Rat brain section microscopic image segmentation method based on markov random field theory
A Markov random field and microscopic image technology, applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that Gaussian distribution cannot accurately describe noise and cell grayscale information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
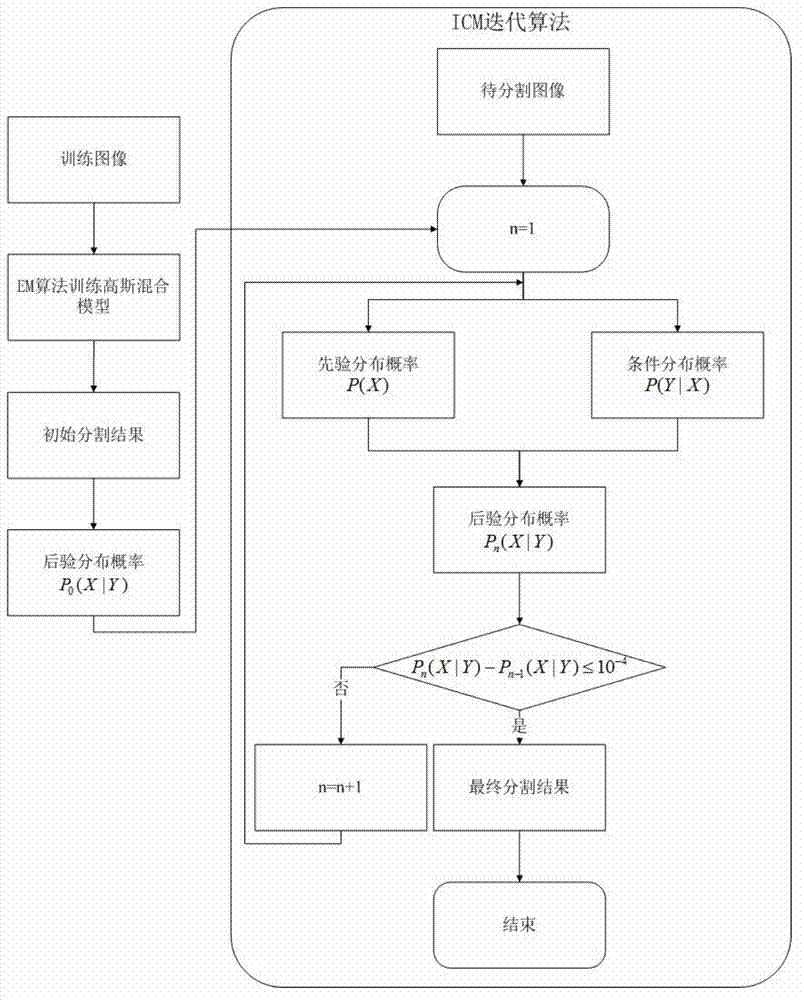
[0054] Now in conjunction with embodiment, accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
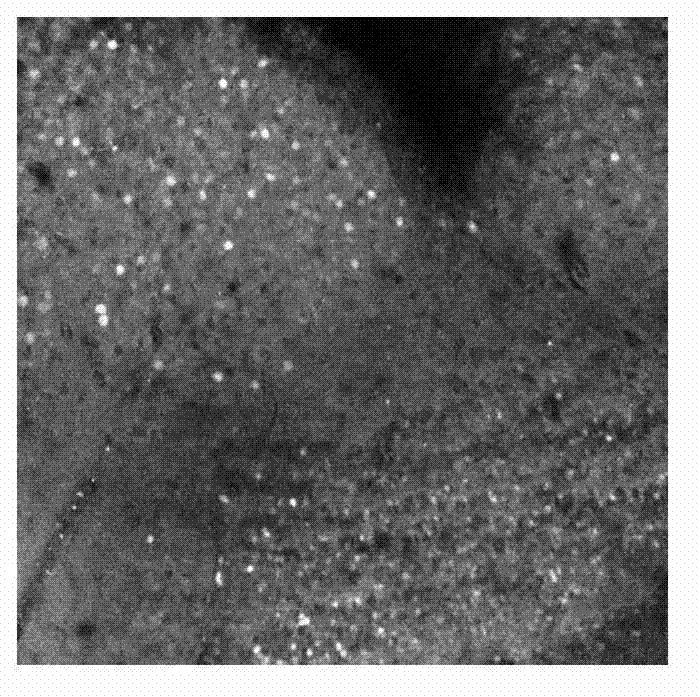
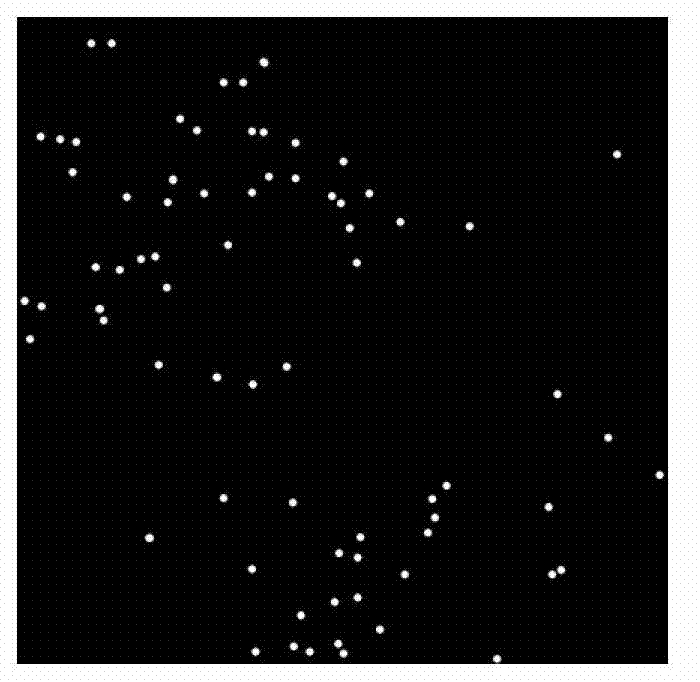
[0055] The hardware environment used for implementation is: Intel Core 2 Duo 2.93G computer, 2.0GB memory, 512M graphics card, and the running software environment is: Windows XP. We have realized the method that the present invention proposes with Matlab7.0 software. The image database includes 600 microscopic images of mouse brain slices with a resolution of 732×732, 400 of which have been segmented and used to train the parameters of the Gaussian mixture model; the remaining 200 are images to be segmented.
[0056] The present invention is specifically implemented as follows:
[0057] Step 1: Learn the parameters of the Gaussian mixture distribution: use the binary Gaussian mixture distribution to model the microscopic image of the mouse brain slice, and estimate the parameters of the Gaussian mixture distribution through the expectation maximization algorith...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com