Multi-core program memory competition recording and replaying method realized by signature
A memory and program technology, applied in the field of multi-core program memory competition recording, can solve the problems of low efficiency during replay, only focus on memory competition recording performance, ignore memory competition replay performance, etc., achieve efficient memory competition replay, improve efficiency, and reduce hardware overhead small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0028] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment in detail, the multi-core program memory contention recording and replay method realized by signature described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0029] Step 1. In the original execution stage of the multi-core program, enable the memory contention recording function, and each processor core starts the memory contention recording;
[0030] Step 2: After the memory contention records of all processor cores are completed, the multi-core program replay stage is entered, and the memory contention replay function is enabled.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific embodiment two, combine figure 2 Describe this embodiment in detail. The difference between this embodiment and the multi-core program memory contention recording and replay method implemented by signatures described in the specific embodiment 1 is: the memory contention recording function is enabled in the original execution stage of the multi-core program as described in step 1. , each processor core starts the memory contention recording operation steps as follows:
[0032] A. The requester issues an instruction. If the instruction is a memory read operation instruction, the value of IC is increased by 1. The value of IC is the instruction count value, and the address of the read memory block is added to all read signature registers. , and at the same time, the requester sends a shared memory request message to the coherence protocol mechanism of each processor, and executes step B; multi-core processors have a coherence protocol control mechanism to ensure...
specific Embodiment approach 3
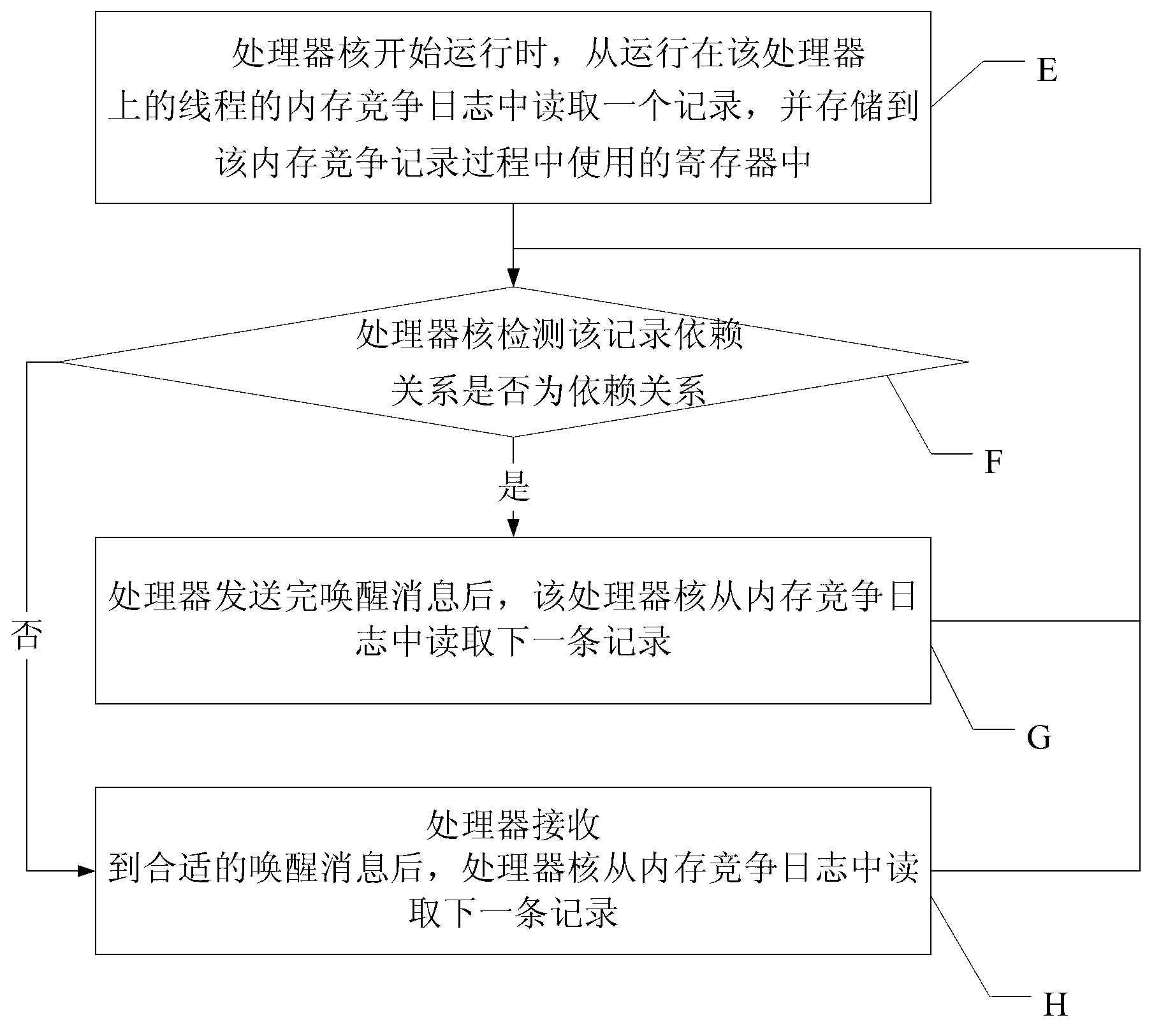
[0039] Specific embodiment three, combine image 3 Specifically explain this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and the multi-core program memory contention recording and replay method implemented by signatures described in the first embodiment is that: after the memory contention recording of all processor cores is completed in step two, Enter the multi-core program playback stage and enable the memory competition playback function. The operation steps of each processor core are as follows:
[0040] E, when the processor core starts running, read a record from the memory competition log of the thread running on the processor, and store it in the register used in the memory competition recording process, and execute step F;
[0041] F. The processor core detects the record dependency. If the record is a false dependency, after executing its corresponding instruction, create a wake-up message and send it to the corresponding processor through the consistency pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com