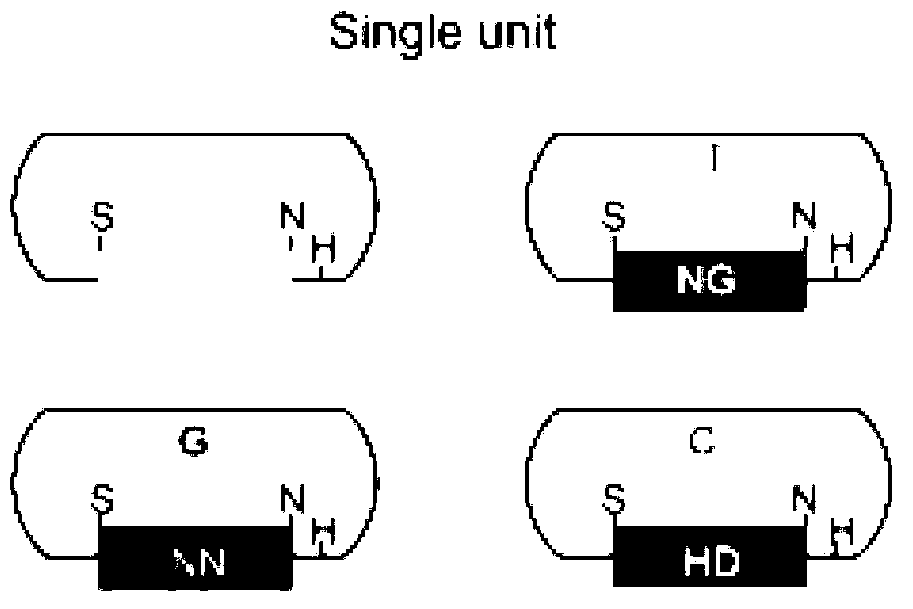
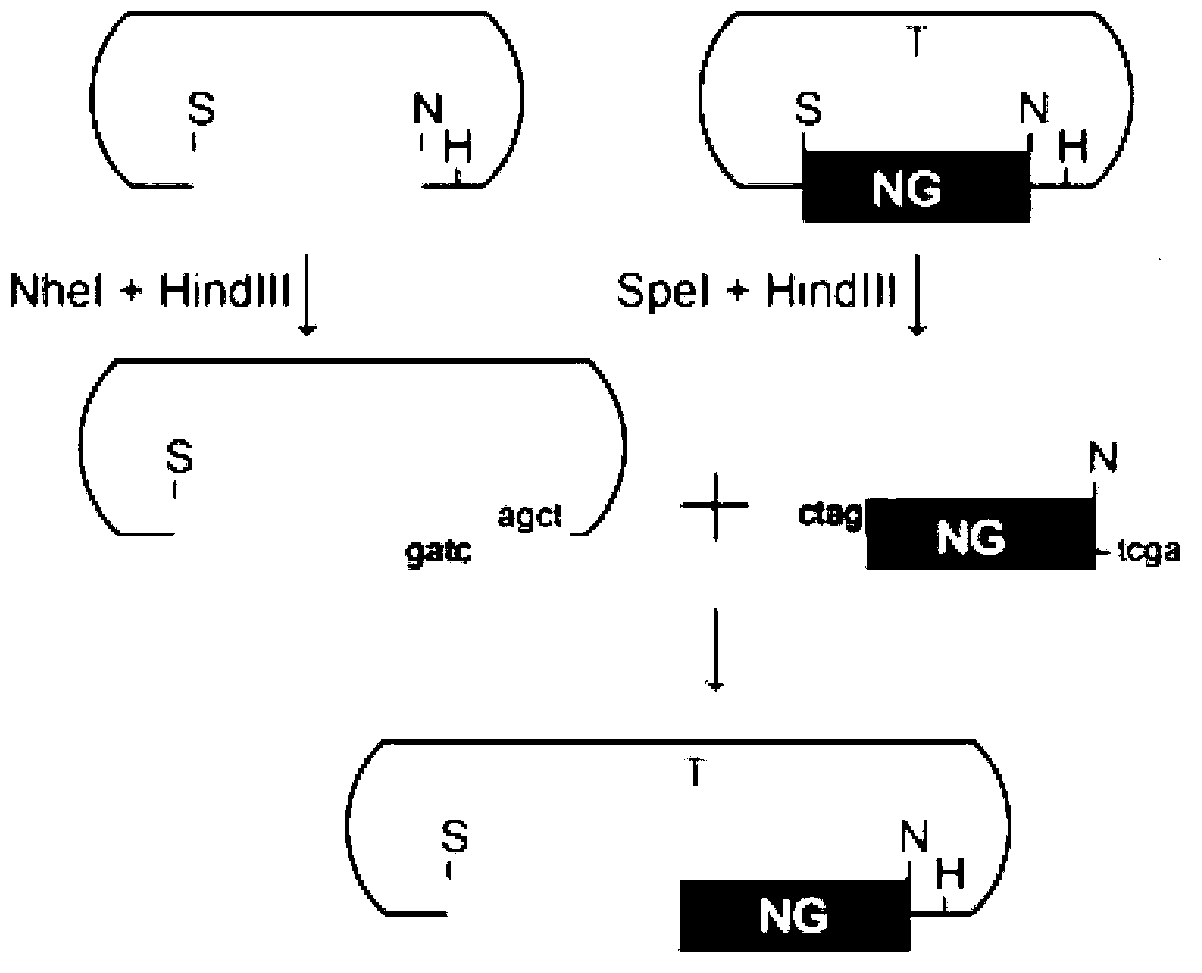
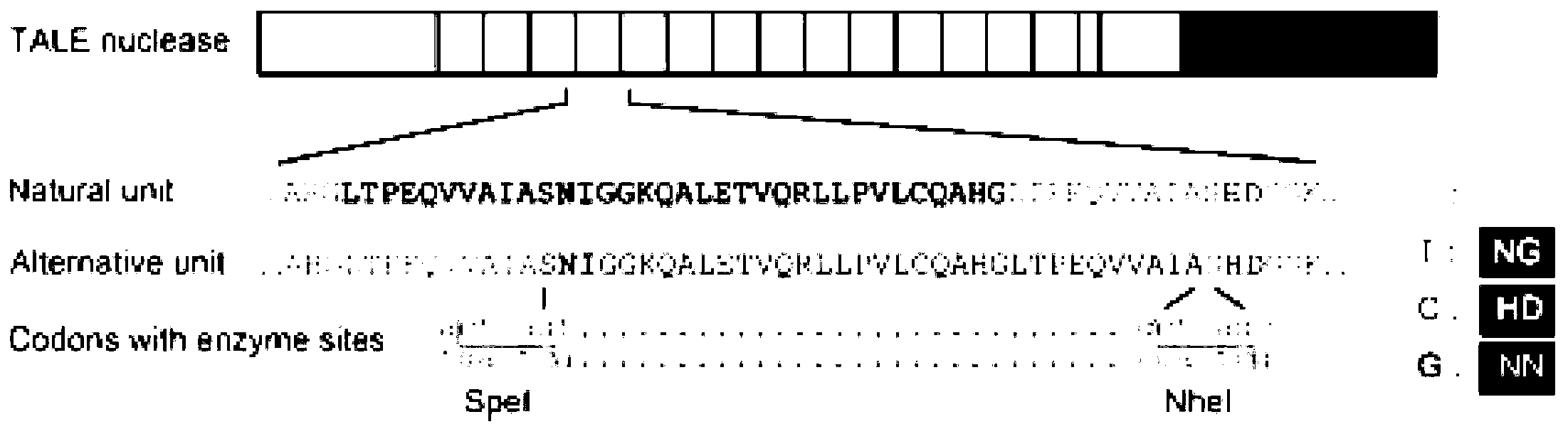Construction method for gene site-specific mutagenesis in embryonic cell of mouse
A gene-directed mutagenesis, mouse embryo technology, applied to other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic materials, using micro-injection methods, etc., can solve the problem of heavy workload, high difficulty, long cycle, etc. problems, to achieve low toxicity, avoid long cycle times, and reduce construction costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Example 1 Construction of Lepr gene knockout in mouse cells
[0062] 1. Prediction of TALE target sites, that is, determination of the target target sequence
[0063] The mouse target genome sequence in this example is the Lepr gene. Log in to the webpage TAL Effector Nucleotide Targeter 2.0 (https: / / boglab.plp.iastate.edu / node / add / talen-old), and follow the instructions to insert the third exon of the target gene Lepr (due to failure in Lepr Find the target site that meets the conditions in the first two exons of ) and paste the sequence into the corresponding text box, and check the selection box of the relevant parameters. Set the range of the number of bases (Repeat Array Length) to be recognized by the TALE module, preferably, set to 15-20 in this embodiment; set the number of bases in the interval region (Spacer), preferably, in this embodiment Set to 15-20. After screening, several candidate target sites were obtained. Further, the target site sequence (SEQ I...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2 Construction of Paklip1 gene knockout and knockin in mouse cells
[0098] 1. Construction and verification of TALEN plasmid targeting Paklip1 knock-in site
[0099] The Paklip1 gene is used as the mouse target genome sequence in this example. Log in to the web page TAL EffectorNucleotide Targeter 2.0 (https: / / boglab.plp.iastate.edu / node / add / talen-old), follow the instructions, paste the first exon sequence of the target gene Paklip1 into the corresponding text box, Tick the checkboxes for the relevant parameters. Set the range of the number of bases (Repeat Array Length) to be recognized by the TALE module, preferably, set to 15-20 in this embodiment; set the number of bases in the spacer region (Spacer), preferably, in this embodiment Set to 15-20. Due to the short length of the first exon of Paklip1, no target sites meeting the conditions were found in it, so the second exon sequence was submitted, and several candidate target sites were obtained after ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com