Method for configuring ECGI (evolution cell global identification) of terrestrial radio access network for relay node
A technology of global cell identification and wireless access network, applied in wireless communication, network planning, network data management, etc., to achieve the effect of ensuring normal operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
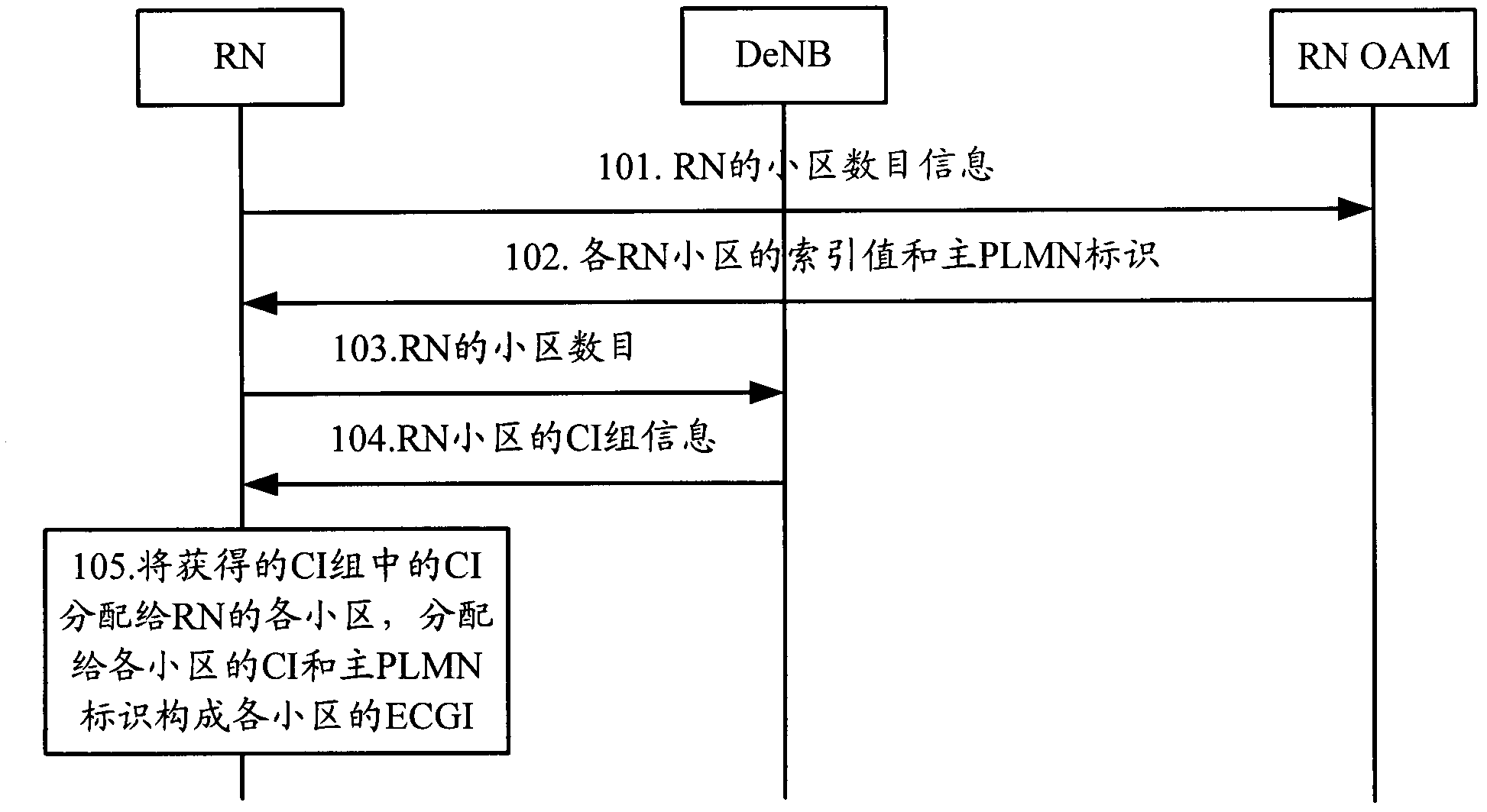
[0064] figure 1 The method flowchart provided for the embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the method may include the following steps:
[0065] Step 101: the RN sends the cell number information of the RN to the RN OAM entity.
[0066] In this step, the RN may send the requested number of cells to the RN OAM entity, or send the number of cells the RN is preparing to generate or the maximum number of cells that the RN can support or the hardware capability of the RN to the RNOAM entity.
[0067] At the same time as step 101, the RN may communicate with the EPC via the eNB. At this time, the cell data information sent by the RN to the RN OAM entity is physically sent to the RN OAM entity via the eNB; or, the RN may also communicate with the EPC via the DeNB, At this time, the cell number information sent by the RN to the RN OAM entity is physically sent to the RN OAM entity via the DeNB.
[0068] In addition, it should be noted that this step 101 is...
Embodiment 2
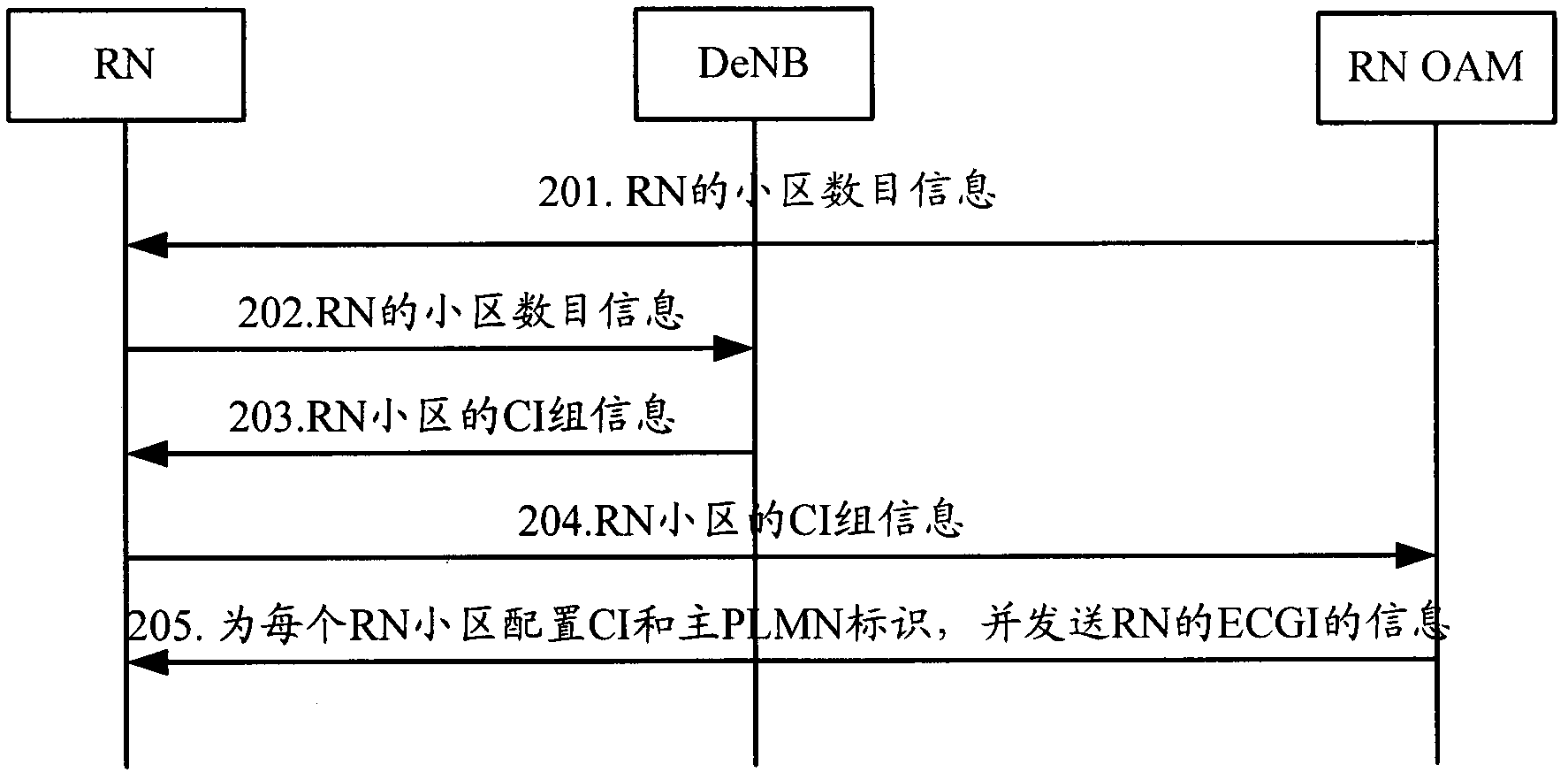
[0092] figure 2 The flow chart of the method provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the method may include the following steps:
[0093] Step 201: The RN OAM entity determines the number of cells configured for the RN, and sends information about the number of cells configured for the RN to the RN.
[0094] The method for the RN OAM entity to determine the number of cells configured for the RN may be the method in step 101 and step 102 in the first embodiment.
[0095] If the RN communicates with the EPC via the eNB, the cell number information sent by the RN to the RN OAM entity is physically via the eNB; or, if the RN communicates with the EPC via the DeNB, the cell number information sent by the RN to the RN OAM entity is physically on via DeNB.
[0096] Step 202: RN sends information about the number of cells configured for the RN to the DeNB.
[0097] After receiving the cell number information configured by the RN OAM entity, ...
Embodiment 3
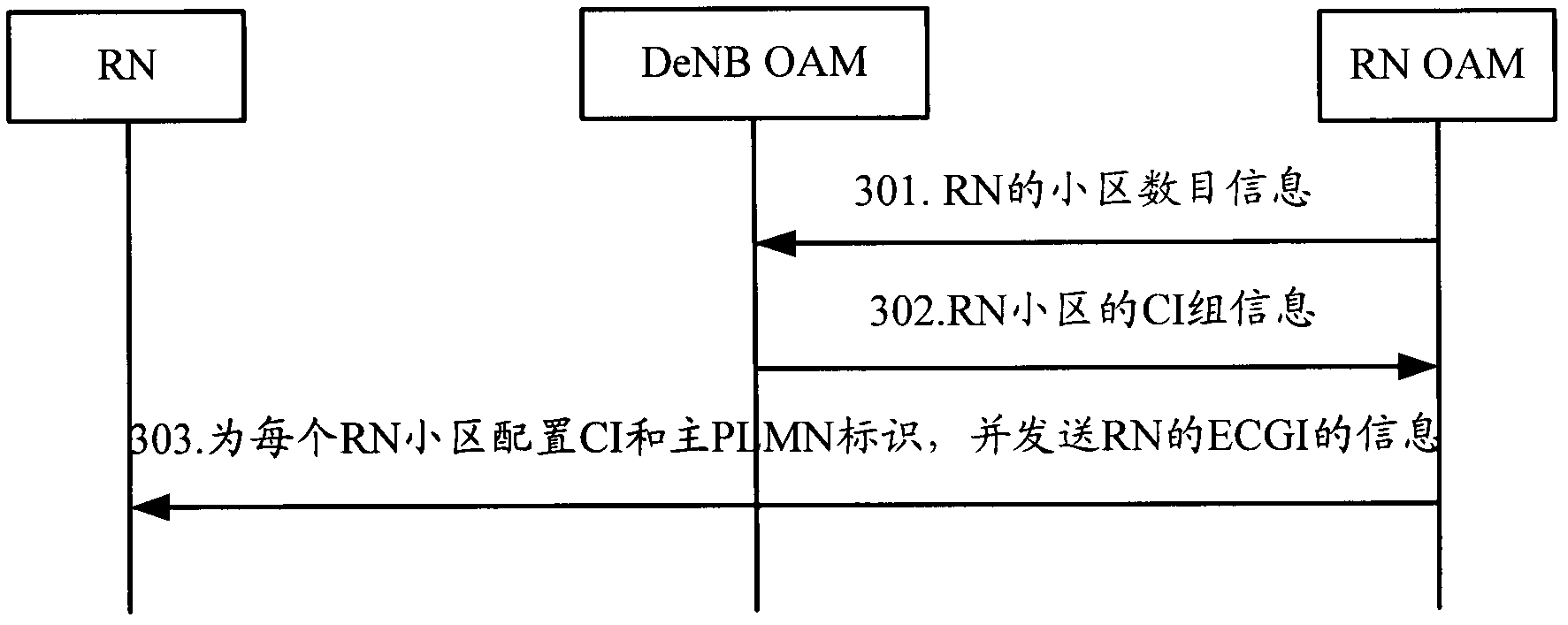
[0118] image 3 The method flowchart provided for the third embodiment of the present invention, such as image 3 As shown, the method may include the following steps:
[0119] Step 301: The RN OAM entity determines the number of cells configured for the RN, and sends information about the number of cells configured for the RN to the DeNB OAM entity.
[0120] The method for the RN OAM entity to determine the number of cells configured for the RN may be the method in step 101 and step 102 in the first embodiment.
[0121] Step 302: The DeNB OAM entity allocates a CI group for the RN according to the received number of cells configured for the RN, and sends the CI group information to the RN OAM entity.
[0122] The DeNB OAM entity determines the number of cells allocated to the RN according to the number of cells received, or according to the number of cells received and the CIs of the cells of the DeNB accessed by the RN and the cells of all the RNs that have accessed the De...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com