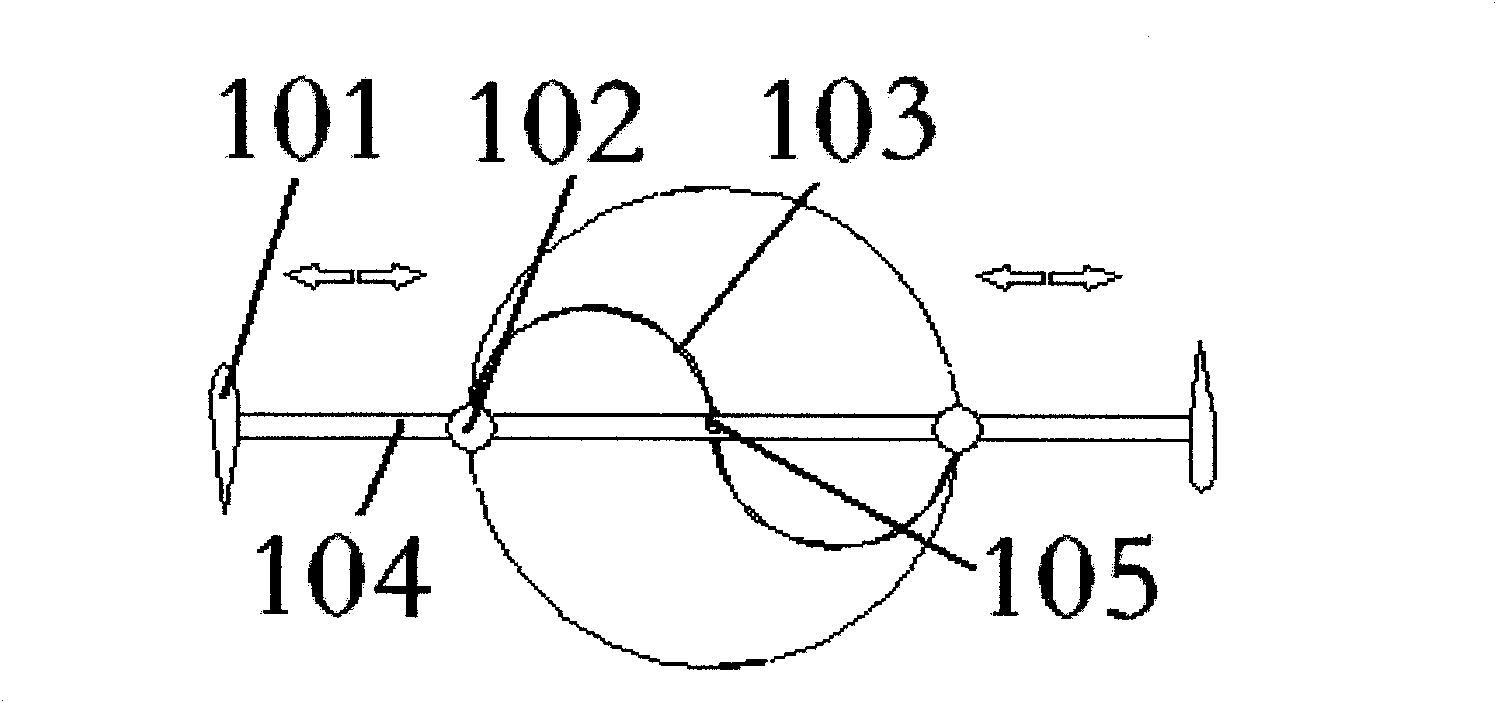
[0043] Embodiment 1 is an example of a vertical-axis wind turbine in which the helical drag-type blades and lift-type blades are complementary adjusted, and its structure is as attached figure 1 , 2 shown.
[0044] In this embodiment, the helical resistance blades 103 and the lift blades 101 are symmetrically distributed in pairs. The lift-type blade 101 is arranged on the outermost end of the beam 104 , and the resistance-type blade 103 can be displaced along the beam 104 between the rotating shaft 105 and the lift-type blade 101 , and its displacement power comes from the resistance-type blade displacement driving mechanism 102 . attached figure 1 , 2 The double-headed arrows in indicate that the resistance blade 103 can be displaced along the support beam 104 .
[0045] In the wind turbine of this embodiment, in order to obtain greater starting power under low wind speed conditions, the helical resistance blades 103 are displaced radially outward along the fan shaft 105...
Embodiment 2
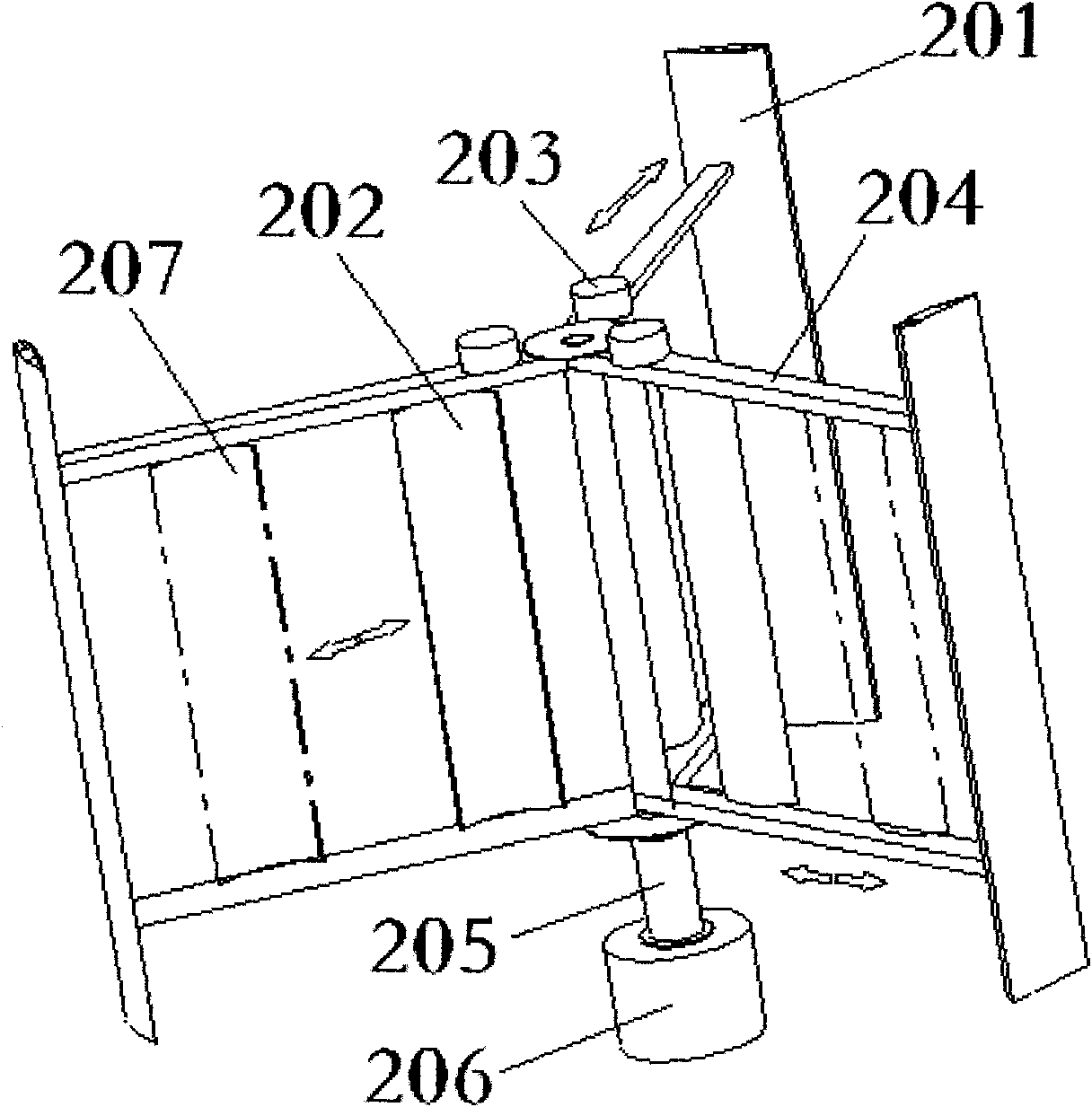
[0050] The second embodiment is an example of a vertical axis wind turbine in which the straight planar resistance blades and the lift blades are complementary adjusted, and its structure is as attached image 3 , 4 shown.
[0051] This embodiment is also a wind power engine in which lift-type blades and resistance-type blades are complementary and adjusted. The displacement between the lift-type blades 201 is powered by the resistance-type blade displacement drive mechanism 203 . attached Figure 9 , 10 The different positions of the drag vanes 207 are indicated by dotted lines in .
[0052] In the fan of this embodiment, under the condition of low wind speed, in order to obtain greater starting power, the resistance blades 202 are displaced radially outwards along the fan shaft. Inwardly displaced, so that within a relatively wide range of wind speeds, the lift-type blades rotate at a linear speed three to five times higher than the wind speed under the condition of low...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The three structures of this embodiment are as attached Figure 5 , 6 , 7, 8 shown.
[0057] This embodiment is also a wind power engine in which lift-type blades and resistance-type blades are complementary and adjusted. In this embodiment, the resistance-type blades 302 are in the shape of a straight plate. Between beams 304 and near the lift blade 301, the major axis of the resistance blade 302 is parallel to the fan shaft 305 and the major axis of the lift blade 301. Driven by the resistance blade angle drive mechanism 303, the resistance blade 302 can rotate around its long axis at any angle between zero and ninety degrees, thereby changing the size of its windward area.
[0058] In this embodiment, the fan in this embodiment is under the condition of low wind speed, in order to obtain a larger starting power for the fan, the resistance-type blades are in the largest windward area, that is, the resistance-type blades are parallel to the plane formed by the upper ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com