Wire rope flaw detection device
A flaw detection device and steel wire rope technology, applied in the direction of material magnetic variables, etc., can solve the problems of false detection signals generated by magnetic sensors, decreased detection sensitivity of damaged parts, and smaller, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing wear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
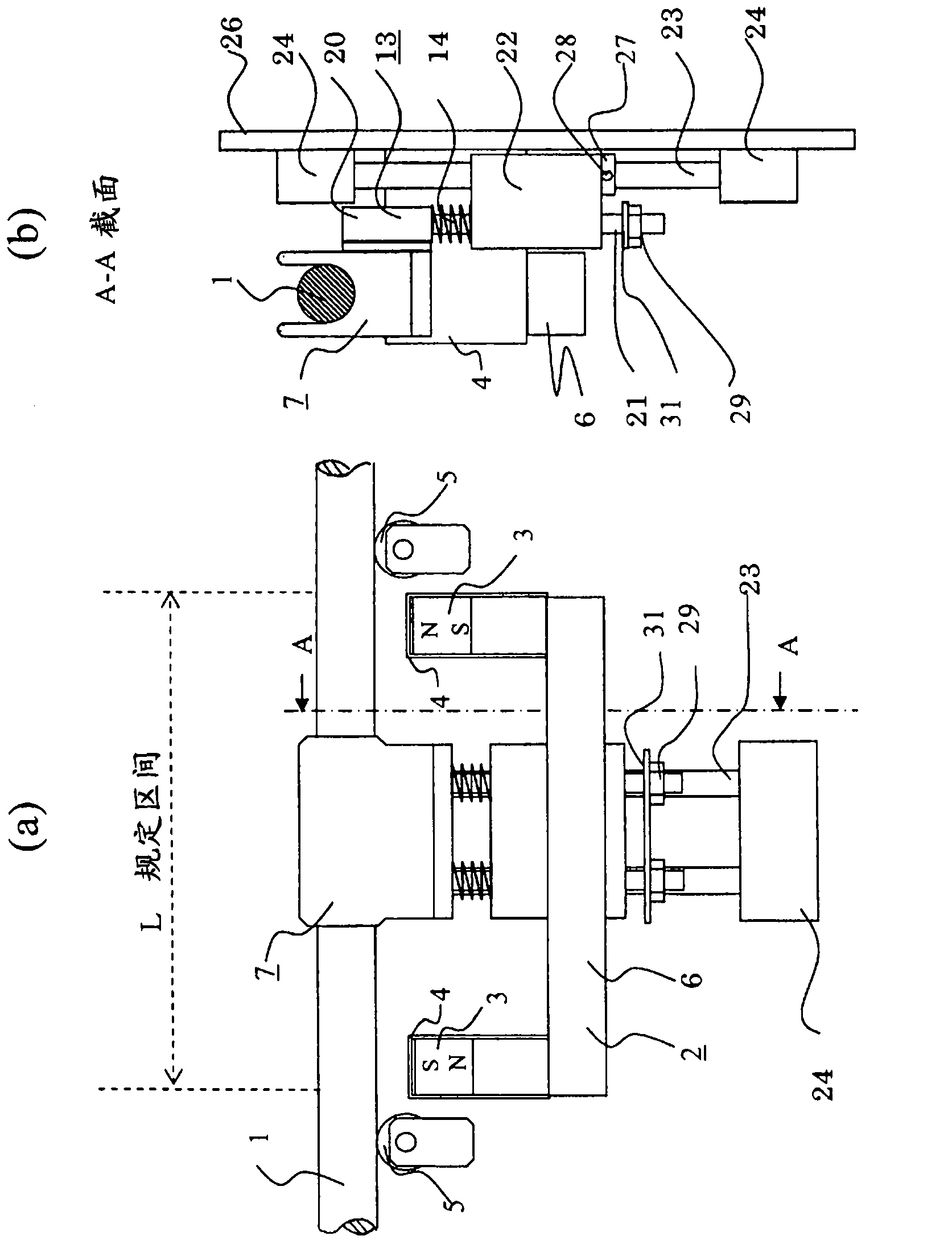
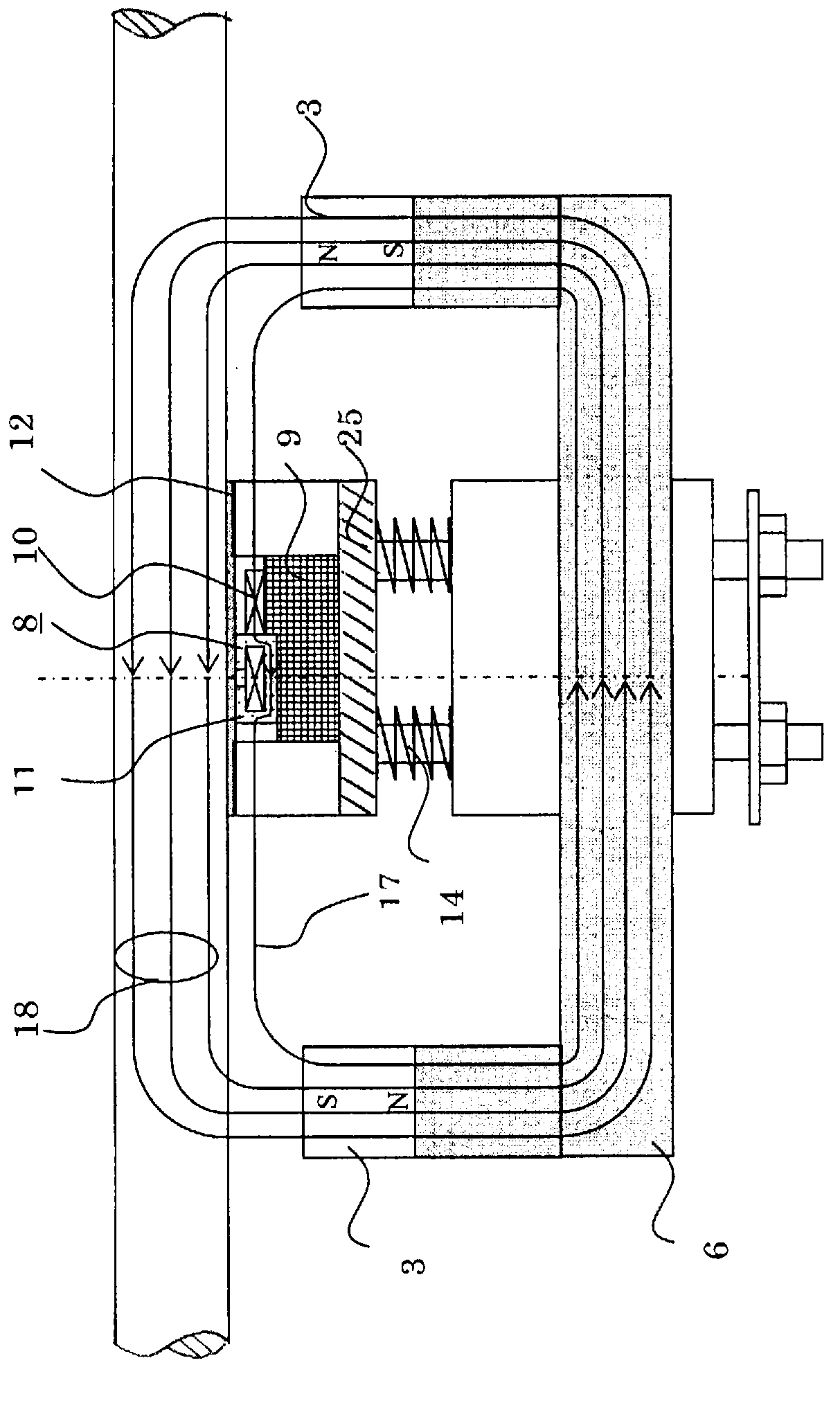
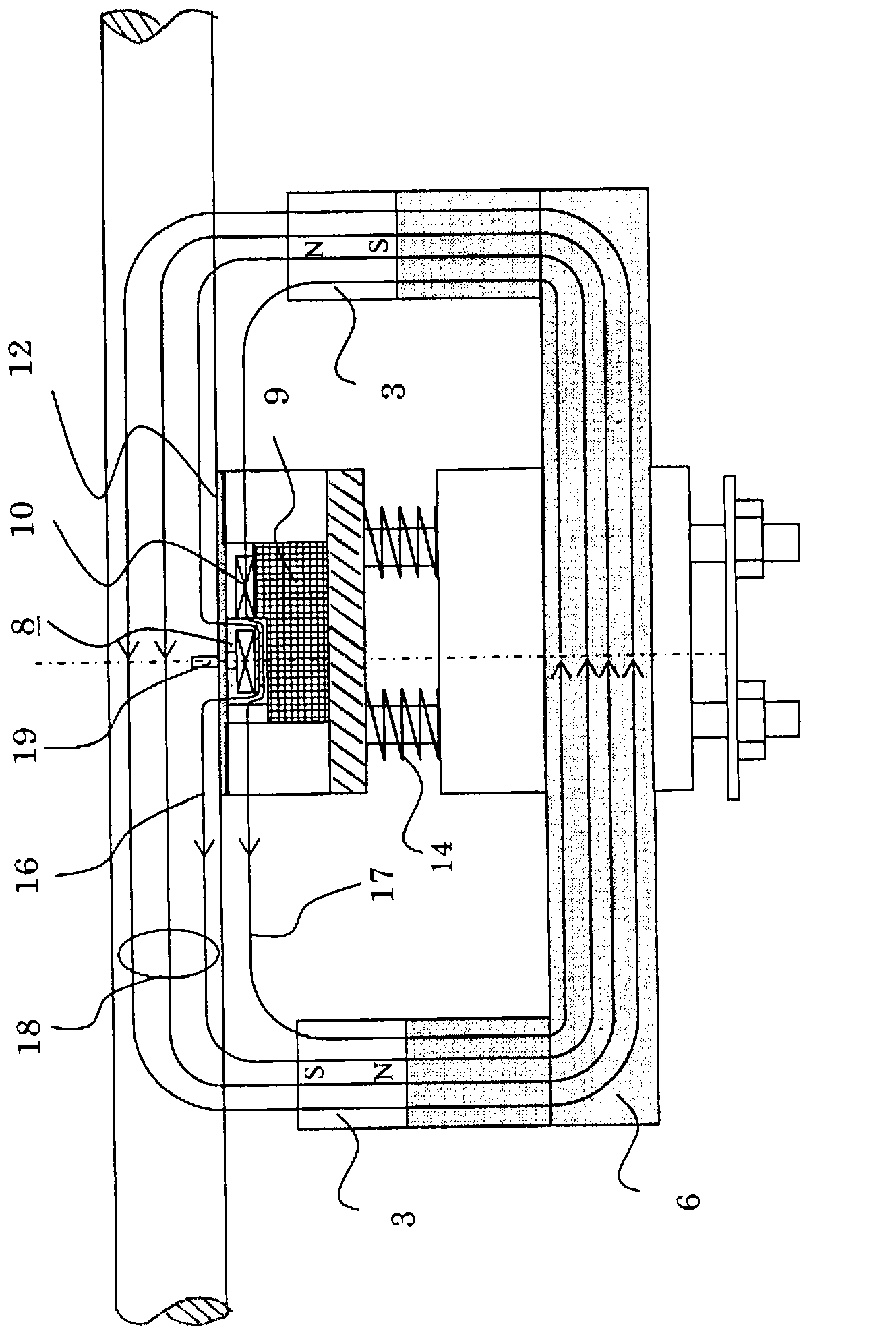
[0023] figure 1 It is a configuration diagram showing a wire rope flaw detection device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 1 (a) is the front view, figure 1 (b) is the A-A line sectional view of (a). figure 2 It is an explanatory diagram showing the detection principle of the wire rope flaw detection device according to Embodiment 1, and shows a case where there is no damaged part of the wire rope. image 3 It is an explanatory diagram showing the detection principle of the wire rope flaw detection device according to the first embodiment, and shows a case where there is a damaged part of the wire rope. Figure 4 It is a perspective view of the wire rope flaw detection device of Embodiment 1. exist Figure 1 to Figure 4 In this case, the wire rope 1 is separated from the magnet cover 4 of the magnet 3 by a predetermined distance (for example, when the diameter of the wire rope 1 is 10 to 15 mm, it is about 5 to 10 mm), and the magnetizer 2 and the ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Next, the wire rope flaw detection device according to Embodiment 2 will be described. Figure 5 It is a configuration diagram showing a wire rope flaw detection device according to Embodiment 2. Figure 6 It is a perspective view showing a wire rope flaw detection device according to Embodiment 2. Also, the same symbols in the drawings represent the same or corresponding parts. In Embodiment 2, two sets of components constituting the wire rope flaw detection device according to Embodiment 1 are respectively provided, and they are arranged in directions facing each other at 180° with respect to the wire rope 1 . A stopper 27 located near the end block 24 is slidable on the lower shaft 23 and fixed at a desired position.
[0035] By arranging two sets of magnetizers 2 in directions facing each other at 180° with respect to the wire rope 1, the uniformity of the magnetic flux distribution in the wire rope 1 increases. In Embodiment 2, the wire rope 1 is separated from ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com