Weighing cell operating on the principle of electromagnetic force compensation with optoelectronic position sensor
A weighing cell, compensation principle technology, applied in the field of balances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
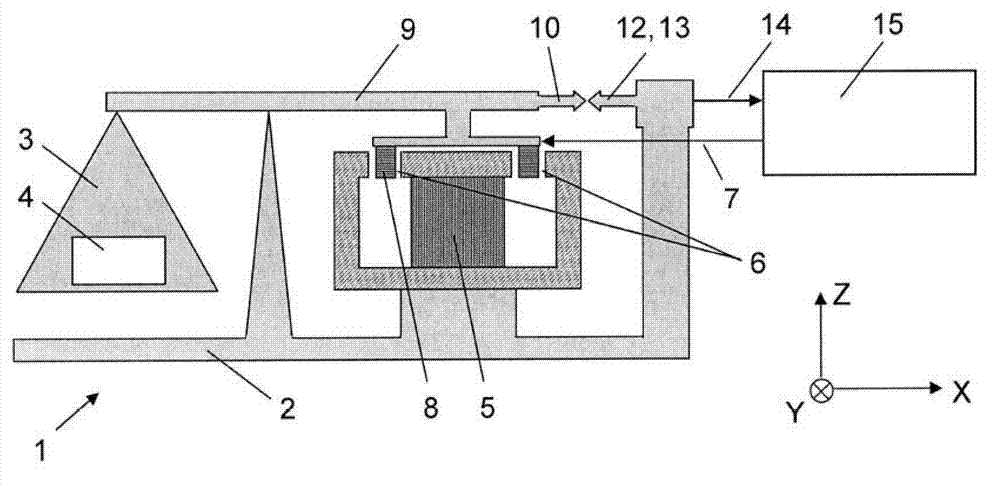
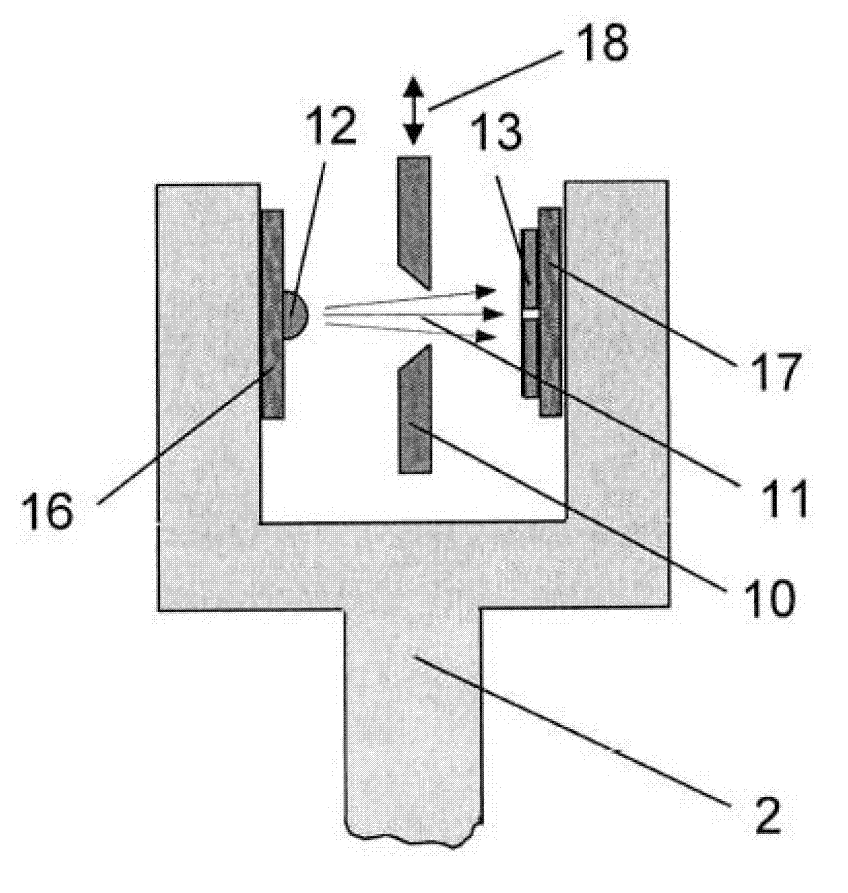
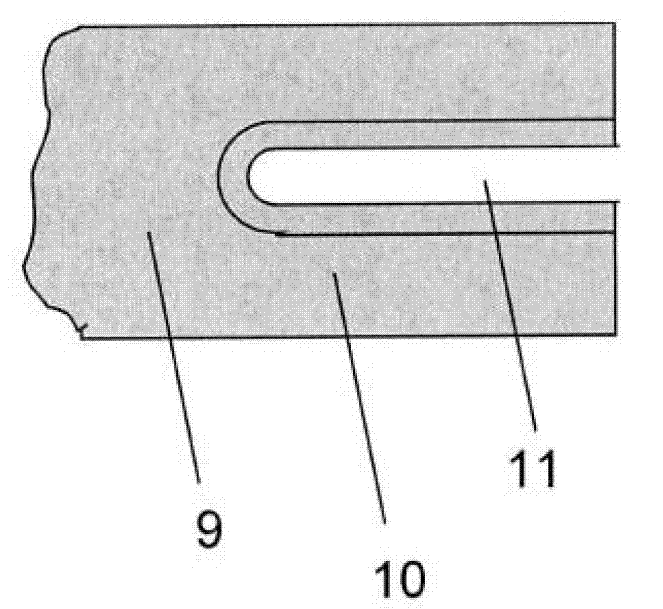
[0041] figure 1 It schematically shows a weighing unit with electromagnetic force compensation and photoelectric position sensor. Add a Cartesian coordinate system X, Y, Z as a reference, where X axis and Z axis are located figure 1 In the drawing plane, and the Y axis points to the space behind the drawing plane. The identifiable elements of the weighing unit 1 in the figure include a fixed base part 2; a load receiver 3, which is constrained by a balance beam 9 to be guided and movable relative to the base part 2; firmly installed on the base part 2 The cup-shaped permanent magnet system 5 (shown in cross-sectional view) of the permanent magnet system; the air gap 6 of the permanent magnet system, the coil 8 conducting the compensation current 7 is movably suspended in the air gap; and the load receiver 3 and the coil 8 The force-transmitting mechanical connection between the two is in the form of a balance beam 9 here. Photoelectric position sensor ( figure 1 Is displayed s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com