Desert planting structure, desert soil amendment method and planting method
A planting structure and desert technology, which is applied in botany equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, and land preparation methods, can solve the problems of poor vegetation planting effect and large water consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
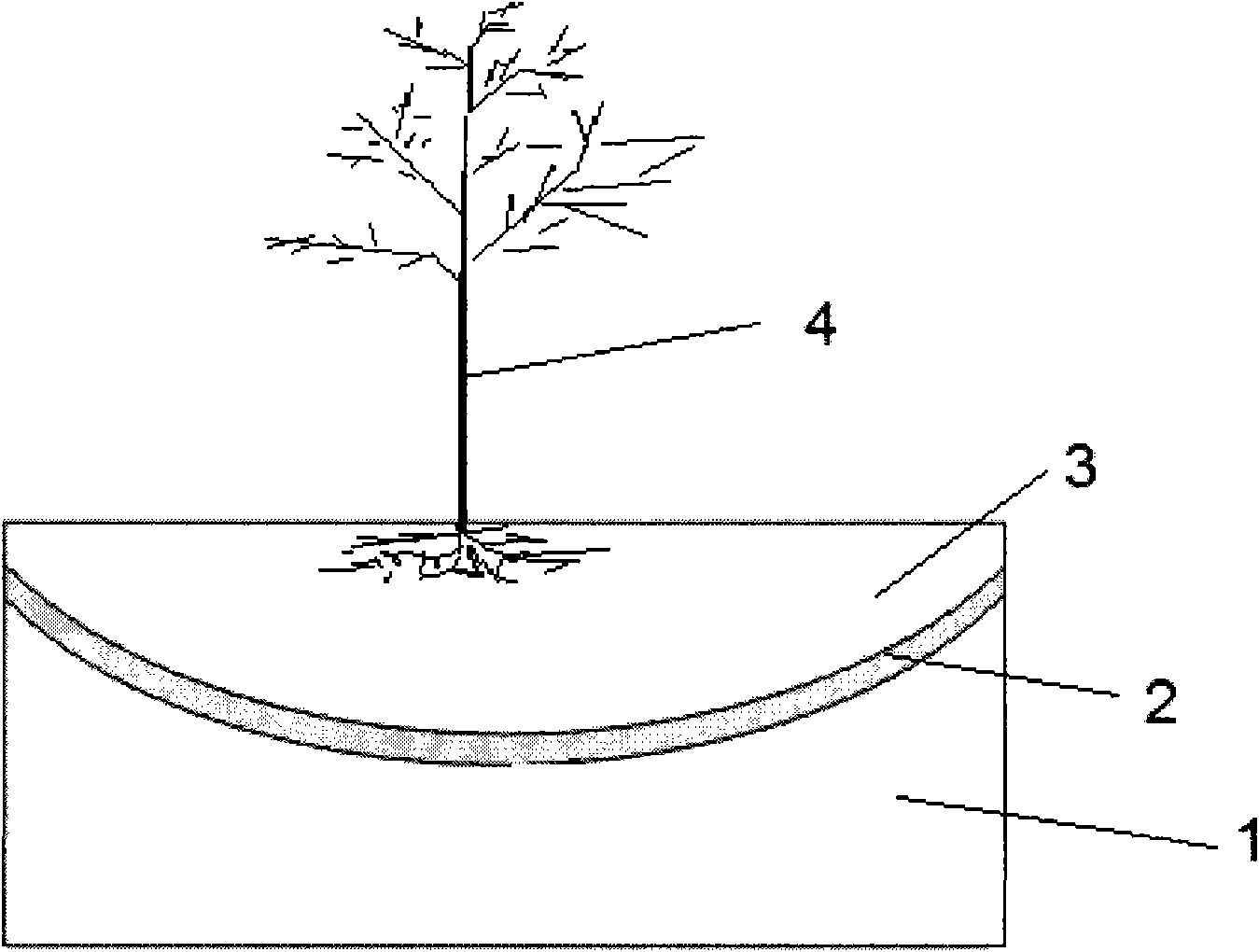
[0056] The basin (150 cm in diameter and 90 cm in height) was filled with desert soil (taken from the Tengger Desert in Zhongwei City, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region) with a height of 20 cm to simulate the desert soil under natural conditions.
[0057] Lay air-permeable anti-seepage sand (Beijing Renchuang Technology Group Co., Ltd., STS-303) with a thickness of 2 cm on the desert soil to form an air-permeable anti-seepage layer, and discharge water through STZ direct-reading air permeability tester and columnar plexiglass tube Test to detect the air permeability and seepage coefficient of the air-permeable anti-seepage layer. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0058] Afterwards, a planting soil layer with a thickness of 68 cm was laid on the air-permeable anti-seepage layer to form the desert planting structure A1.
Embodiment 2
[0060] Desert soil (sandy soil in Alxa Right Banner, Inner Mongolia) is filled in the pot (150 cm in diameter and 90 cm in height) to simulate the desert soil under natural conditions.
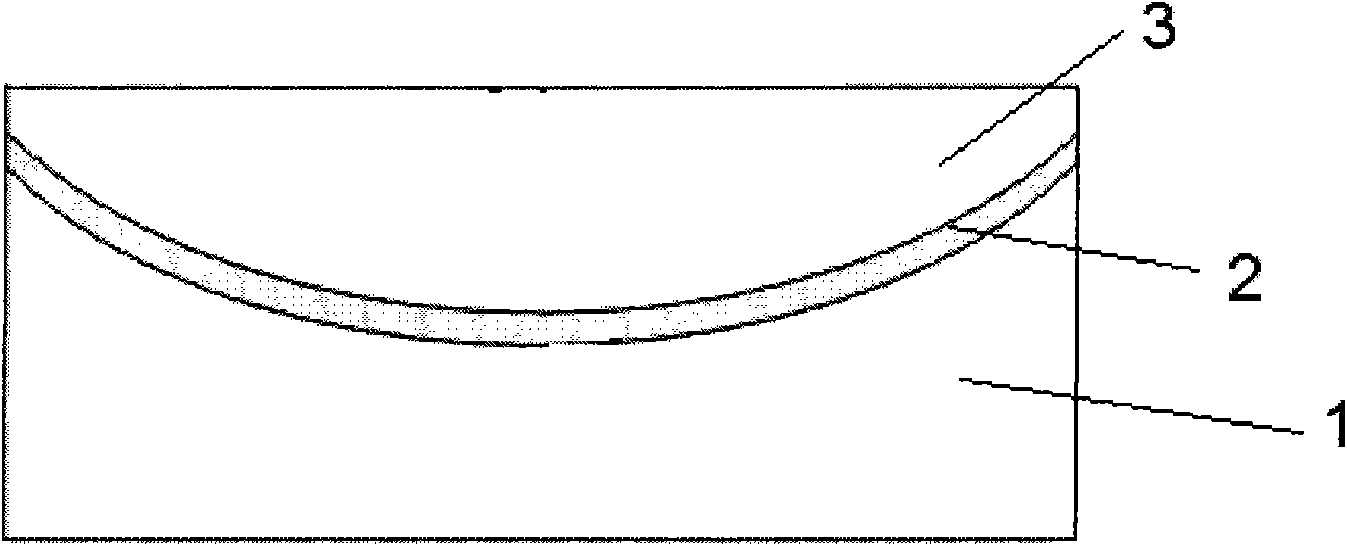
[0061] The top layer of desert soil (the depth is 50 centimeters) is removed, and the soil layer after removing the top layer of soil is carried out leveling treatment to make it form such as figure 1 For the concave pit shown, lay breathable anti-seepage sand (Beijing Renchuang Technology Group Co., Ltd., STS-303) with a thickness of 3 cm on the concave pit to form a breathable anti-seepage layer, and pass the STZ direct-reading air permeability Test instrument and columnar plexiglass tube for water discharge test to detect the air permeability and seepage coefficient of the air-permeable anti-seepage layer. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0062] Afterwards, a planting soil layer with a thickness of 47 cm was laid on the air-permeable anti-seepage layer to form the desert planting struct...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Desert soil (sandy soil in Lingwu area, Ningxia) was filled in the basin (150 cm in diameter and 90 cm in height) to simulate the desert soil under natural conditions.
[0065] The top layer of the desert soil (the depth is 60 cm) is removed, and the soil layer after the removal of the top layer of soil is carried out leveling to make it form as figure 1 As shown in the concave pit, lay breathable anti-seepage sand (Beijing Renchuang Technology Group Co., Ltd., STS-303) with a thickness of 5 cm on the concave pit to form an air-permeable anti-seepage layer, and pass the STZ direct-reading air permeability Test instrument and columnar plexiglass tube for water discharge test to detect the air permeability and seepage coefficient of the air-permeable anti-seepage layer. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0066] After that, a planting soil layer with a thickness of 55 cm was laid on the air-permeable anti-seepage layer to form the desert planting structure A3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com