Overvoltage circuit, and motor starter, overload relay and low-power system including the same
A technology of overvoltage and relay, applied in the fields of overload relay or low power system, voltage clamping circuit, motor starter, which can solve high cost and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
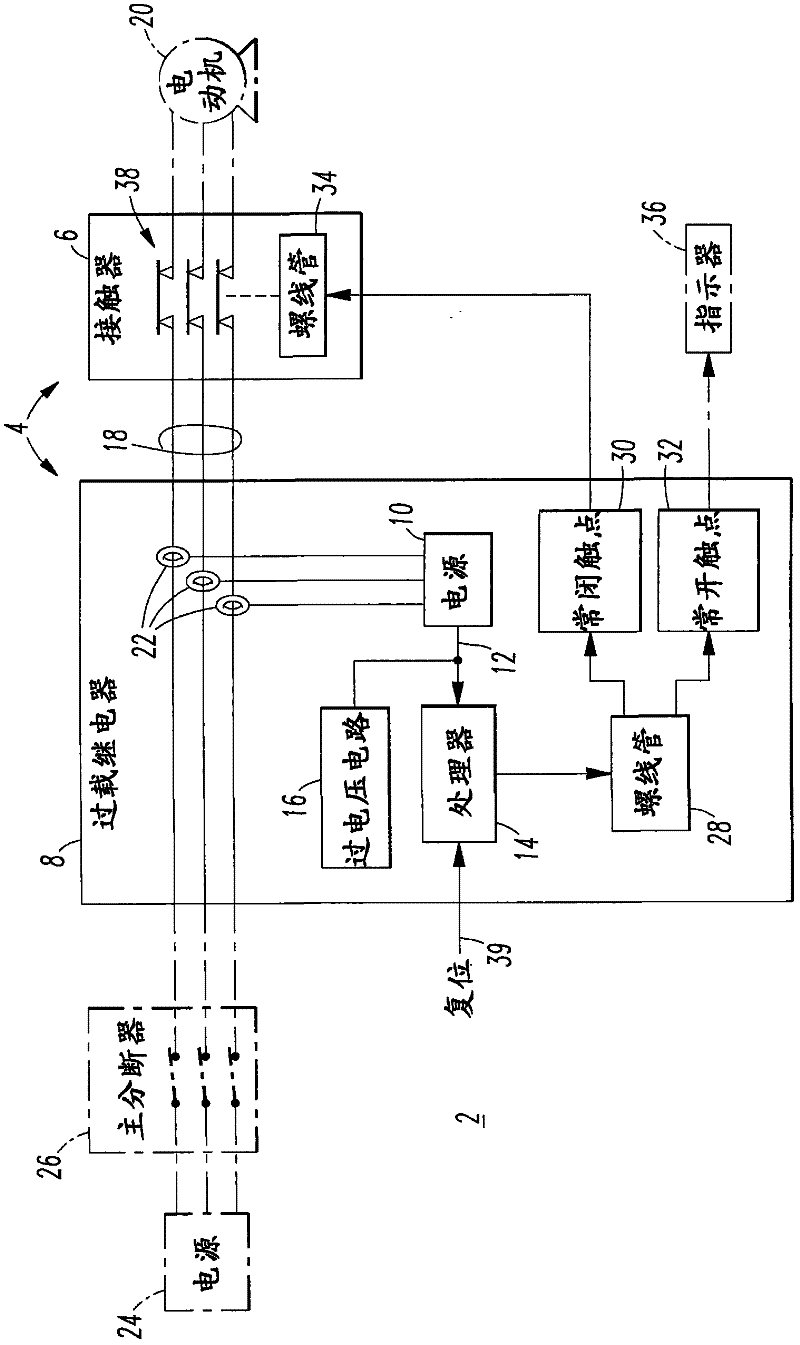
[0033] Preferably, the power supply 10 of the overload relay 8 is configured to be parasitically powered by several power lines 18 to the electric motor 20 (shown in phantom line drawing). In that case, the overload relay 8 also includes several current transformers 22 configured to detect the current flowing to the motor 20 and to supply power to the power source 10 .
[0034] The exemplary motor starter system 2 also includes a power source 24 (shown in phantom line drawing) and a main disconnect 26 (shown in phantom line drawing), which supplies power to overload relay 8 .
[0035] The exemplary processor 14 controls a solenoid 28 which in turn controls a normally closed contact 30 and a normally open contact 32 . An exemplary normally closed contact 30 controls a solenoid 34 of the contactor 6 . Exemplary normally open contacts 32 control a display 36 that shows the status of separable contacts 38 of contactor 6 . The exemplary processor 14 may also input a reset signal ...
example 2
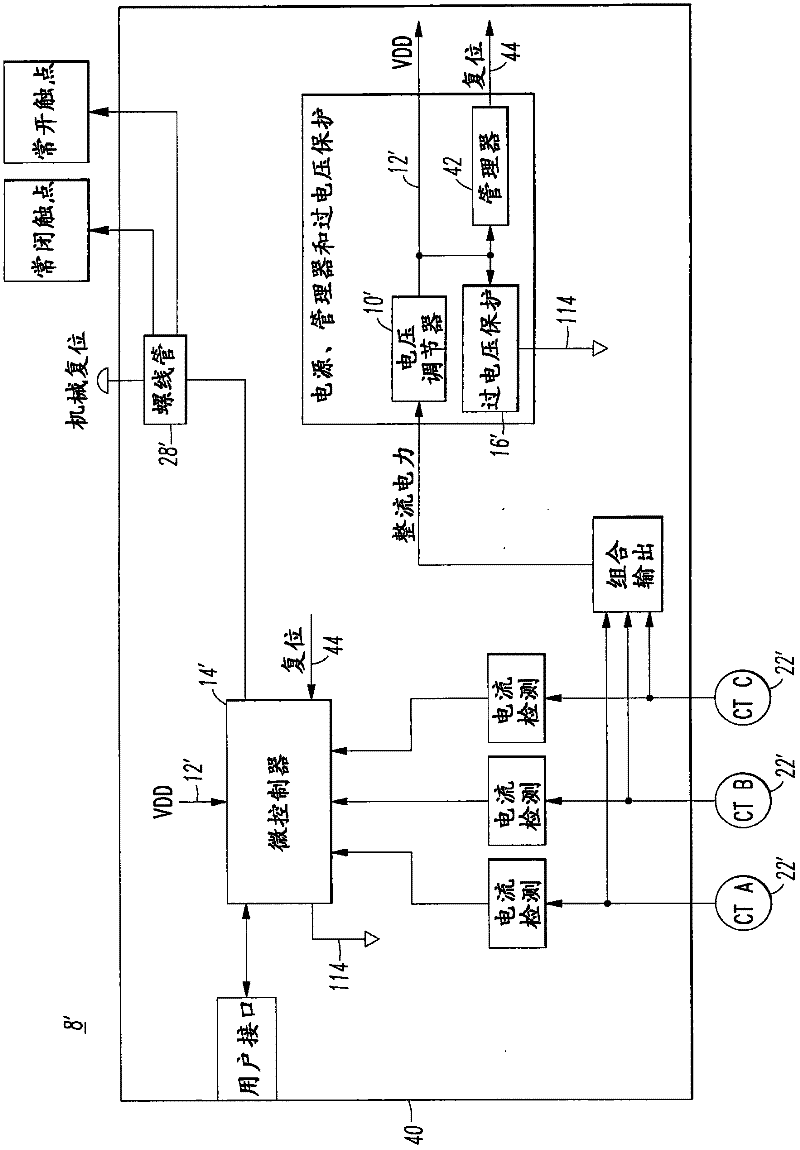
[0037] figure 2 shows that it can be used with figure 1 The overload relay 8 is the same as or similar to the overload relay 8'. The overload relay 8' similarly includes: a power supply 10' having a voltage 12' (such as, but not limited to, +2.5V); a microcontroller 14' (such as, but not limited to, a ); overvoltage protection circuit 16'; solenoid 28'.
[0038] The disclosed solid state overload relay 8' is a parasitic powered motor protection device. The current transformer 22' is used to transfer the current from the current to the motor (not shown, but see figure 1 The electromagnetic field generated by the alternating current (AC) of the electric motor 20) is converted into electric power for the solid-state overload relay 8'. As such, the corresponding control circuit 40 can operate on relatively little power (eg, but not limited to, approximately 1.5 mW). By significantly reducing the amount of power required to operate the control circuit 40, the size of the curr...
example 3
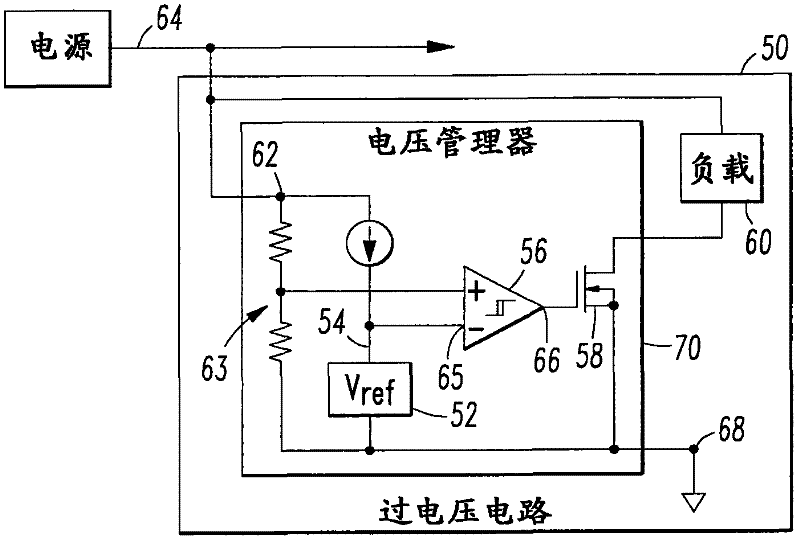
[0041] image 3 shows the overvoltage circuit 50, which can be used with figure 1 and2 The overvoltage circuits 16, 16' are the same or similar. The overvoltage circuit 50 includes a voltage reference 52 having a voltage 54 , a comparator 56 , a switch 58 and a load 60 . The comparator 56 includes: a first input 62 for the supply voltage 64 to be protected; a second input 65 (−) for the voltage reference voltage 54 ; and an output 66 . In this example, the input 62 includes a voltage divider 63 that cooperates with the voltage 54 of the voltage reference 52 to determine the threshold voltage. And, in this example, voltage 54 is less than the threshold voltage. Switch 58 is controlled by comparator output 66 and is configured to electrically connect supply voltage 64 through load 60 to ground 68 whenever supply voltage 64 exceeds a threshold voltage.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com