Optical module structure
An optical module and structure technology, applied in the coupling of optical waveguides, etc., can solve problems such as high flatness, troublesome manufacturing, and low optical coupling efficiency of received light
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] In order to make the above-mentioned purposes, features and advantages of the present invention more obvious and understandable, the preferred embodiments of the present invention will be specifically cited below, together with the accompanying drawings, for a detailed description as follows:
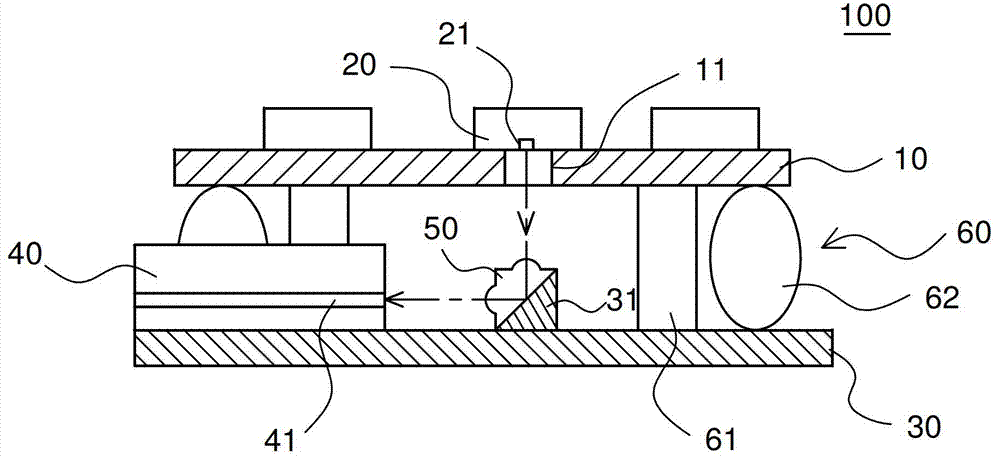
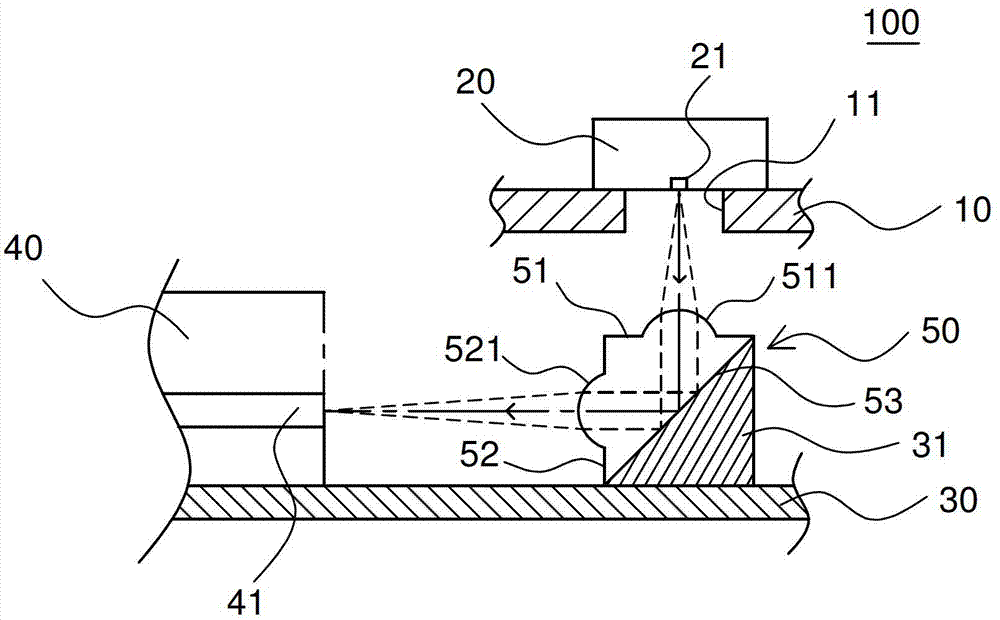
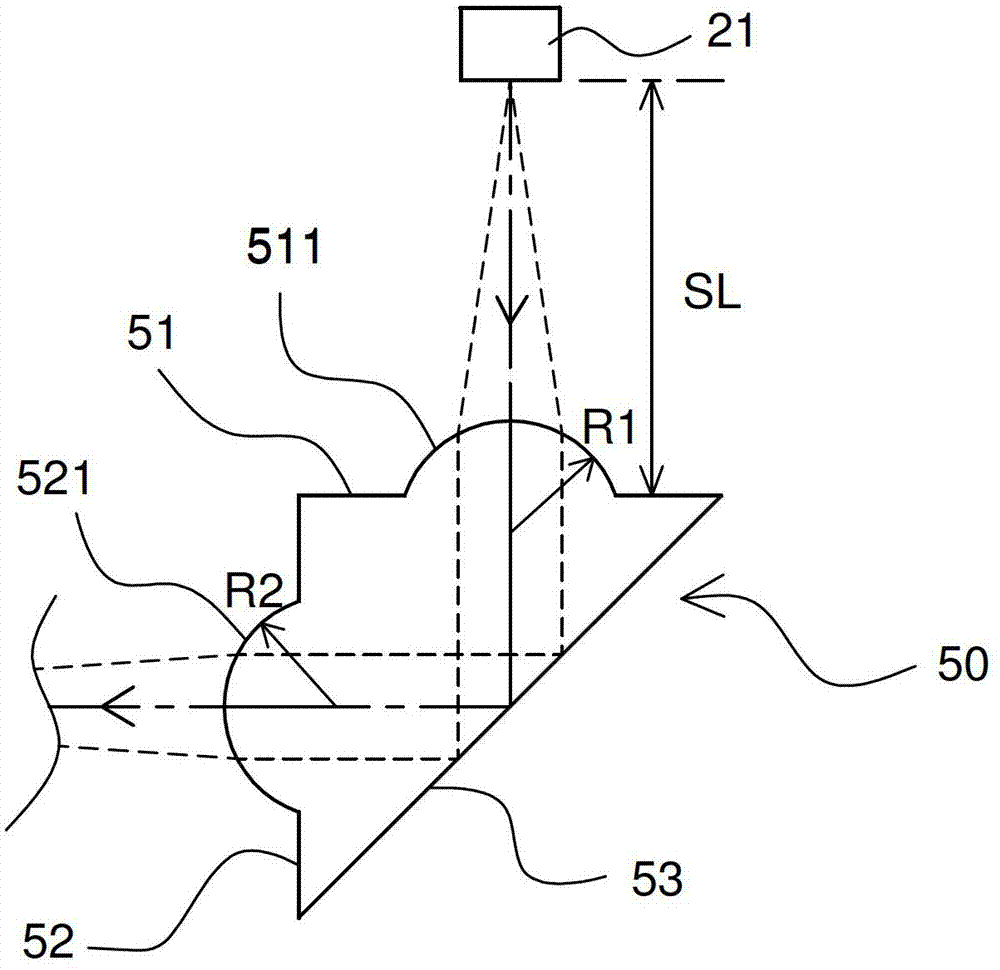
[0016] Please refer to figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is a side sectional view of an optical module structure according to an embodiment of the present invention. An optical module structure 100, for example, is a packaging module structure made by micro-electromechanical (MEMS) technology, and the optical module structure 100 includes: a first substrate 10, a first optical element 20, a second substrate 30, a The second optical element 40 and a prism 50 . The first optical element 20 is disposed on the upper surface of the first substrate 10 , and the first optical element 20 has a first optical function portion 21 vertically downward. In this embodiment, the first optical el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com