Fixed-point fatigue identification method for diagnosing faults of bearing and gear of transmission system
A fixed-point fatigue identification, bearing gear technology, applied in the direction of machine gear/transmission mechanism testing, etc., can solve the problems of failures that cannot be covered, damage, limited, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
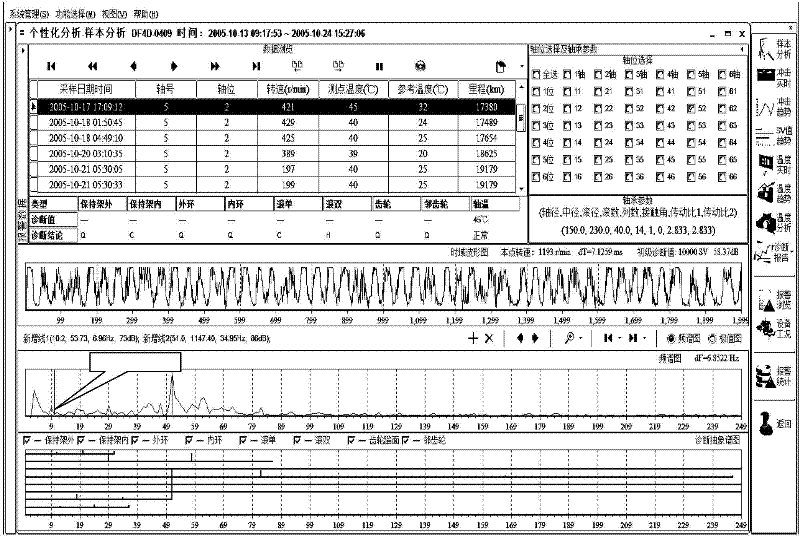
[0077] Example 1. Theoretical calculation and verification of "mutually fixed point fatigue" for a certain type of locomotive gear:
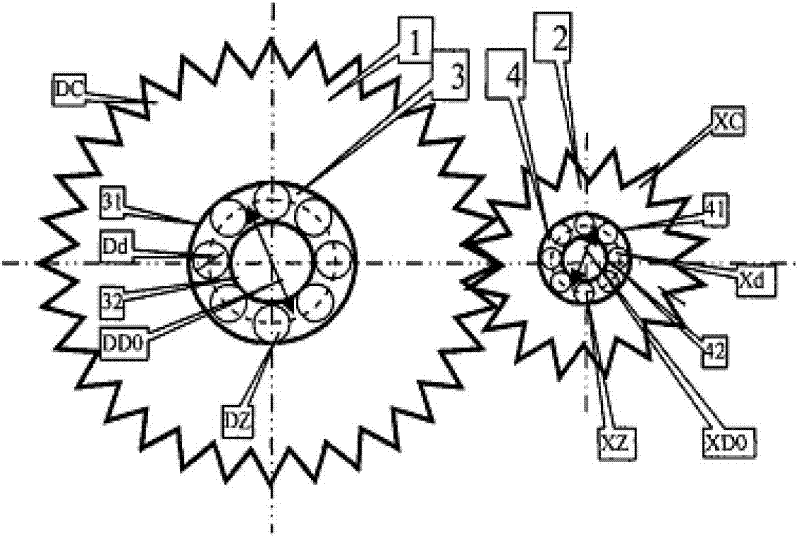
[0078] A fixed-point fatigue identification method for diagnosing transmission system bearing gear faults. If the bearing raceway (inner raceway is N or outer raceway is W) bearing area rolls over an integer X (the number of passes through the inner raceway is XN or through the outer raceway) When the number is XW) rollers, the gear meshing times Y is close to an integer +0.5 with a deviation not greater than S, and the ratio of the gear teeth C (the small gear is CX or the large gear is CD) to the meshing times Y is J=C / Y (the small gear is JX or the large gear is JD) is close to an integer with a deviation not greater than S, that is, ABS[J-CINT(J)]≤S, then it is identified as the gear fixed point fatigue of the gear matching the corresponding bearing The order is J (the small gear is JX or the big gear is JD), and both the damage spectrum and t...
Embodiment 2
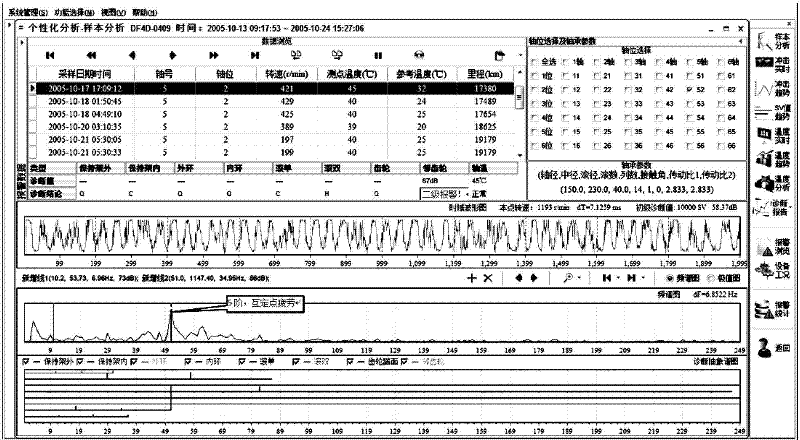
[0098] Example 2, one of the theoretical calculation and verification of "quasi-fixed-point fatigue" for a certain type of locomotive gear:
[0099] A fixed-point fatigue identification method for diagnosing transmission system bearing gear faults. If the bearing raceway (inner raceway is N or outer raceway is W) bearing area rolls over an integer X (the number of passes through the inner raceway is XN or through the outer raceway) When the number is XW) rollers, the gear meshing times Y is close to an integer with a deviation not greater than S, and the gear tooth number C (small gear is CX, large gear is CD) and the ratio of the meshing times Y J=C / Y (The small gear is JX, the big gear is JD), the deviation from a similar integer is not more than 0.5, and when the gear rotates for an integer K cycles, FC=J*K is close to an integer with a deviation not greater than S, that is, ABS[FC- CINT(FC)]≤S, and INT(FC)≤C, it is recognized that the quasi-fixed-point fatigue of the gear mat...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Example 3, the second part of theoretical calculation and verification of "quasi-fixed-point fatigue" for a certain type of locomotive gear:
[0119] A fixed-point fatigue identification method for diagnosing transmission system bearing gear faults. If the bearing raceway (inner raceway is N or outer raceway is W) bearing area rolls over an integer X (the number of passes through the inner raceway is XN or through the outer raceway) When the number is XW) rollers, the gear meshing times Y is close to an integer with a deviation not greater than S, and the ratio of the number of teeth C of the gear (the small gear is CX or the large gear is CD) to the meshing times Y is J=C / Y( The small gear is JX or the large gear is JD) and the deviation of a similar integer is not more than 0.5, and when the gear rotates for an integer K cycles, FC=J*K is close to the integer with a deviation not greater than S, that is, ABS[FC-CINT( FC)]≤S, and INT(FC)≤C, it is recognized that the quasi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com