A wireless channel allocation method based on cells along the train
A cell and wireless channel technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as resource shortage, and achieve the effect of avoiding waste and solving resource shortage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
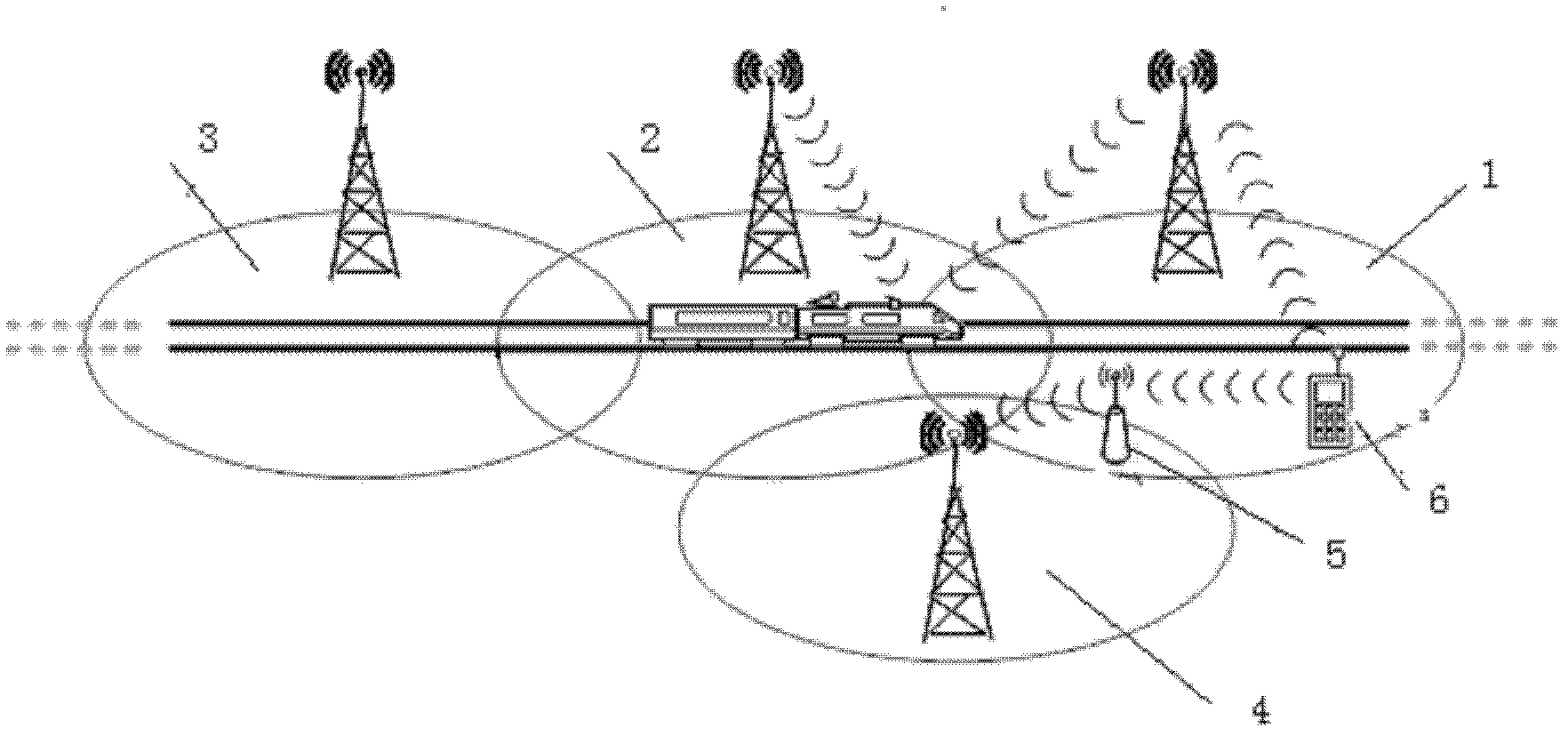
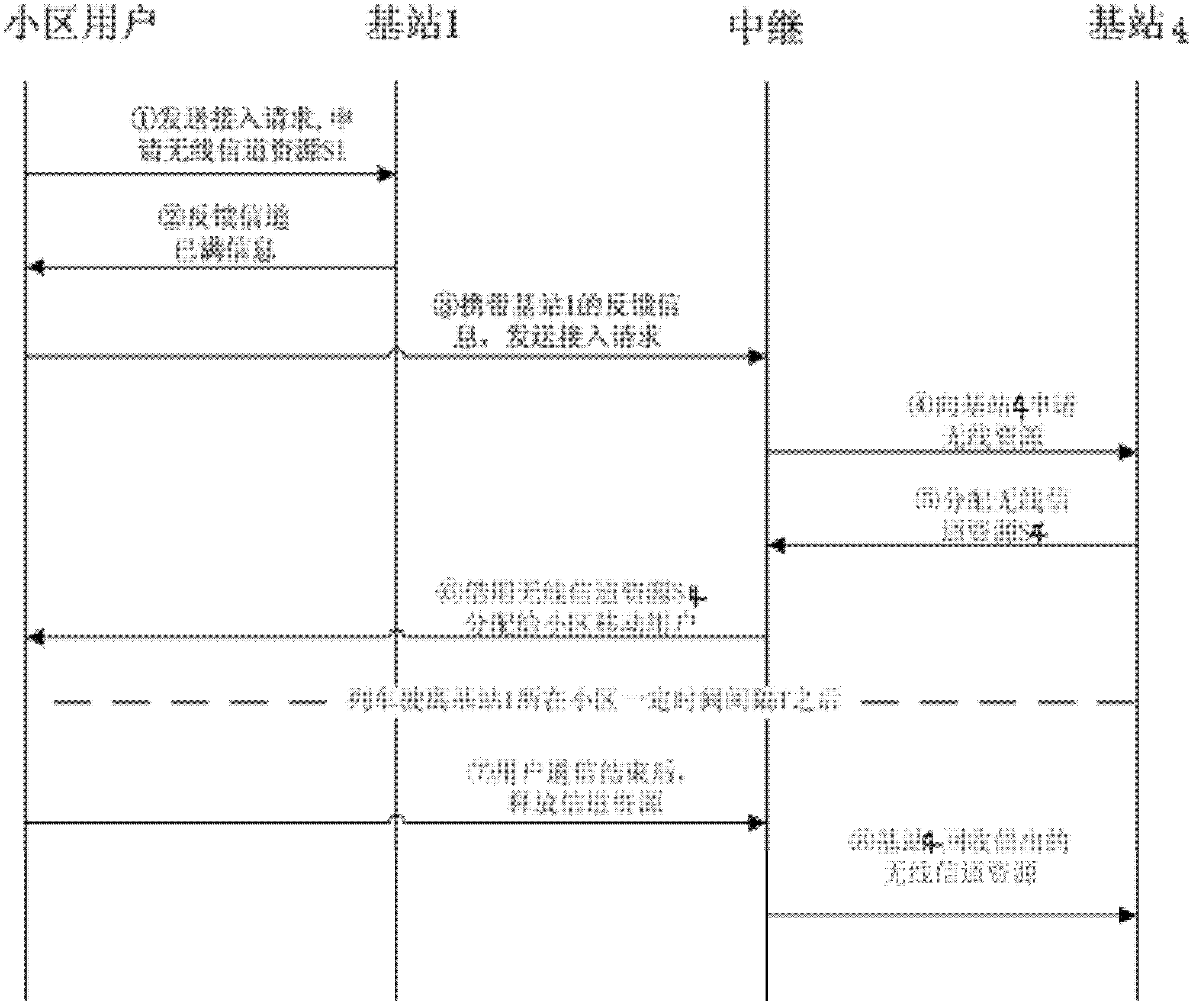
[0024] In the present invention, based on the train number, the cell type covered on the train running route is a linear cell, so the traveling direction is fixed, and combined with the train number to perform predictive wireless channel allocation. Specifically, since the route of each train is fixed, according to the train number, the list of cells that each train passes along the way within the control range of the network side can be stored in the network side database. When a train is about to leave, it needs to register the train number in the network, and the network side can know the districts that the train will pass along the way according to the train number.
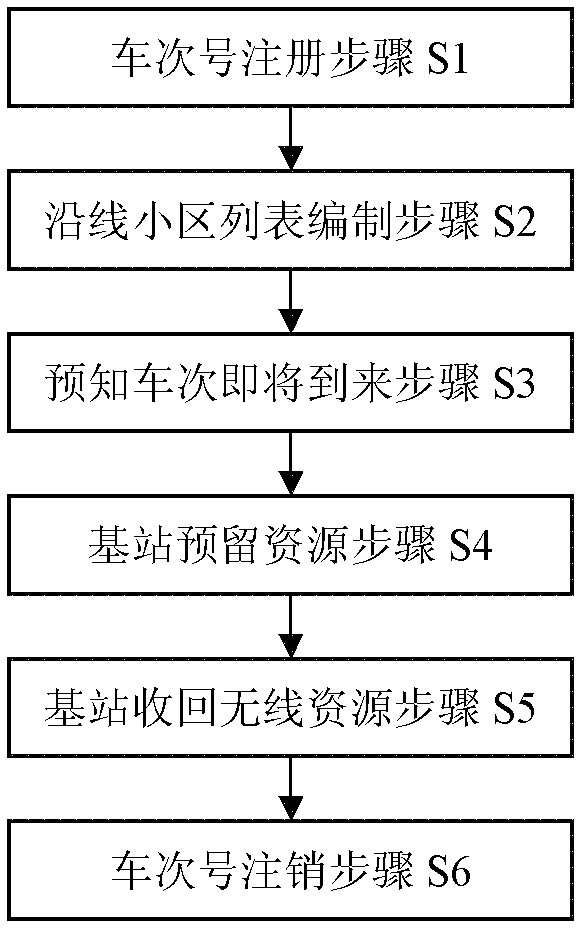
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for allocating wireless channels based on cells along the train, comprising the steps of:
[0026] (1) train number registration s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com