Static Wear Leveling Method and System for Solid State Disk
A wear-leveling, solid-state drive technology, applied in memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., can solve the problem of inability to guarantee the performance of wear-leveling algorithm by memory CPU time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
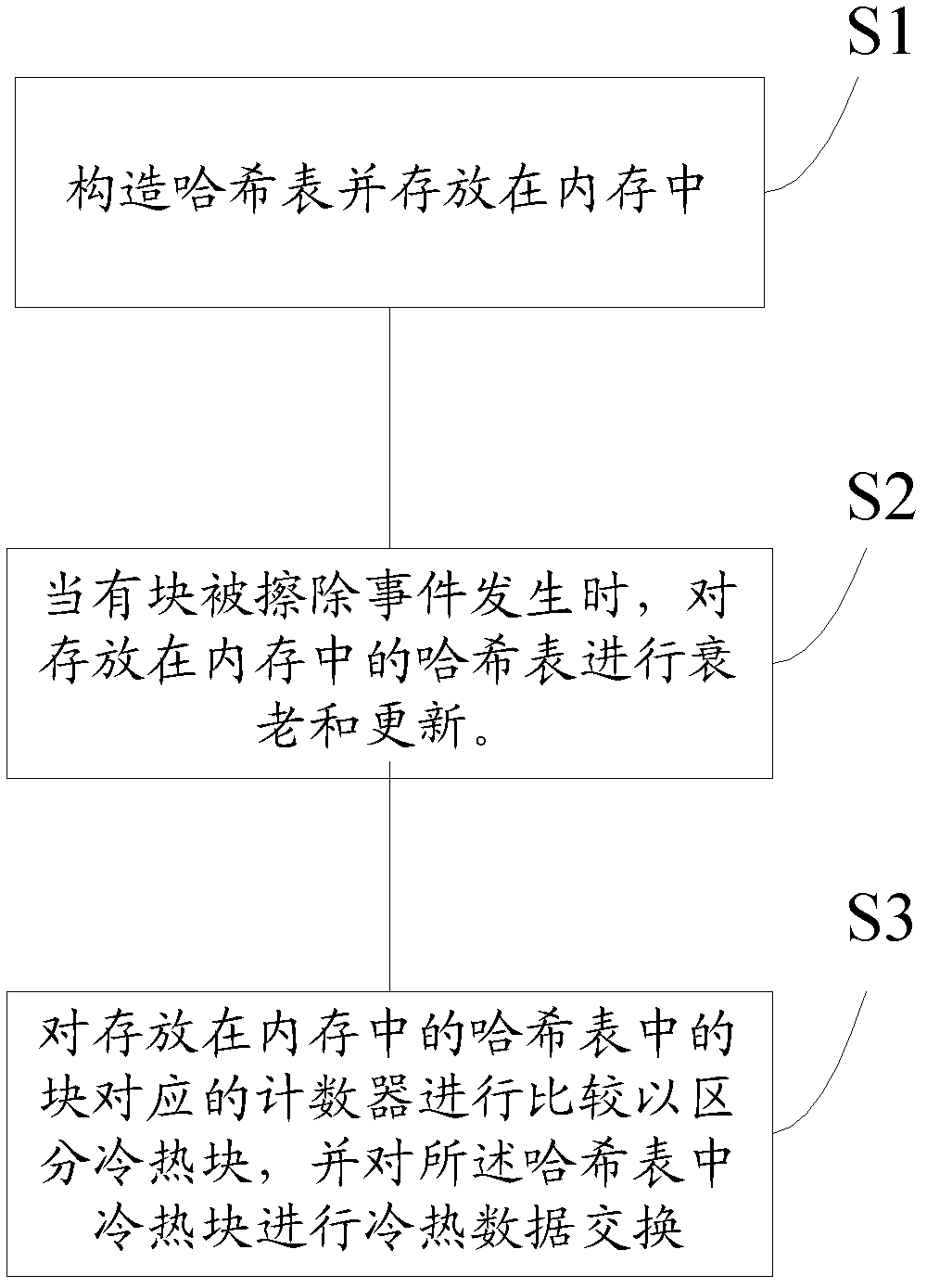
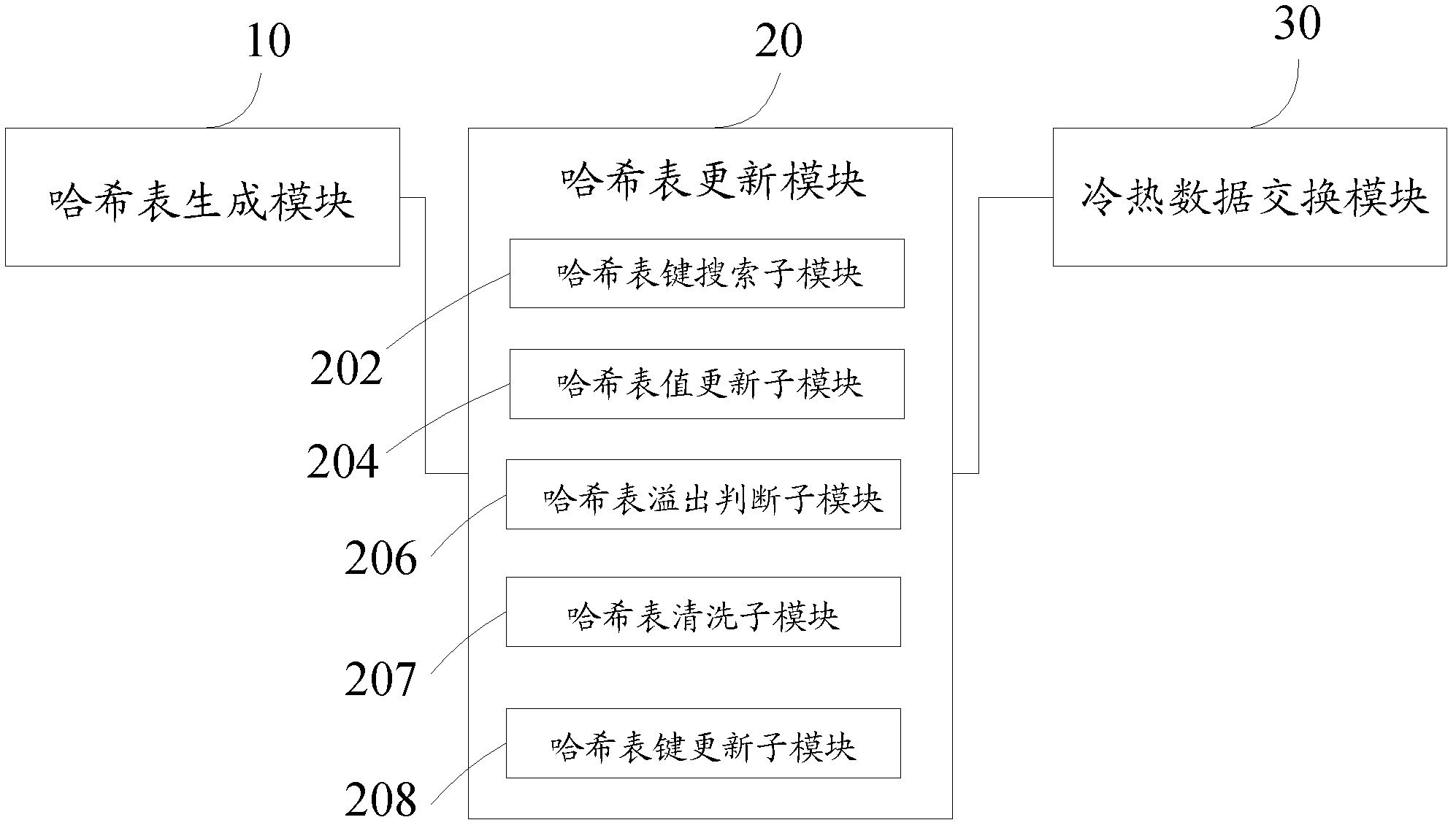
[0053] The storage technology and control algorithm of flash memory (flash memory) or SSD (Solid-State Drives) based on flash memory of the present invention adopt the least recent algorithm (LRU) statistics and processing of aging mechanism on the basis of hash table The hot and cold properties of the block and take corresponding actions to achieve the purpose of wear leveling. The invention is a wear leveling algorithm based on a hash table to overcome the problem that the cost of the previous wear leveling algorithm is too high or the cost is low but the performance cannot be guaranteed, and the wear leveling algorithm prolongs the life of the flash memory as much as possible while reducing the overhead.
[0054] The invention is based on the observation that in flash memory some blocks are frequently erased and need to be cooled, and some blocks which store cold data are rarely erased and need to be updated more often. Therefore, different from the previous implementation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com