Optical axis controller of automotive headlamp
A technology for headlights and controllers, which is applied to headlights, vehicle components, optical signals, etc., can solve problems such as inability to improve accuracy, accurately determine the operating state of non-interfering optical axis correction, etc., to improve convenience, The effect of prolonging life and increasing production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0039] [1. Device structure]
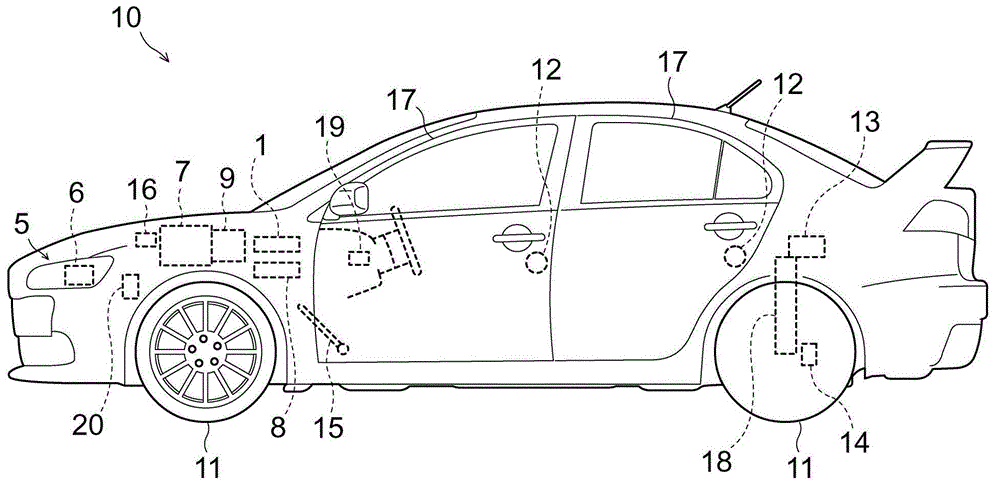
[0040] The optical axis controller of the vehicle headlamp according to the first embodiment is mounted on figure 1 Vehicle 10 is shown. Vehicle 10 is a gasoline powered vehicle driven by engine 7 . The engine 7 generates drive power, which is transmitted to drive wheels of wheels 11 via a transmission (gearbox) 9 and a drive force transmission path (not shown).
[0041] Furthermore, the vehicle 10 includes a pair of left and right headlamps 5 at the front. Each headlamp 5 includes an actuator (adjuster) 6 for adjusting the direction of illumination. The actuator 6 adjusts the optical axis angle in response to the attitude of the vehicle 10 .
[0042] For example, if figure 2Schematically shown, the headlamp 5 includes a vertically movable reflector 5b arranged around a light source 5a. The mirror 5 b has an optical axis 5 c in the lateral direction of the vehicle 10 . The actuator 6 extending or shortening in the horizontal direction (th...
no. 2 approach
[0106] [1. Control block configuration]
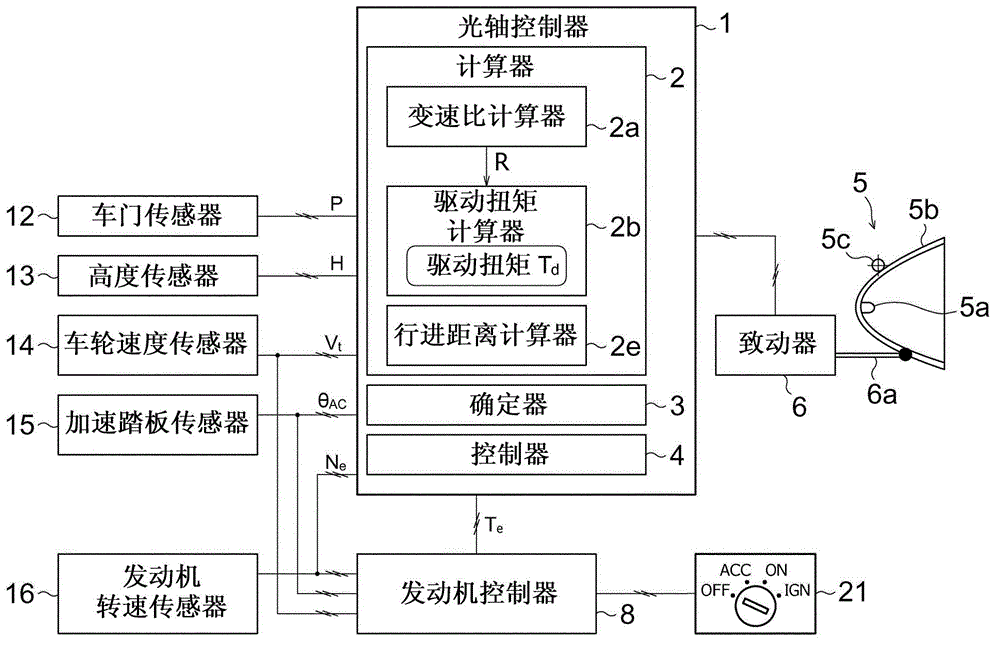
[0107] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the optical axis controller of a vehicle headlamp according to the second embodiment includes a calculator 2 having a different configuration from that of the first embodiment. In this section, the same reference numerals designate the same components as those of the first embodiment, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0108] The calculator 2 performs calculations related to the above-mentioned control of the optical axis, and the calculator 2 includes a gear ratio calculator 2a, a drive torque calculator 2b, a resistance torque calculator 2c, a pitching influence torque calculator 2d, and a travel distance calculator 2e . It should be noted that Figure 6 The flow of parameters computed by each component is schematically shown.
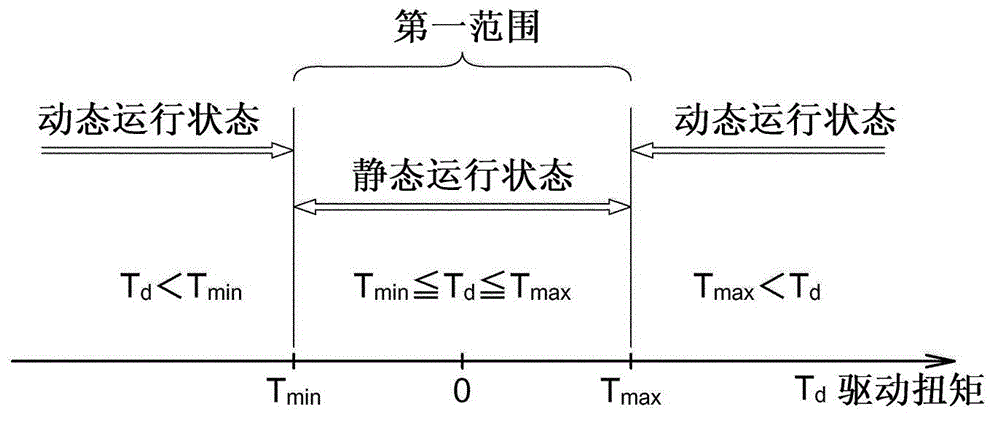
[0109] The resistance torque calculator 2 c calculates the resistance torque T while the vehicle 10 is running (during the running mode of the vehicle 10 ) r . Re...
no. 3 approach
[0126] Optical axis controllers are known which are able to adjust the optical axis angle not only during the idle mode but also during other operating modes. Unfortunately, its traditional control logic sometimes fails to determine the vehicle's precise attitude during the vehicle's cornering maneuvers. For example, when a vehicle is running at a constant speed on an expressway ramp (a spiral ramp connecting two roads with a height difference), the vehicle's attitude in the left-right direction is sometimes unstable, even though the vehicle's attitude in the front-rear direction is stable of. Therefore, in order to control the optical axis in an appropriate manner, it is desirable to accurately determine not only the attitude of the vehicle in the pitch direction but also the attitude of the vehicle in the roll direction.
[0127] Therefore, the optical axis controller according to the third embodiment includes a configuration to solve this problem.
[0128] [1. Device conf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com