Passive clamping type piezoelectric actuator
A piezoelectric driver and clamping technology, applied in the direction of piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, electrical components, generators/motors, etc., can solve the problem of poor control flexibility, clamp amplification structure form Complexity and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing machining accuracy, simple structure and accurate positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
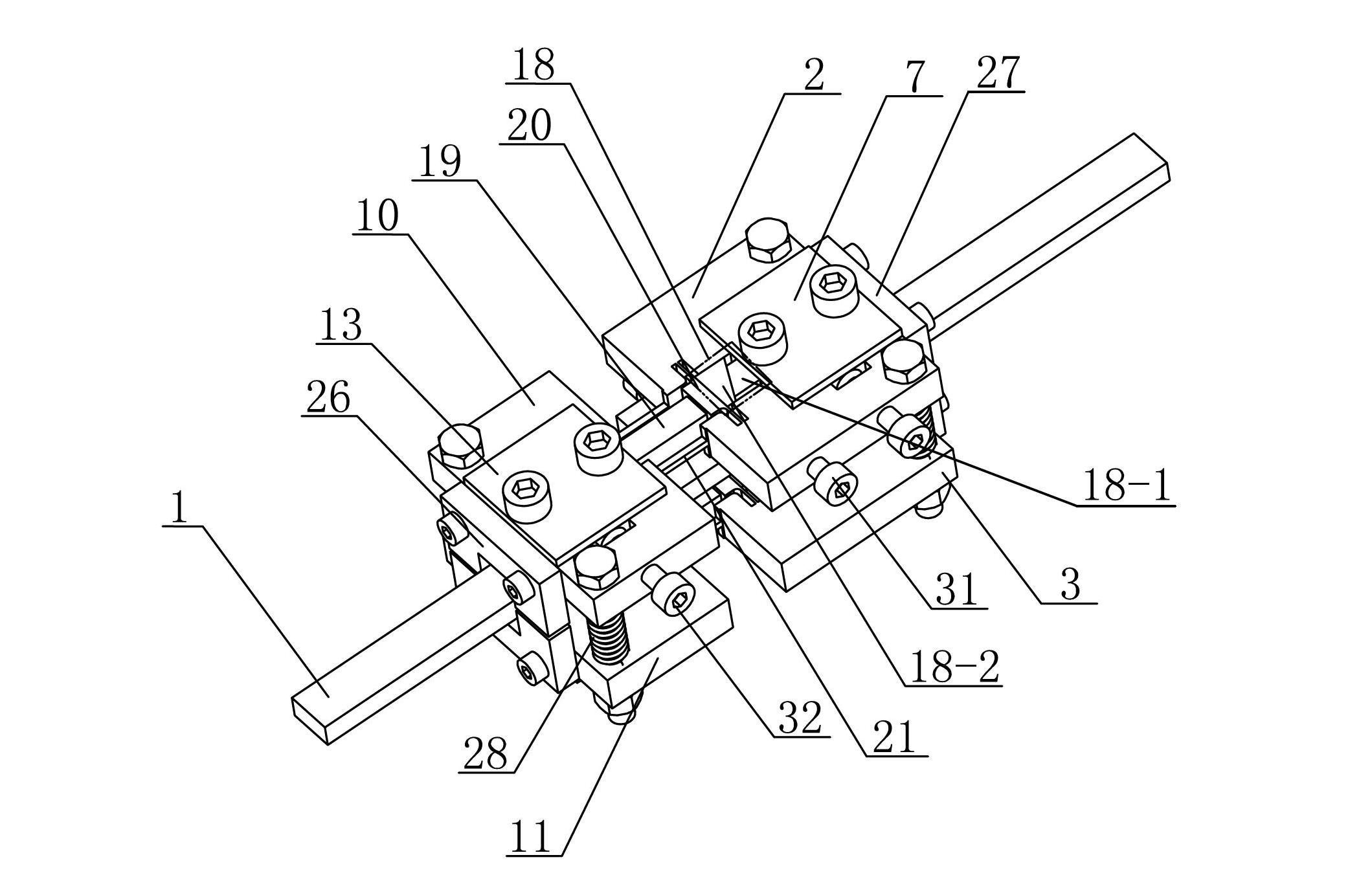
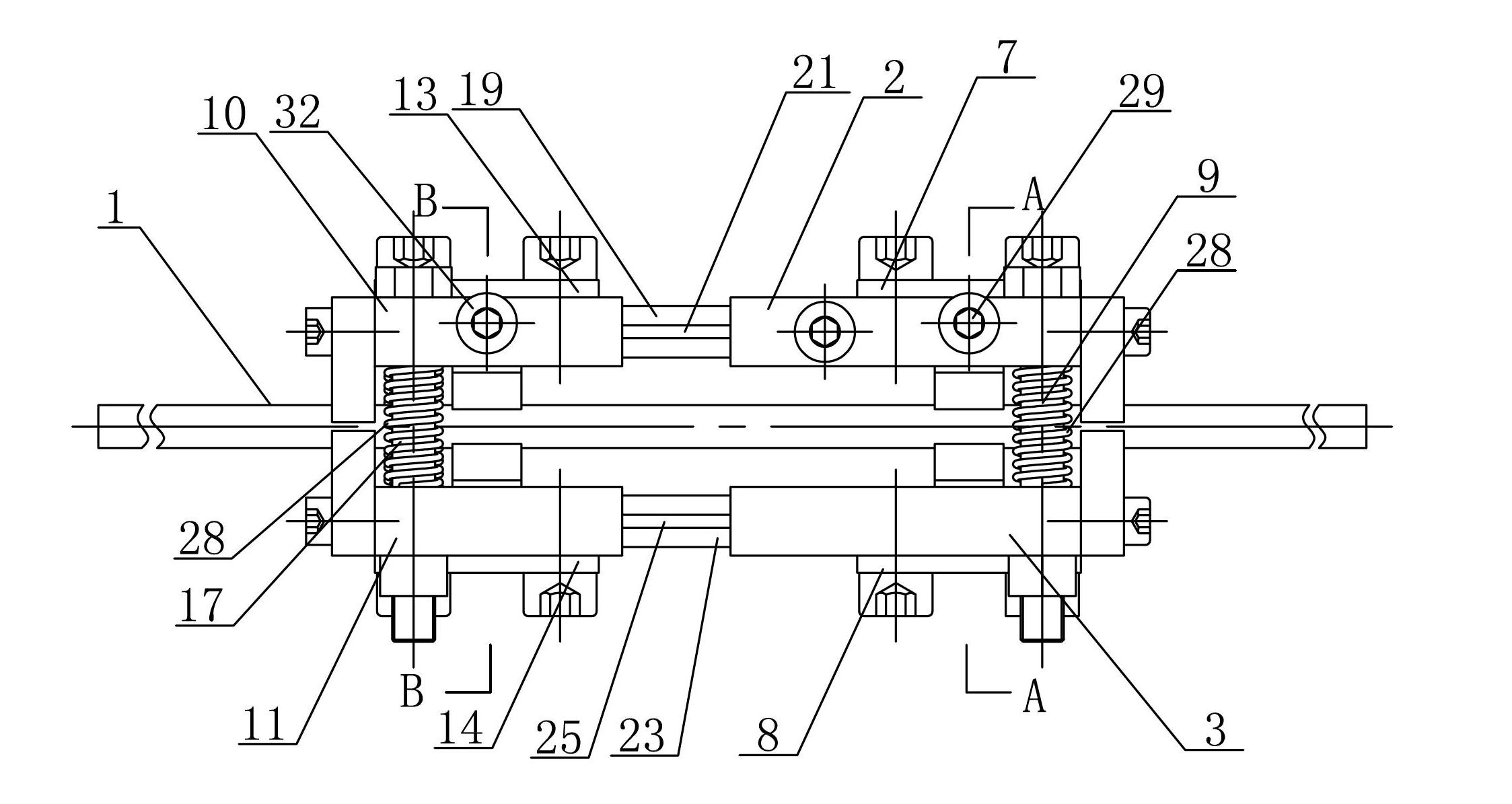
[0014] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1-Figure 6 Describe this embodiment, the passive clamping type piezoelectric actuator of this embodiment includes a first clamping mechanism, a driving mechanism, a second clamping mechanism and a guide rail 1,
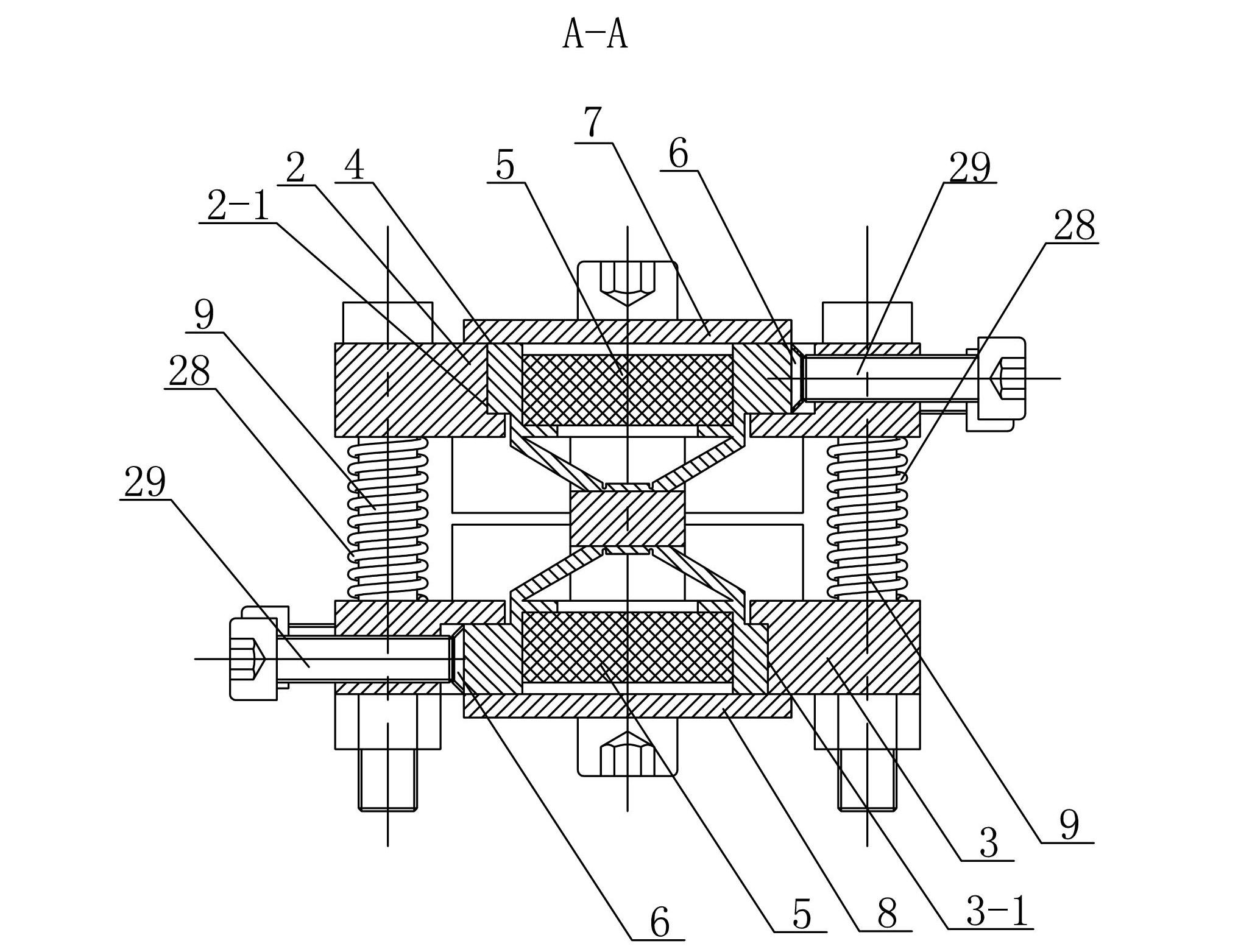
[0015] The first clamp mechanism includes a first upper base plate 2, a first lower base plate 3, a first clamp triangular amplification mechanism 4, a first upper cover plate 7, a first lower cover plate 8, two first clamp piezoelectric stacks Stack 5, two first disc springs 6 and two first cylinders 9, the first upper base plate 2 and the first lower base plate 3 are arranged in parallel up and down, and the first upper base plate 2 and the first lower base plate 3 pass through two The first cylinder 9 is supported and connected, and the centers of the first upper base plate 2 and the first lower base plate 3 are respectively provided with a first upper clamping piezoelectric stack placement hole 2-1 and a fir...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific implementation mode two: combination image 3 and Figure 5 Describe this embodiment, the stiffness of the first disc spring 6 of this embodiment is greater than the stiffness of the first clamping triangular amplifying mechanism 4 and smaller than the output stiffness of the first clamping piezoelectric stack 5, the stiffness of the second disc spring 16 is greater than The stiffness of the second clamping triangular amplification mechanism 12 is smaller than the output stiffness of the second clamping piezoelectric stack 15 . In this way, when the first clamping piezoelectric stack 5 is pre-tightened, the first disc spring 6 is connected in series with the rigidity of the first clamping triangular amplifying mechanism 4, and the deformation mainly occurs in the first clamping triangular amplifying mechanism 4; When the second clamping piezoelectric stack 15 is pre-tightened, the stiffness of the second disc spring 16 is connected in series with the second cl...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0029] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 1 To describe this embodiment, the tensile stiffness of the upper telescopic rod 21 of this embodiment is smaller than the output stiffness of the upper driving piezoelectric stack 19 , and the tensile stiffness of the lower telescopic rod 25 is smaller than the output stiffness of the lower driving piezoelectric stack 23 . In this way, the tensile stiffness of the telescopic rod should be smaller than the output stiffness of the driven piezoelectric stack as much as possible under the premise of satisfying the stiffness conditions, so as to give full play to the output capacity of the driven piezoelectric stack. In addition, it has a simple structure and is easy to process. , the amount of deformation has a linear relationship with the output force of the piezoelectric stack, and has the advantages of precise positioning. Other compositions and connections are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com