Method to measure structures of human brain
A technique for measuring shaft and structural parameters, applied in the direction of using magnetic variable measurement, magnetic resonance measurement, measurement using nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
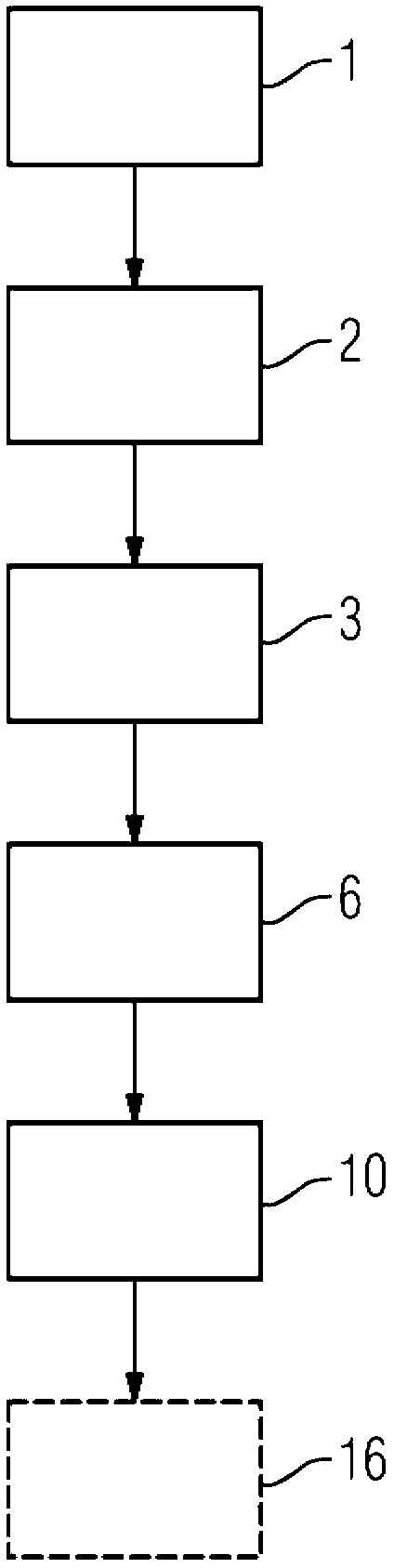
[0026] figure 1 A flow chart of the method according to the invention is shown in an exemplary embodiment. In step 1 , a magnetic resonance pre-examination, in particular an overview of the brain to be examined, is initially recorded. Conventional techniques for recording such overview images can be used here.
[0027] During the magnetic resonance pre-examination, the hippocampal region in the brain is automatically segmented and localized in step 2 using segmentation algorithms known from the prior art.
[0028] Since the position and state of the hippocampus is now known, in step 3 several measurement axes are automatically arranged through the hippocampus and thus through the entire brain, which are to be measured underneath. However, it is also conceivable here to determine these measuring axes manually by an operator.
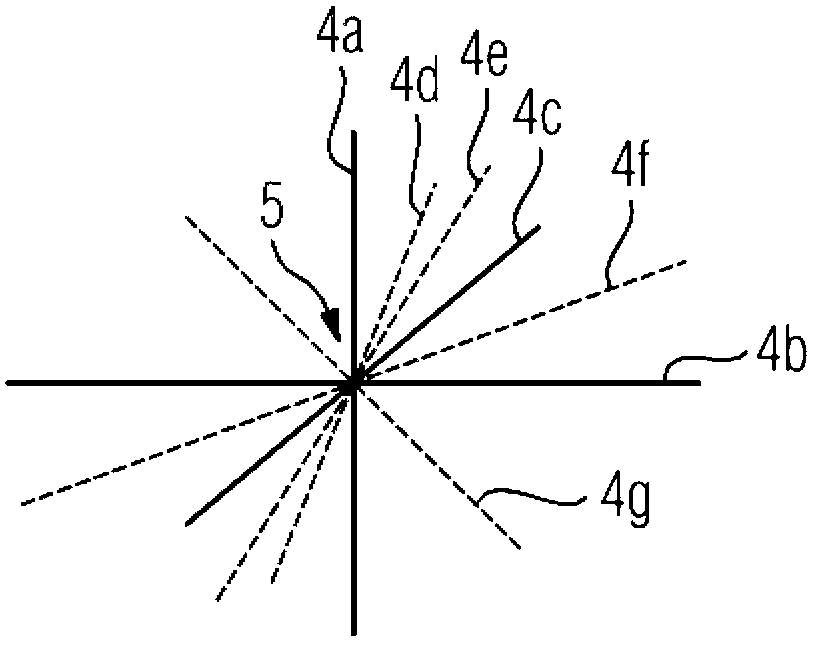
[0029] figure 2 A possible selection of measuring axes 4 a - 4 g that covers the space as well as possible and provides information in as many direc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com