Control method for hierarchical saturation PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) controller based on integral separation
A technology of integral separation and control method, applied in the control field of hierarchical saturated PID controller, can solve the problems of system oscillation, large system overshoot, PID operation integral accumulation, etc., to achieve good control effect and remove adverse effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
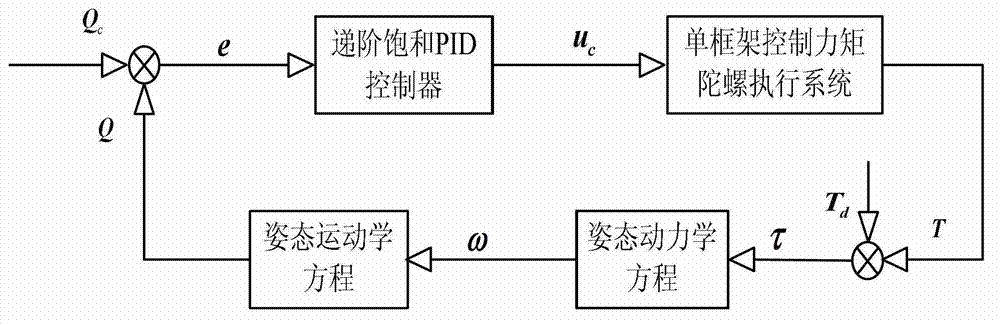
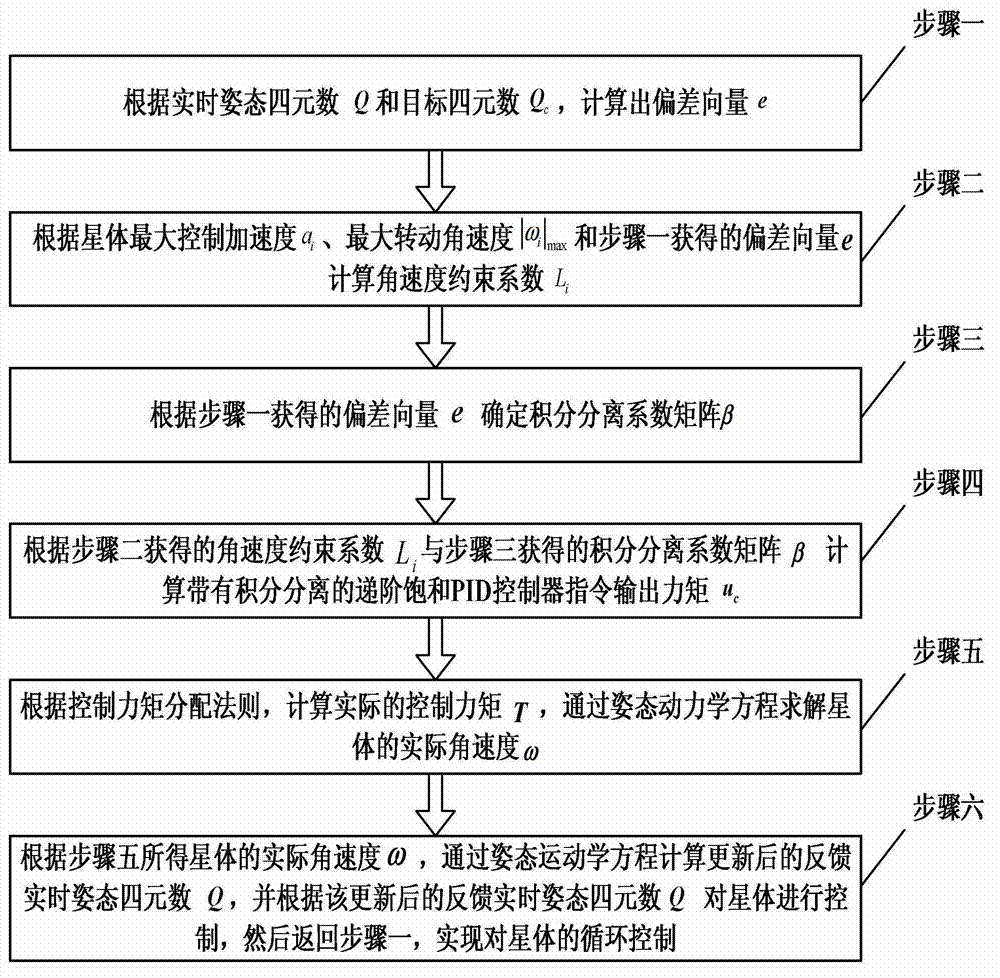
[0016] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figure 1-2 Illustrate this specific embodiment, the control method based on the hierarchical saturation PID controller of integral separation, the control object of this control method is agile satellite spacecraft, hereinafter referred to as agile satellite spacecraft is a star, and described control method comprises the following steps:
[0017] Step 1: According to the real-time attitude quaternion Q of the star and the quaternion Q of the star target c , calculate the deviation vector e;
[0018] Step 2: According to the maximum control acceleration a of the i-th axis of the star coordinate system i , the maximum rotational angular velocity of each axis of the star|ω i | max Calculate the angular velocity constraint coefficient L with the deviation vector e obtained in step 1 i ;
[0019] Step 3: Determine the integral separation coefficient matrix β according to the deviation vector e obtained in step 1;
[0020] S...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the step 1 is based on the real-time posture quaternion Q and the target quaternion Q. c , the method to calculate the deviation vector e is as follows:
[0025] The form of the real-time attitude quaternion Q is as follows:
[0026] Q = q 0 q 1 q 2 q 3 = cos θ 2 i x ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
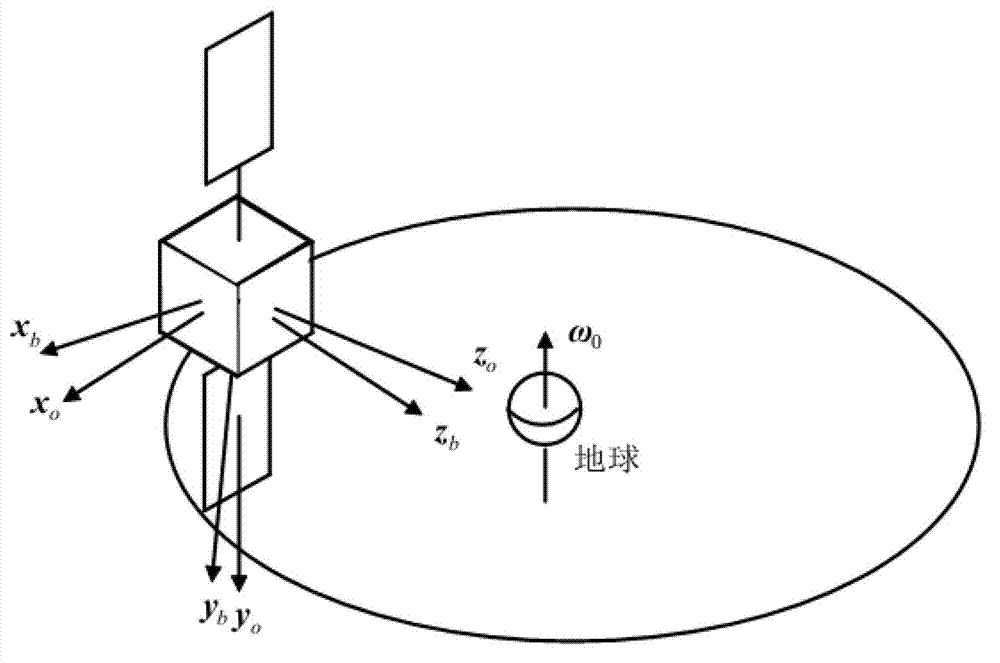
[0032] Specific embodiment three, combine image 3 This specific embodiment will be described. The difference between this specific embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is the step 2: the deviation vector e obtained according to the step 1, the maximum control acceleration a of the star i and the maximum rotational angular velocity |ω i | max Calculate the angular velocity constraint coefficient L i The method is as follows:
[0033] L i = ( c / 2 k ) min { 4 a i | e i | , | ω i | max }
[0034] Among them, k, c are gain coefficients;
[0035] a i =40% U / J ii is the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com