Highly sensitive mutated gene detection method
A technology for mutant genes and detection methods, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, recombinant DNA technology, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
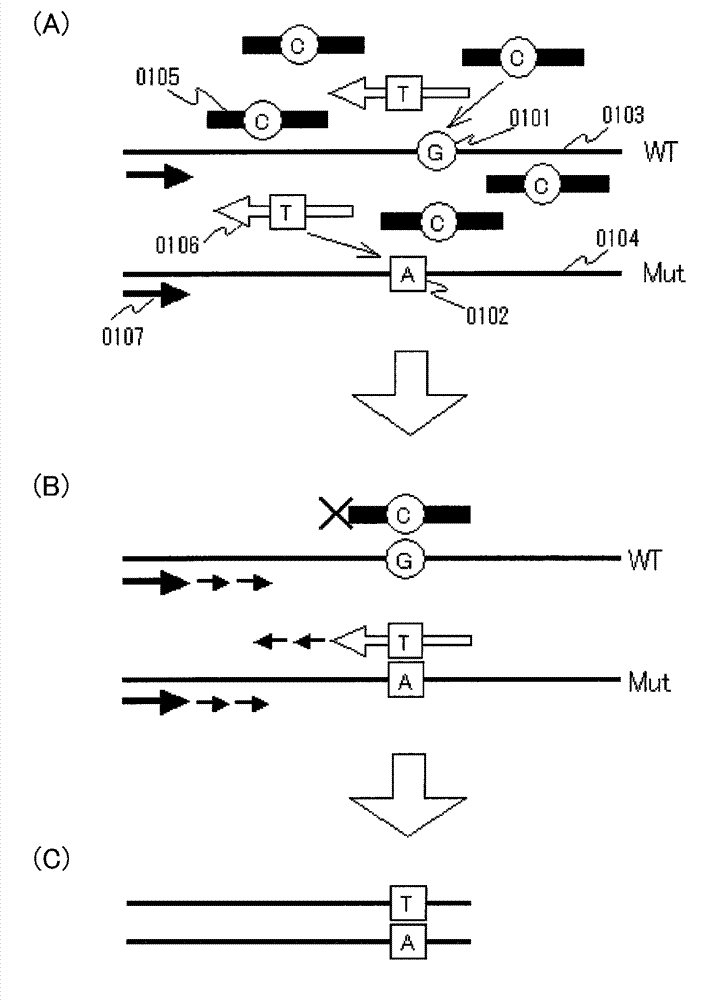
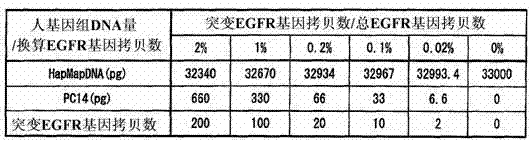
[0065] Embodiment 1 will be described. This embodiment mainly relates to claim 2 . The summary of this embodiment is a method for detecting a mutant gene, which is a method for detecting the presence or absence of a known mutant gene mixed in a gene pool, in which all or part of a target site having a sequence of a wild-type gene is hybridized with A clamp primer composed of PNA, a mutation probe that hybridizes to all or part of the target site having the sequence of the mutated gene and at least a part of the sequence is composed of LNA, coexists with the aforementioned gene library in the reaction solution for gene amplification, and passes the gene The amplification method selectively amplifies a detection region including a target site of a mutated gene, thereby detecting the presence or absence of the mutated gene.
[0066] Requirements of Embodiment 1 will be described. First of all, in the present invention, the definitions of terms such as DNA, RNA, nucleic acid, ge...
Embodiment approach 2
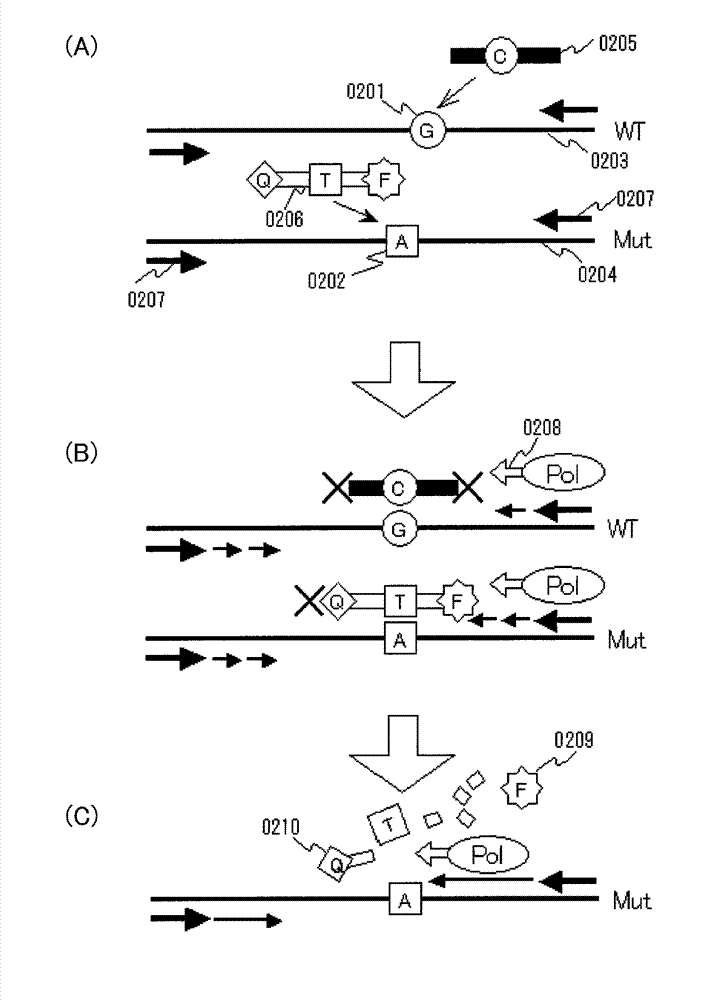
[0093] Embodiment 2 will be described. This embodiment mainly relates to claim 3 . The summary of this embodiment is a method for detecting a mutant gene, which is a method for detecting the presence or absence of a known mutant gene mixed in a gene pool, in which all or part of a target site having a sequence complementary to a wild-type gene is used A clamp primer composed of hybridized PNA, a mutation probe that hybridizes to all or a part of the target site having a complementary sequence of the mutated gene and at least a part of the sequence is composed of LNA, coexists with the aforementioned gene library in a reaction solution for gene amplification, The presence or absence of the mutated gene is detected by selectively amplifying the detection region including the target site of the mutated gene by a gene amplification method.
[0094] That is, the aforementioned Embodiment 1 uses the sequence on the sense side of the gene to be detected as a template to detect a mut...
Embodiment approach 3
[0097] Embodiment 3 will be described. This embodiment mainly relates to claim 4 . The summary of this embodiment is a method for detecting a mutant gene, wherein, based on the method of Embodiment 1 or 2 above, the gene amplification method is a PCR method. In this embodiment, descriptions of the same requirements and the like as those in the first embodiment will be omitted, and only the characteristic requirements and the like of this embodiment will be described here.
[0098] The "PCR method" in the present invention includes not only the PCR method based on the most fundamental principle, but also a modified method of the PCR method developed based on it. For example, it corresponds to nested PCR method, RT-PCR method, and the like.
[0099] The conditions of the reaction solution for gene amplification of this embodiment are the same as those of the reaction solution for gene amplification of Embodiment 1, and therefore description thereof is omitted here, and the cha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com