After-test simulation method for inner and outer fault recognition of ultra-high voltage alternating-current power transmission line based on lumped parameter T model
A technology of UHV AC and concentrated parameters, which is applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., can solve the problems of poor setting of the setting value, difficult capture of traveling wave signals, and non-repeatable limitations, etc., and achieve excellent operation reliability and sensitivity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
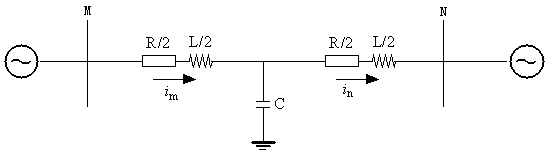
[0022] Example 1: 1000kV UHV AC transmission line (transmission system structure such as figure 1shown). The line is an eight-split conductor, using a distributed parameter model considering the influence of frequency variation (J.Marti line model according to frequency), the total length of the line is 400km, of which, , , . The C-phase ground fault (C-G) in the UHV AC transmission line area is 200km away from the M terminal, and the transition resistance is 10Ω.
[0023] The steps of the method for simulating and identifying faults inside and outside the UHV AC transmission line area after the test are as follows:
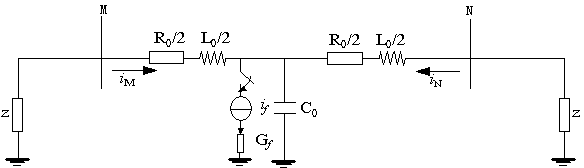
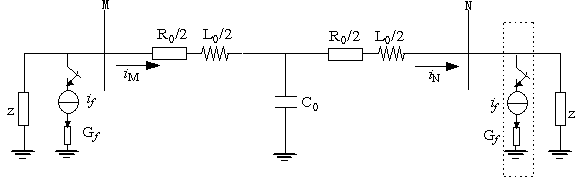
[0024] (1) After a fault occurs on the UHV AC transmission line, the start-up element of the measurement protection is activated, and within a short data window of 3 ms, the zero-sequence voltage on both sides of point M and N at both ends of the UHV AC transmission line is actually measured u M 、u N and zero sequence current i M 、i N (sampling fre...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: The structure and parameters of the UHV AC power transmission system are the same as Example 1. Phase C ground fault (C-G) occurs outside the UHV AC transmission line in the opposite direction, the transition resistance is 10Ω, the length of the short data window (time window) is 3ms, and the sampling frequency is 20kHz.
[0029] After the extra-high voltage AC transmission line has an external fault in the opposite direction, according to the same method as in Example 1, the zero-sequence voltage on both sides of point M and point N at both ends of the UHV AC transmission line is actually measured u M 、u N and zero sequence current i M 、i N , to calculate the analog current waveform and its correlation coefficient with the measured current waveform, we get =0.3002>0, based on which it is judged as an out-of-area fault.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: The structure and parameters of the UHV AC power transmission system are the same as in Example 1. Phase C ground fault (C-G) occurs outside the positive direction of the UHV AC transmission line, the transition resistance is 10Ω, the length of the short data window (time window) is 3ms, and the sampling frequency is 20kHz.
[0031] After the UHV AC transmission line fails, according to the same method as in Example 1, the zero-sequence voltage on both sides of the M point and N point at both ends of the UHV AC transmission line is actually measured u M 、u N and zero sequence current i M 、i N , to calculate the analog voltage waveform and its correlation coefficient with the measured current waveform, we get =0.6350﹥0, according to which it is judged as an out-of-area fault.
[0032] Principle of the present invention is:
[0033] 1. Short-window description of fault characteristics inside and outside the UHV AC transmission line area
[0034]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com