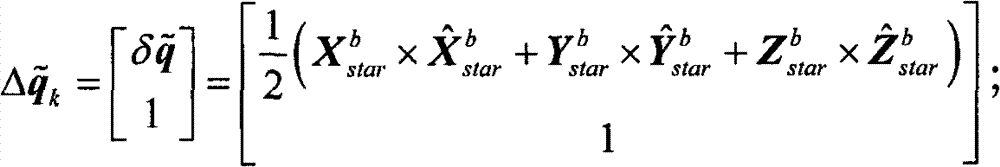Lunar inertial navigation alignment method assisted by star sensor
A technology of star sensors and detectors, which can be used in instruments, integrated navigators, measuring devices, etc., and can solve problems such as low accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
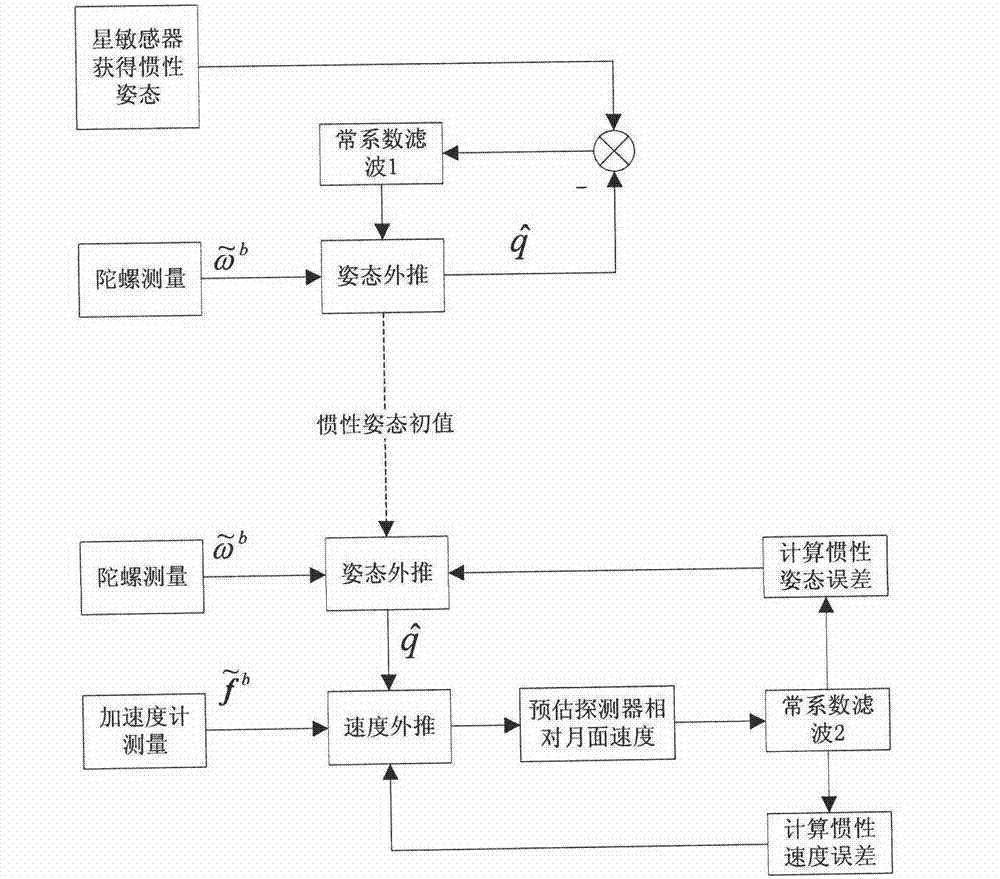
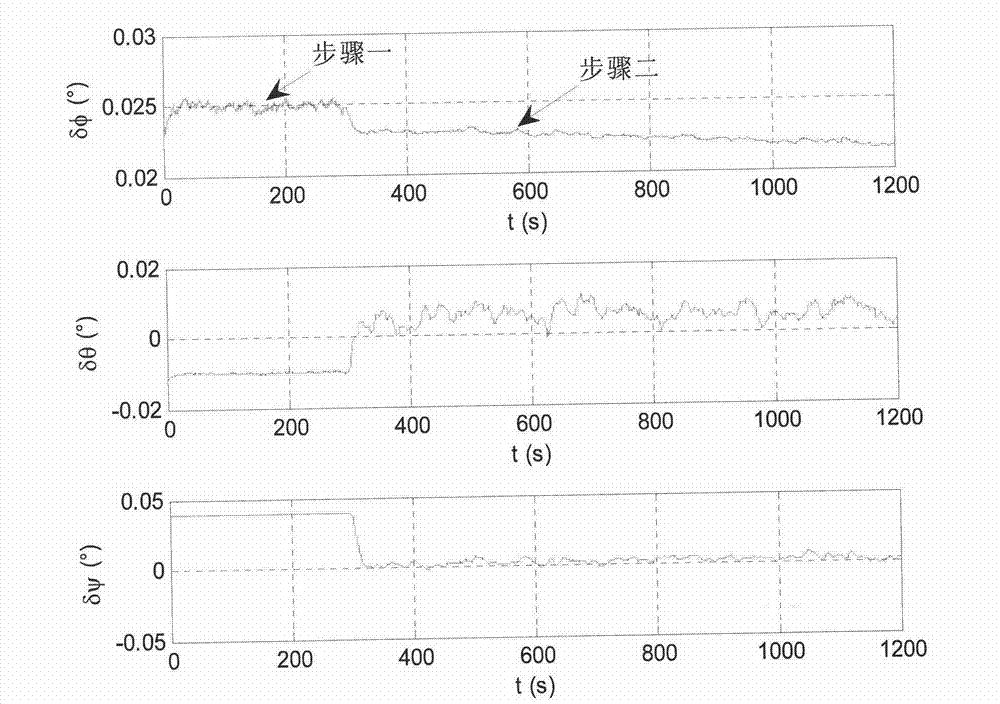
[0149] Here, a simulation example is used to verify the lunar surface take-off and alignment method proposed by the present invention. Assume that the position of the detector on the lunar surface is 45° north latitude, 60° west longitude, and 0m in height, and the longitudinal axis of the detector is upward, but there is a 15° inclination relative to the lunar surface. The detector position given on the ground has an error of 500m (3σ) in longitude, latitude and altitude.
[0150] The probe is equipped with a star sensor and an IMU. Among them, the nominal direction of the optical axis of the star sensor is [cos(38°), cos(54.7°), cos(102.2°)] T , the optical axis error is 3", and the transverse axis error is 24" (3σ); the IMU contains three gyroscopes and three accelerometers, and their input axes point to the same. respectively
[0151] P 1 [cos(54°44′8”), sin(54°44′8”) cos(90°), sin(54°44′8”) sin(90°)] T
[0152] P 2 =[cos(54°44′8”), sin(54°44′8”) cos(210°), sin(54°4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com