Method for managing distributed dynamic spectrums in digital subscriber line uplink system
A dynamic spectrum management, digital subscriber line technology, applied in the field of spectrum management, can solve the problems of high algorithm complexity, inability to work, and inability to meet cooperation conditions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
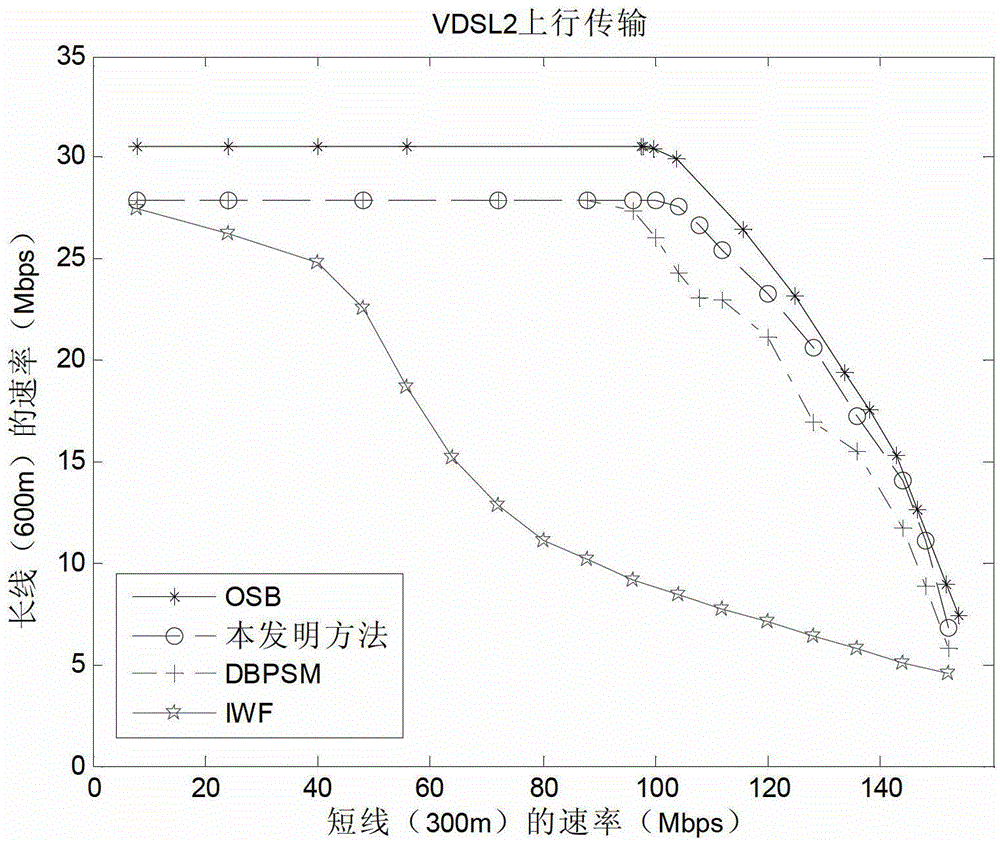
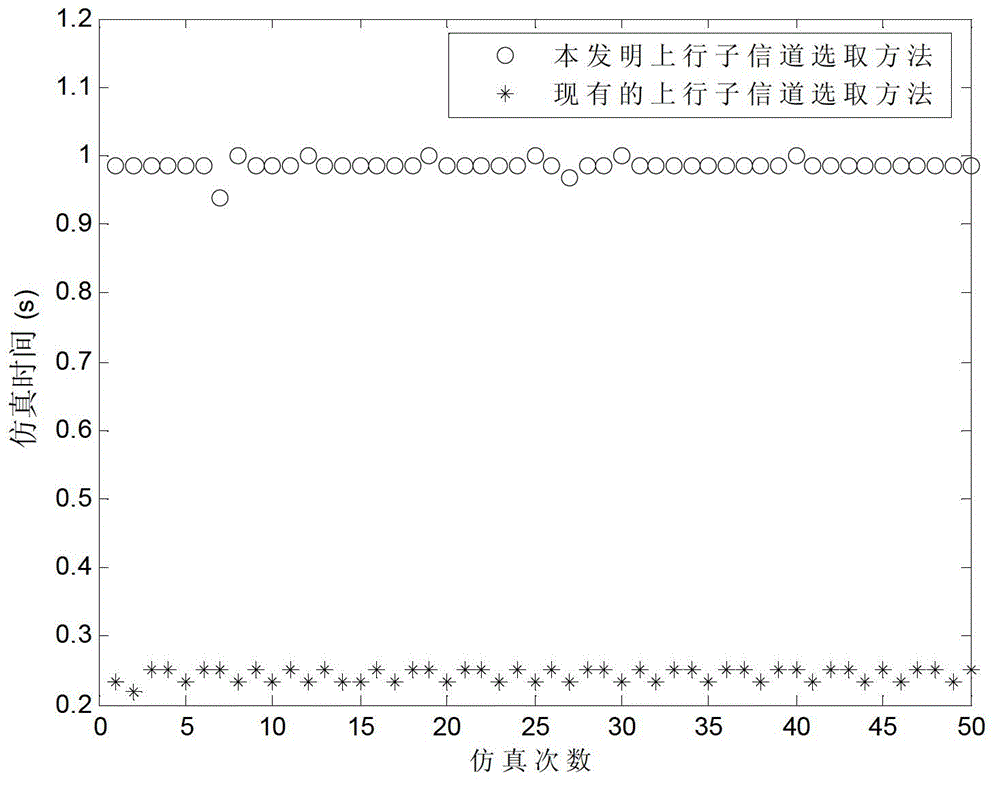
[0033] A distributed dynamic spectrum management method in a digital subscriber line uplink system proposed by the present invention comprises the following steps:
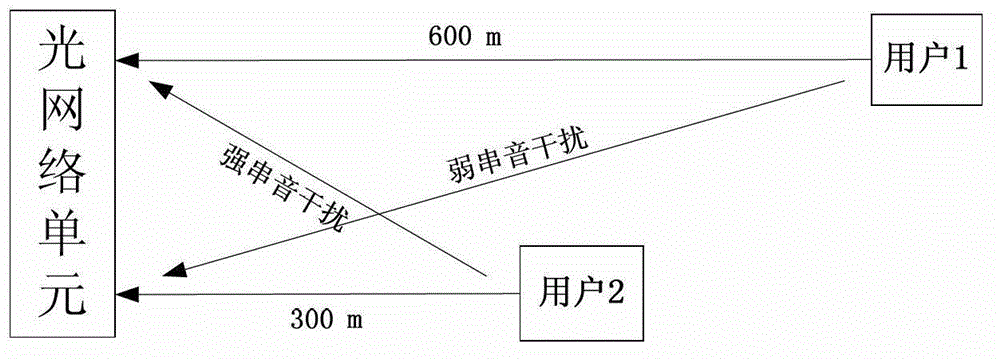
[0034] ①The digital subscriber line system adopts discrete multi-tone modulation (DMT, Discrete Multi-tone), divides the entire channel into multiple independent sub-channels, and then divides all sub-channels into uplink and downlink, and uses sub-channels for uplink information transmission As the uplink sub-channel, the sub-channel used for downlink information transmission is used as the downlink sub-channel.
[0035] ②Digital subscriber line system is divided into digital subscriber line uplink system and digital subscriber line downlink system according to uplink and downlink transmission directions. The Spectrum Management Center (SMC) in the digital subscriber line uplink...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com