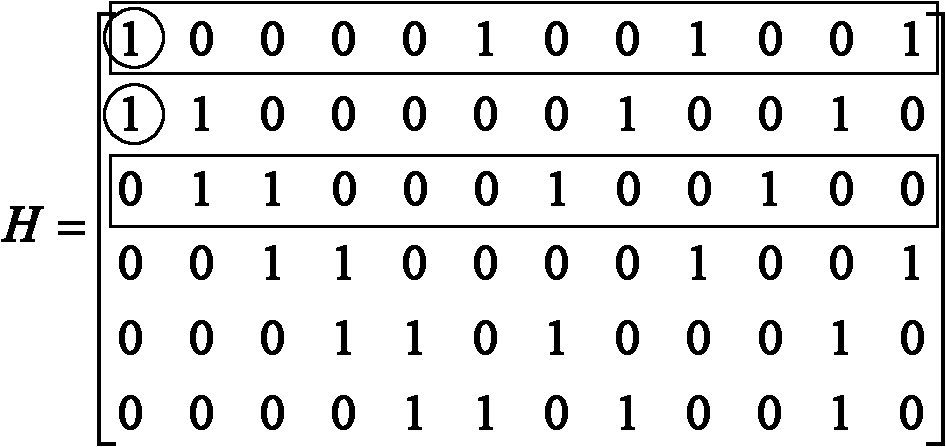Method for constructing LDPC (low density parity check) codes based on row-column combined iterative decoding
An LDPC code and joint iteration technology, applied in the field of information, can solve the problems of not fully exploiting the high-speed performance of the row-column joint iterative decoding algorithm, unable to obtain the LDPC code set, and restricting the decoding speed, so as to improve the throughput and reduce the delay. , the effect of improving the decoding rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Embodiment 1, constructing LDPC code based on PEG algorithm
[0063] Include steps:
[0064] 1) Initialize the parameters of the LDPC code, including the dimension distribution function of code length N, code rate R, check matrix H;
[0065] 2) The elements of each row of the check matrix H are regarded as check nodes, and the elements of each column are regarded as variable nodes, and the arrangement order of the check nodes during operation is set;
[0066] 3) Utilize the Peg algorithm to construct the parity check matrix H of the LDPC code, constructing the H matrix includes the following steps:
[0067] (a) each row of the H matrix is regarded as a check node, each column is regarded as a variable node, and the bipartite graph of the initialization H matrix has m=N (1-R) check nodes and n=N variable nodes;
[0068] (b) Add m check nodes to the bipartite graph, add variable nodes one by one, and establish a connection path with qualified destination check nodes...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2, construct QC-LDPC code based on Block-PEG algorithm
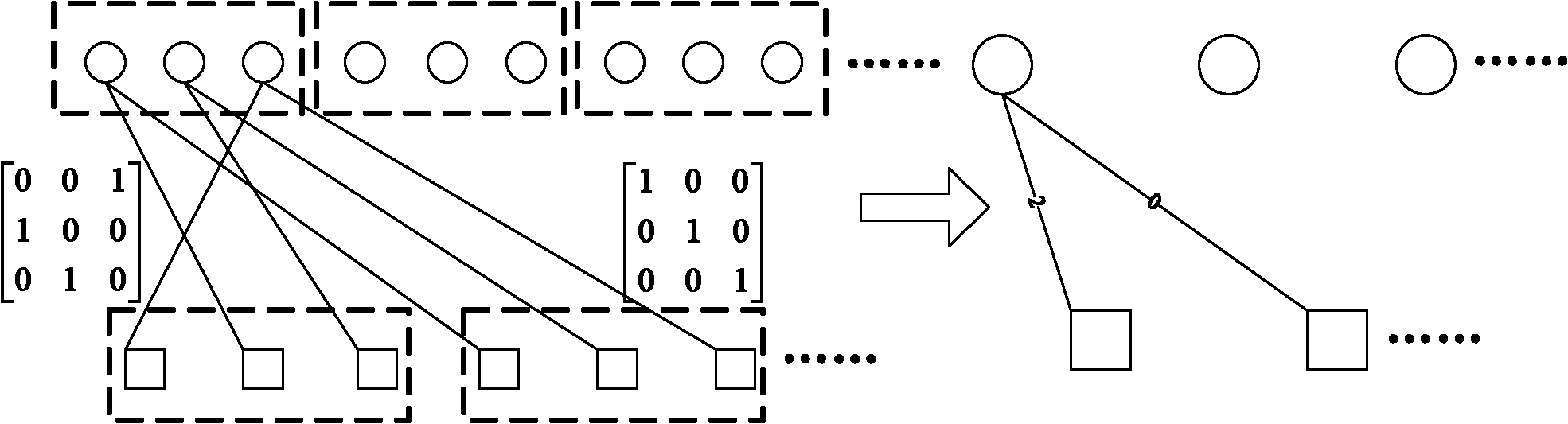
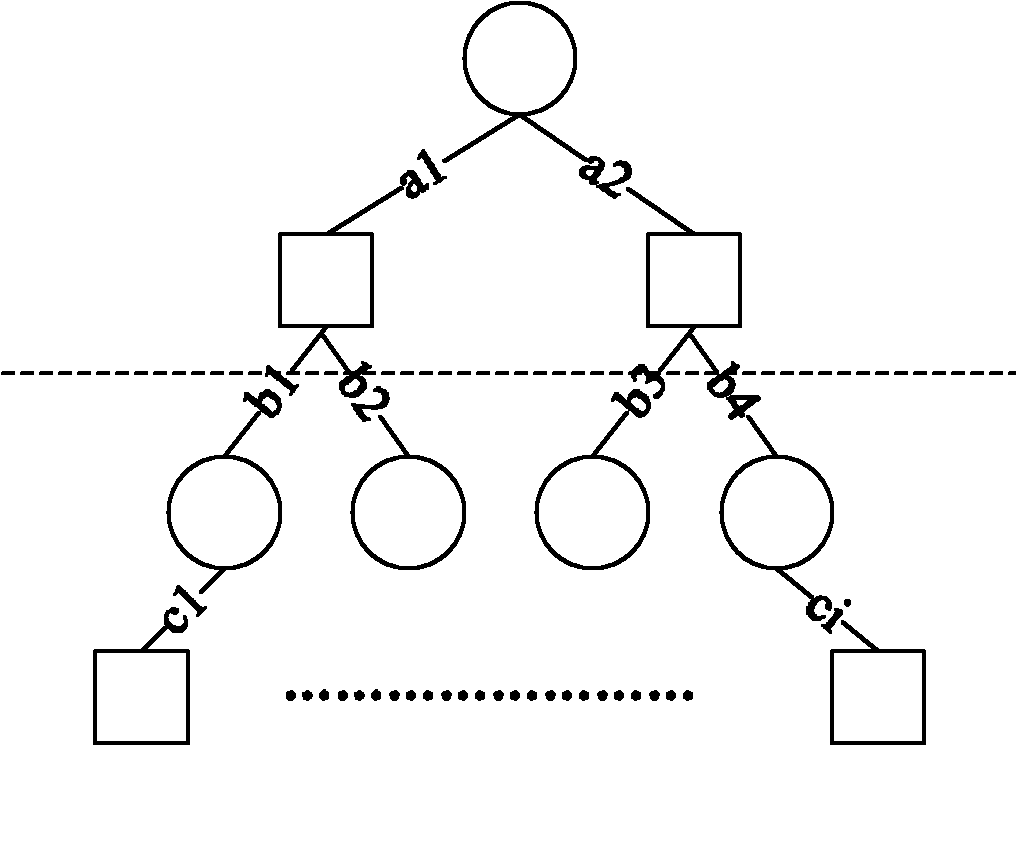
[0076] Since it is more commonly used to construct QC-LDPC codes based on the Block-PEG algorithm, the following introduces in detail the present invention based on the Block-PEG algorithm, a QC-LDPC code construction method given, and the LDPC code constructed by this method is in the row operation order The non-zero blocks in the upper two adjacent rows do not share one column at the same time, thereby solving the delay problem of data update between rows in the row-column combination decoder, and improving the decoding rate.
[0077] The process of constructing QC-LDPC code is the process of constructing its base matrix. The base matrix contains two key parameters of the QC-LDPC code: the position of each unit cyclic shift matrix and the corresponding cyclic shift offset. Therefore, the construction algorithm can be divided into two main steps: first, determine the position of the cyclic shift matri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com