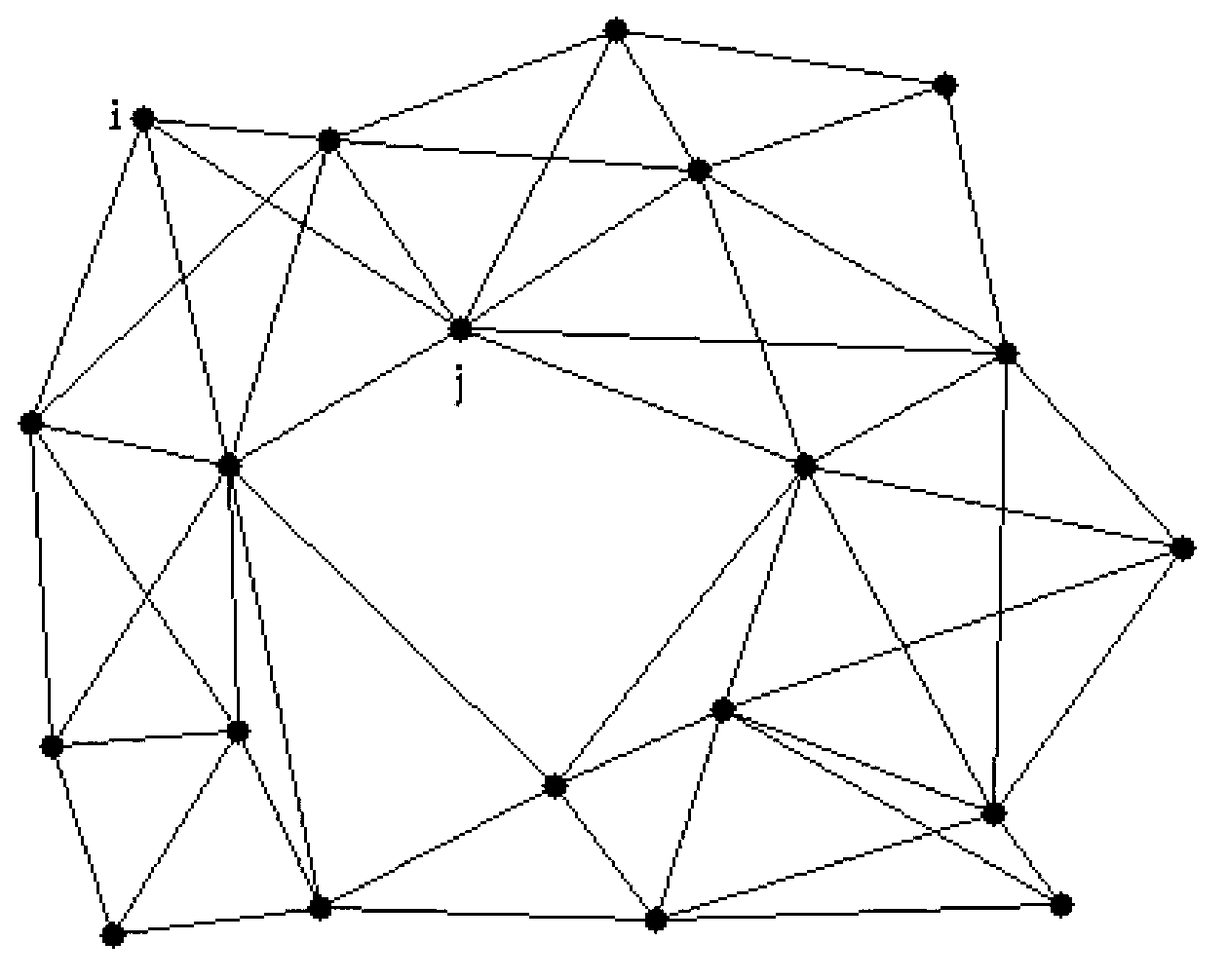
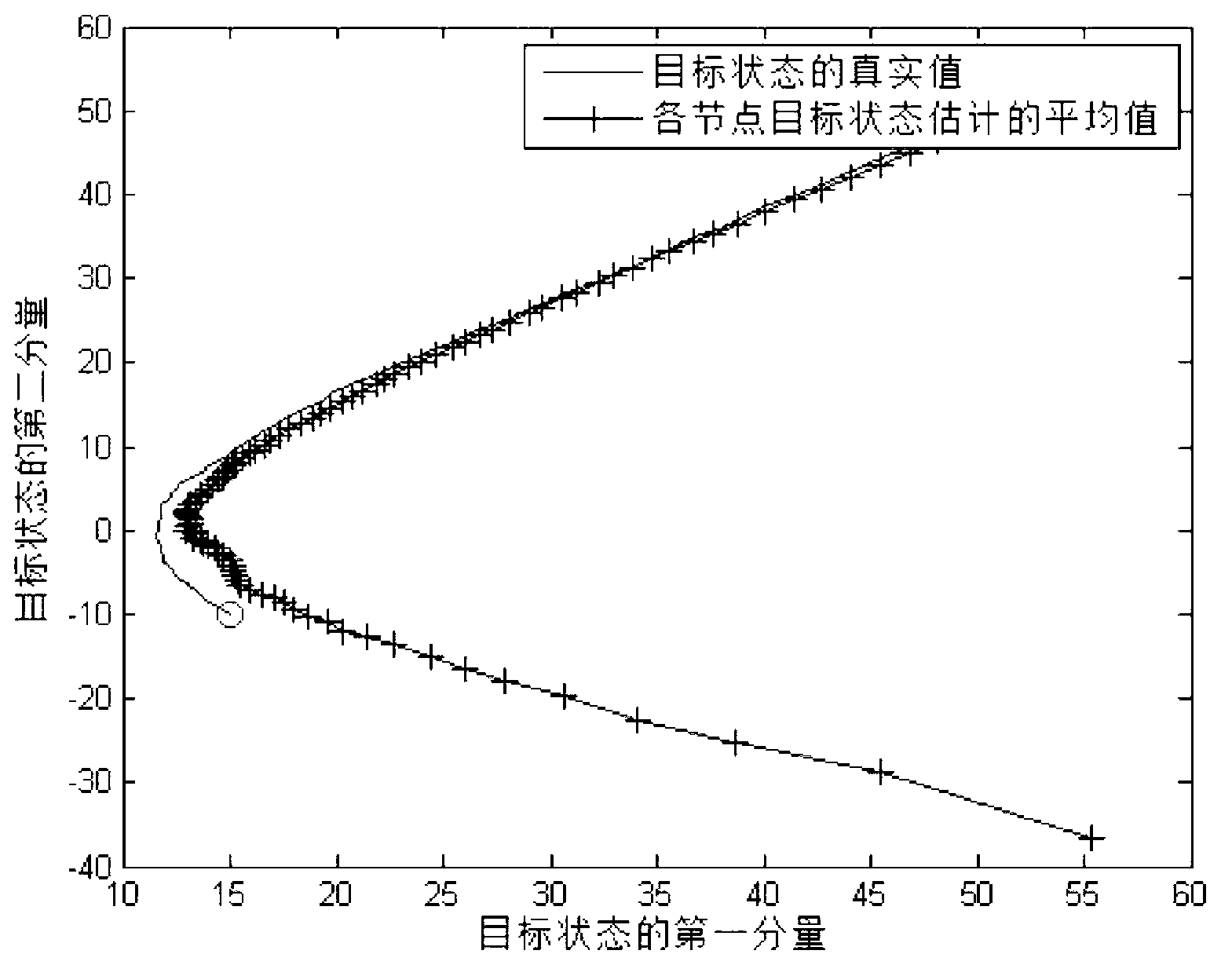
Wireless sensor network target tracking method based on informational consistency
A wireless sensor network and target tracking technology, which is applied in the field of wireless sensor network target tracking based on information consistency, can solve the problem that the estimated error covariance matrix has not been improved, the uncertainty is different, and the uncertainty of neighbor nodes is ignored. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] Suppose the state model (3) of a two-dimensional target to be tracked is expressed as follows:
[0112] x ( k ) = 1.0005 0.03 0.03 1.0005 x ( k - 1 ) + 0.015 0 0 0.015 w ( k ) - - - ( 29 )
[0113] where x(k)∈R 2 Including two state components that can be regarded as the horizontal and vertical positions o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com