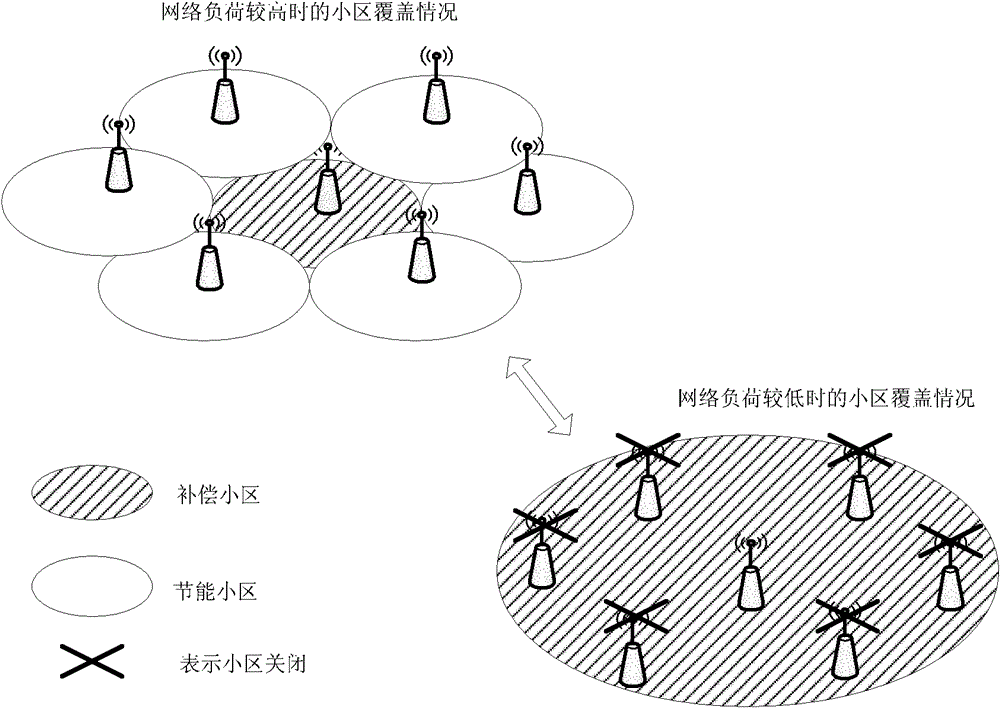
Cell energy saving method, base station and long term evolution system
A cell and base station technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve problems such as strong radio frequency interference, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy, network performance and user experience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057]This embodiment provides a method for saving energy in a cell. This embodiment combines the above embodiments and preferred implementation modes therein. The method includes the following two methods:
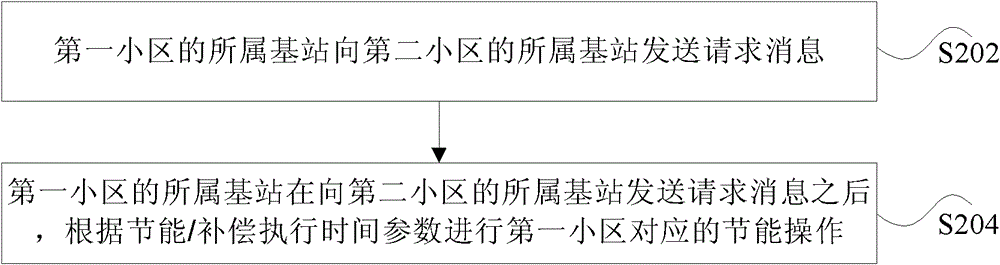
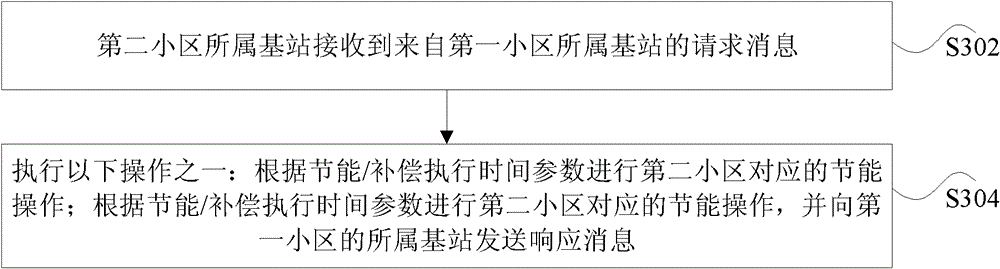
[0058] Method 1: On the X2 interface between base stations (such as cell energy saving request message, cell compensation request message), by transmitting the cell energy saving / compensation execution absolute time Tabs, and / or the absolute time drift amount ΔTabs to make the coordinated base stations perform cell compensation and compensation The operation of shutting down the cell can be carried out synchronously. In the case that ΔTabs is sufficiently small (at least less than 1 second), or both coordinating nodes know ΔTabs, only the cell energy saving / compensation execution absolute time Tabs may be transmitted.
[0059] Method 2: On the X2 interface between base stations (such as cell energy saving request message, cell compensation request message), pass the cell ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] This embodiment provides a method for calculating the absolute time drift / interface message transmission delay. In this embodiment, it is assumed that the source eNB (S-eNB) and the target eNB (T-eNB) are two with X2 interface In principle, the eNB can select any pair of request / response messages on the X2 interface to realize the calculation of ΔTabs / Δtdelay by carrying timestamp information. Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the calculation principle of ΔTabs / Δtdelay according to an embodiment of the present invention, in Figure 4 Middle: t1 is the time when the S-eNB sends the request message, t2 is the time when the T-eNB receives the request message, t3 is the time when the T-eNB sends the response message, and t4 is the time when the S-eNB receives the response message. Assuming that the absolute time drift of T-eNB relative to S-eNB is ΔTabs, here it is assumed that the time it takes for messages to go back and forth between S-eNB and T-eNB is the same, that i...
Embodiment 3
[0071] In this embodiment, a cell energy saving method is provided. This embodiment combines the above embodiments and the preferred implementation modes. This embodiment adopts the absolute time coordination mode, and the compensation cell initiates the process, and the S-eNB indicates the process of initiating the process. The control base station of the compensation cell, T-eNB(s) represents the control base station (possibly multiple) of the target energy-saving cell. This embodiment involves two time parameters: the absolute time point Tabs and the absolute time drift ΔTabs, where ΔTabs can be Calculate according to the formula in Example 2. Figure 5 It is an implementation flow chart (compensation cell initiation process) of using the absolute time coordination mode according to an embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 5 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0072] Step S502: S-eNB sends a cell compensation preparation request to T-eNB(s),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com