Complement factor h-based assays for serum bactericidal activity against neisseria meningitidis
A Neisseria and bactericidal technology, which is applied in the field of identification of the bactericidal activity of Neisseria meningitidis serum based on complement factor H, and can solve problems such as the actual mechanism of vaccine-induced antibody protection that cannot be accurately or completely reflected.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
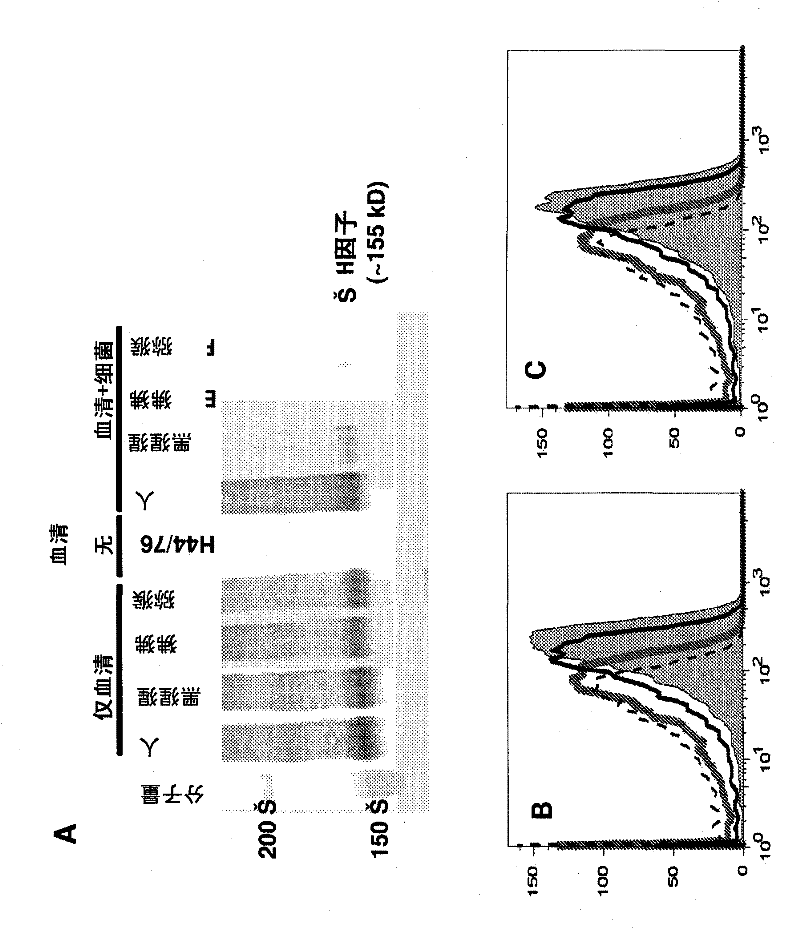
[0153] Example 1: Species specificity of binding of primate fH to N. meningitidis
[0154] Polyclonal anti-human fH recognizes fH in heat-inactivated sera from humans as well as non-human primates ( figure 1 A, Lane labeled ("serum only")), thus can be used to test the binding of primate fH to bacteria. Binding of fH to strain H44 / 76 in primate heat-inactivated serum is shown in the lane labeled "serum + bacteria". Heat treatment does not affect the binding properties of fH (Jarva, H. et al. (2002) J Immunol 168:1886-1894; Ram, S. et al. (1998) J Exp Med 188:671-680). Bacteria incubated with human serum (positive control) showed the greatest fH binding, whereas fH binding was at low levels in chimpanzee serum and undetectable in baboon and rhesus monkey sera.
Embodiment 2
[0155] Example 2: Rat or rabbit fH does not compete with human fH for binding to Neisseria meningitidis
[0156] Indirect flow cytometric assays were used to determine whether heat-inactivated rat or rabbit fH (in their respective heat-inactivated sera) competed with biotinylated human fH for binding to the same ligand on live N. meningitidis. Addition of 40% heat-inactivated rat or rabbit serum (highest concentration tested) did not inhibit binding of biotinylated human fH to N. meningitidis, whereas addition of 40% heat-inactivated human serum as a positive control did Binding of biotinylated human fH ( figure 1 B and 1C). These data indicate that rat and rabbit fH bind different ligands on N. meningitidis than human fH. Although the possibility that the binding sites of rat and rabbit fH on meningococci differ from that of human fH cannot be ruled out, an amino acid sequence alignment of human fH, macaque fH, and rat fH (from the NCBI database) shows that , human and ma...
Embodiment 3
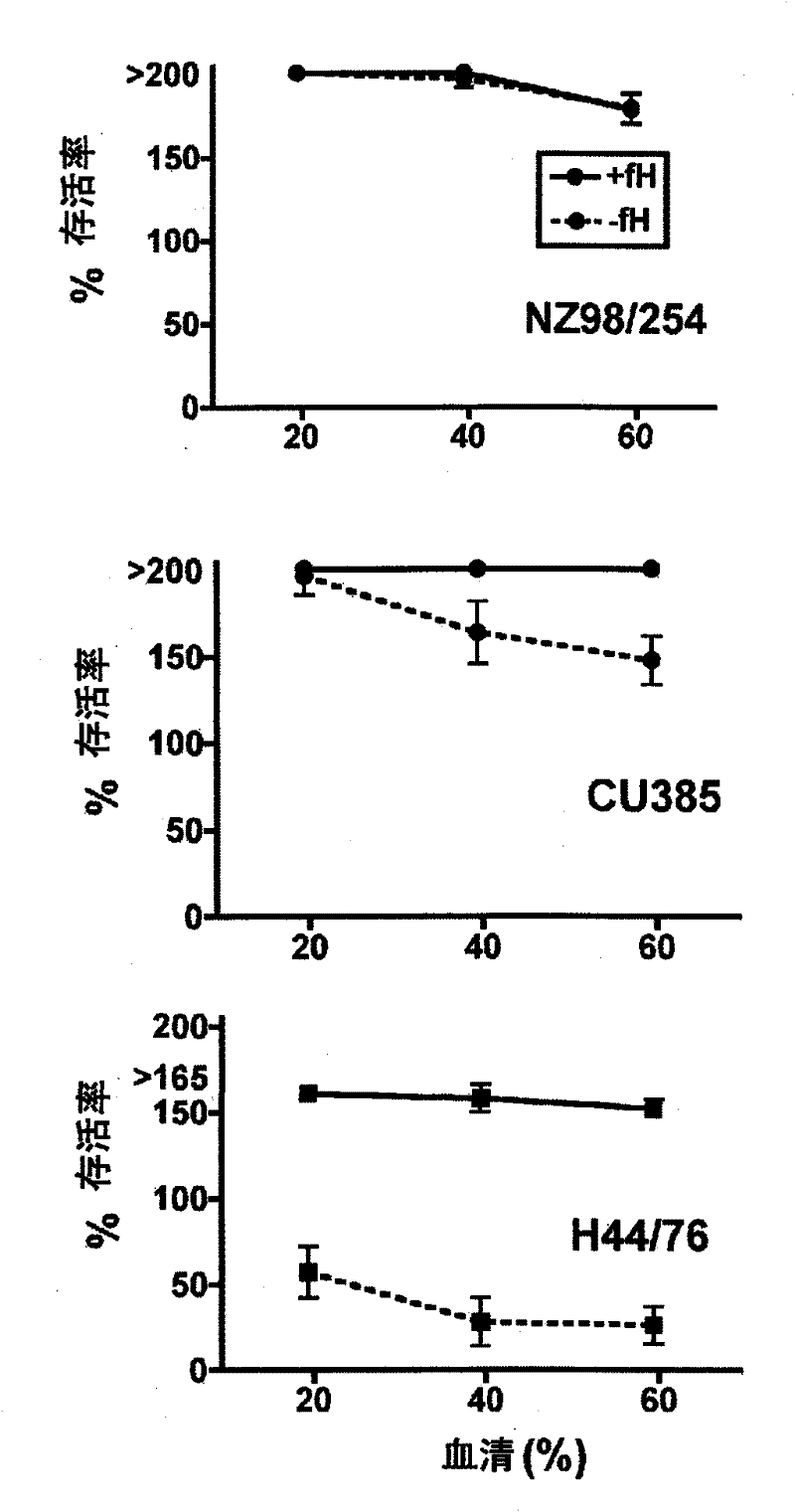
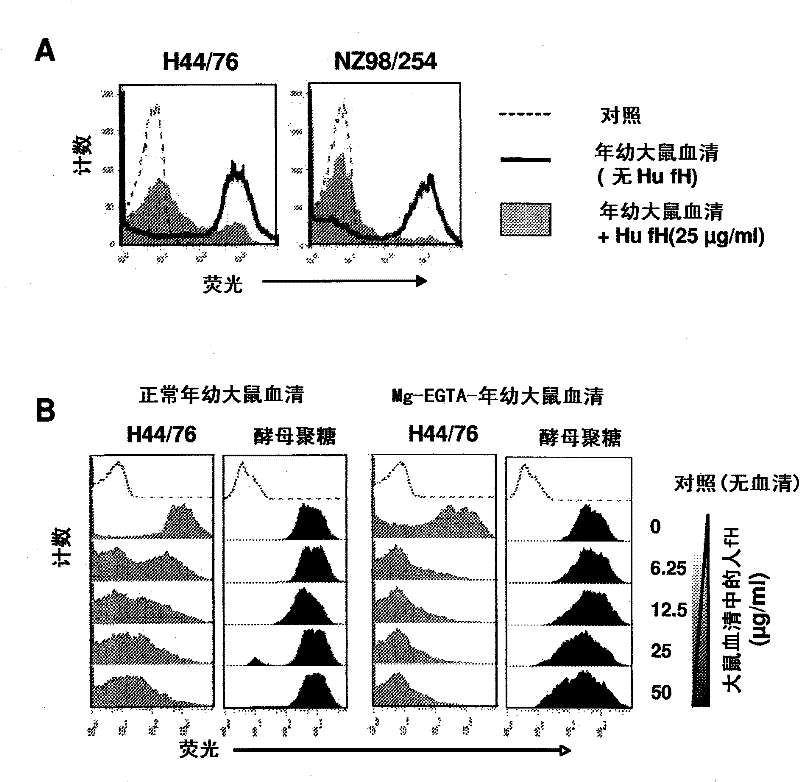
[0157] Example 3: Effect of Human fH Added to Juvenile Rat Serum on Neisseria meningitidis Survival
[0158] The effect of adding human fH to the sera of young rats was determined on the survival of three strains of N. meningitidis in a mixture incubated at 37°C for 1 hour ( figure 2 ). Each serum was tested at concentrations of 20%, 40% and 60%. When no fH was added, compared with their respective zero-time survival rates, the two strains NZ98 / 254 and Cu385 (respectively figure 2 The survival rate increased by more than 150% during the incubation period. In contrast, the third strain H44 / 76 survived at all three serum concentrations ( figure 2 lower graph) were reduced by 40% -60%. When human fH was added to the reaction at a concentration of 50 μg / ml, the corresponding survival rate of strain H44 / 76 was increased by >150% (e.g., 60% serum containing human fH compared to 26% survival without human fH The survival rate in was 152%, P<0.001). The survival of one of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com