Synchronous control apparatus and synchronous control method
A technology of synchronous control and control section, applied in the direction of digital control, program control, electrical program control, etc., can solve problems such as spindle speed changes, achieve reliable synchronous control, and alleviate impact effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
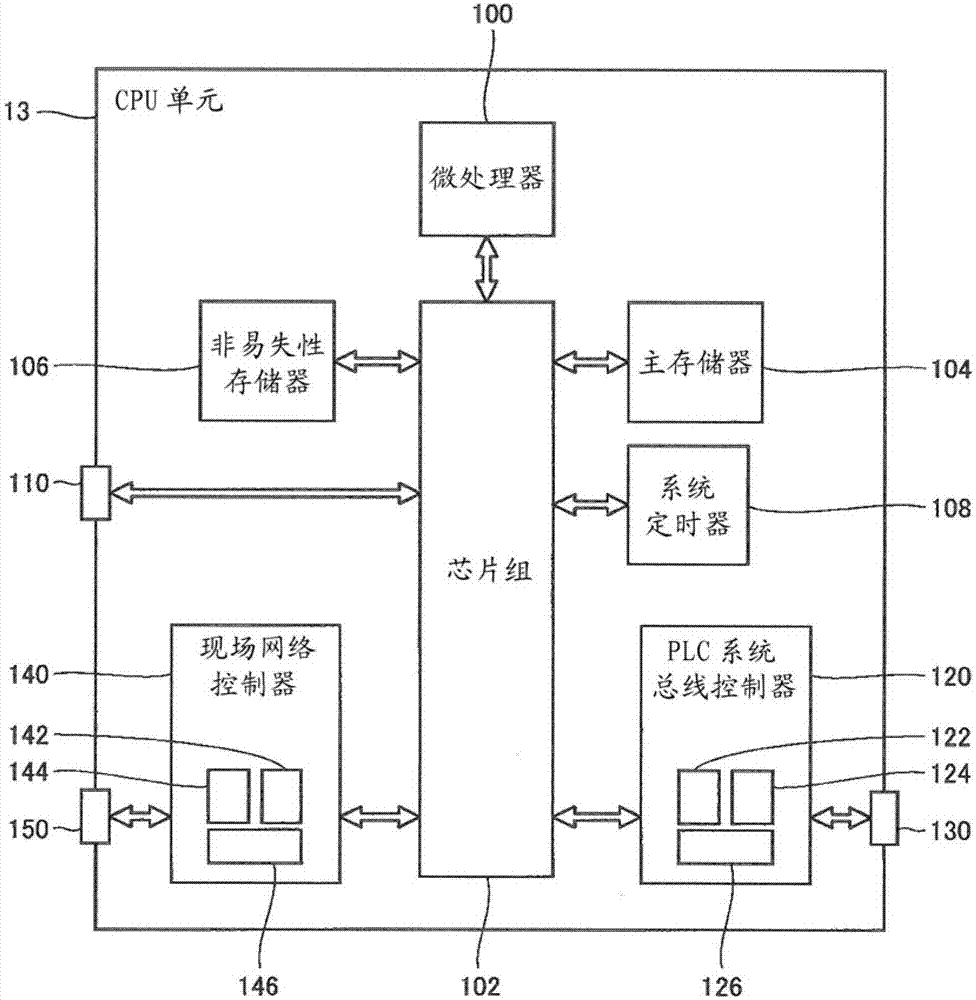
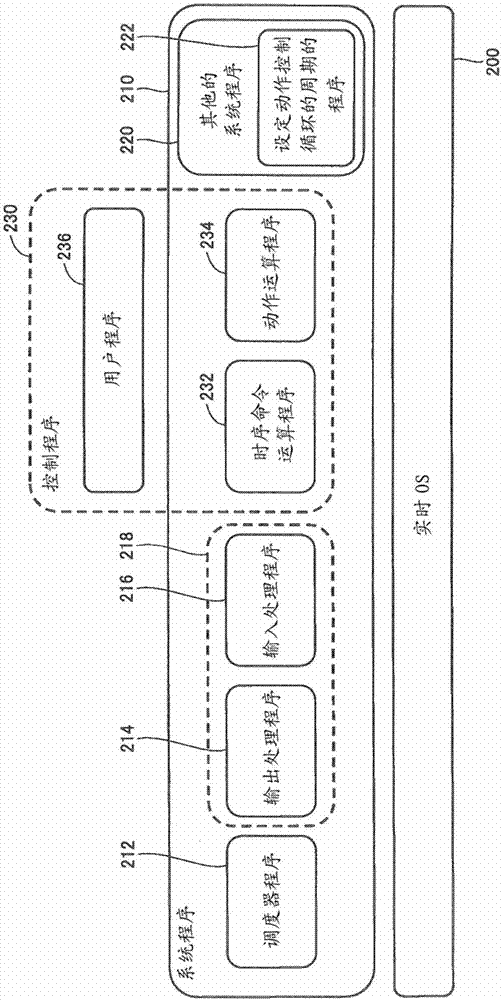
[0034] Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In addition, the same code|symbol is attached|subjected to the same or equivalent part in a figure, and the description is not repeated.
[0035]
[0036] The PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) of this embodiment has an operation control function for controlling the motion of the motor. First, refer to figure 1 , and the system configuration of PLC 1 according to the present embodiment will be described.
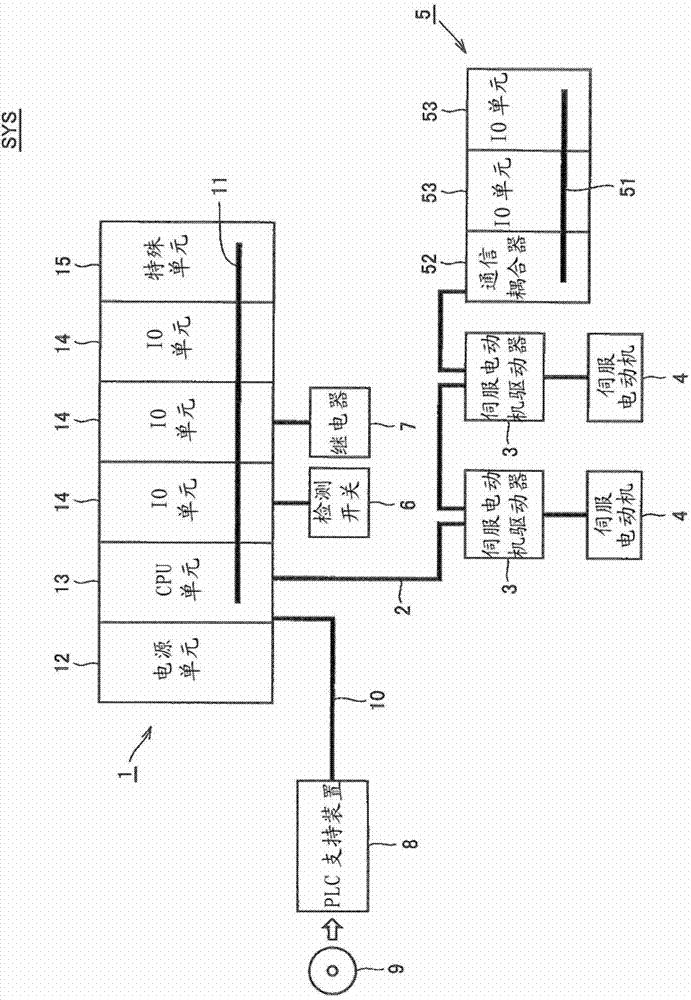
[0037] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram which shows the schematic structure of the PLC system which concerns on embodiment of this invention. refer to figure 1, the PLC system SYS includes a PLC1, a servo motor driver 3 connected to the PLC1 via a field network (field network) 2, a remote IO terminal 5, a detection switch 6 and a relay 7 as field devices. Moreover, the PLC support apparatus 8 is connected to PLC1 via the connection cable 10 grade|etc.,.
[0038]...
no. 2 approach
[0111] In the second embodiment, a further embodiment of a method for synchronizing the master shaft and the slave shaft at a predetermined position when the speed of the master shaft changes from the time of the catch-up operation will be described.
[0112] Figure 7 It is a flowchart showing the operation procedure of the synchronous control in the second embodiment.
[0113] First, the user command value 62 inputs command values of the synchronization start master position SPM, synchronization start slave position SPD, gear ratio GR, target speed VTD, target acceleration ATD, and target deceleration BTD specified by the user (step S101).
[0114] Next, the scheduling unit 63 instructs the start of the follow-up operation of the driven shaft (step S102 ).
[0115] The detection unit 65 acquires the count value (position) of the pulses from the encoder 67 for the main shaft at the time Ts at which the start is instructed, and sets it as the position PM (Ts) of the main sh...
Deformed example 1
[0135] In addition, in this embodiment, as shown in the figure, the cam curve accelerates in a straight line, then becomes a constant speed, and then decelerates, but the present invention is not limited thereto. As the cam curve, for example, a generally known cycloid curve, a trapecloid curve, or the like may be used. Examples of literature on cam curves include "CamDesign and Manufacturing Handbook Second Edition (written by Robert L. Norton INDUSTRIAL PRESS INC2009)", "Mechanics of Mechanics by Mechanics Technician のための実" (by Masao Nishioka, Nikkan Kogyo Shimbunsha, 2003), etc. . In addition, the cam curve can also be represented by a polynomial.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com