Cluster analysis based lithium battery unit matching method
A technology of battery unit and cluster analysis, which is applied in secondary battery repair/maintenance, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., and can solve problems such as battery performance failure, battery capacity attenuation, and initial performance inconsistency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
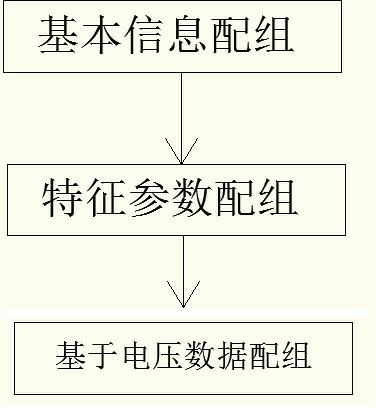
[0134] refer to figure 1 , a method for grouping lithium battery cells based on cluster analysis, comprising the following steps:
[0135] (1) For the battery unit set B={B that needs to be matched 1 , B 2 ...B sum} for group matching, sum is the total number of battery units that need to be grouped, sum>1; Any battery unit set with the number of battery units greater than 1 can enter the next step of grouping. A battery unit set with the number of elements being 1 indicates that the battery units in this set cannot be used in groups with any other battery units and are formed independently. ;
[0136] (2) Based on the battery unit set B'={B obtained in the previous step 1 , B 2 ...B m}, m is the number of battery cells that need to be further assembled in this step, 1<m≤sum; select a combination of more than one factor in health status, self-discharge rate, internal resistance, open circuit voltage, charging efficiency, and cycle times The battery unit set B' is group...
Embodiment 2
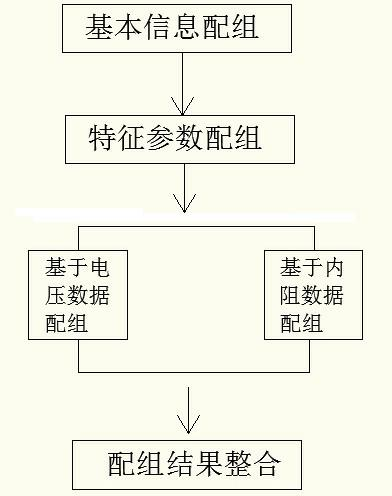
[0147] refer to figure 2 , the present embodiment also includes step (3) on the basis of embodiment 1:
[0148] (3) to the new group of battery cell B "={B that step (2) produces 1 , B 2 ...B z} for grouping, z is the number of battery cells that need to be further grouped, 1<z≤m and z is an integer;
[0149] Select the voltage data at point a as the matching data, a is an integer greater than 1; the voltage data at any point includes z voltage values, and the SOC value corresponding to each voltage value is the same, and the charge and discharge state is the same; the initial setting of each battery The unit is a class, namely C i ={B i}, i=1, 2, ..., z, C i is the i-th battery cell class, the number of classes z′=z;
[0150] Any two types of C h , C k distance d kh The calculation method is as follows:
[0151] when class C h , C k When both contain only one battery cell, set C h ={B i}, C k ={B j}:
[0152] d kh ...
Embodiment 3
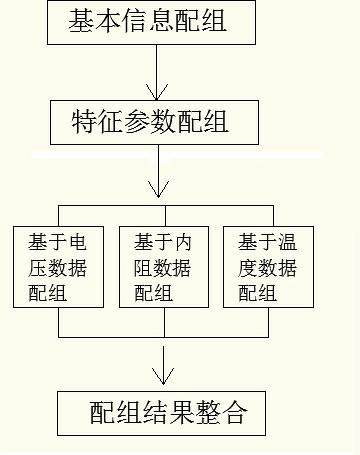
[0166] refer to image 3 , the present embodiment also includes steps (3), (4) and (6) on the basis of embodiment 1:
[0167] (3) to the new group of battery cell B "={B that step (2) produces 1 , B 2 ...B z} for grouping, z is the number of battery cells that need to be further grouped, 1<z≤m and z is an integer;
[0168] Select the voltage data at point a as the matching data, a is an integer greater than 1; the voltage data at any point includes z voltage values, and the SOC value corresponding to each voltage value is the same, and the charge and discharge state is the same; the initial setting of each battery The unit is a class, namely C i ={B i}, i=1, 2, ..., z, C i is the i-th battery cell class, the number of classes z′=z;
[0169] Any two types of C h , C k distance d kh The calculation method is as follows:
[0170] when class C h , C k When both contain only one battery cell, set C h ={B i}, C k ={B j}:
[0171] d ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com