Energy saving method for IPv6 wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and network technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, energy-saving ICT, etc., can solve the problems of large number of sensor nodes, impracticality, and complex deployment area environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
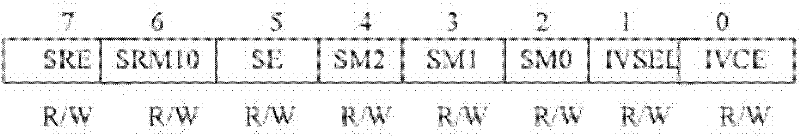
[0018] A miniature sensor node is mainly composed of four parts: power supply, sensing unit, processing unit and transceiver unit. In addition to the power supply unit that generates energy, the sensing unit, processing unit and transceiver unit are all energy sources of sensor nodes, and the data transceiver unit is the main part of energy consumption.
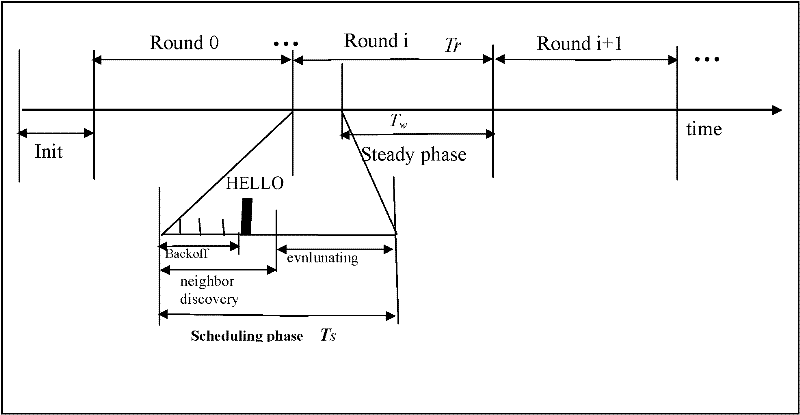
[0019] The methods of energy control mainly focus on the dormancy mechanism, data fusion, conflict avoidance and error correction, etc. They are applied to all aspects of the computing module and communication module. The specific analysis is as follows:
[0020] 1) Hardware energy saving
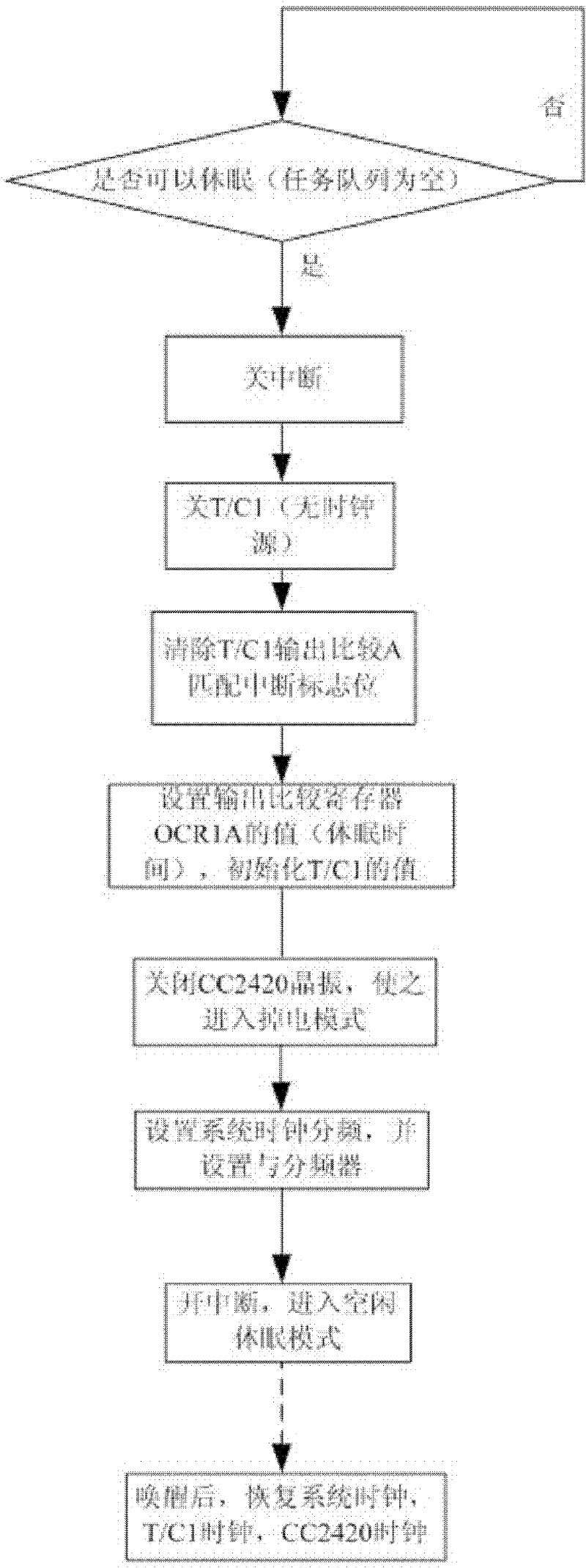
[0021] In hardware selection, low-power components should be used to make a compromise between performance and power consumption to reduce the overall power consumption of the system. The processor should support the adjustment of the operating voltage and operating frequency, so as to provide the necessary conditions for the dormancy of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com