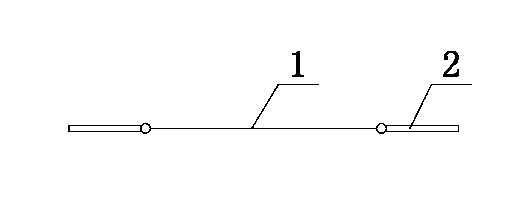Method for detecting residual stress for high-molecular injection molding processing
A residual stress, injection molding technology, applied in the direction of measuring force, measuring device, instrument, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
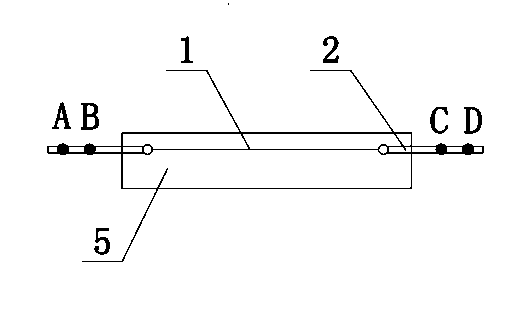
[0066] In this embodiment, the residual stress of the polypropylene injection molded part along the injection flow direction is measured. The sample 5 of the injection molded part has a length of 180mm, a width of 40mm, and a thickness of 3mm. The specific measurement steps are as follows:
[0067] Step 1: Making the Stress Sensor
[0068] Such as figure 1As shown, electrode lead wires 2 are arranged at both ends of the conductive fiber 1, and the conductive fiber 1 and the electrode lead wires 2 at both ends constitute a stress sensor. The conductive fiber 1 is a conductive fiber deposited with polyaniline on the surface.
[0069] Step 2: Clamping
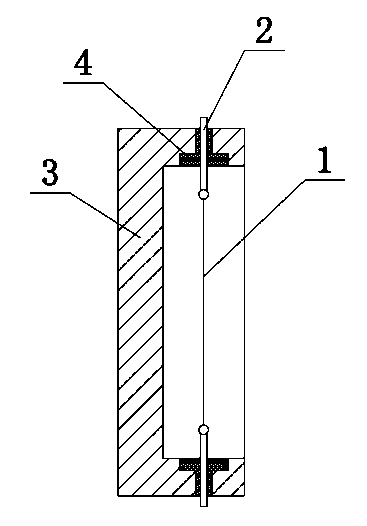
[0070] Such as figure 2 As shown, punch a hole on the movable template 3 of the injection mold, then set the rubber sleeve in the hole, pre-install the assembled stress sensor in the movable mold cavity of the injection mold, and connect the electrode lead wire 2 through the rubber sleeve fixed, thereby fixing the stress sen...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Repeat Example 1 with the following differences. In this example, the residual stress of the polycarbonate injection molded part is measured, and the glass transition temperature of polycarbonate is 150°C.
[0103] Step 2: Clamping
[0104] The stress sensor is arranged along the length direction of the polycarbonate injection molded part and installed at 0.1mm in the thickness direction of the cavity.
[0105] Step Six: Heat Treatment
[0106] Heat the polycarbonate injection molded parts to 100°C and then anneal for 4 hours,
[0107] The measurement and calculation results are shown in Table 2.
[0108] Table 2: Measurement of fiber resistivity change and residual stress calculation results of six polycarbonate samples
[0109] Fiber resistivity before annealing Fiber resistivity after annealing treatment Change rate (%) strain(%) Residual stress (MPa) 3.656 3.608 -1.31 -0.326 6.84 3.666 3.615 -1.39 -0.345 7.24 3....
Embodiment 3
[0112] Repeat Example 2 with the following differences. In this example, the residual stress of the ABS injection molded part is measured, and the glass transition temperature of ABS is 90°C. In the heat treatment, the ABS injection molded part is heated to 100°C, and then annealed for 4 hours.
[0113] Step Eight: Stress Calculation
[0114] Since ABS is an amorphous material whose glass transition temperature is lower than the heat treatment temperature, in order to improve the calculation accuracy, ABS is considered to be in a viscoelastic state, and the corresponding residual stress of polymer injection molded parts is:
[0115]
[0116]
[0117] In the formula,
[0118] - is the calculated stress;
[0119] - is the elastic modulus of ABS;
[0120] - is the Poisson's ratio of ABS;
[0121] , - is the strain in the length direction and width direction of the ABS injection molded part;
[0122] - is the magnitude of creep generated during heat treatmen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com