Unknown-node locating method based on underground wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and unknown node technology, applied in the field of self-location of unknown mobile nodes, can solve the problems of low positioning accuracy, instability, and high node cost, and achieve the effects of low node cost, improved positioning accuracy, and easy implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1: Simulation experiment of distance-independent positioning of a section of horizontal shaft roadway in an underground mine.
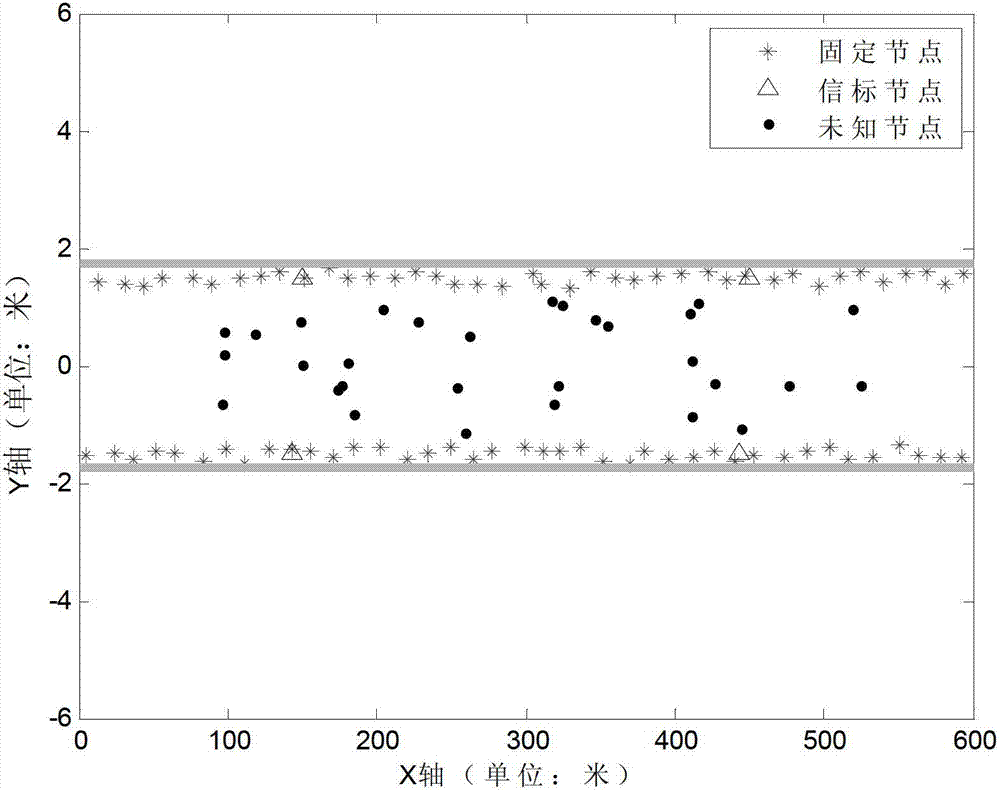
[0051] The distribution of nodes in the simulation experiment is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the x and y axes are the length and width directions of the horizontal well roadway respectively. The roadway is 600 meters long and 3.5 meters wide. The two thick solid lines parallel to the x-axis in the figure represent the roadway wall, and 80 "*" represent the roadway along the roadway. Fixed nodes placed on the wall with low precision, 4 "△" indicate beacon nodes with known positions, and beacon nodes are also arranged along the roadway wall, 30 "◆" represent unknown nodes randomly distributed in the roadway, adjacent fixed nodes The average distance between nodes along the x-axis direction D x =15m, the average distance along the y-axis direction D y = 3m, the deployment error of the fixed node along the x-axis and y-axis directio...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2: Simulation experiment of distance-independent positioning in underground roadway with branches.
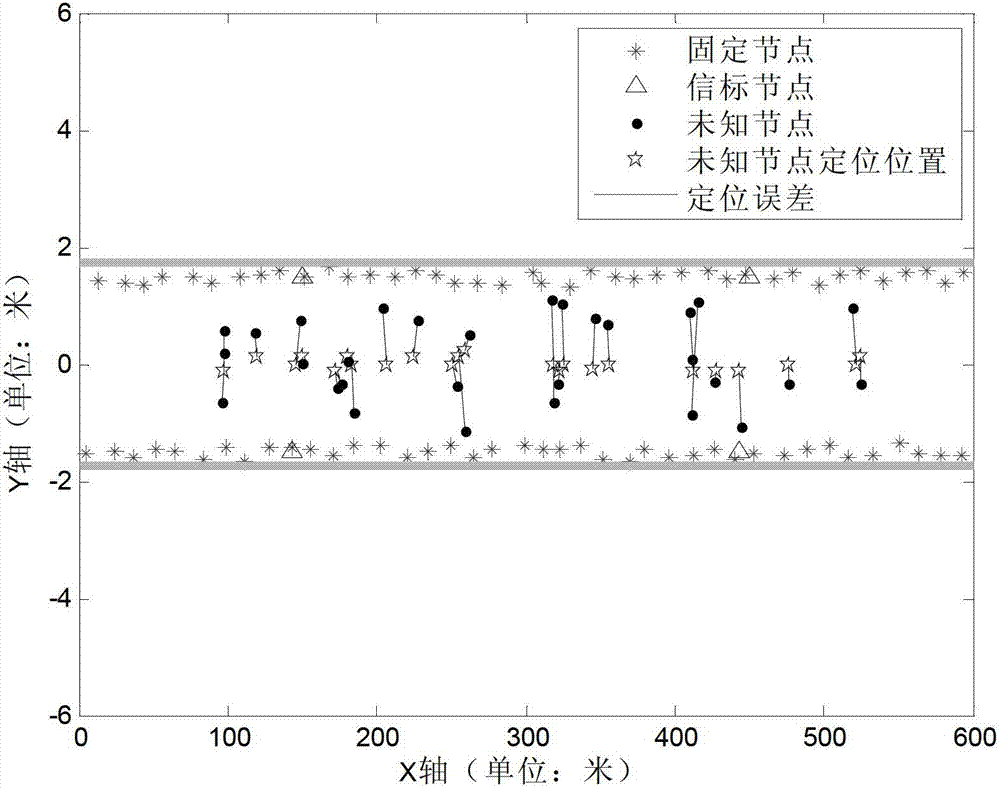
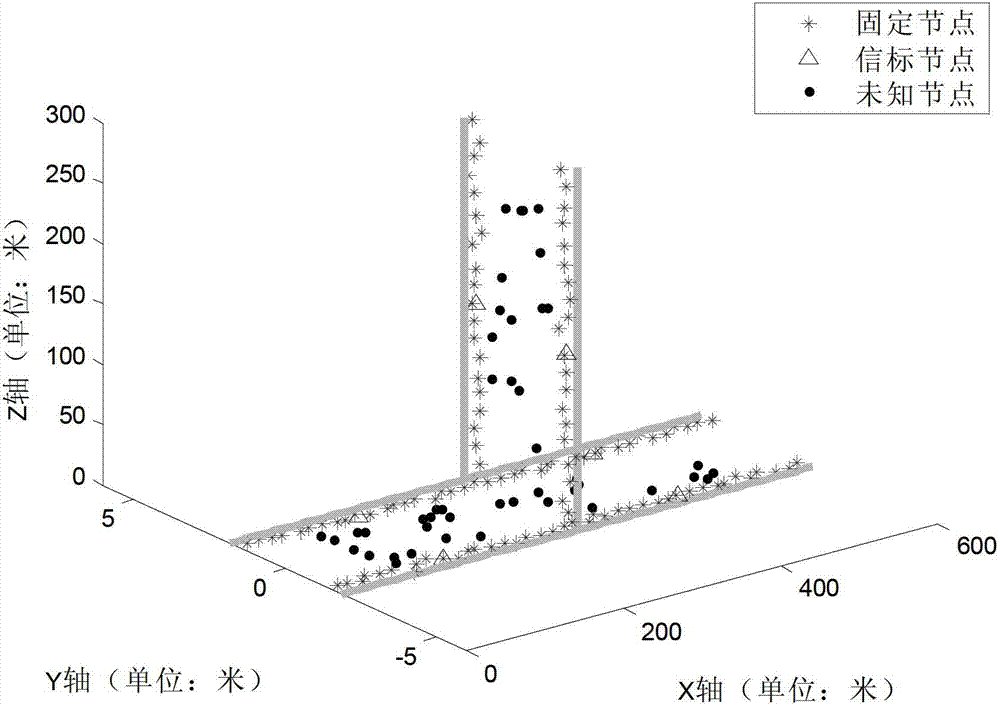
[0053] The distribution of nodes in the simulation experiment is as follows: image 3 As shown, the roadway is composed of a section of horizontal shaft and a section of intersecting vertical shaft. The horizontal shaft is 600 meters long along the x-axis direction, and the vertical shaft is 300 meters long along the z-axis direction. The placement interval and placement error are the same as in Embodiment 1. The positioning result of embodiment 2 is as follows Figure 4 As shown, "☆" indicates the positioning result of the unknown node, and the positioning result and the unknown node are also connected by a solid line. It can be calculated that the average positioning error of the present invention is about 1.78m, and the average positioning accuracy relative to the communication distance is 0.036. It can be seen that the present invention also has higher ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com