Robot system
A robot system and robot technology, applied in the field of robot systems, can solve problems such as increased equipment costs and robots exceeding the limit range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
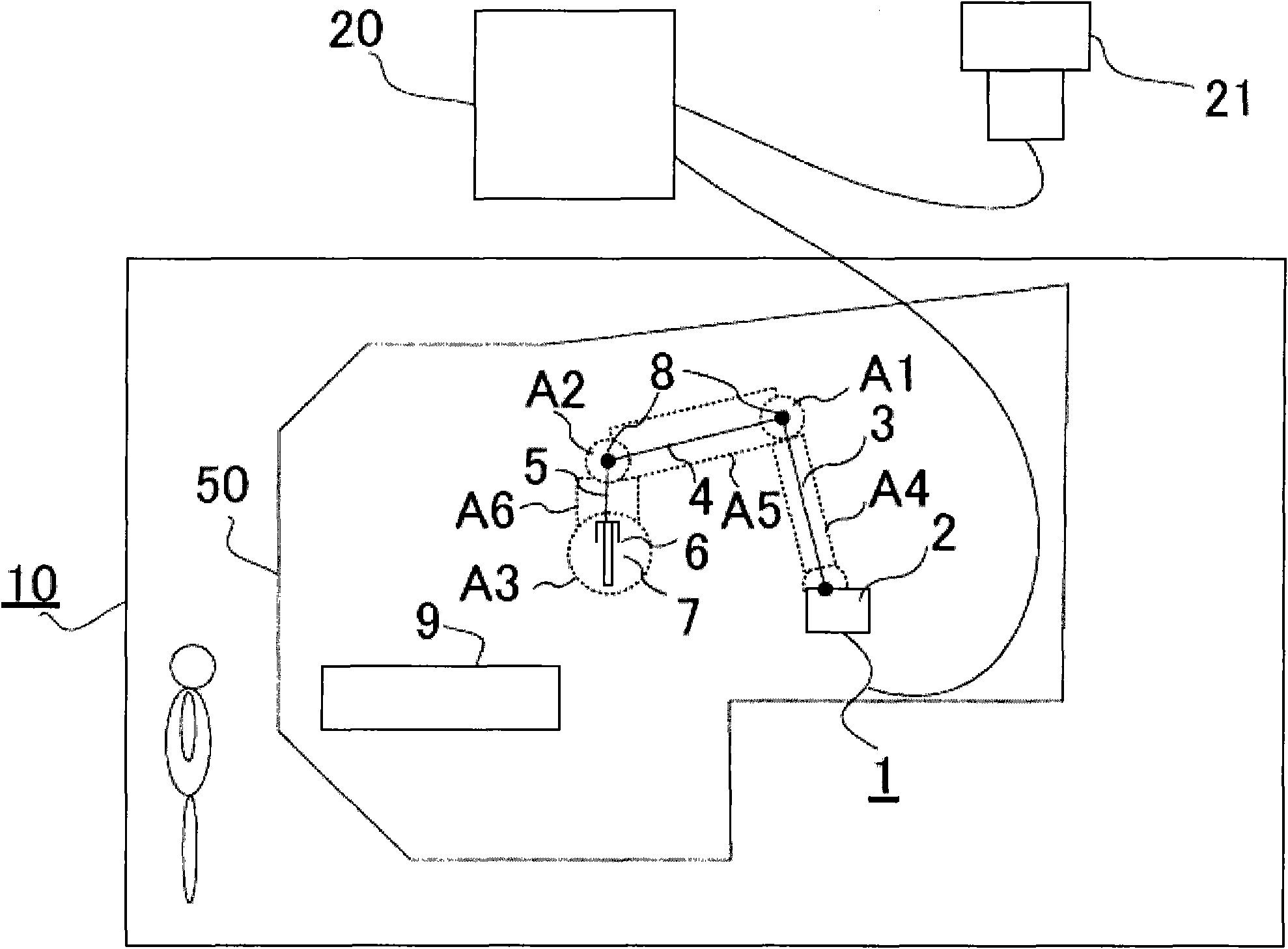
[0029] In this example, the robot 1 has a base 2 and three arms 3 , 4 , 5 . A tool 7 is provided on the arm 5 via a gripping device 6 . As the tool 7, a welding torch for arc welding, a torch for spot welding, a hand for carrying, and the like are attached. Joints 8 are used to connect arms 3, 4, and 5, respectively. The workpiece 9 is an object to be welded, a conveyed object, or the like. For example, in the safety fence 10, welding of the workpiece|work 9 and assembly work of a conveyance are performed.
[0030] A necessary signal is sent from the control device 20 to the robot 1, and the arms 3, 4, 5 perform predetermined movements according to a predetermined operation program, and the gripping device 6 or tool 7 moves along a desired trajectory.
[0031] A teaching tool 21 is connected to the control device 20, and performs teaching to the robot 1, rewriting of work programs, and the like.
[0032] Before the robot is introduced, installed, and operated, the virtual ...
Embodiment 2
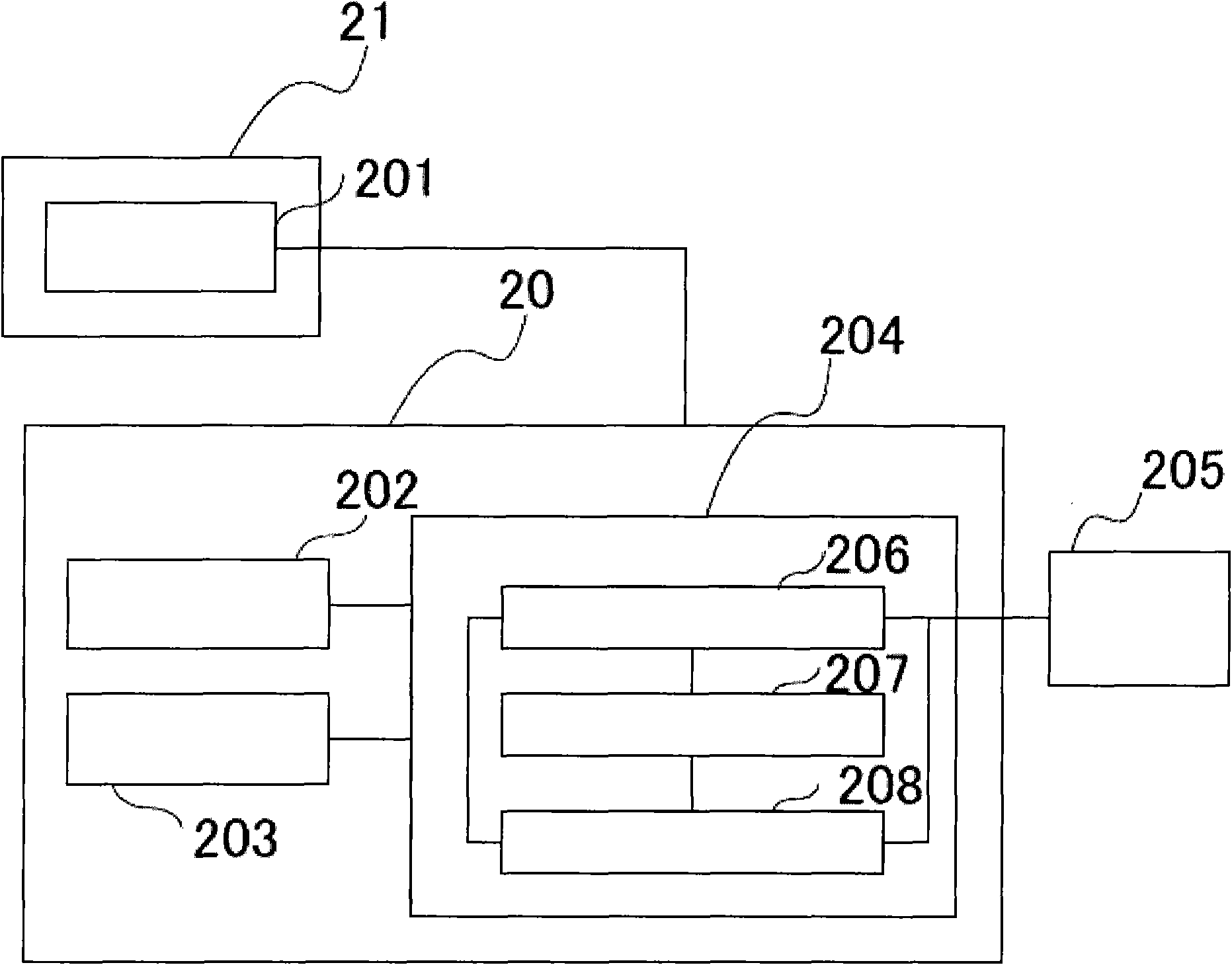
[0082] As the configuration of Example 2, using Figure 6 An embodiment in which the aforementioned monitoring and stop control devices are made independent will be described.
[0083] Figure 6 is true figure 2The configuration of the operating region monitoring device 601 is added to the system. The operating area monitoring device 601 obtains the current position of the robot (the position of the workpiece or tool) through the drive unit 205 in each specified monitoring period according to the position of the motor 605 of each axis. For the current position of the robot, it touches and monitors the position on the virtual safety barrier. Contact with the virtual safety barrier is checked in section 604 . In addition, based on the motor position 605 information read by the current position detection unit 602 , the coasting predicted position calculation unit 603 calculates the position where the motor coasts and stops when the emergency stop is performed at this point in...
Embodiment 3
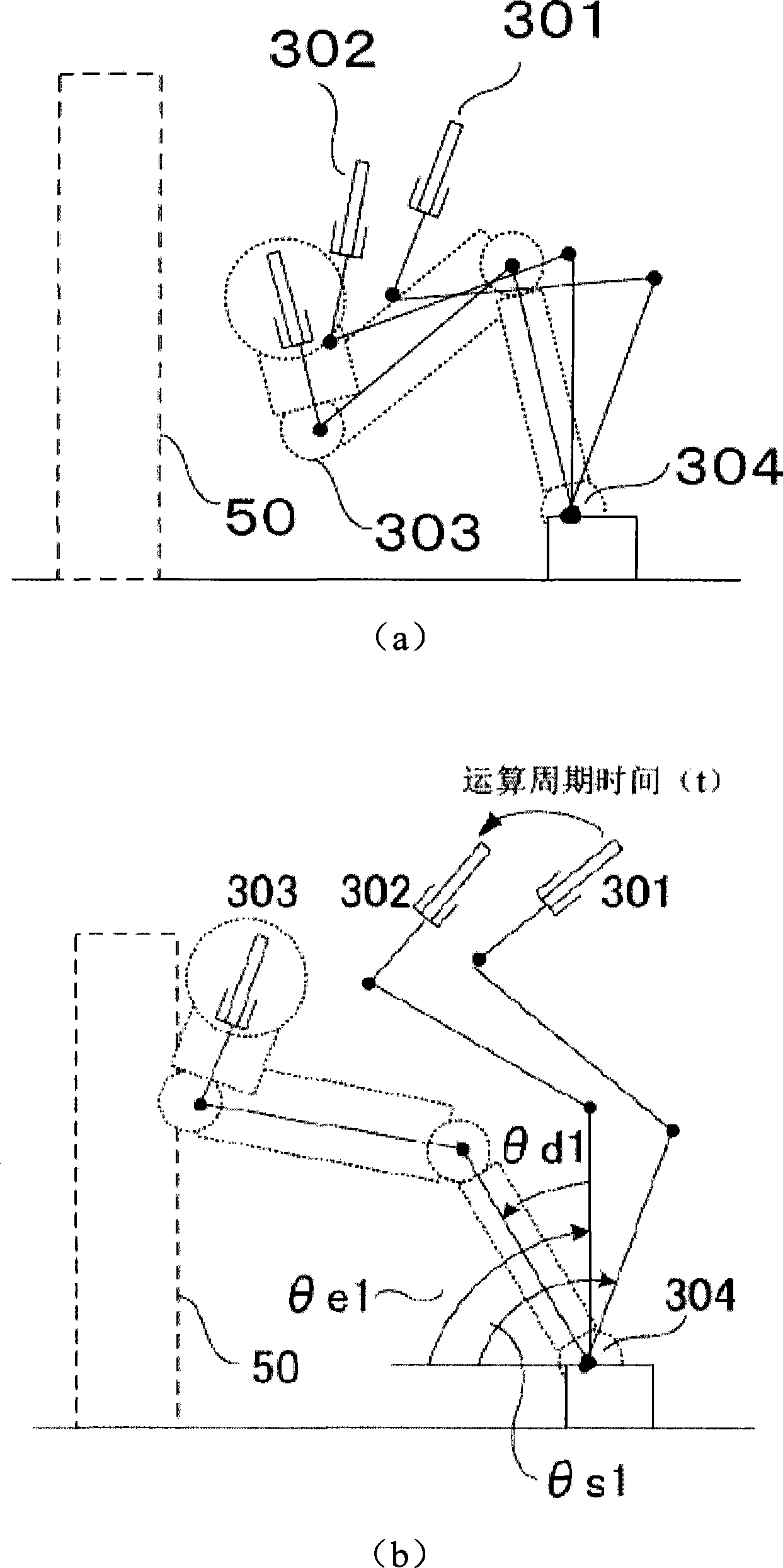
[0104] use Figure 8 A robot system including the robot motion limiting method and device of the third embodiment will be described. Mechanical safety devices such as mechanical limiters are installed on each axis of a general robot to limit the movement of each axis of the robot. On the other hand, instead of the mechanical limiter, it is possible to reduce the mechanical limiter by defining and monitoring the movable range 60 of each axis.
[0105] Figure 9 It is a diagram showing another structure of the third embodiment, and an embodiment in which the operation restriction of each axis is performed in the above-mentioned monitoring and stop control device will be described.
[0106] The next target position is calculated in the next target position calculation unit 206 . With respect to the next target position obtained here, it is checked in the movement range limit monitoring unit 901 of each axis whether the movement exceeds the movement range 60 of each axis. In a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com