Query workload estimation-based extensible markup language (XML) fragmentation method
A workload and XML tree technology, applied in the field of efficient XML sharding, can solve problems such as large data overhead, achieve good load balancing, improve acceleration ratio and scaling ratio indicators, and improve the effect of load balancing when querying
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0030] First, the principle of the method of the present invention will be described.
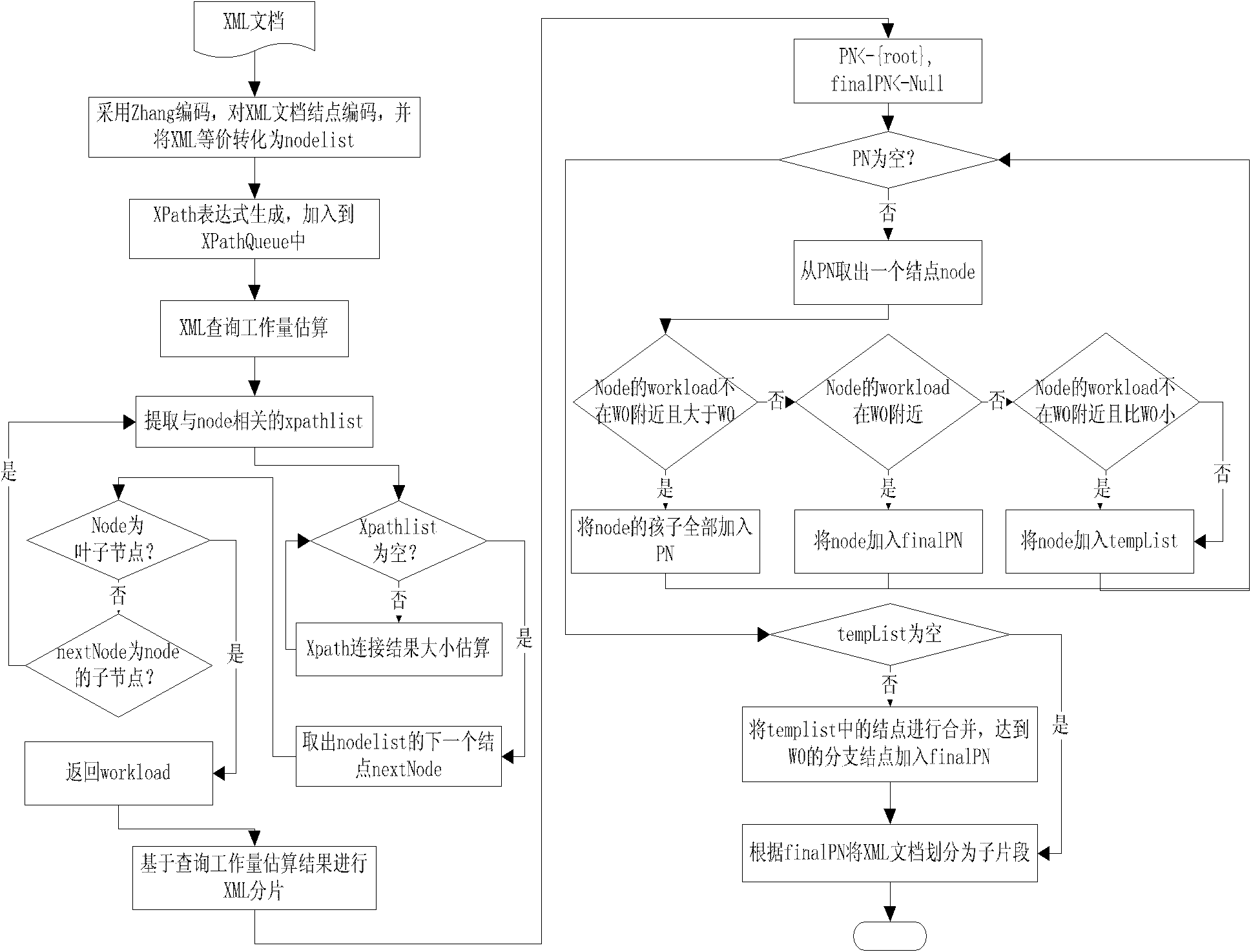
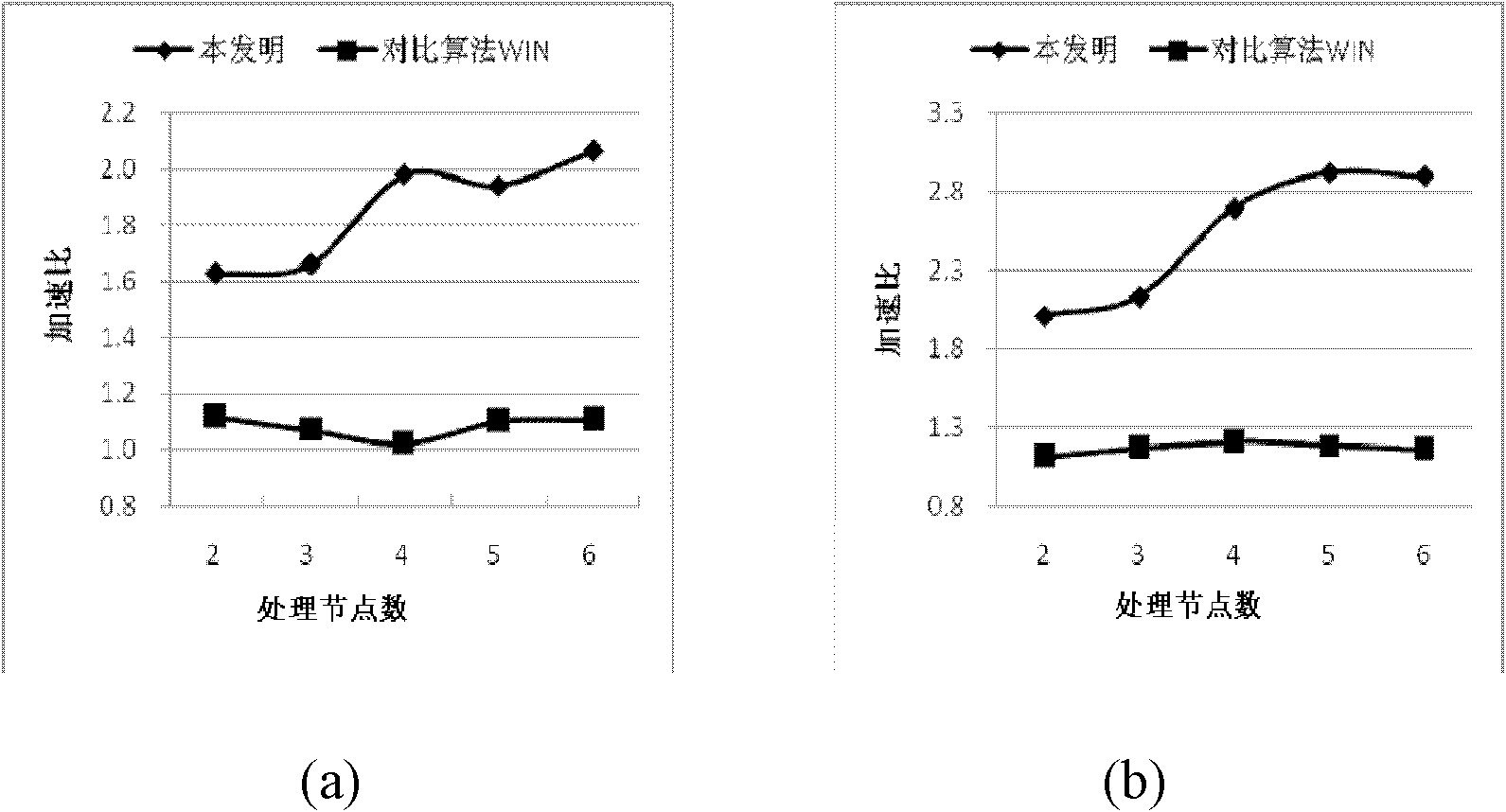
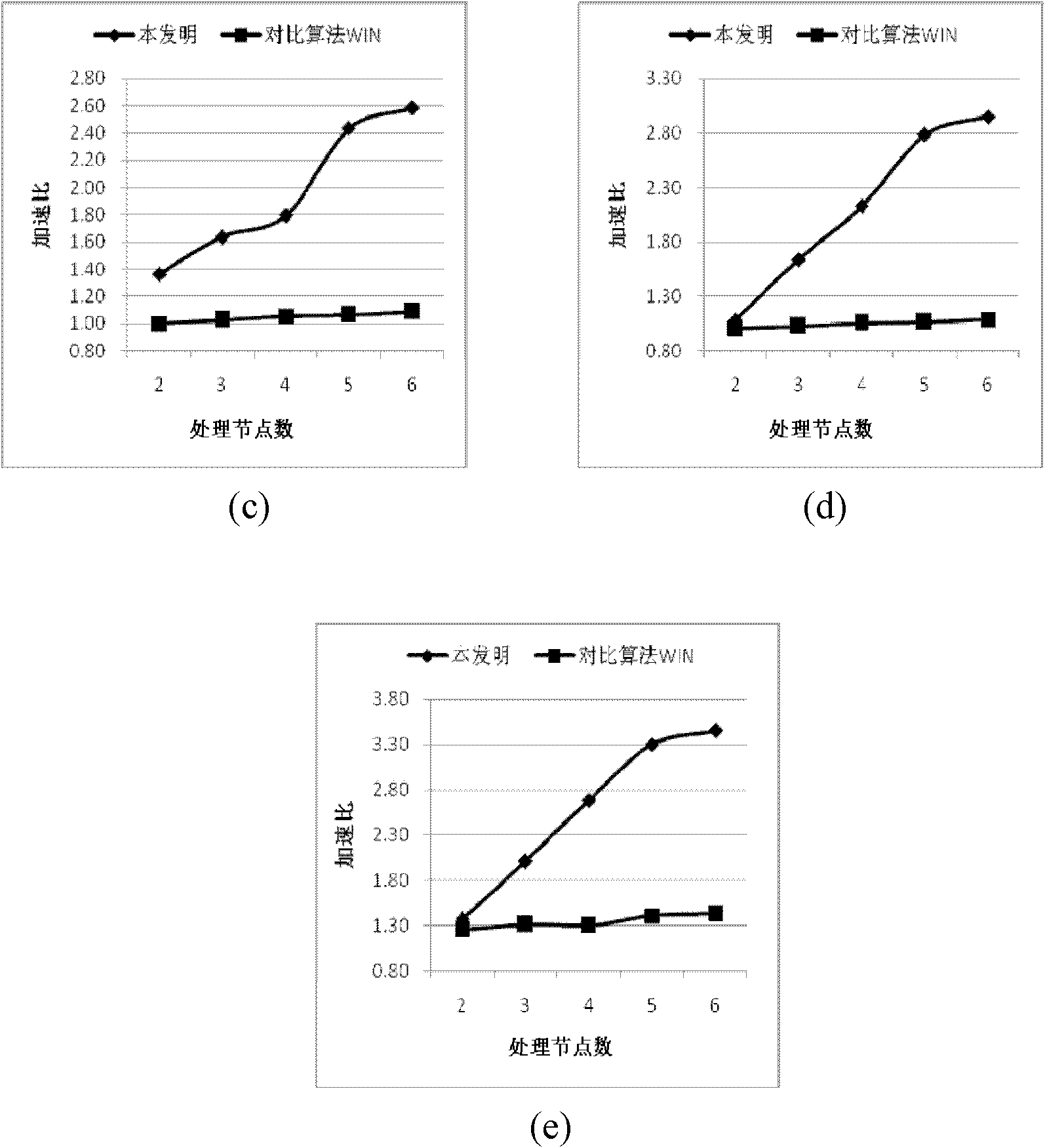
[0031] The research shows that in the XML fragmentation method considering query load balancing, the estimated value of the query workload will greatly affect the XML fragmentation results, and then affect the performance of the entire parallel system. To estimate the query workload using only XML structure, it is necessary to explore the relationship between XML structure and XML query. The XPath language is most commonly used to select and locate nodes in XML queries. For complex XPath expressions, such as "a / b / / c[attr="XX"]")", the general XML query engine will split it into multiple sub-query steps, such as "a / b", "b / / c", "c[attr]" and "attr="XX"". Then calculate the result of each subquery step, and finally combine these results as the query result of the orig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com