Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing thin film transistor, display and electronic device
一种薄膜晶体管、显示器的技术,应用在晶体管、半导体/固态器件制造、电固体器件等方向,能够解决电浅杂质能级氧化物半导体电阻降低等问题,达到抑制晶格缺陷、防止劣化的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0068] [structure]
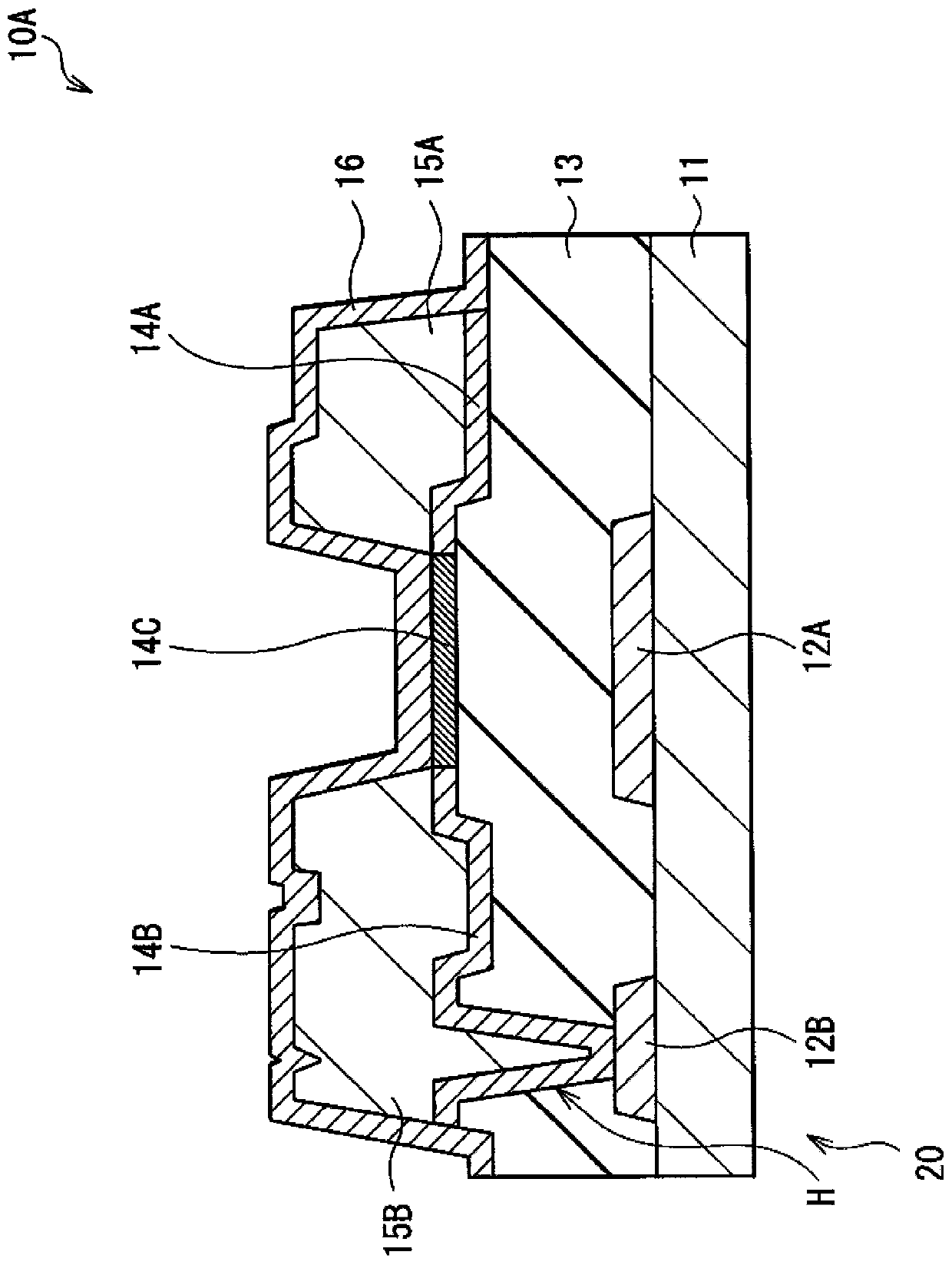
[0069] figure 1 A cross-sectional structure of the thin film transistor (thin film transistor 10A) according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure is shown. The thin film transistor 10A can be used as a driving device in, for example, an active matrix organic EL display (described later) and a liquid crystal display. In the thin film transistor 10A, the oxide semiconductor layer 14C is provided on one surface side of the gate electrode 12A, the gate insulating film 13 is provided between the gate electrode 12A and the oxide semiconductor layer 14C, and the paired source / drain The pole electrodes 15A and 15B are provided to be electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor layer 14C.
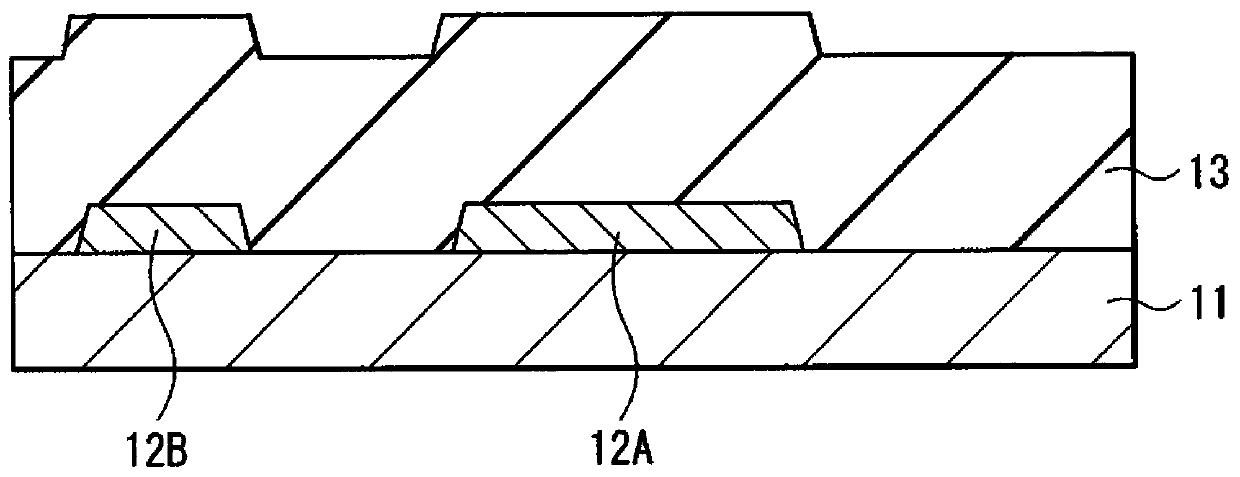
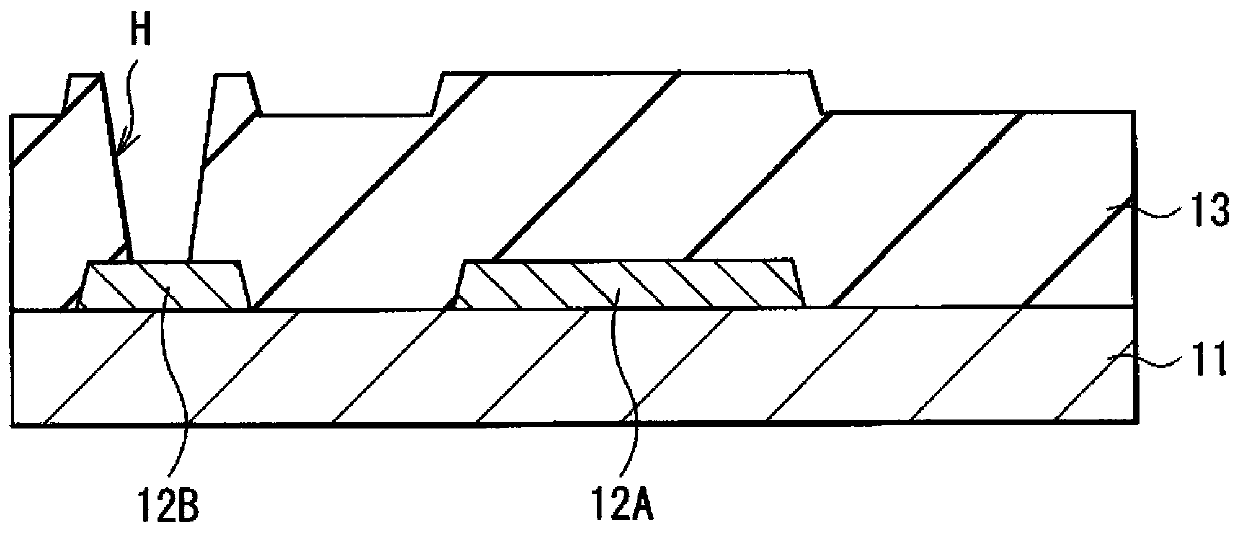
[0070] Here, the thin film transistor 10A has a so-called bottom gate structure (reversed overlap structure) and has a gate electrode 12A in a selected region on a substrate 11 formed of, for example, glass. Gate insulating film 13 is formed on the entire su...
no. 2 example
[0107] Figure 12 A cross-sectional configuration of a thin film transistor (thin film transistor 10B) according to the second embodiment of the present disclosure is shown. The thin film transistor 10B has a bottom gate structure like the thin film transistor 10A of the first embodiment described above, and an oxide semiconductor layer 17C is formed on the gate insulating film 13 in a region not facing the source / drain electrodes 15A and 15B. In addition, in regions adjacent to the oxide semiconductor layer 17C and facing the source / drain electrodes 15A and 15B, respectively, low-resistance oxide layers 17A and 17B are formed.
[0108] Each of the oxide semiconductor layer 17C and the low-resistance oxide layers 17A and 17B is formed of an oxide containing an element (for example, indium) similar to that in the oxide semiconductor layer 14C of the first embodiment described above. In addition, each of the low-resistance oxide layers 17A and 17B has a lower resistivity than t...
no. 3 example (
[0123] [Third Embodiment (Thin Film Transistor)]
[0124] Figure 18 A schematic structure (cross-sectional structure) of a thin film transistor (thin film transistor 1020 ) according to the third embodiment is shown. Figure 18 The illustrated thin film transistor 1020 includes a gate electrode 1012, an insulating layer 1013, a channel-formed semiconductor layer 1014, and an electrode layer 1016 formed on an insulating substrate 1011 constructed of a glass substrate or the like. In addition, the insulating layer 1018 is formed to cover the entire thin film transistor 1020 .
[0125] The gate electrode 1012 is formed of metal or alloy such as Mo and Al, and is formed in a predetermined pattern. The insulating layer 1013 will become a gate insulating layer of the thin film transistor 1020 and is formed to cover the gate electrode 1012 . For example, silicon oxide (SiOx) is used as a material of the insulating layer 1013 . The semiconductor layer 1014 is formed of an oxide s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com