Pseudorange difference location method and device
A positioning method and position positioning technology, which is applied in the direction of location information-based services, transmission monitoring, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome workload and low positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
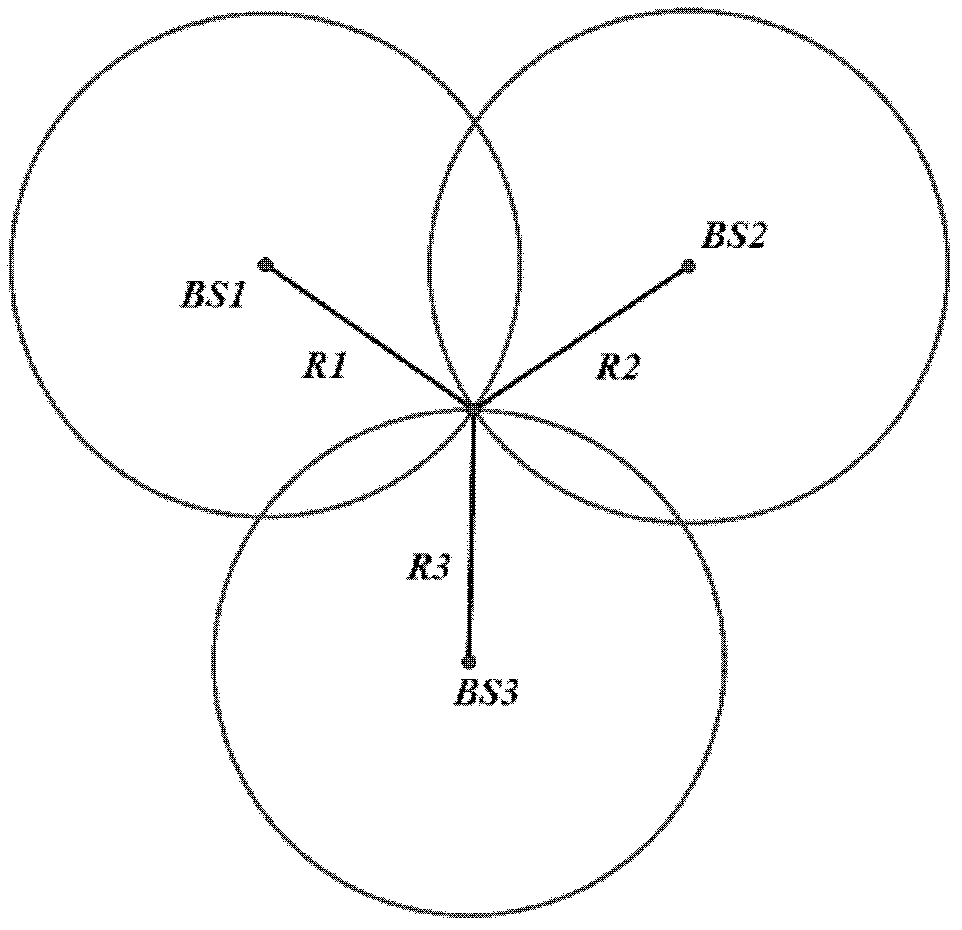
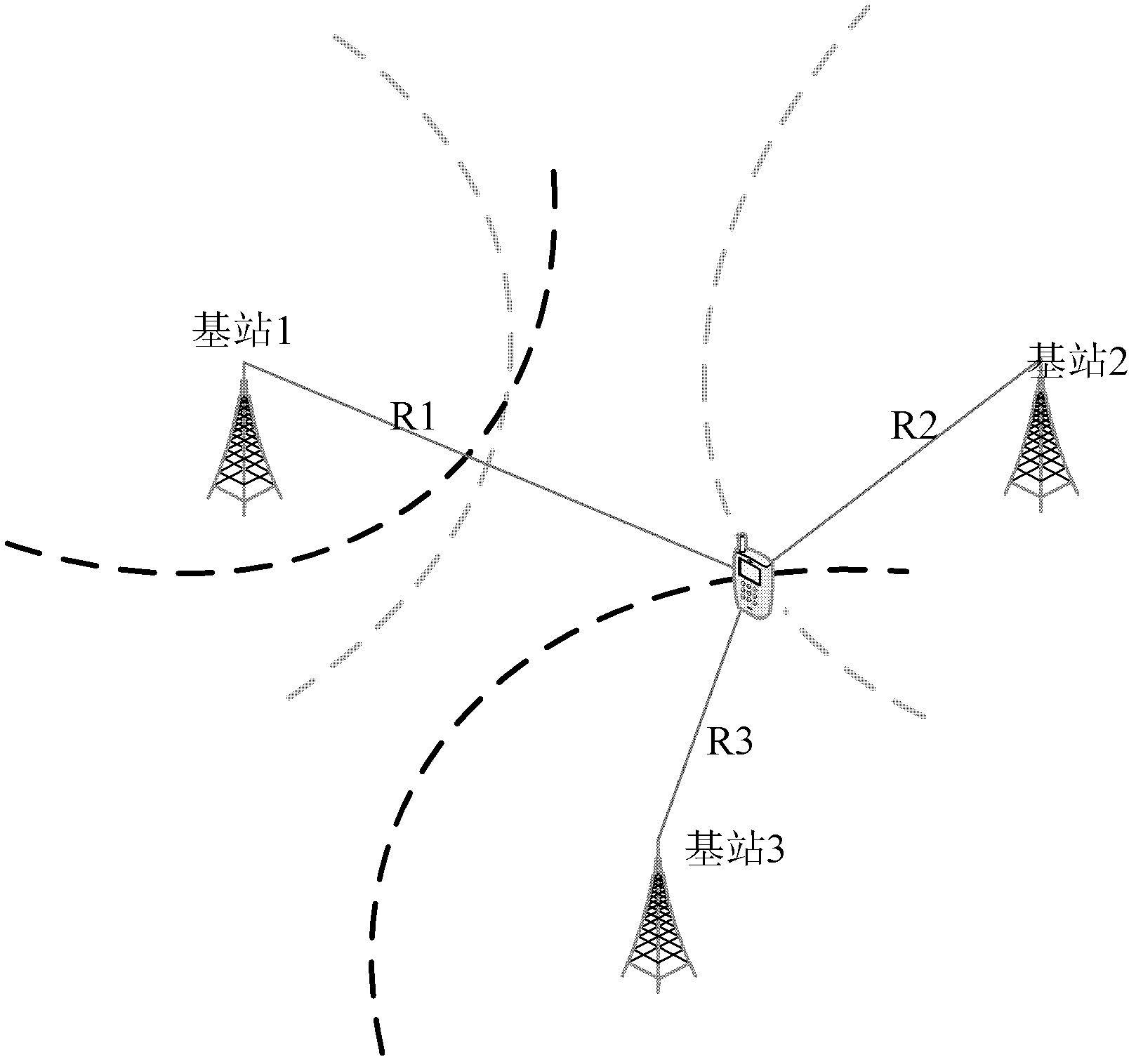
[0090] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a pseudorange difference positioning method, such as Figure 6 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0091] Step 10, selecting a calibration point, and pre-determining the coordinates of the calibration point and the corresponding TDOA value.
[0092] User positioning is a systematic work, and the primary task is to select a small number of calibration points in the entire positioning area as the reference point of the positioning area. The selection of calibration points can be carried out according to actual needs, and the number of calibration points can be selected according to the workload that can be tolerated.
[0093] After the calibration points are selected, the coordinates of the calibration points and the corresponding TDOA values need to be determined in advance. The measurement of the coordinates can be carried out according to positioning methods such as GPS, and the measurement of the TDOA...
Embodiment 2
[0121] In Embodiment 2 of the present invention, the method of first measuring the grid points in the above-mentioned Embodiment 1 is used to locate the user, wherein,
[0122] Firstly, the calibration points are selected at certain intervals, and the coordinates of the calibration points and the corresponding TDOA values at the calibration points are determined in advance.
[0123] Then generate grid point coordinates required for positioning according to predetermined rules. The predetermined rule can be that the grid points are distributed at equal intervals, or can be divided irregularly according to information such as indoor room coordinates.
[0124] Then, generate the TDOA value of the grid point according to the required grid point coordinates, calibration point coordinates, base station coordinates, and calibration point pre-stored TDOA values. The generation rules are as follows:
[0125] Find three calibration points A, B, and C, and satisfy the following condi...
Embodiment 3
[0130] In Embodiment 3 of the present invention, the method of user positioning without measuring grid points in the above-mentioned Embodiment 1 is adopted, wherein,
[0131] Firstly, the calibration points are selected at certain intervals, and the coordinates of the calibration points and the corresponding TDOA values at the calibration points are determined in advance.
[0132] Then find three calibration points A, B, and C according to the method of finding calibration points based on the grid points in the above two embodiments, and satisfy the following conditions: the triangular area surrounded by the three calibration points contains the estimated user The position coordinates, and the sum of the distances from the three calibration points to the position point is the minimum. The coordinates of the marked calibration points are (x A ,y A ), (x B ,y B ), (x C ,y C ).
[0133] Let the n TDOA values measured at points A, B, and C be T A1 , T A2 ......T An ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com