Method and device of wirelessly outputting thermoelectric force signal for multi-point temperature measuring of rotator
A thermoelectric potential signal, multi-point temperature technology, applied in the direction of auxiliary devices, measuring/indicating equipment, turning equipment, etc., can solve the problems of complex structure, difficulty in fidelity of thermoelectric signal output, and affecting measurement accuracy, so as to achieve simple device and avoid The effect of high-speed rotating centrifugal force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the scope of protection claimed by the present invention is not limited to the scope described in the embodiments.
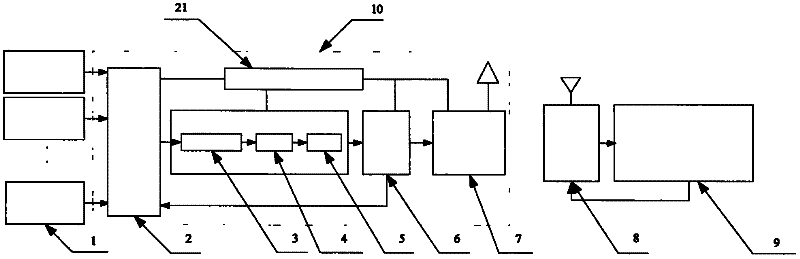
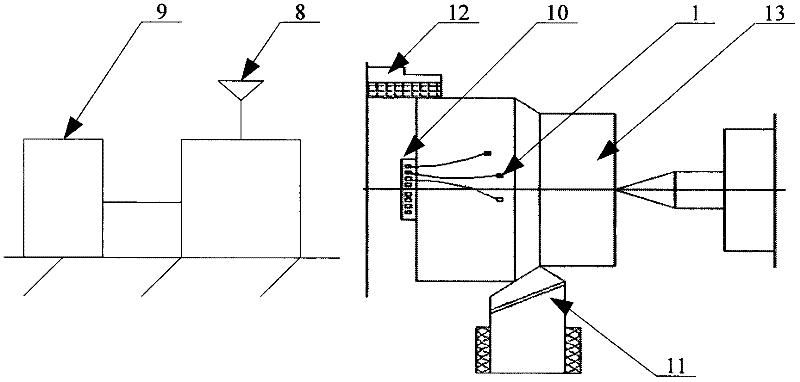
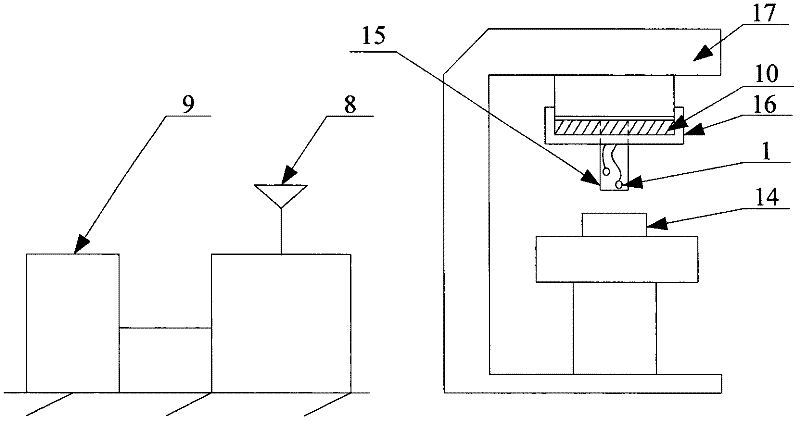
[0021] Such as figure 1 As shown, a wireless output device for measuring thermoelectric potential signals at multiple points on a rotating body includes a K-type thermocouple 1, a thermoelectric potential signal acquisition and transmission module 10, a wireless receiving module 8 and a PC 9; a thermoelectric potential signal acquisition and transmission module 10 includes multi-channel electronic switch 2, amplifier circuit 3, filter circuit 4, A / D conversion circuit 5, CPU6, wireless transmitting module 7 and battery 21, multi-channel electronic switch 2, amplifier circuit 3, filter circuit 4, A / D The conversion circuit 5 and the CPU6 are sequentially connected by signals, and the CPU6 is also respectively connected with the multi-channel e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com